Hyaluronoglucosaminidase
Bee venom hyaluronidase is an endo-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidase that specifically cleaves the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc) and D-glucuronic acid (GlcA) in hyaluronic acid. It degrades hyaluronic acid in the extracellular matrix of skin, so facilitating penetration of venom constituents into the body. The bee venom enzyme shows some sequence identity with human hyaluronidases, which are involved in hyaluronic acid turnover and also in fertilisation. Bee venom hyaluronidase has been classified with the mammalian enzymes in the glycosidase family 56.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q08169
 (3.2.1.35)
(3.2.1.35)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Apis mellifera (Honey bee)

- PDB
-
1fcq
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE (MONOCLINIC) OF BEE VENOM HYALURONIDASE
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 1fcq)
(see all for 1fcq)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.2.1.35)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
As in the chitinolytic enzymes, the sugar ring is distorted towards the transition state, with the antibonding orbital of the scissile bond held in a favourable orientation to overlap with the non-bonding orbital containing one of the ring oxygen lone pairs. In addition, the carbonyl of the substrate N-acetyl moiety is directed towards the C1 carbon. The reaction can then proceed either via an oxocarbonium ion intermediate or an oxozolium ion with a covalent bond between the N-acetyl carbonyl oxygen and the C1 atom. The oxygen of the departing sugar is protonated by Glu 113 acting as a general acid. Later Glu 113 acts as a general base to deprotonate a water molecule as it attacks the intermediate to complete the reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fcq) | ||
| Asp143 | Asp111A | Elevates pKa and protonation state of Glu 113. Backbone NH interacts with the substrate N-acetyl sidechain and forces deformation of the sugar ring towards the transition state. Directs the carbonyl group of the N-acetyl moiety towards the C1 of the sugar ring. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Glu145 | Glu113A | Protonates C4 OH of departing sugar. Later deprotonates attacking water molecule. | proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, increase nucleophilicity, promote heterolysis |
| Tyr259 | Tyr227A | Interacts via phenolic OH with the substrate N-acetyl sidechain and forces deformation of the sugar ring towards the transition state. Directs the carbonyl group of the N-acetyl moiety towards the C1 of the sugar ring. The acidic phenol group of this residue is also thought to stabilise the positive charge of the intermediate. | transition state stabiliser, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr216, Trp333 | Tyr184A, Trp301A | Interacts hydrophobically with the substrate N-acetyl sidechain and forces deformation of the sugar ring towards the transition state. Directs the carbonyl group of the N-acetyl moiety towards the C1 of the sugar ring. | steric role |
Chemical Components
intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, decyclisation, hydrolysis, bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionReferences
- Marković-Housley Z et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 1025-1035. Crystal Structure of Hyaluronidase, a Major Allergen of Bee Venom. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00511-6. PMID:11080624.
- Zhang L et al. (2009), J Biol Chem, 284, 9433-9442. Hyaluronidase activity of human Hyal1 requires active site acidic and tyrosine residues. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M900210200. PMID:19201751.
- Tews I et al. (1997), J Am Chem Soc, 119, 7954-7959. Substrate-Assisted Catalysis Unifies Two Families of Chitinolytic Enzymes. DOI:10.1021/ja970674i.
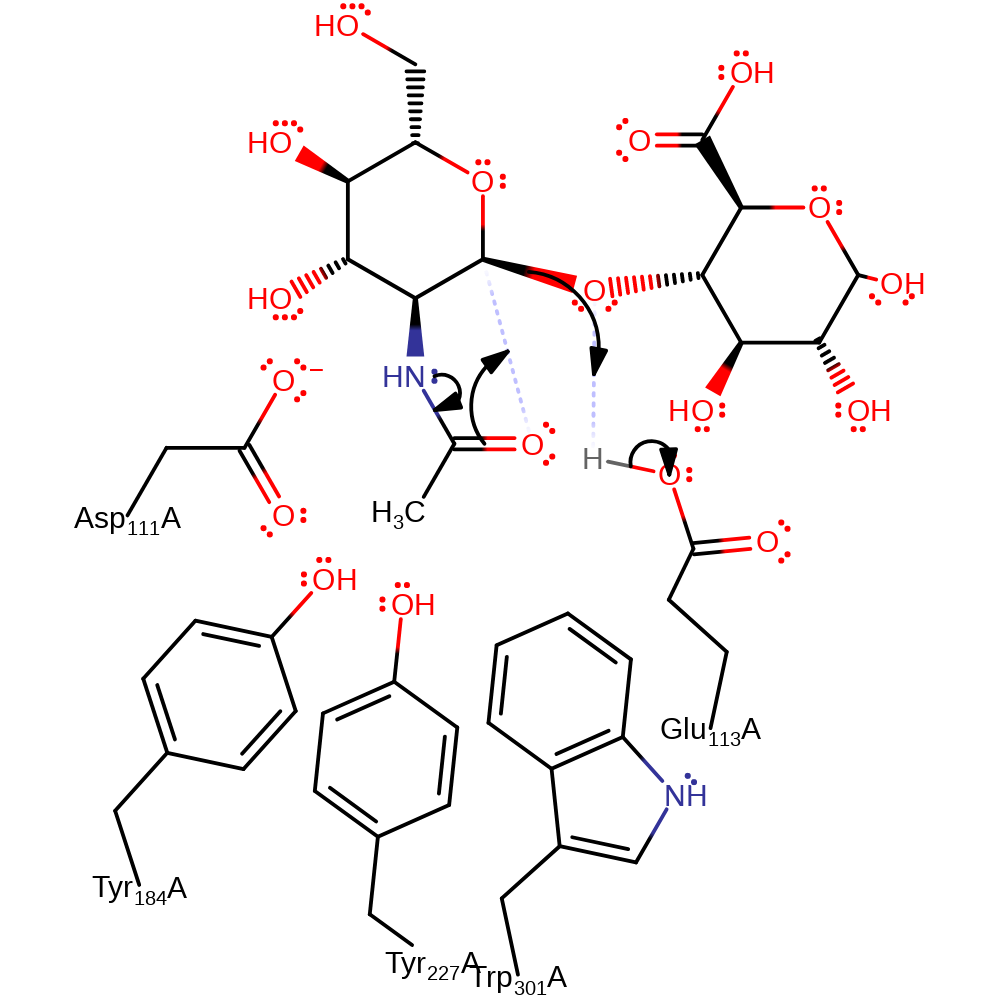
Step 1. Tyr184, Ty227 and Trp301 forces the substrate into a conformation toward the transition state. This causes an intramolecular nucleophilic addition reaction where the oxygen of the N-acetyl group attacks C1 causing the glycosidic bond to break. Glu113 acts as an acid by protonating the leaving group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp111A | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr184A | steric role |
| Tyr227A | steric role |
| Trp301A | steric role |
| Tyr227A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp111A | modifies pKa |
| Glu113A | promote heterolysis |
| Tyr227A | transition state stabiliser |
| Glu113A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used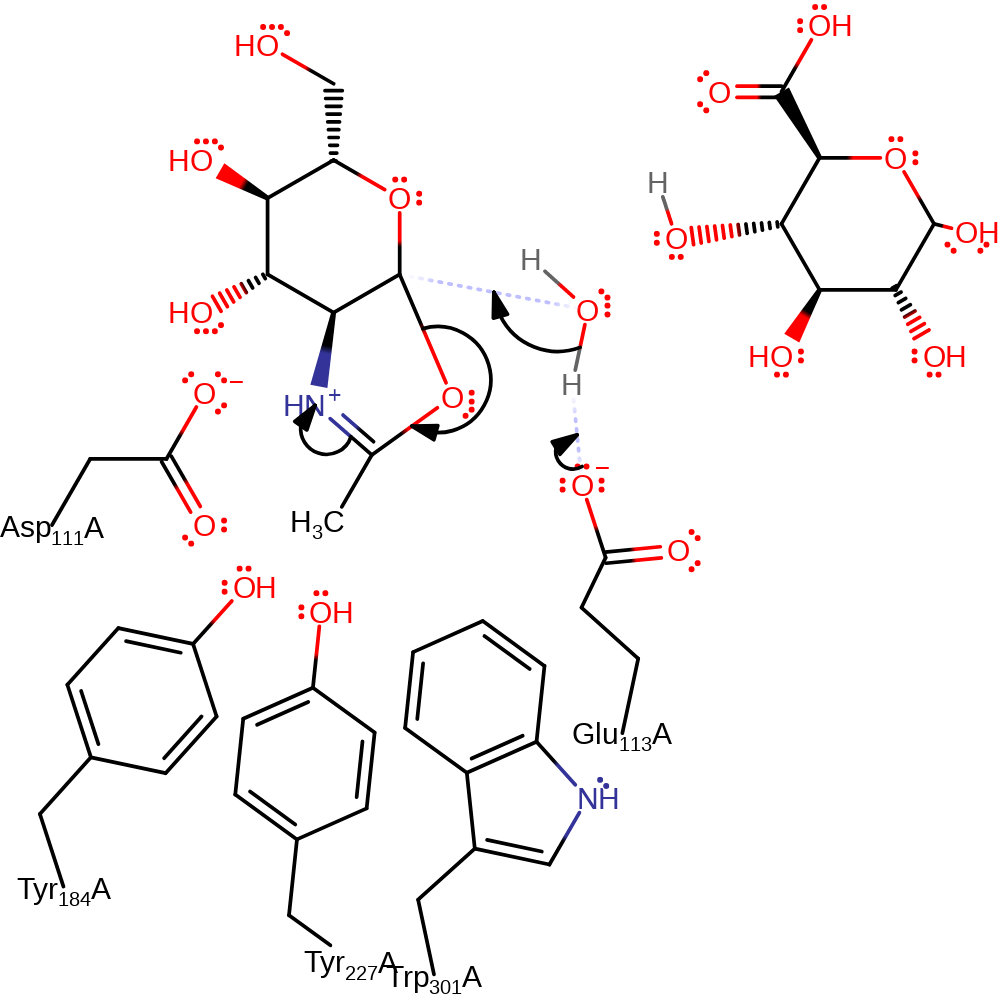
Step 2. Glu113 now acts as a base activating a water molecule to hydrolyse the cyclic intermediate and form the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr184A | steric role |
| Tyr227A | steric role |
| Trp301A | steric role |
| Asp111A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr227A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp111A | steric role, modifies pKa |
| Glu113A | activator, increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor |




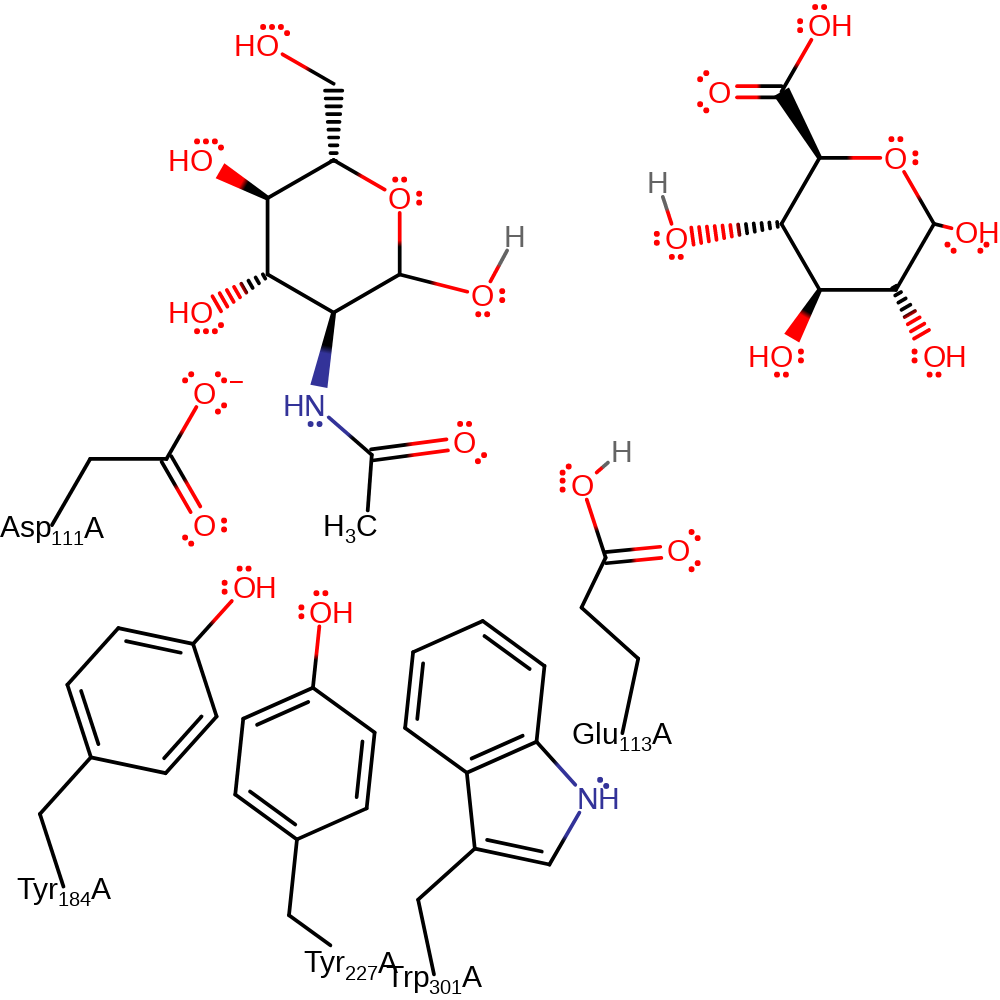 Download:
Download: