Caspase-1
Caspases are thiol endopeptidases that cleave specific proteins after Asp residues and drive apoptosis or inflammation. Caspase-1 is part of the family of inflammatory-caspases, which also includes caspase-4 and caspase-5 in humans and caspase-11, -12, -13 and -14 in mice. Activation of caspase-1 requires oligomerisation of inactive monomeric proenzyme forms. Caspase-1 has a recognition site of Tyr-Val-Ala-Asp-|-. Caspase-1 is also known as interleukin converting enzyme (ICE) and cleaves precursors of the inflammatory interleukin1β and interleukin18 which converts them into mature, active peptides which can initiate a proinflammatory pathway. These often contribute to the pathophysioiogy of many inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including septic shock, rheumatoid arthritis, and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P29466
 (3.4.22.36)
(3.4.22.36)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
2fqq
- Crystal structure of human caspase-1 (Cys285->Ala, Cys362->Ala, Cys364->Ala, Cys397->Ala) in complex with 1-methyl-3-trifluoromethyl-1H-thieno[2,3-c]pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid (2-mercapto-ethyl)-amide
(3.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.70.1470
 3.40.50.1460
3.40.50.1460  (see all for 2fqq)
(see all for 2fqq)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.22.36)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
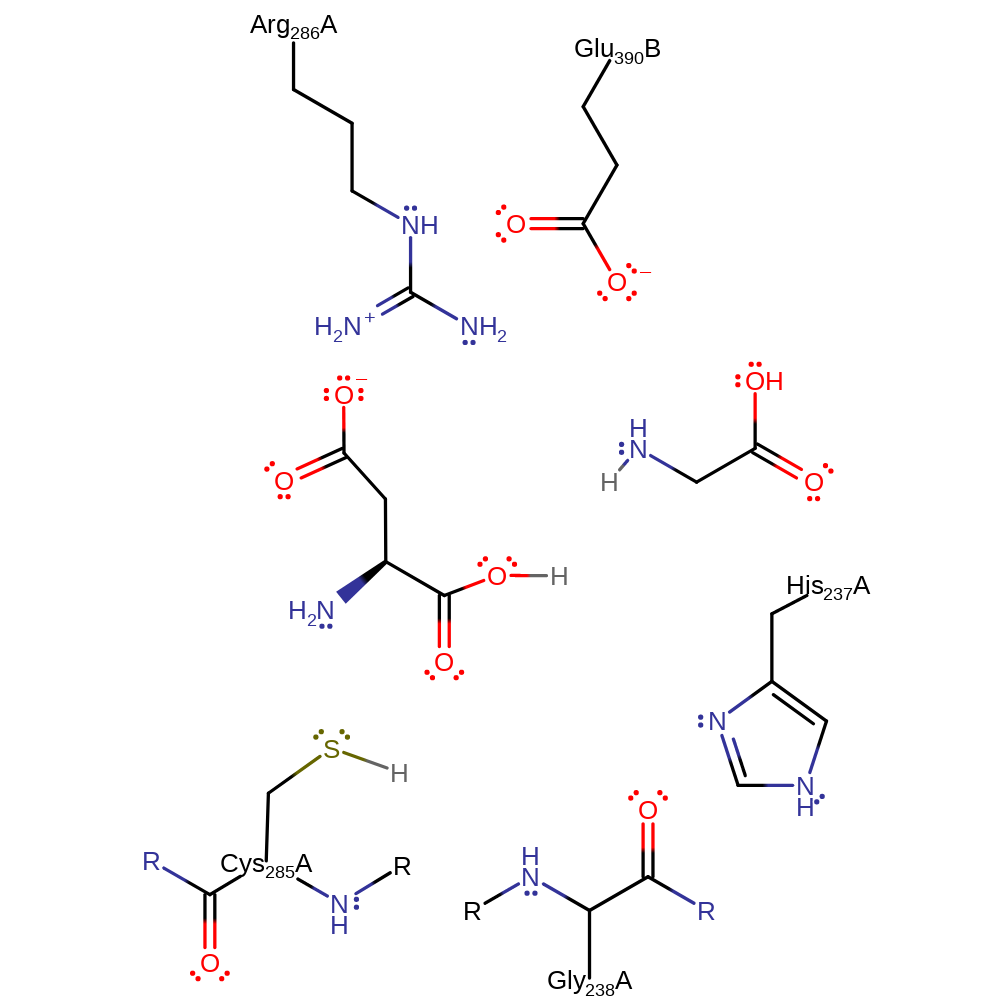
During the acylaton step, the carbonyl oxygen of the non-covalently bonded P1 (usually Asp) residue is anchored through hydrogen bonds to the backbone nitrogen atoms of Gly238 and Cys285 which from the oxyanion hole. This increases the polarisation of the C-O bond and therefore facilitates nucleophilic attack of the S atom of Cys285 on the highly electrophilic carbonyl carbon. The result is a covalent enzyme-substrate adduct - high energy tetrahedral intermediate. The imidazole moiety of His237 acts as a general acid by protonating the alpha-amino group of the leaving peptide product, thus avoiding re-formation of the peptide bond. Deacylation of the acyl-enzyme complex occurs in a similar way. The deprotonatad His237 side chain abstracts a proton from a water molecule, activating it as a nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon of the thioester bond, forming a second tetrahedral intermediate. Rupture of the S-C bond regenerates the enzyme in a non-covalent complex with the N-terminal peptide product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2fqq) | ||
| Cys285 (main-N), Cys285 | Ala285(166)A (main-N), Ala285(166)A | Cys285 backbone N forms part of the oxyanion hole which is involved in increasing the electrophicity of the taget carbon. Cys285 also acts as a nucleophile in the acylation step, attacking the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the substrate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg286 | Arg286(167)A | Works together with Glu290 to stabilise the transition state intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly238 (main-N) | Gly238(119)A (main-N) | The backbone N of this residue forms part of te oxyanion hole with Cys285. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His237 | His237(118)A | His237 activates water by proton abstraction to perform nucleophilic attack on the thioester bond of the acyl-enzyme intermediate in the deacylation step. The His237 delta-N atom is also involved in stabilising the leaving group to prevent peptide re-formation. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu390 | Glu390(74)B | Glu390 works with Arg286 to stabilise the transition state intermediate together. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Scheer JM et al. (2006), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103, 7595-7600. A common allosteric site and mechanism in caspases. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0602571103. PMID:16682620.
- Wilson KP et al. (1994), Nature, 370, 270-275. Structure and mechanism of interleukin-lβ converting enzyme. DOI:10.1038/370270a0. PMID:8035875.
- Walker NP et al. (1994), Cell, 78, 343-352. Crystal structure of the cysteine protease interleukin-1β-converting enzyme: A (p20/p10)2 homodimer. DOI:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90303-4. PMID:8044845.
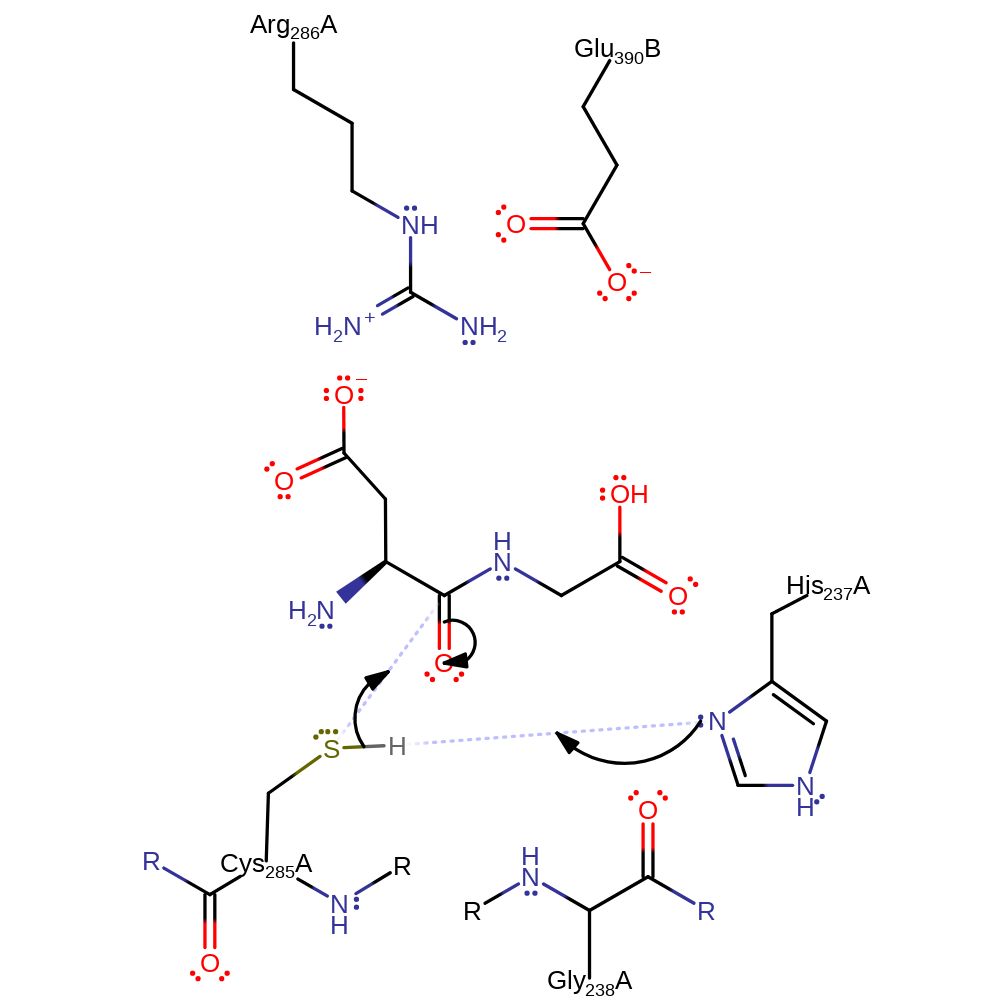
Step 1. His237 deprotonates Cys55 which activates it to attack the carbonyl group of the peptide bond by nucleophilic addition which produces the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg286(167)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly238(119)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu390(74)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala285(166)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His237(118)A | proton acceptor |
| Ala285(166)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used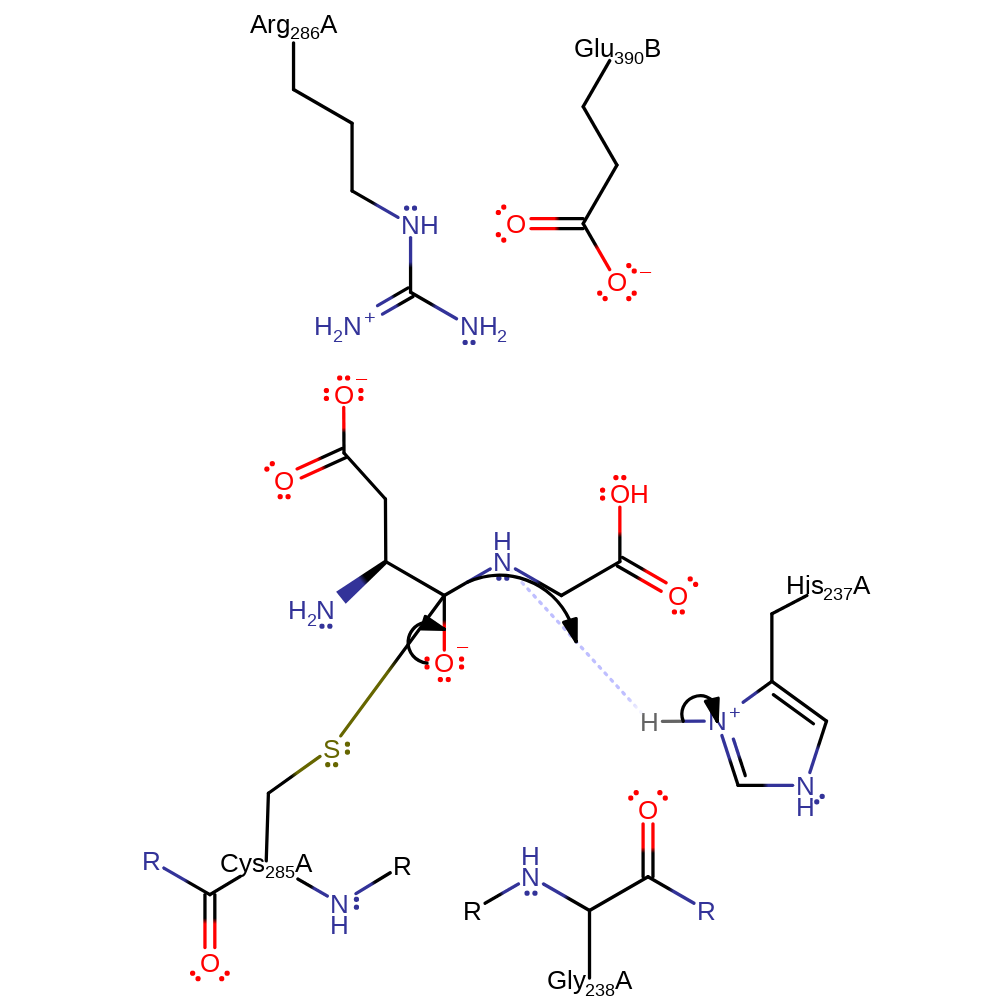
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimantion resulting in the cleavage of the peptide bond, the N-terminal product then accepts a proton from His237.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly238(119)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala285(166)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg286(167)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu390(74)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His237(118)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed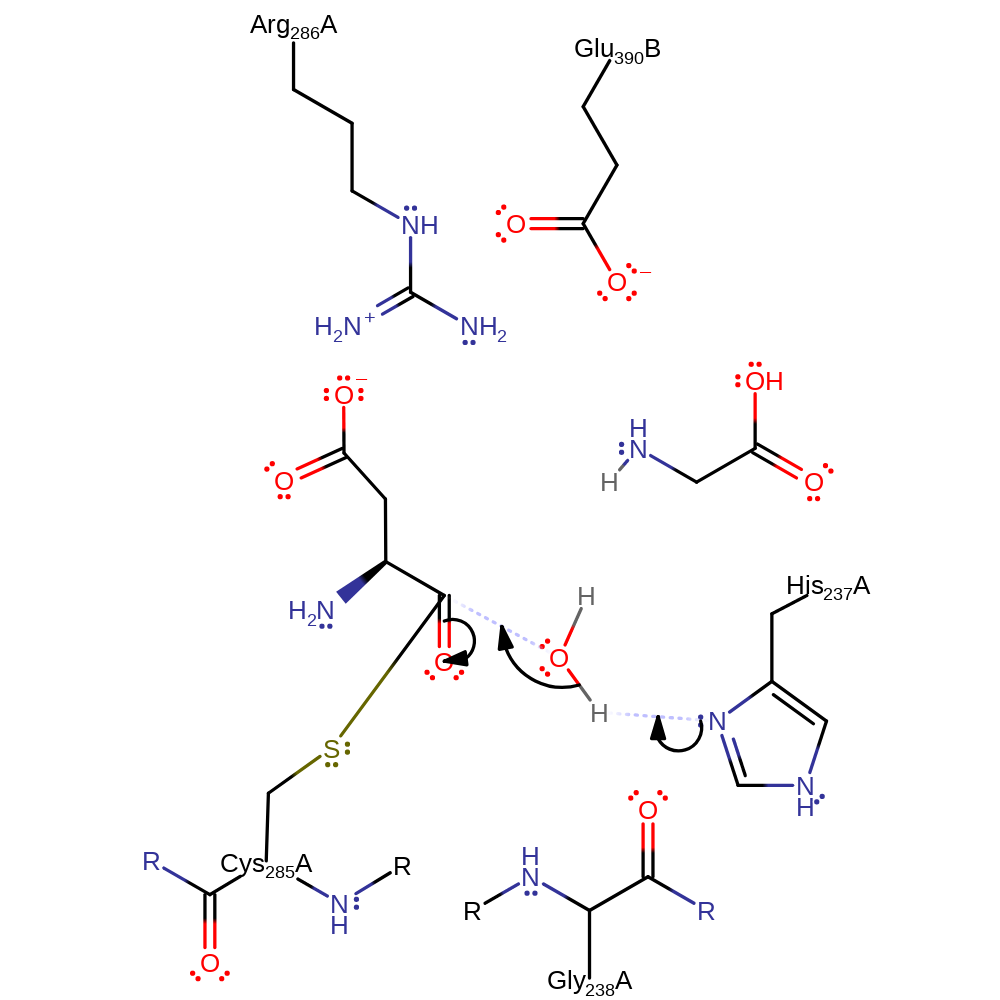
Step 3. His237 deprotonates water activating it to attack the carbon of the carbonyl carbon of the thioester bond by nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly238(119)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala285(166)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg286(167)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu390(74)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His237(118)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used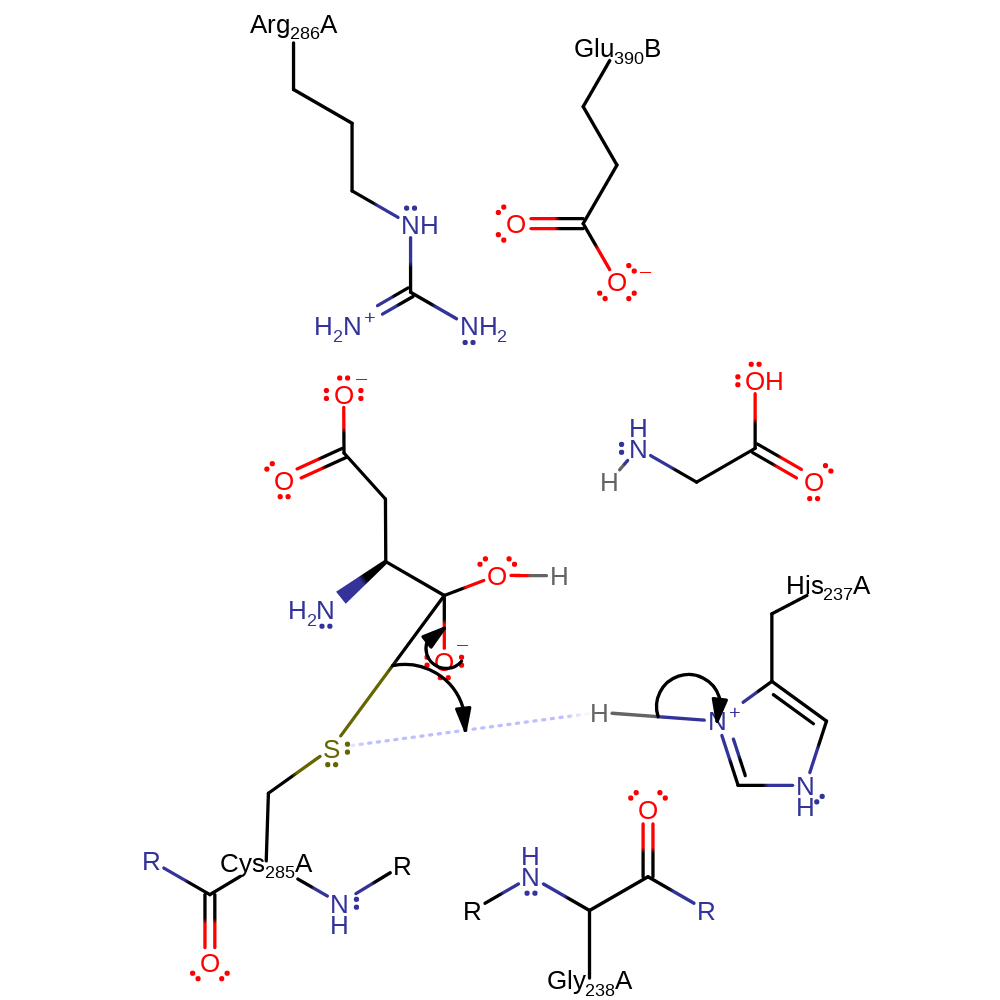
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the thioester bond and thus releasing the C-terminal product. Cys285 will then accept a proton from His237 returning the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly238(119)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala285(166)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg286(167)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu390(74)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His237(118)A | proton donor |
| Ala285(166)A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |




 Download:
Download: