Vesicle-fusing ATPase
N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor is responsible for the destabilisation and disassembly of the proteins in the SNARE complex thus has a key role in vesicular trafficking inside the cell. The structure described in this pdb code is of the ATP binding domain which contains the active site necessary for ATP hydrolysis: conformational changes that occur as a result of the hydrolysis lead to the breaking up of the SNARE complex. The ATP binding domain of the protein shares homology with other Rossmann fold containing proteins, particularly with E. coli DNA polymerase III.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P18708
 (3.6.4.6)
(3.6.4.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster)

- PDB
-
1nsf
- D2 HEXAMERIZATION DOMAIN OF N-ETHYLMALEIMIDE SENSITIVE FACTOR (NSF)
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.8.60
 3.40.50.300
3.40.50.300  (see all for 1nsf)
(see all for 1nsf)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
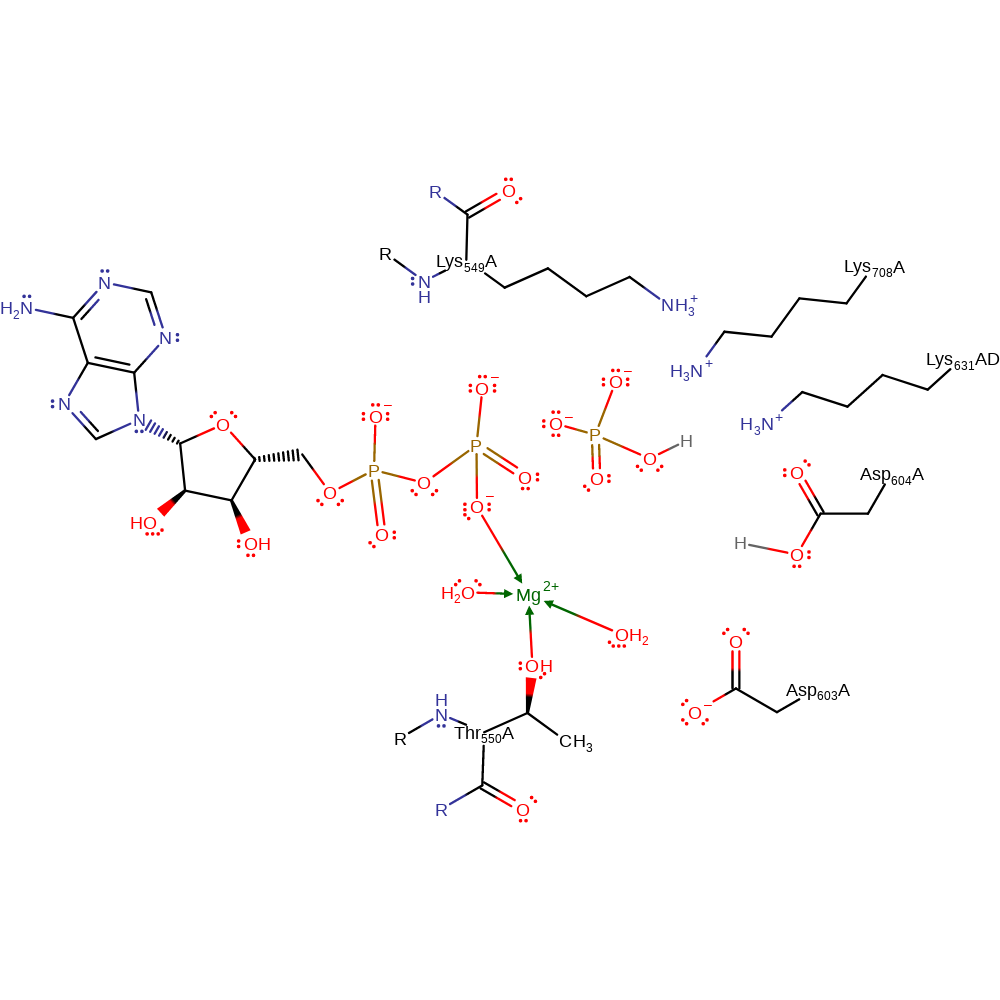
Hydrolysis of ATP is facilitated by a Mg2+ ion and two Lysine residues (Lys 549 and Lys 708) and Thr 550 which contact the beta and gamma phosphates of the ATP and Asp 504 and Mg2+ aid in the deprotonation of water so that it can nucleophilically attack the gamma phosphate of ATP. This enables the conformational changes that cause the breaking up of the hexameric protein and the collapse of the SNARE complex. However, in order to reduce the rate that this occurs to allow the protein to interact with the SNARE complex before breaking up, Lys 631 acts to reduce the rate of hydrolysis so that ATP stays bound for as long as possible.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1nsf) | ||
| Thr550 | Thr550(77)A | Coordinates to Mg2+ | metal ligand |
| Thr550 (main-N) | Thr550(77)A (main-N) | Forms electrostatic contacts to the beta phosphate of ATP, thus stabilising the pentavalent phosphate intermediate thus facilitating hydrolysis of ATP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp603 | Asp603(130)A | Forms an electrostatic interaction with a water molecule that is coordinated to Mg2+ | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp604 | Asp604(131)A | Activates water by deprotonating it so it can nucleophilically attack the gamma phosphate of ATP | proton acceptor |
| Lys549 | Lys549(76)A | Forms electrostatic contacts to the gamma and beta phosphate of ATP, thus stabilising the pentavalent phosphate intermediate thus facilitating hydrolysis of ATP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys708 | Lys708(235)A | Forms electrostatic contact with the gamma phosphate of ATP thus stabilises the pentavalent phosphate that forms when hydrolysis occurs. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys631 | Lys631(158)A(AD) | Acts to reduce the rate at which incoming water molecules are deprotonated, thus reducing the rate of nucleophilic attack on the ATP. This has the overall effect of speeding up the dissociation of the SNARE complex because it allows the hexamer to remain intact whilst binding to the SNARE complex. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme is not regeneratedReferences
- Yu RC et al. (1998), Nat Struct Biol, 5, 803-811. Structure of the ATP-dependent oligomerization domain of N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor complexed with ATP. DOI:10.1038/1843. PMID:9731775.
- Zhao C et al. (2012), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1823, 159-171. Requirements for the catalytic cycle of the N-ethylmaleimide-Sensitive Factor (NSF). DOI:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.003. PMID:21689688.

Step 1. Asp 604 deprotonates the polarised water molecule which activates it to nucleophilically attack the gamma phosphate which results in the cleavage of the phosphoanhydride bond and release of the gamma phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys708(235)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys631(158)A(AD) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys549(76)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys549(76)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr550(77)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp603(130)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr550(77)A | metal ligand |
| Asp604(131)A | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: