Fatty acid amide hydrolase
Mammalian fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) degrades fatty acid primary amides and ethanolamides such as anandamide and oleamide. Anandamide binds and activates cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors exerting an analgesic and cannabinoid effects while oleamide has been found to be sleep inducing. Rat FAAH is an integral membrane protein. The wild type protein hydrolyses esters and amides at the same rate but the Lys142Ala mutant hydrolyses esters more rapidly than amides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P97612
 (3.1.1.-, 3.5.1.99)
(3.1.1.-, 3.5.1.99)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)

- PDB
-
1mt5
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF FATTY ACID AMIDE HYDROLASE
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.1300.10
 (see all for 1mt5)
(see all for 1mt5)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.1.99)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
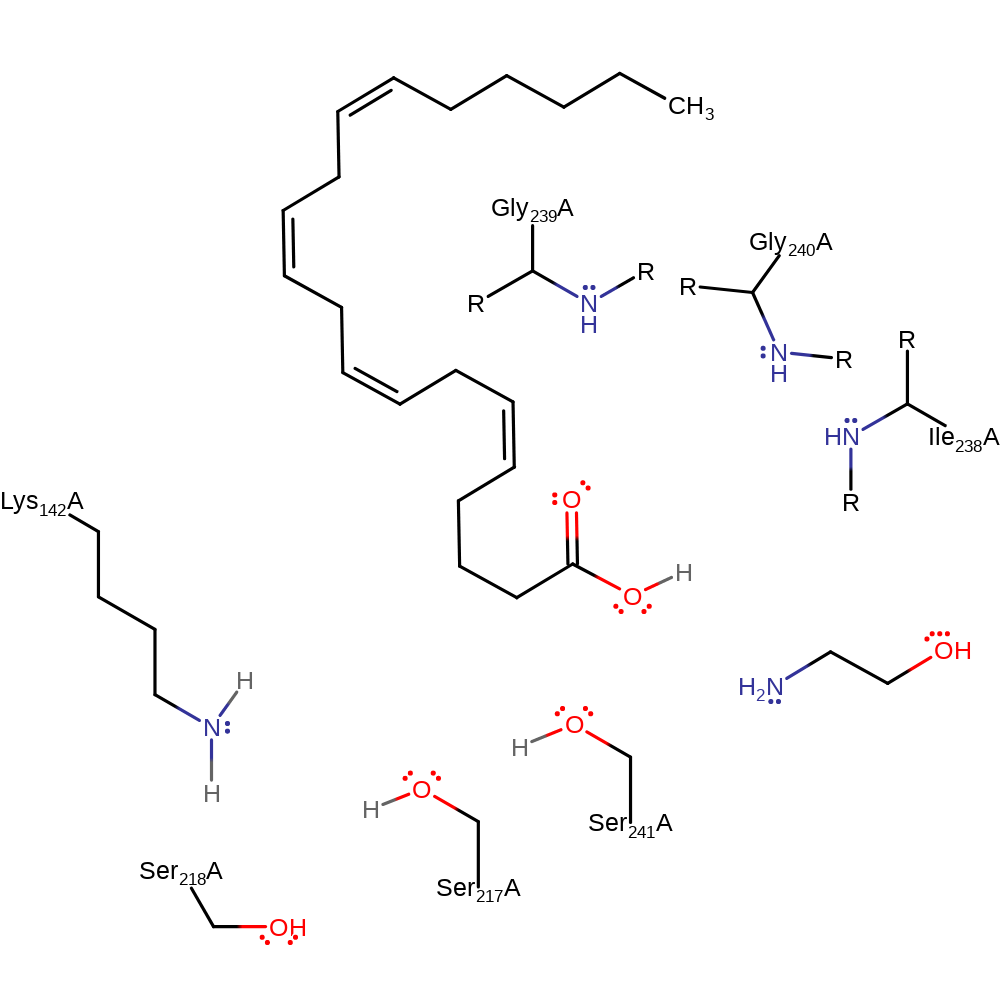
FAAH has a catalytic triad consisting of Ser217, Ser241 and Lys142. Initially Lys142 deprotonates Ser217. Ser241 acts as a nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon of the substrate. The tetrahedral intermediate is formed in a concerted process with the deprotonation of Ser241 by the alkoxide of Ser217. The negative charge on the tetrahedral intermediate is stabilised by strong hydrogen bonds with the backbone NH groups of Ile238, Gly239, Gly240 and Ser241 which form an oxyanion hole. The acylation of the enzyme is the rate limiting step. Deacylation occurs with a water molecule from the solvent acting as the nucleophile. There are four water molecules near the active site. Water-bridging proton transfer is thought to be necessary for the hydrolysis of the acyl intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mt5) | ||
| Ile238 (main-N), Gly239 (main-N), Gly240 (main-N) | Ile238(202)A (main-N), Gly239(203)A (main-N), Gly240(204)A (main-N) | Forms part of the oxyanion hole. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys142 | Lys142(106)A | Lys142 initially acts as a base, deprotonating Ser217 and later as an a acid, protonating Ser217. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser217 | Ser217(181)A | Ser217 is deprotonated by Lys142 and then acts as a general base for the deprotonation of Ser241 which is the nucleophile. Then, it acts a general acid by protonating the leaving group of the substrate. Finally, the alkoxide is restored to an OH group by obtaining a proton from Lys142. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser218 | Ser218(182)A | The exact function of Ser218 is uncertain but it may be hydrogen bonding to Ser217 and stabilising the negative charge on it. S218A mutants have a decreased kcat with no significant change in Km. |
electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser241 | Ser241(205)A | Ser241 is the nucleophile that attacks the carbonyl carbon of the substrate. The backbone NH group of Ser241 contributes to the oxyanion hole. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Tubert-Brohman I et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 16904-16913. Elucidation of Hydrolysis Mechanisms for Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase and Its Lys142Ala Variant via QM/MM Simulations. DOI:10.1021/ja065863s. PMID:17177441.
- Chudyk EI et al. (2013), J Phys Chem B, 117, 6656-6666. Nonempirical Energetic Analysis of Reactivity and Covalent Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jp401834v.
- Capoferri L et al. (2011), J Mol Model, 17, 2375-2383. Application of a SCC-DFTB QM/MM approach to the investigation of the catalytic mechanism of fatty acid amide hydrolase. DOI:10.1007/s00894-011-0981-z. PMID:21365225.
- Lodola A et al. (2005), Chem Commun (Camb), 4399-. QM/MM modelling of oleamide hydrolysis in fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) reveals a new mechanism of nucleophile activation. DOI:10.1039/b503887a. PMID:16136230.
- McKinney MK et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 37393-37399. Evidence for Distinct Roles in Catalysis for Residues of the Serine-Serine-Lysine Catalytic Triad of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m303922200. PMID:12734197.
- Patricelli MP et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 9804-9812. Chemical and Mutagenic Investigations of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase: Evidence for a Family of Serine Hydrolases with Distinct Catalytic Properties†. DOI:10.1021/bi990637z. PMID:10433686.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser218(182)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile238(202)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly240(204)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly239(203)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys142(106)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser217(181)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer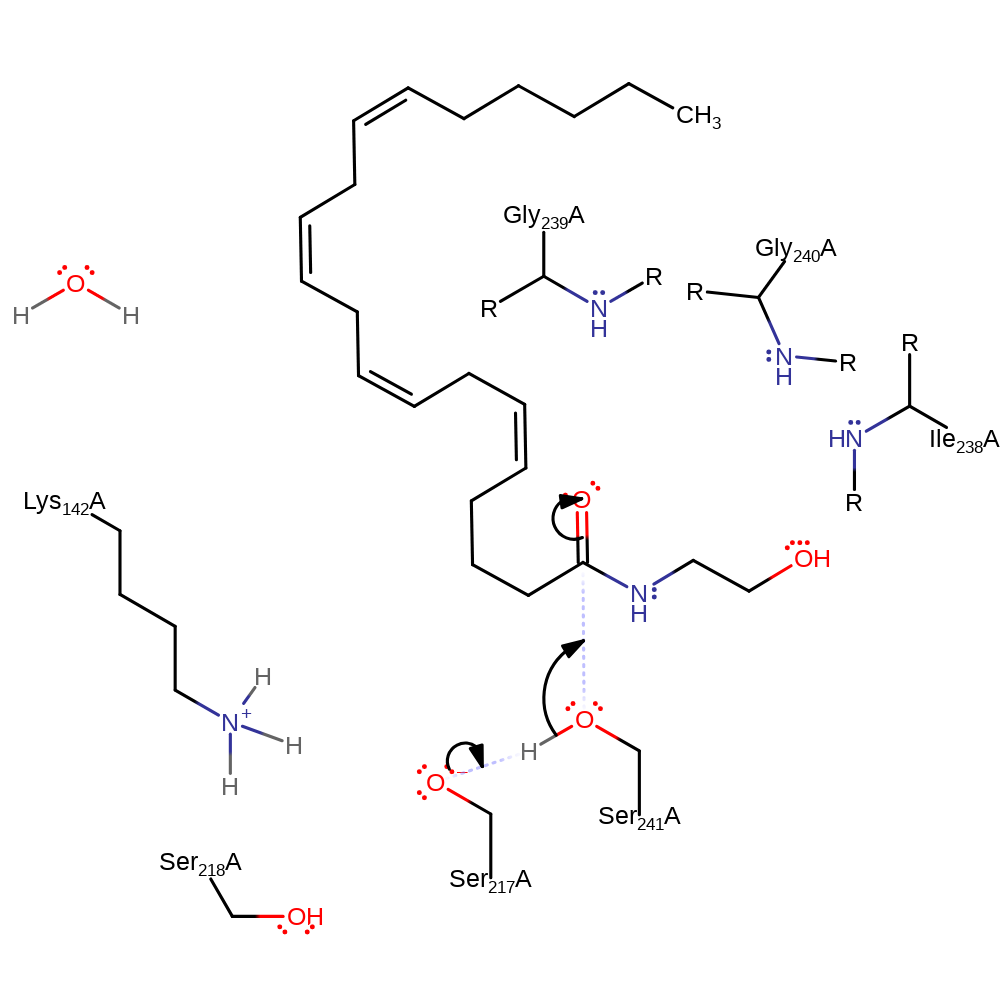
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate formed by nucleophilic attack by Ser241 concerted with proton transfer from Ser241 to Ser217.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser218(182)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile238(202)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly239(203)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly240(204)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser217(181)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser241(205)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step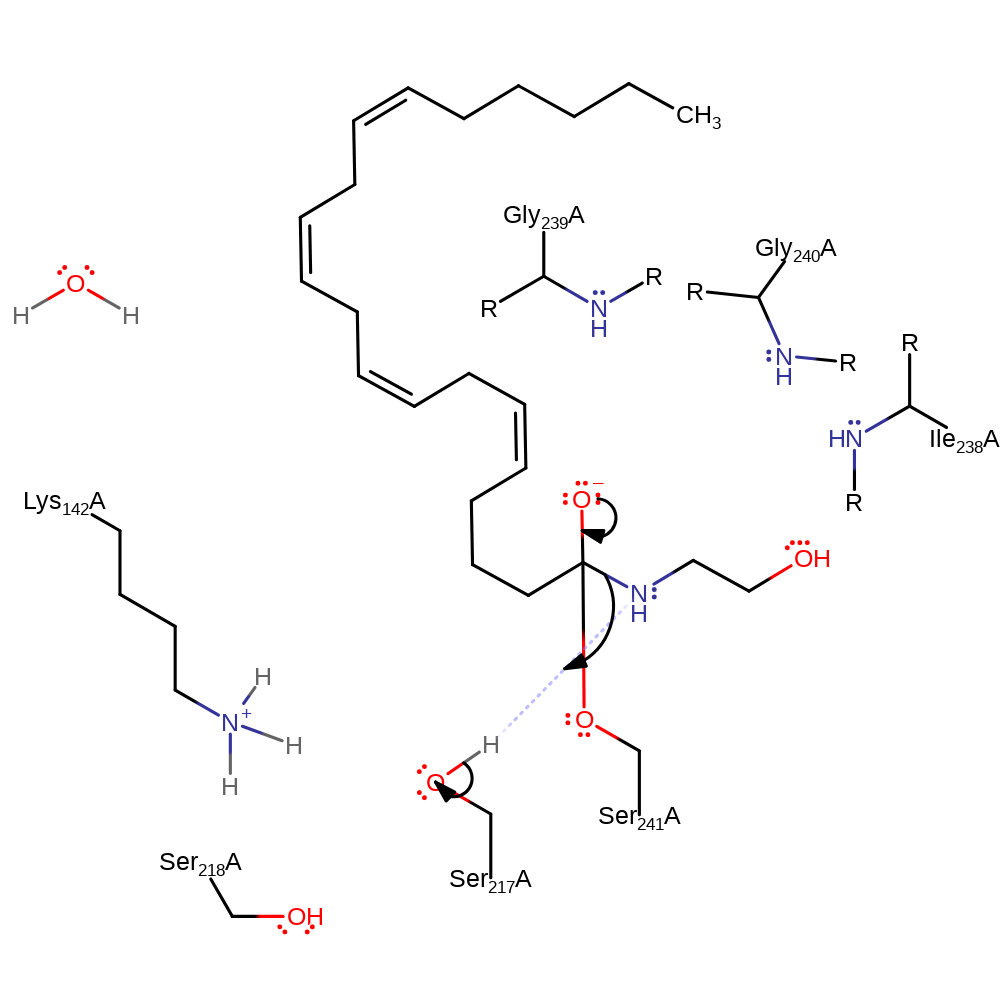
Step 3. The nitrogen of the amide bond accepts a proton from Ser217 which initiates an elimination from the oxyanion resulting in the cleavage of the amide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser218(182)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile238(202)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly239(203)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly240(204)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser217(181)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed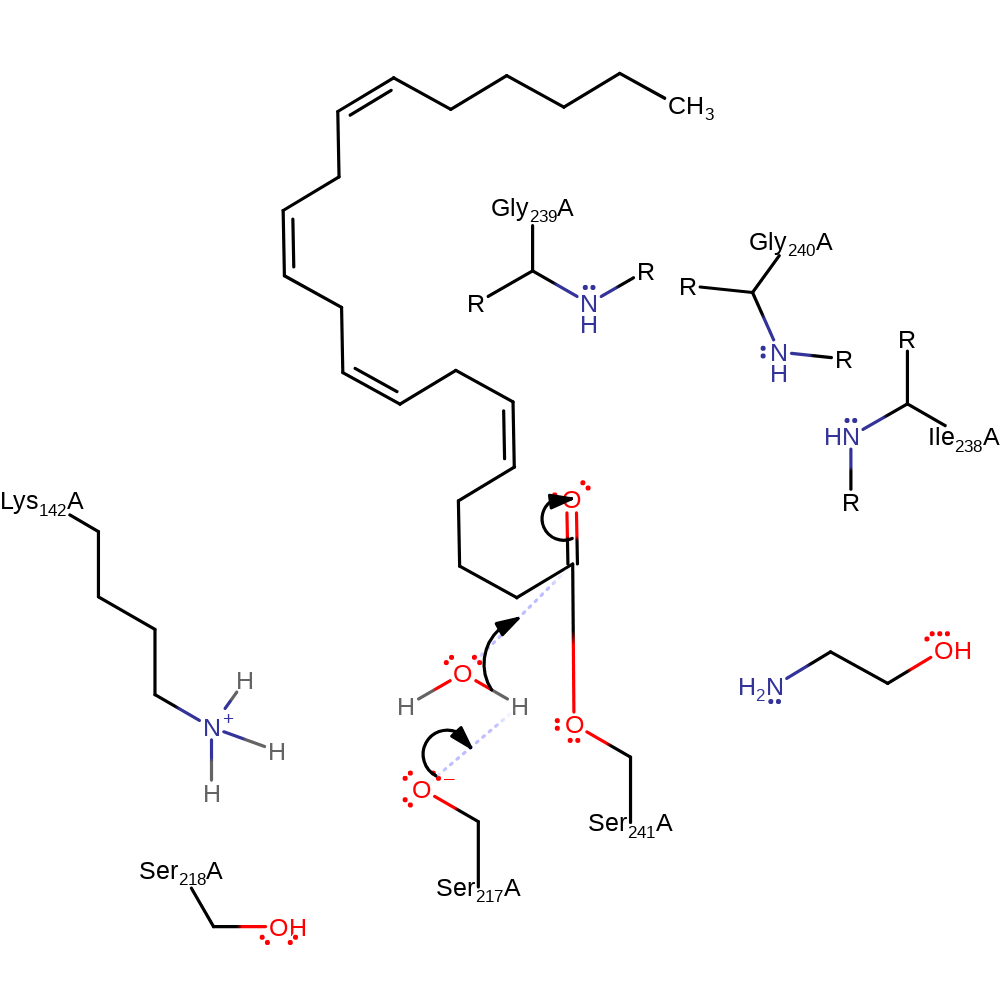
Step 4. Ser217 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the carbonyl group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser218(182)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile238(202)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly239(203)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly240(204)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser217(181)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 5. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the acyl-enzyme intermediate releasing Ser241 which is then protonated by Ser217. Ser 217 then is protonated by Lys142 which returns the active site to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser218(182)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile238(202)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly239(203)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly240(204)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser241(205)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser217(181)A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys142(106)A | proton donor |
| Ser217(181)A | proton relay |
| Ser241(205)A | nucleofuge |




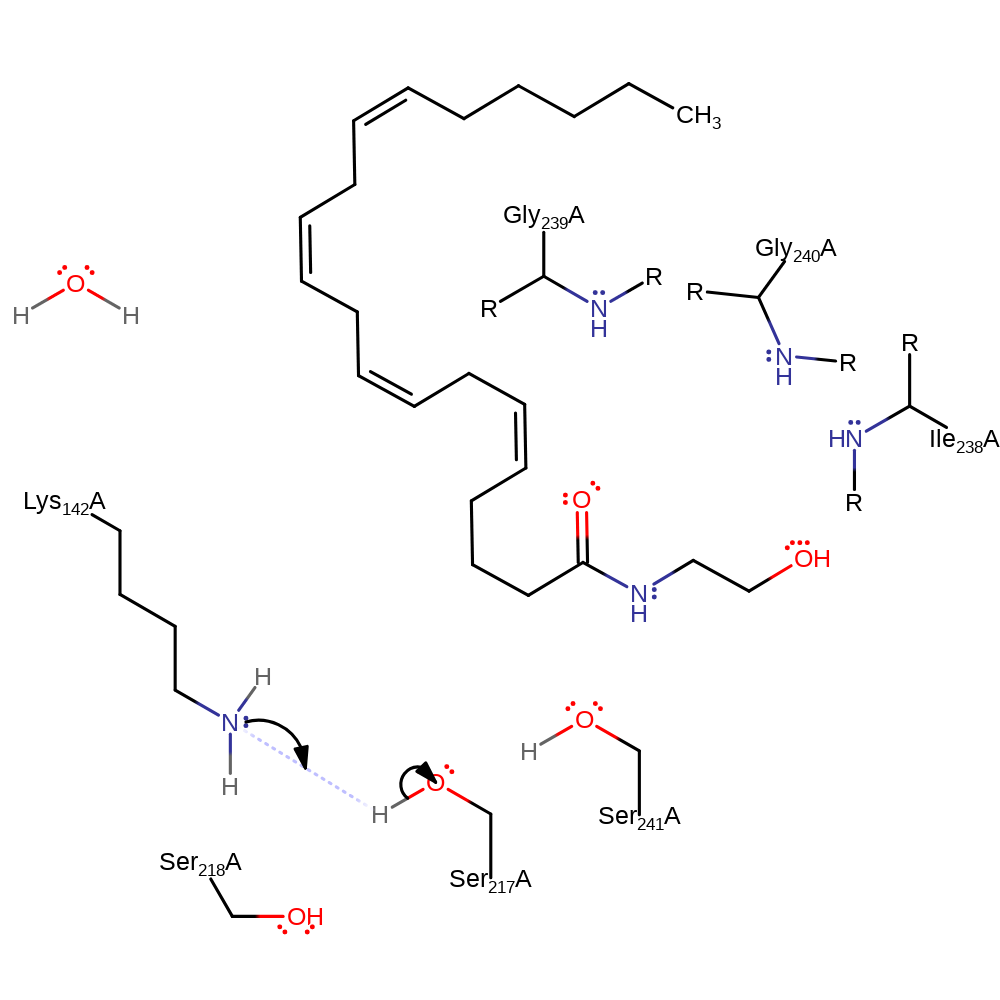
 Download:
Download: