DCTP deaminase
Deoxycytidine triphosphate deaminase (dCTP deaminase) from E. coli catalyses the deamination of dCTP producing ammonia and dUTP. The dUTP can be hydrolysed by dUTPase producing dUMP which is a precursor of dTTP. dCTP deaminase is inhibited by dTTP and by inorganic phosphate. Deamination of dCTP by dCTP deaminase provides about 80% of the dUMP used for dTMP synthesis in E. coli. The substrate of dCTP deaminase is the dCTP.Mg2+ complex but the magnesium does not have a catalytic role and no other metal ions are involved in catalysis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P28248
 (3.5.4.13)
(3.5.4.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1xs1
- dCTP deaminase from Escherichia coli in complex with dUTP
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.70.40.10
 (see all for 1xs1)
(see all for 1xs1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.4.13)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
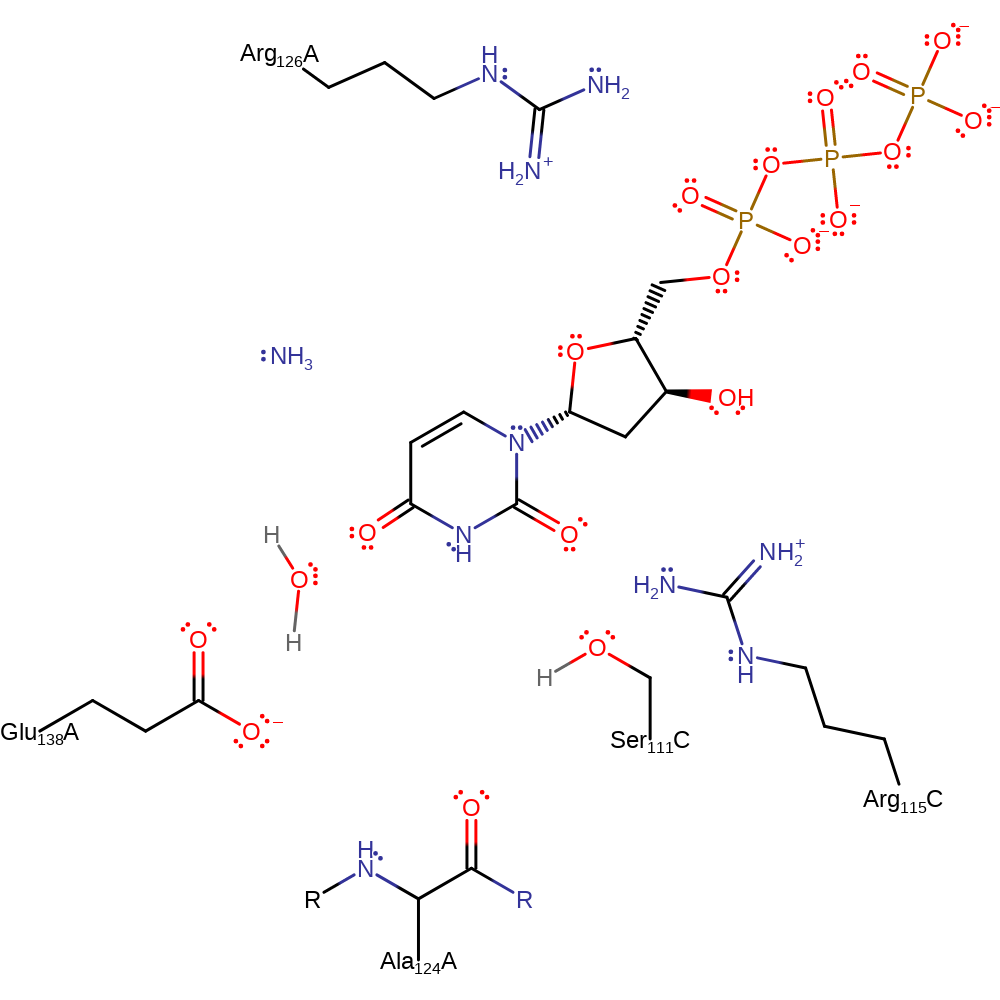
Glu138 abstracts a proton from a water molecule (HOH5) creating a hydroxide ion which attacks C4 of the pyrimidine ring of dCTP forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The amine group on C4 is protonated by another water molecule (HOH251) and the tetrahedral intermediate breaks down releasing a molecule of ammonia. The hydroxide produced from HOH251 is then neutralised by a proton transferred from the intermediate via Glu138.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xs1) | ||
| Ala124 (main-C) | Ala124A (main-C) | Helps stabilise the hydroxide ion in the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126 | Arg126A | Prevents the dCTP deaminase from also functioning as a dUTPase by taking up the space in which a nucleophilic water molecule could otherwise be located. This suggestion comes from a comparison of the E. coli dCTPdeaminase with the E. coli dUTPase. Arg126 also forms a salt bridge with Asp128. | steric role |
| Glu138 | Glu138A | Glu138 deprotonates water molecule HOH5 to create the hydroxide ion which acts as the nucleophile and protonate the hydroxide formed from the deprotonation of HOH251 by the C4 amino group. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser111 | Ser111C | Stabilises and positions the hydroxide ion in the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115 | Arg115C | Arg115 forms a hydrogen bond to Ser111 and prevents it's deprotonation by the hydroxide ion. The positive charge on Arg115 may also polarise the substrate for attack by the hydroxide ion. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Johansson E et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 3051-3059. Structures of dCTP Deaminase from Escherichia coli with Bound Substrate and Product: REACTION MECHANISM AND DETERMINANTS OF MONO- AND BIFUNCTIONALITY FOR A FAMILY OF ENZYMES. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m409534200. PMID:15539408.
- Thymark M et al. (2008), Arch Biochem Biophys, 470, 20-26. Mutational analysis of the nucleotide binding site of Escherichia coli dCTP deaminase. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2007.10.013. PMID:17996716.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg126A | steric role |
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu138A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 2. The hydroxide ion nucleophilically attacks the C4 carbon which results in double bond rearrangement as dCTP acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation
Step 3. The electrons are fed back resulting in the cleavage of the amino group which accepts a proton from another water (HOH251)
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, proton transfer
Step 4. The hydroxide accepts a proton from Glu138 and there is a tautomerisation which results in changes the C4 enol to a keto.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
| Glu138A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, keto-enol tautomerisation, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
The reaction is initiated by the deprotonation of a water (HOH5) by Glu138 which then transfers the proton to N3's nitrogen. The hydroxide then nucleophilically attacks the C4 carbon. Glu138 then deprotonates the C4 hydroxyl which initiates an elimination that results in the release dUTP and the amino group which accepts a proton from another water (HOH251) which produces ammonia. The hydroxide then accepts a proton from Glu138 which regenerates the native state of the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xs1) | ||
| Ala124 (main-C) | Ala124A (main-C) | Helps stabilise the hydroxide ion in the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126 | Arg126A | Prevents the dCTP deaminase from also functioning as a dUTPase by taking up the space in which a nucleophilic water molecule could otherwise be located. This suggestion comes from a comparison of the E. coli dCTPdeaminase with the E. coli dUTPase. Arg126 also forms a salt bridge with Asp128. | steric role |
| Glu138 | Glu138A | Deprotonates HOH5 so it can act as nucleophile and attack the C4 carbon of dCTP. Also transfer a proton to N3 which enables the nucleophilic attack of C4 as it increases C4's electrophilicity. Deprotonates the C4 hydroxyl to initiate an elimination and protonate the HOH251 hydroxide. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser111 | Ser111C | Stabilises and positions the hydroxide ion in the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115 | Arg115C | Arg115 forms a hydrogen bond to Ser111 and prevents it's deprotonation by the hydroxide ion. The positive charge on Arg115 may also polarise the substrate for attack by the hydroxide ion. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Johansson E et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 3051-3059. Structures of dCTP Deaminase from Escherichia coli with Bound Substrate and Product: REACTION MECHANISM AND DETERMINANTS OF MONO- AND BIFUNCTIONALITY FOR A FAMILY OF ENZYMES. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m409534200. PMID:15539408.
- Thymark M et al. (2008), Arch Biochem Biophys, 470, 20-26. Mutational analysis of the nucleotide binding site of Escherichia coli dCTP deaminase. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2007.10.013. PMID:17996716.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
| Glu138A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 2. The N3 nitrogen accepts a proton from Glu138 and the hydroxide nucleophilically attacks the C3 carbon which is more electrophilic due to protonation at N3.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
| Glu138A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 3. Glu138 deprotonates hydroxyl group which initiates an elimination resulting in the release of the amino group which accepts a proton from a water (HOH251).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
| Glu138A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 4. The hydroxide accepts a proton from Glu138 to regenerate the active site's native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala124A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser111C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg115C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126A | steric role |
| Glu138A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: