Acetolactate synthase (catabolic)
Acetolactate synthase (ALS) is a thiamin pyrophosphate (ThDP)-dependent enzyme that combines two molecules of pyruvate to yield 2-acetolactate with the release of CO2. It exists in two distinct forms (biosynthetic and catabolic). This entry represents the catabolic form that is found only in some bacteria, and participates in butanediol fermentation. It does not contain FAD. Another oddity is that the N-3 of ALS is thought to be pyramidal while all other ThDP-dependent enzymes possess a planar N-3. This is thought to account for the unusually high kcat of ALS by increasing the acidity of the C-2 proton.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P27696
 (2.2.1.6)
(2.2.1.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ozh
- The crystal structure of Klebsiella pneumoniae acetolactate synthase with enzyme-bound cofactor and with an unusual intermediate.
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.970
 (see all for 1ozh)
(see all for 1ozh)
- Cofactors
- Thiamine(1+) diphosphate(3-) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.2.1.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The thiazolium ring of ThDP ionises at the C-2 position with the 4'-amino group acting as the base (activated by the interaction between a conserved glutamate residue and N-1'). The negative charge on C-2 is stabilised by forming a covalent bond to the 4'-amino group. There is nucleophilic attack on the C-2'' of the carbonyl of pyruvate by C-2 to form tricyclic lactyl-ThDP. Subsequent decarboxylation produces carbon dioxide and an enamine with no bond between C-2 and the 4'-amino group. This bond reforms and causes the C-2'' to act as the nucleophile in the attack on the carbonyl of a second pyruvate. The reformation of the carbonyl at C-2'' breaks the C-2" bond, releasing acetolactate and returning ThDP to its ionised form.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ozh) | ||
| Asp447, Asp474, Gly476 (main-C) | Asp447A, Asp474A, Gly476A (main-C) | The residues are coordinated to the magnesium ion. The ion is also coordinated to two of the ThDP phosphate oxygen atoms and a water molecule. | metal ligand |
| Met394 | Met394A | The backbone carbonyl is able to stabilise a positive charge on the S-1 of ThDP, thus stabilising the form in which N-3 is pyramidal and leading to a more acidic C-2 proton. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met422 | Met422A | Met422 projects between the thiazolium and methylaminopyrimidine rings of ThDP and forces the cofactor into a V conformation. This positions the 4'-amino group close to C-2 which is necessary for the deprotonation of C-2 and the subsequent formation of the tricyclic form of ThDP. | steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, cyclisation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, decarboxylation, decyclisation, overall product formed, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), native state of cofactor regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Pang SS et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 2242-2253. The Crystal Structures of Klebsiella pneumoniae Acetolactate Synthase with Enzyme-bound Cofactor and with an Unusual Intermediate. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m304038200. PMID:14557277.
- Pang SS et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 7639-7644. Molecular Basis of Sulfonylurea Herbicide Inhibition of Acetohydroxyacid Synthase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m211648200. PMID:12496246.
- Kern D et al. (1997), Science, 275, 67-70. How Thiamin Diphosphate Is Activated in Enzymes. DOI:10.1126/science.275.5296.67. PMID:8974393.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used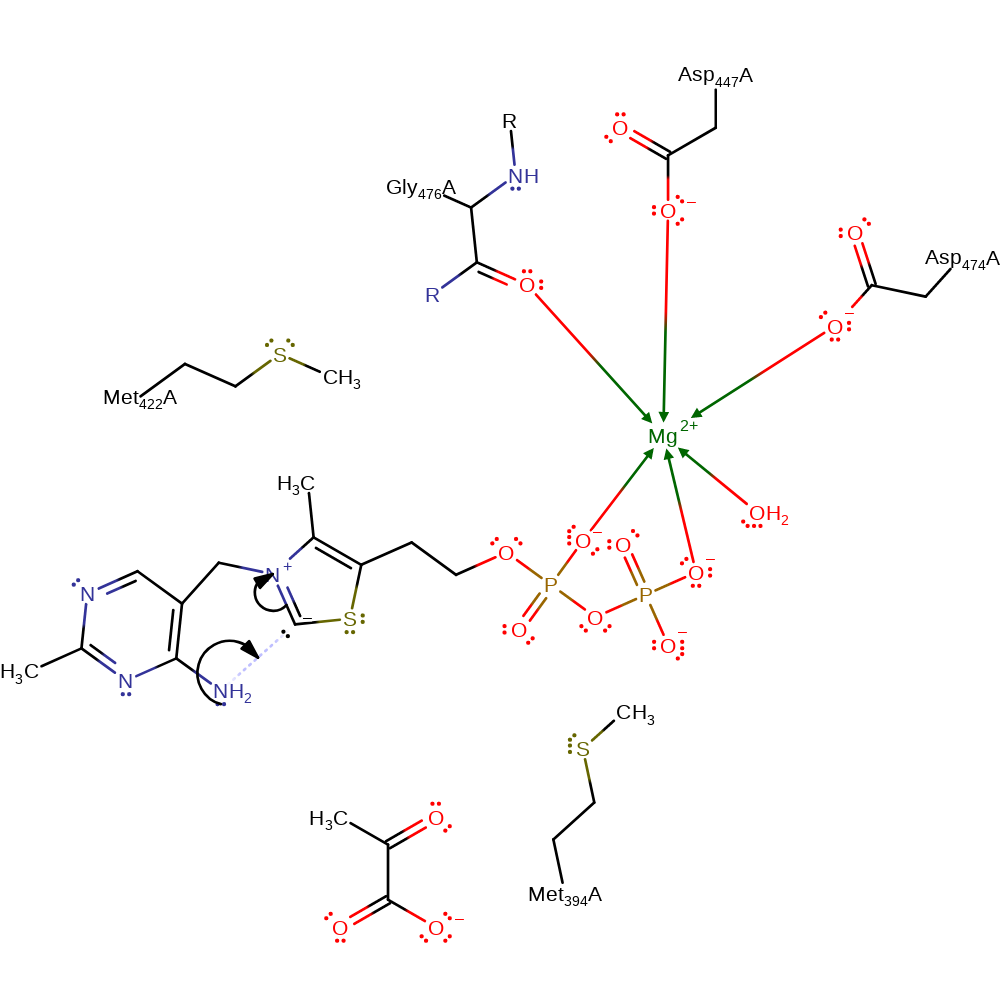
Step 2. The negative charge on the C2 carbon of ThDP is stabilised by forming a covalent bond to the 4'-amino group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
cyclisation
Step 3. The ThDP C2 carbanion attacks the ketone group of pyruvate. The developing oxyanion is subsequently protonated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used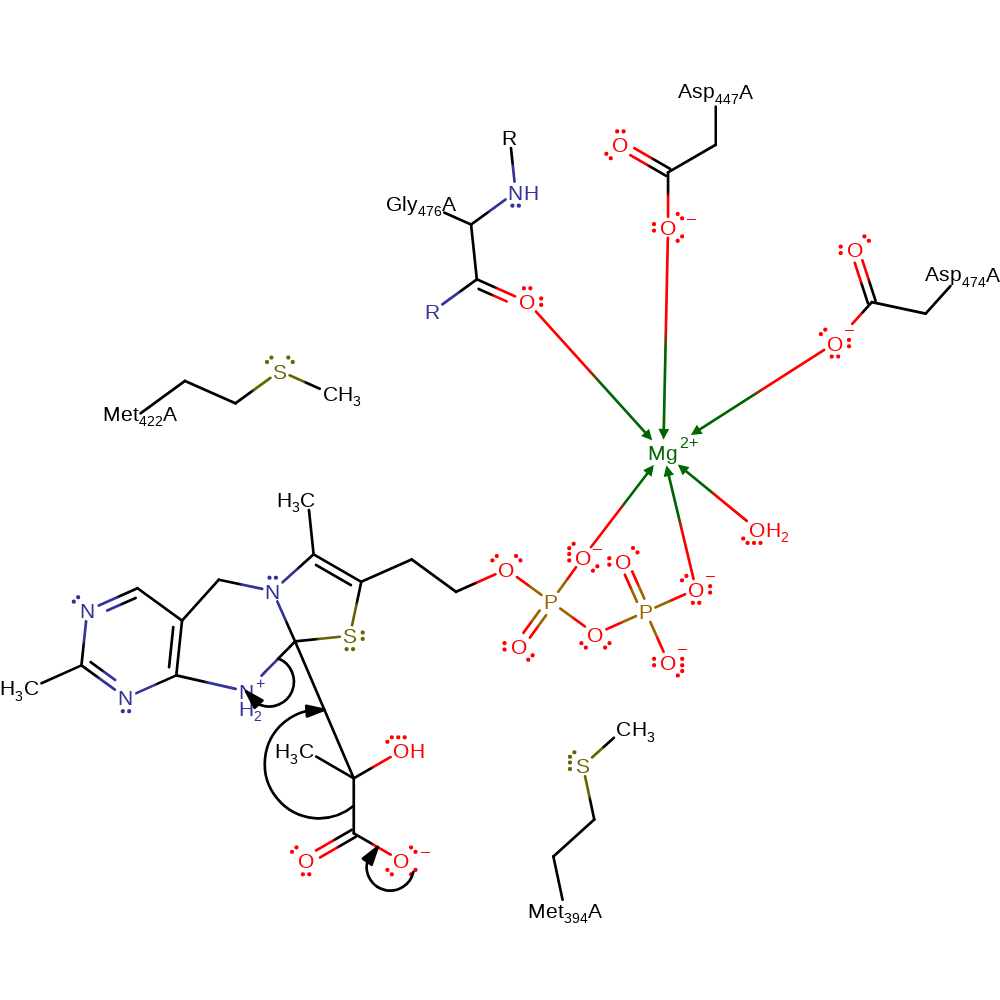
Step 4. Pyruvate undergoes decarboxylation with the formation of a carbon-carbon double bond and lysis of the ThDP C2 - 4'-amino group bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, decyclisation, overall product formed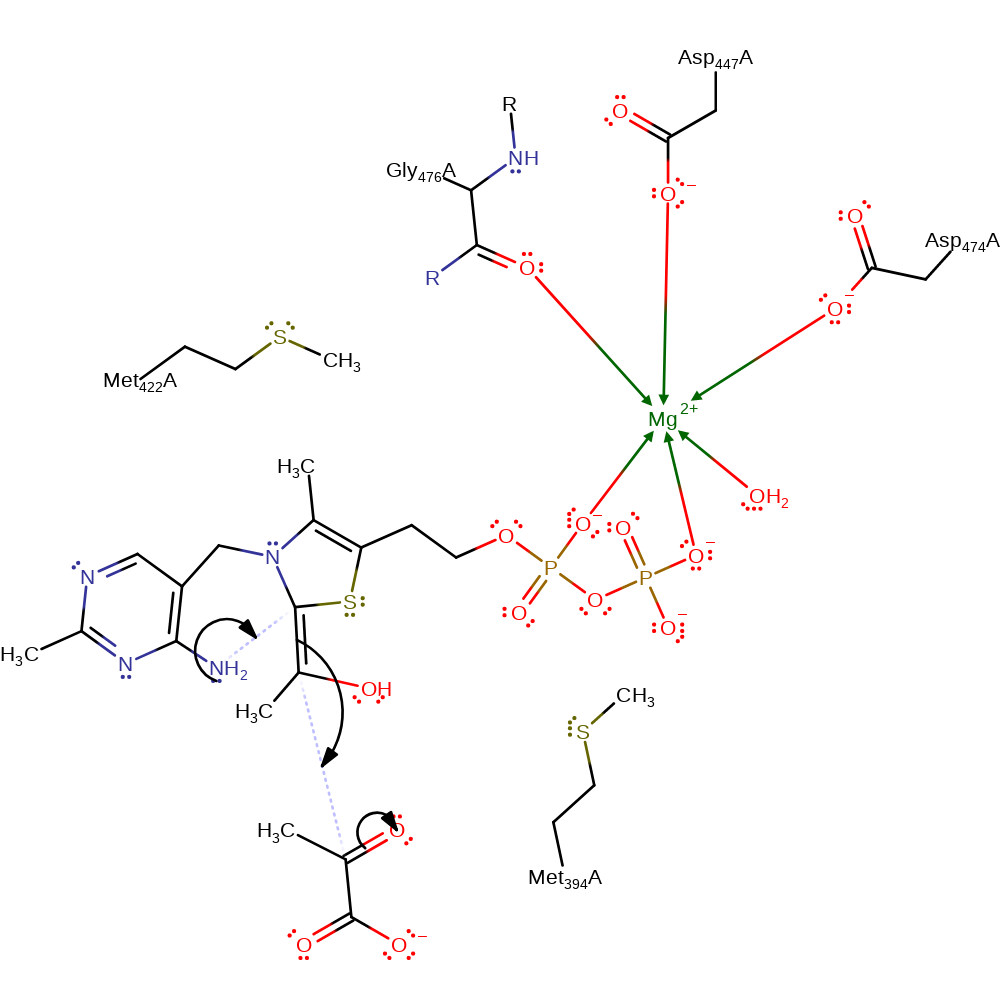
Step 5. The ThDP C-2 and the 4'-amino group bond reforms which causes nucleophilic attack of the double bond on a second equivalent of pyruvate. A proton is subsequently transferred between the developing oxyanion on the second pyruvate and the other hydroxyl group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cyclisation, intermediate formation
Step 6. The tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate collapses, releasing ThDP and the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intermediate collapse, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall product formed, decyclisation
Step 7. In an inferred step the C2 carbanion of ThDP is reprotonated to regenerate the neutral state of the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp447A | metal ligand |
| Asp474A | metal ligand |
| Gly476A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Met422A | steric role |
| Met394A | electrostatic stabiliser |




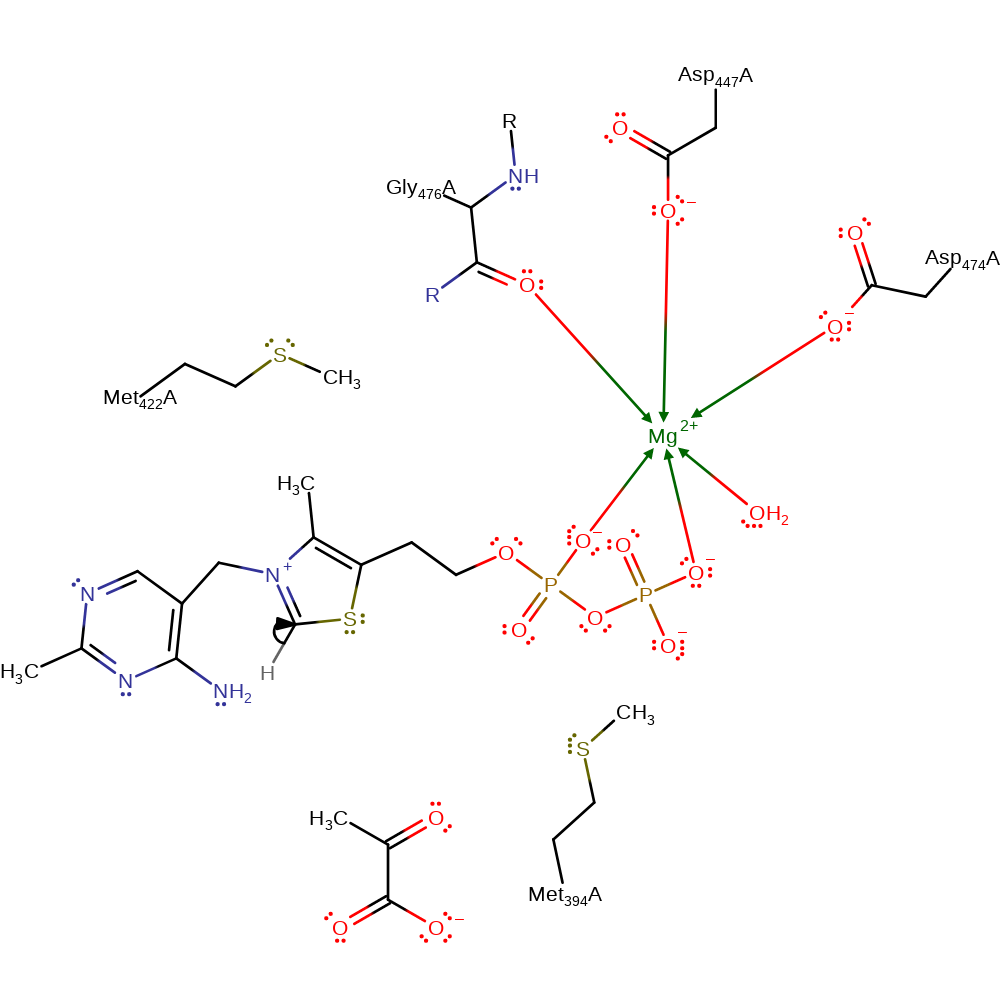
 Download:
Download: