L-peptidase
The leader protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus FMDV Lpro is a papain-like protease where, as well as cleaving itself from the nascent viral polyprotein, disables host cell protein synthesis by specific proteolysis of a cellular protein: the eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G). Its sole role in viral maturation is to free itself from the polyprotein by cleavage between its own C-terminus and the N-terminus of VP4 at the sequence ArgLys LeuLys-|-GlyAlaGlySer.
Later it plays the role of lysing the host cell protein eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4G at the sequence AlaAsnLeuGly-|-ArgThrThrLeu and other eIF4G sequences. As a result, the domain of eIF4G which binds the cap-binding protein eIF4E is separated from the domain of eIF4G which binds eIF3, so that the infected cell is unable to recruit its own capped mRNA to the 40S ribosome. Substrate specificity is achieved with four acidic residues 163-166, not seen in other papain-like proteases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P03305
 (2.7.7.48, 3.4.22.28, 3.4.22.46, 3.6.1.15)
(2.7.7.48, 3.4.22.28, 3.4.22.46, 3.6.1.15)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (strain O1) (Virus)

- PDB
-
1qol
- STRUCTURE OF THE FMDV LEADER PROTEASE
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.70.10
 (see all for 1qol)
(see all for 1qol)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
FMDV Leader protease is a classic cysteine protease with a unique binding domain which allows specific selection of its substrates - its own C terminus and eIF4G. His148 is positioned by Asp163 so as to be able to deprotonate Cys51, increasing its nucleophilicity, prior to Cys51 attacking the carbon of carbonyl group of the peptide bond. This results in the formation of a charged tetrahedral intermediate which susequently collapses with the elimination of the amine group. This is aided by proton donation from His148 to the leaving group. Thus the acyl enzyme is formed which must be cleared before the next catalytic cycle may begin. His148 removes a proton from the active site water, increasing its nucleophilicity, as it attacks the carbonyl group of the acyl enzyme. The resulting tetrahedral intermediate collapses with the formation of a carboxylic acid group and the free enzyme. His148 aids donates a proton it picked up from water to Cys51 thiol group.
The leader protease differs from the papain enzyme with Asn46 replacing Gln19 (in papain) which alongside the main chain amide on the catalytic cysteine, stabilises the negative charge on the oxyanion intermediate - the oxyanion hole. Furthermore, Asp163 replaces His159 in papain to position the nucleophilic cysteine
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qol) | ||
| Asn46, Cys51 (main-N) | Asn46(18)B, Ala51(23)B (main-N) | The main chain nitrogen of Cys51 and side chain amide on Asn46 form the oxyanion hole to stabilise the developing negative charge on the oxyanion intermediate . | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Cys51 | Ala51(23)B | Performs a nucleophic attack on the carbonyl group of the peptide bond followed by acting as the leaving group during lysis of the acyl-enzyme intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His148 | His148(120)B | Deprotonates Cys51 increasing its nucleophilicity then protonates the amine leaving group. Deprotonates water increasing its nucleophilicity then protonates the thiol leaving group. | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp163 | Asp163(135)B | Electrostatic stabilisation of the charged His148 allowing it to accept a proton. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Guarné A et al. (1998), EMBO J, 17, 7469-7479. Structure of the foot-and-mouth disease virus leader protease: a papain-like fold adapted for self-processing and eIF4G recognition. DOI:10.1093/emboj/17.24.7469. PMID:9857201.
- Steinberger J et al. (2014), Virology, 468-470, 397-408. Foot-and-mouth disease virus leader proteinase: structural insights into the mechanism of intermolecular cleavage. DOI:10.1016/j.virol.2014.08.023. PMID:25240326.
- Tong L (2002), Chem Rev, 102, 4609-4626. Viral Proteases. DOI:10.1021/cr010184f. PMID:12475203.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp163(135)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn46(18)B | polar interaction |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | polar interaction |
| His148(120)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
| Ala51(23)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. Thiolate of Cys51 attacks the carbonyl carbon in the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn46(18)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Asn46(18)B | polar interaction |
| Asp163(135)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| His148(120)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ala51(23)B | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation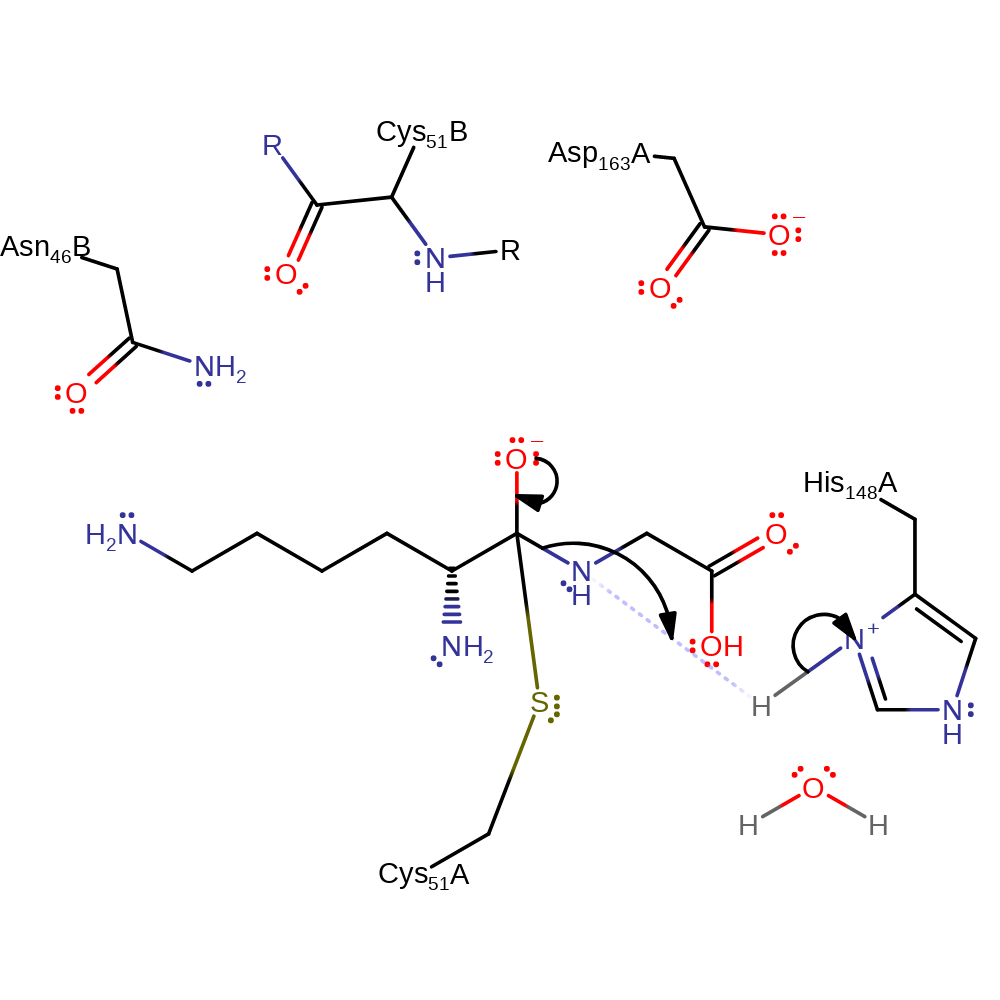
Step 3. Peptide bond cleavage occurs by elimination of the amine leaving group, aided by His148 proton donation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala51(23)B | covalently attached |
| Asn46(18)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn46(18)B | polar interaction |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Asp163(135)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| His148(120)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, proton transfer, overall product formed
Step 4. His148 deprotonates a water molecule, increasing its nucleophilicity to attack the C-terminal carbonyl carbon, releasing covalently attached cysteine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala51(23)B | covalently attached |
| Asn46(18)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn46(18)B | polar interaction |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | polar interaction |
| His148(120)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp163(135)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ala51(23)B | nucleofuge |
| His148(120)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer
Step 5. To regenerate the active site, His148 protonates Cys51, ready for another round of catalysis.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His148(120)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp163(135)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn46(18)B | polar interaction |
| Ala51(23)B (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Ala51(23)B | proton acceptor |
| His148(120)B | proton donor |




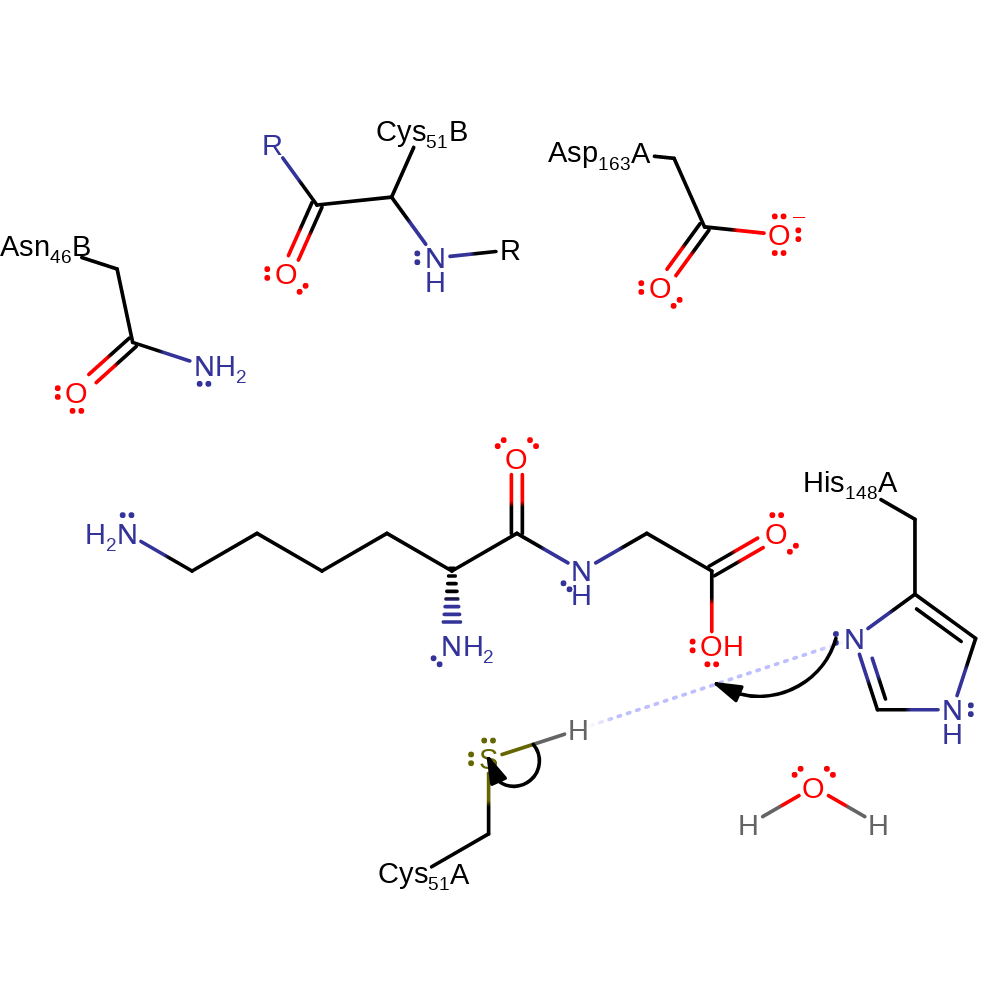
 Download:
Download: