Subtilisin
Subtilisin is an extracellular enzyme secreted by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and belongs to the alpha/beta subtilase family. It is a serine-class endoprotease, hydrolysing peptide bonds with broad specificity and a preference for a large uncharged residue in the P1 binding site.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00782
 (3.4.21.62)
(3.4.21.62)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1s01
- LARGE INCREASES IN GENERAL STABILITY FOR SUBTILISIN BPN(PRIME) THROUGH INCREMENTAL CHANGES IN THE FREE ENERGY OF UNFOLDING
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.200
 (see all for 1s01)
(see all for 1s01)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.21.62)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His 171 acts as a general base, deprotonating Ser 328. Ser 328 performs nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the amide bond. This results in a tetrahedral transition state, which is stabilised through Coulombic interactions with protonated His 171, hydrogen bonding with the backbone amide of Ser 328 and the amide side-chain of Asn 262. The transition state is also stabilised by hydrogen bonding between the P1 amide nitrogen and the carbonyl oxygen of Ser 232. His 171 is stabilised by electrostatic interactions with Asp 139. The tetrahedral transition state collapses, forming an acyl-enzyme and His 171 acts as a general acid, protonating the amide leaving group. His 171 acts as a general base, deprotonating a water molecule. The activated water molecule performs nucleophilic attack upon the acyl enzyme, forming a tetrahedral transition state. The tetrahedral transition state collapses, forming the acid component of the substrate and Ser 328. His 171 acts as a general acid, protonating the leaving group Ser 328.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1s01) | ||
| Ser328 (main-N) | Ser221A (main-N) | The backbone amide group of Ser 328 hydrogen bonds with the tetrahedral transition state, stabilising it. | electrostatic interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser328 | Ser221A | Ser 328 is deprotonated by His 171 and performs nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the amide bond, resulting in a tetrahedral transition state. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn262 | Asn155A | The amide side-chain of Asn 262 stabilises the first tetrahedral transition state through hydrogen bonding. | electrostatic interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp139 | Asp32A | Asp 139 stabilises the positive charge on His 171 through electrostatic interactions. | electrostatic interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His171 | His64A | 1: His 171 acts as a general base, deprotonating Ser 328. 2: Protonated His 171 stabilises the tetrahedral transition state through Coulombic interactions. 3: Protonated His 171 acts as a general acid, protonating the amide leaving group. 4: His 171 acts as a general base, deprotonating a water molecule. 5: Protonated His 171 acts as a general acid, protonating the leaving group Ser 328. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Bryan P et al. (1986), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 83, 3743-3745. Site-directed mutagenesis and the role of the oxyanion hole in subtilisin. DOI:10.1073/pnas.83.11.3743. PMID:3520553.
- Plou FJ et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 257, 1088-1111. Characterization of the Electrostatic Perturbation of a Catalytic Site (Cys)-S–/(His)-Im+H Ion-pair in One Type of Serine Proteinase Architecture by Kinetic and Computational Studies on Chemically Mutated Subtilisin Variants. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0225.
- Takeuchi Y et al. (1991), J Mol Biol, 221, 309-325. Refined crystal structure of the complex of subtilisin BPN? and Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor at 1.8 p resolution. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(91)90821-m. PMID:1920411.
- Carter P et al. (1990), Proteins, 7, 335-342. Functional interaction among catalytic residues in subtilisin BPN′. DOI:10.1002/prot.340070405. PMID:2199971.
- Blow DM et al. (1969), Nature, 221, 337-340. Role of a Buried Acid Group in the Mechanism of Action of Chymotrypsin. DOI:10.1038/221337a0. PMID:5764436.
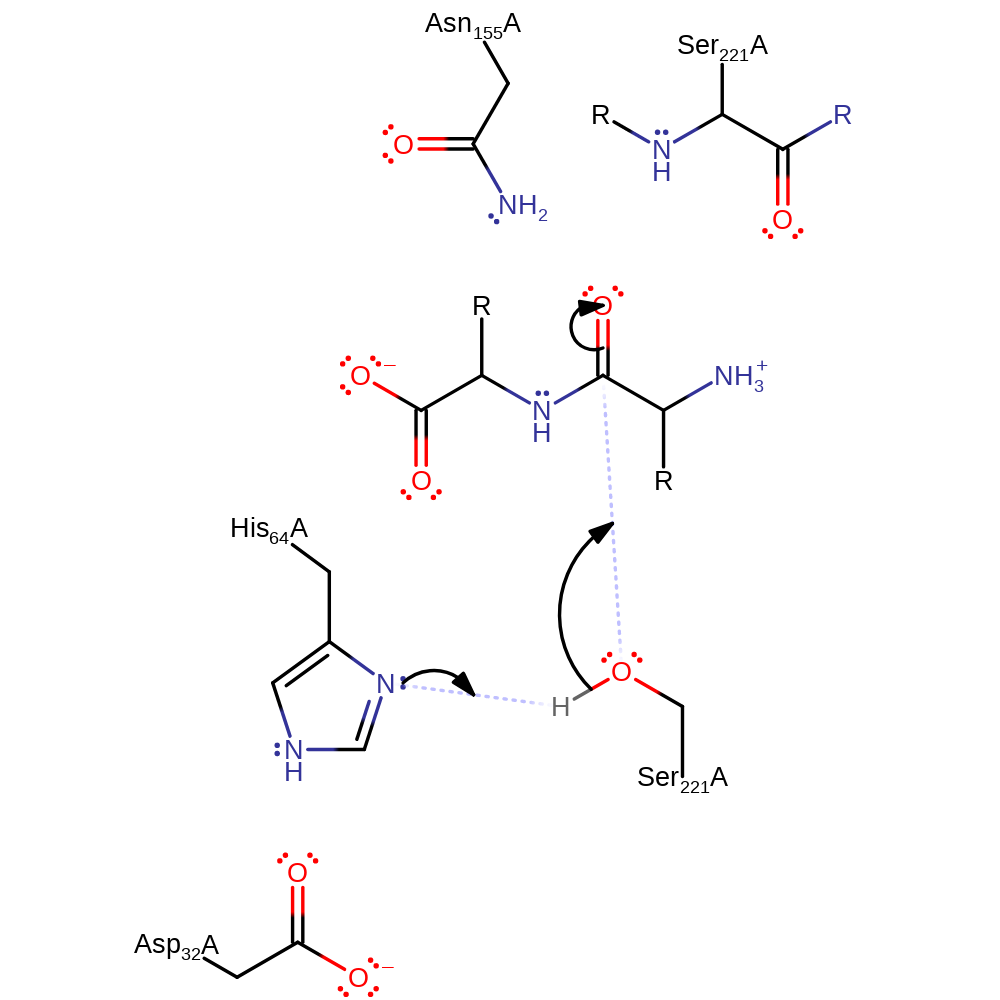
Step 1. His171 deprotonates Ser328 activating it to attack the carbon of the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp32A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser221A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser221A | nucleophile, proton donor |
| His64A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, rate-determining step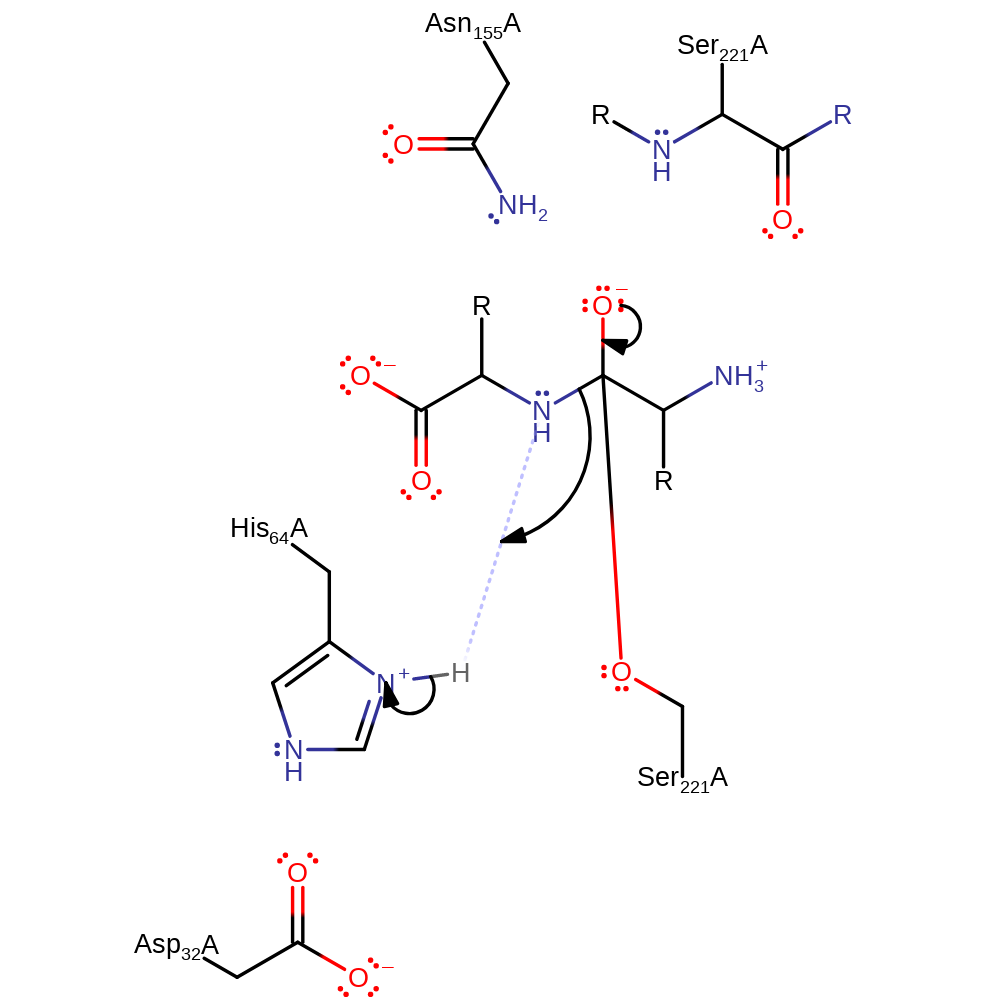
Step 2. The tetrahedral transition state collapses, forming an acyl-enzyme and His171 acts as a general acid, protonating the amide leaving group
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp32A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser221A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His64A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 3. His171 abstracts a proton from a water which in turn activates it to attack the carbon of the ester bond in a nucleophilic addition to produce another transition state tetrahedral intermediate
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp32A | electrostatic interaction |
| Asn155A | electrostatic interaction |
| Ser221A (main-N) | electrostatic interaction |
| His64A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used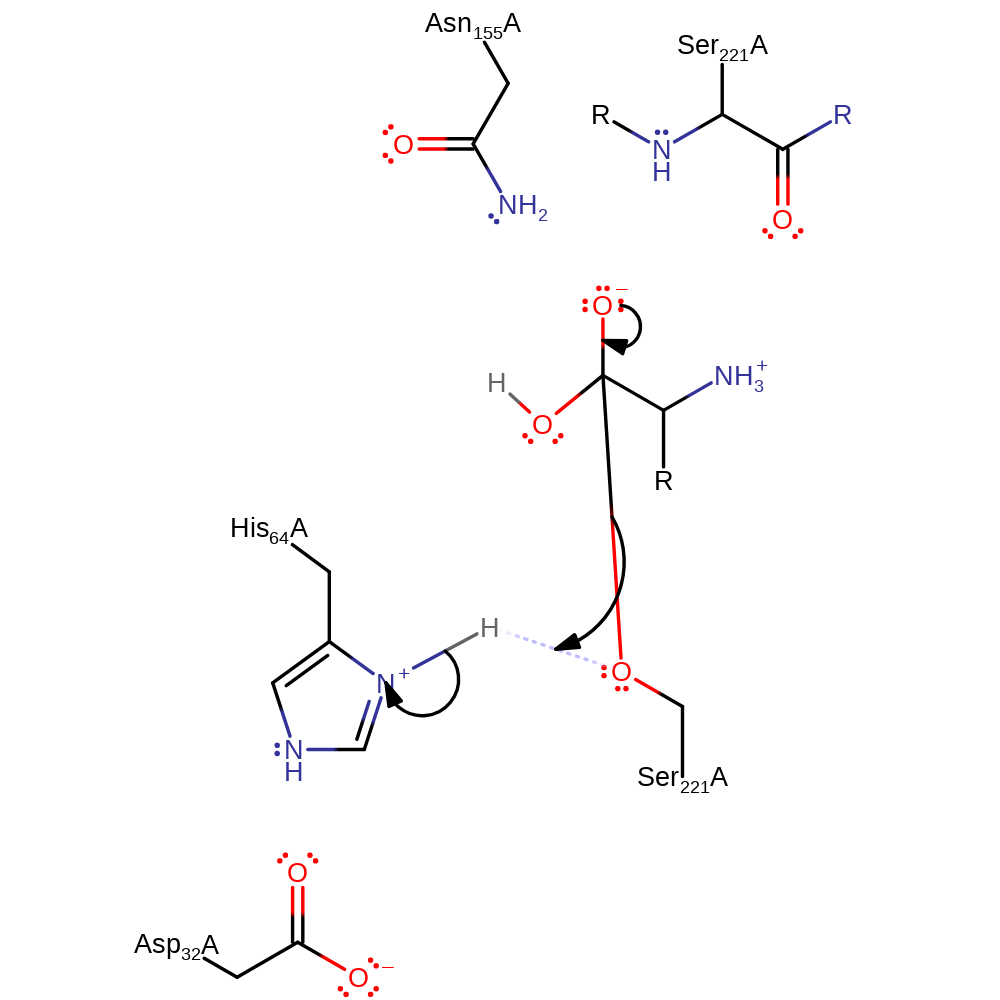
Step 4. The tetrahedral transition state collapses, forming the acid component of the substrate and Ser328. His171 acts as a general acid, protonating the leaving group Ser328 which returns the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp32A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser221A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser221A | proton acceptor |
| His64A | proton donor |
| Ser221A | nucleofuge |



 Download:
Download: