Arylsulfatase
Sulfatase enzymes are a highly homologous enzyme family which catalyse the hydrolysis of sulphate-ester bonds.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P51691
 (3.1.6.1)
(3.1.6.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1hdh
- Arylsulfatase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
(1.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.720.10
 (see all for 1hdh)
(see all for 1hdh)
- Cofactors
- Calcium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.6.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The sulfate ester cleavage involves an aldehyde hydrate, a modified residue FGly 51, as the functional group that initiates the reaction through a nucleophilic attack on the sulphur atom of the substrate. Lys 113 and FGly 51 contribute to electron density withdrawal from the sulfate oxygen atoms to give increased electrophilicity at the sulphur centre. The nucleophilicity of the oxygen in the aldehyde hydrate is enhanced by coordination to the Ca cation and facilitated proton transfer by Asp 317. An alcohol is eliminated in an SN2 substitution reaction, and the pentacoordinate sulphur intermediate is stabilised by Lys 375, His 211 and the Ca cation - the His or the Lys can act as proton donors to the alcoholate depending on the pH conditions. Sulfate elimination regenerates the aldehyde, by deprotonation of FGly 51 with His 115 acting as a proton acceptor. The aldehyde is hydrated by water, with the C-O bond being polarised by His 115, Arg 55, Asn 318 and the Ca cation.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hdh) | ||
| Lys113 | Lys113A | Contributes to electron density withdrawal on substrate to increase electrophilicity of sulphur atom. | increase electrophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115, Arg55 | His115A, Arg55A | Activates aldehyde for hydration. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211 | His211A | Stabilises the transition state and may act as a base depending on the pH conditions. | electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp317 | Asp317A | Increases the nucleophilicity of the aldehyde hydrate attacking oxygen by proton abstraction. | increase nucleophilicity, activator, metal ligand, proton acceptor |
| Lys375 | Lys375A | Stabilises the transition state, and may act as a base depending on the pH conditions. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, heterolysis, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Boltes I et al. (2001), Structure, 9, 483-491. 1.3 Å Structure of Arylsulfatase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Establishes the Catalytic Mechanism of Sulfate Ester Cleavage in the Sulfatase Family. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00609-8. PMID:11435113.
- Marino T et al. (2013), Chemistry, 19, 2185-2192. Catalytic mechanism of the arylsulfatase promiscuous enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. DOI:10.1002/chem.201201943. PMID:23280779.
- Waldow A et al. (1999), J Biol Chem, 274, 12284-12288. Amino Acid Residues Forming the Active Site of Arylsulfatase A: ROLE IN CATALYTIC ACTIVITY AND SUBSTRATE BINDING. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.18.12284. PMID:10212197.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys375A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys113A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg55A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp317A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Asp13A | metal ligand |
| Asp14A | metal ligand |
| X51A (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Asp317A | metal ligand |
| Asn318A | metal ligand |
| Asp317A | activator |
| X51A (ptm) | proton donor |
| Asp317A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer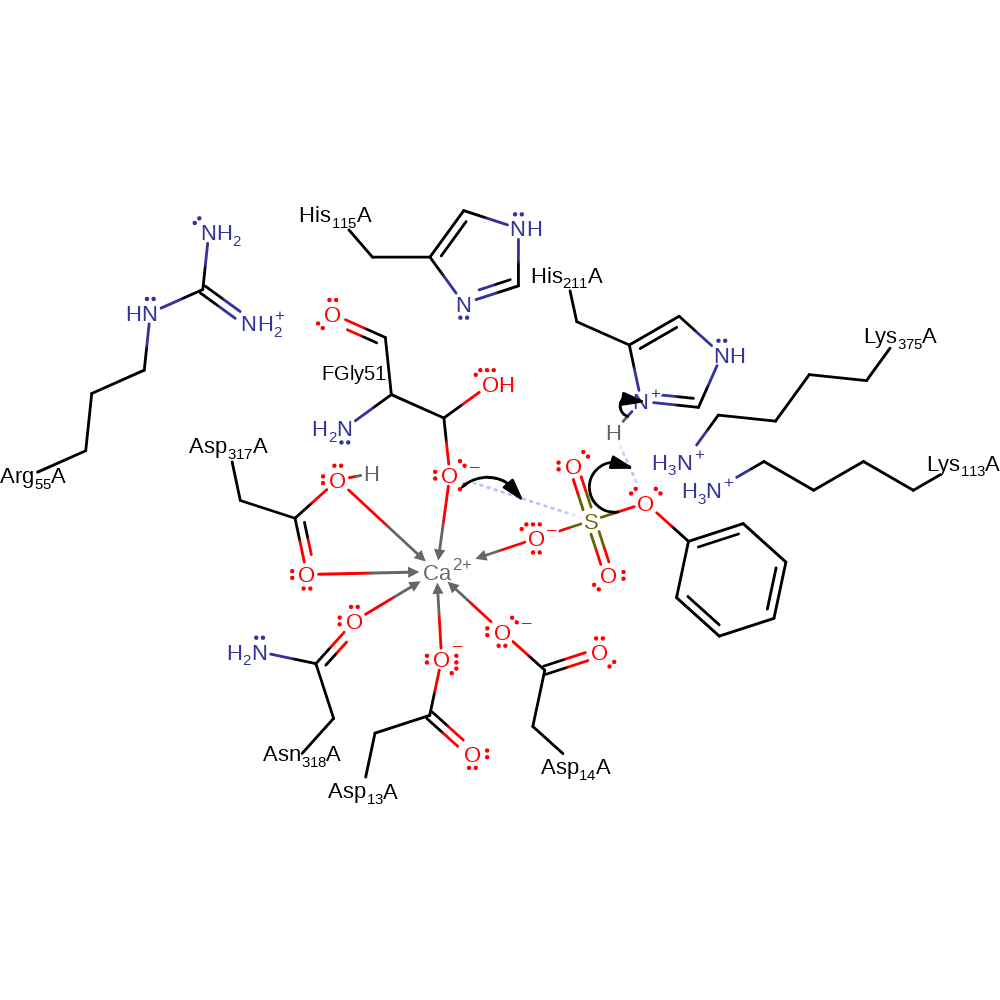
Step 2. The activated hydrate attacks the sulfate group, and the bond between the sulfate and the phenol is cleaved.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| X51A (ptm) | nucleophile |
| Arg55A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys113A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys375A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp13A | metal ligand |
| Asp14A | metal ligand |
| X51A (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Asp317A | metal ligand |
| Asn318A | metal ligand |
| X51A (ptm) | covalently attached |
| X51A (ptm) | increase electrophilicity |
| Lys113A | increase electrophilicity |
| His211A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, overall product formed, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, proton transfer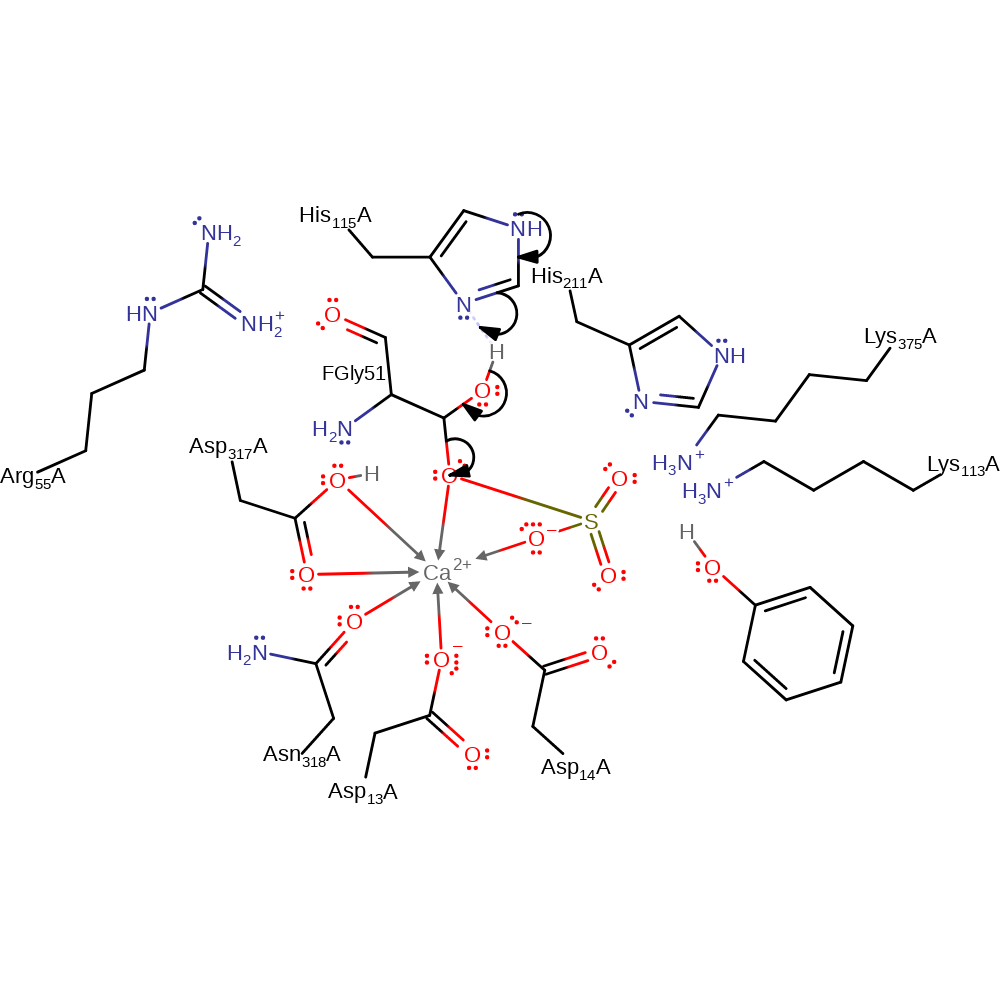
Step 3. The hydrate collapses into an aldehyde and sulfate is released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp13A | metal ligand |
| Asp14A | metal ligand |
| X51A (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Asp317A | metal ligand |
| Asn318A | metal ligand |
| Arg55A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys113A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys375A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115A | proton acceptor |





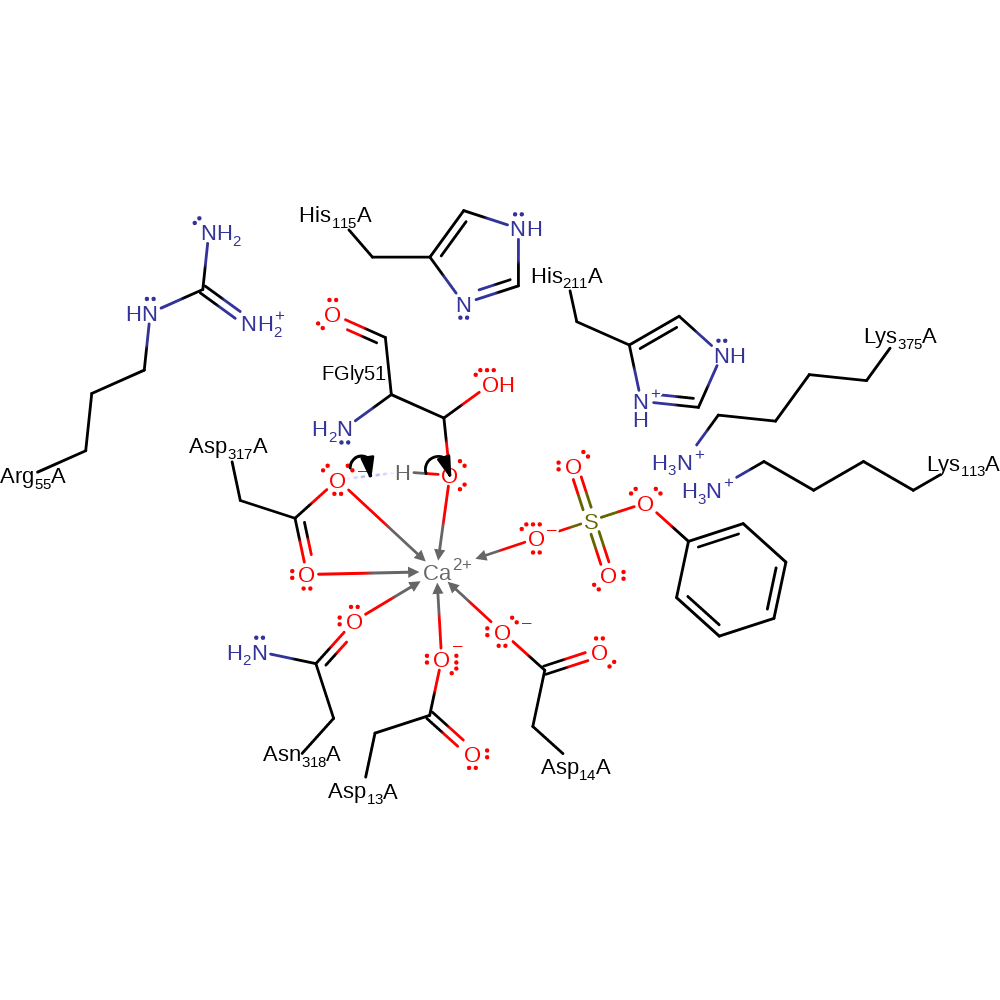
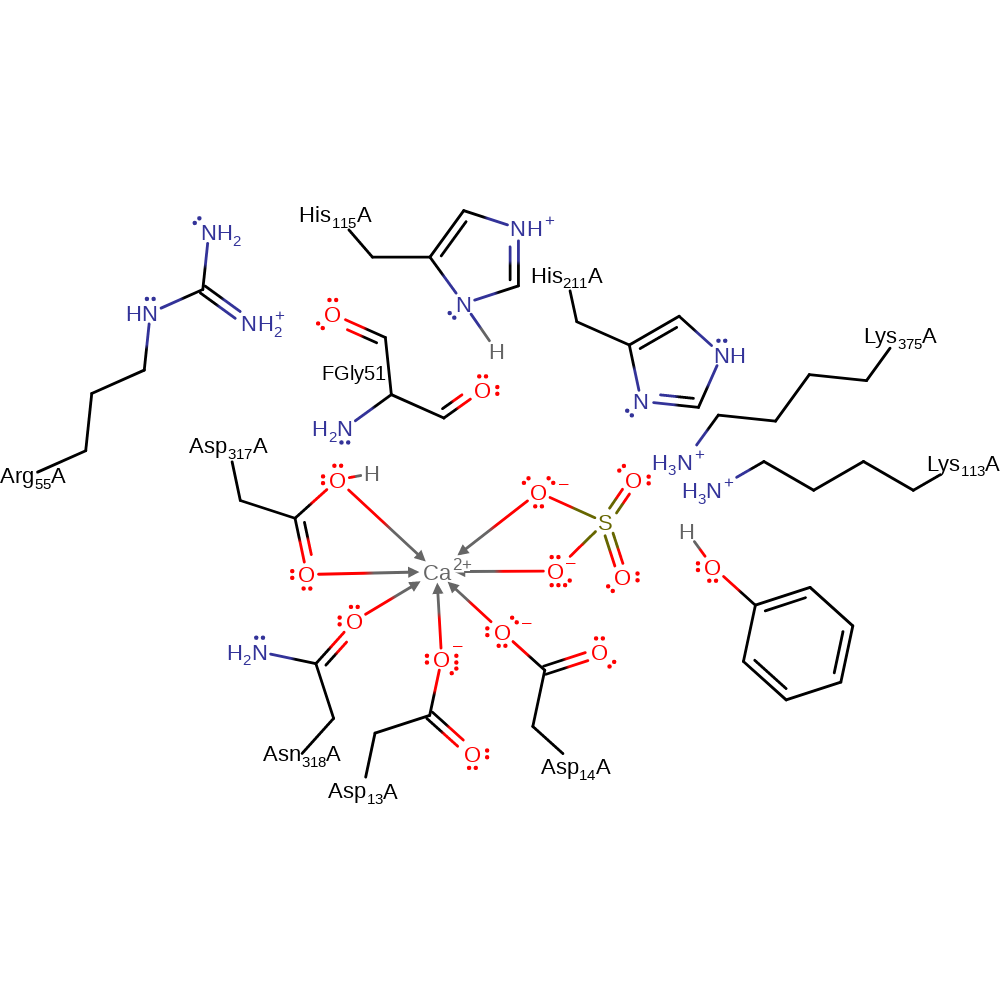 Download:
Download: