Protein-arginine deiminase
In the presence of calcium ions, Protein-arginine deiminase (PAD) enzymes catalyse the post-translational modification reaction responsible for the formation of citrulline residues from protein-bound arginine residues. The gene for this enzyme is a susceptibility locus for rheumatoid arthritis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9UM07
 (3.5.3.15)
(3.5.3.15)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1wd8
- Calcium free form of human peptidylarginine deiminase type4 (PAD4)
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.75.10.10
 (see all for 1wd8)
(see all for 1wd8)
- Cofactors
- Calcium(2+) (5)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Calcium binding causes conformational changes that order the reaction centre. A nucleophilic attack is made by the thiol group of Cys 645 onto the zeta-carbon of peptidyl-L-arginine. The carboxyl groups of Asp 350 and Asp 473 activate the substrate by formation of hydrogen bonds and a salt bridge to increase the nucleophilicity of the zeta carbon. Cleavage of the bond between the zeta-carbon and the nu-nitrogen-2 to generate ammonia. The general base His 471 then activates water so that the water may undertake a nucleophilic attack. Hydrolysis of the tetrahedral adduct yields peptidyl-L-citrulline.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1wd8) | ||
| Asp350 | Asp350(357)A | The carboxyl group activates the substrate by hydrogen bond and salt bridge formation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His471 | His471(478)A | Acts as a general base and activates Cys 645 and water to allow them to attack as a nucleophile. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp473 | Asp473(480)A | Activates substrate by hydrogen bond and salt bridge formation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys645 | Cys645(652)A | Thiol group attacks zeta-carbon of peptidyl-L-arginine as a nucleophile. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Arita K et al. (2004), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 11, 777-783. Structural basis for Ca2+-induced activation of human PAD4. DOI:10.1038/nsmb799. PMID:15247907.
- Slade DJ et al. (2015), ACS Chem Biol, 10, 1043-1053. Protein arginine deiminase 2 binds calcium in an ordered fashion: implications for inhibitor design. DOI:10.1021/cb500933j. PMID:25621824.
- Dreyton CJ et al. (2014), Biochemistry, 53, 4426-4433. Mechanistic studies of protein arginine deiminase 2: evidence for a substrate-assisted mechanism. DOI:10.1021/bi500554b. PMID:24989433.
- Kubota K et al. (2005), Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom, 19, 683-688. Determination of sites citrullinated by peptidylarginine deiminase using18O stable isotope labeling and mass spectrometry. DOI:10.1002/rcm.1842. PMID:15700232.
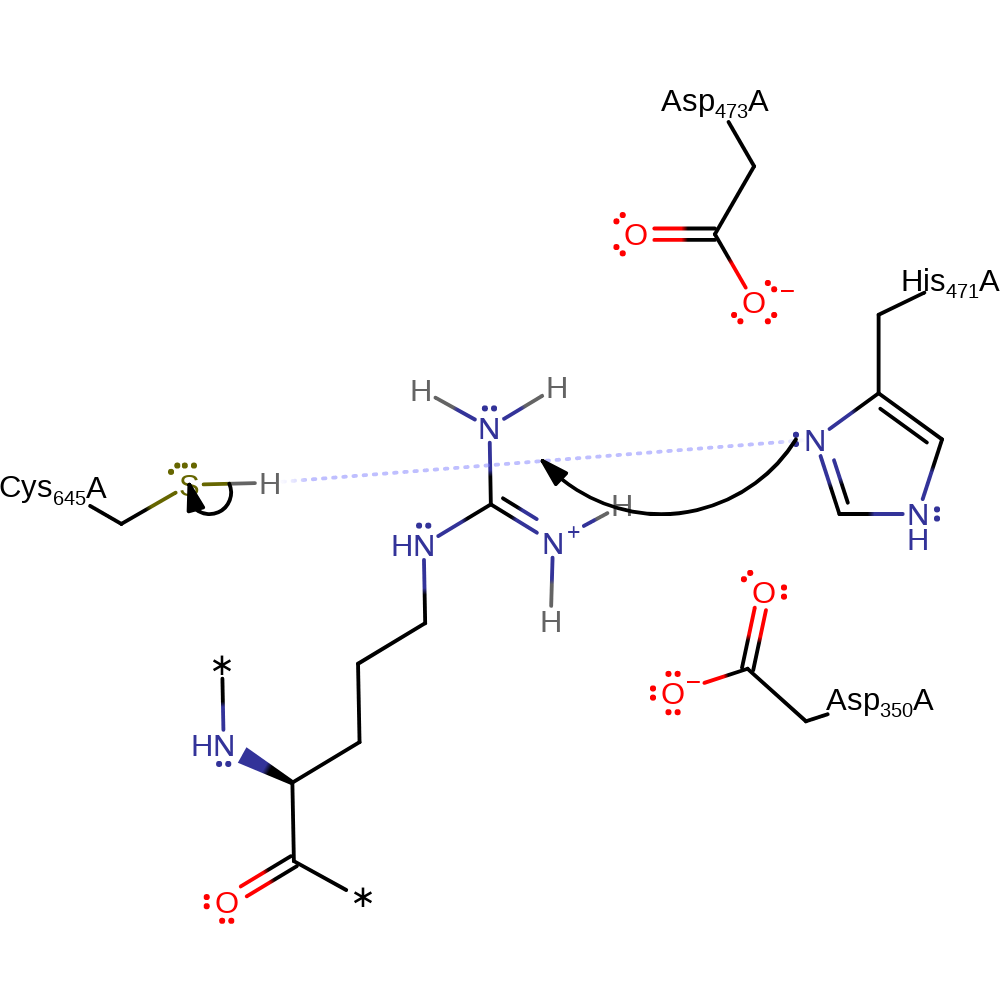
Step 1. His471 deprotonates Cys645 to activate it for nucleophilic attack.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp473(480)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp350(357)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His471(478)A | proton acceptor |
| Cys645(652)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer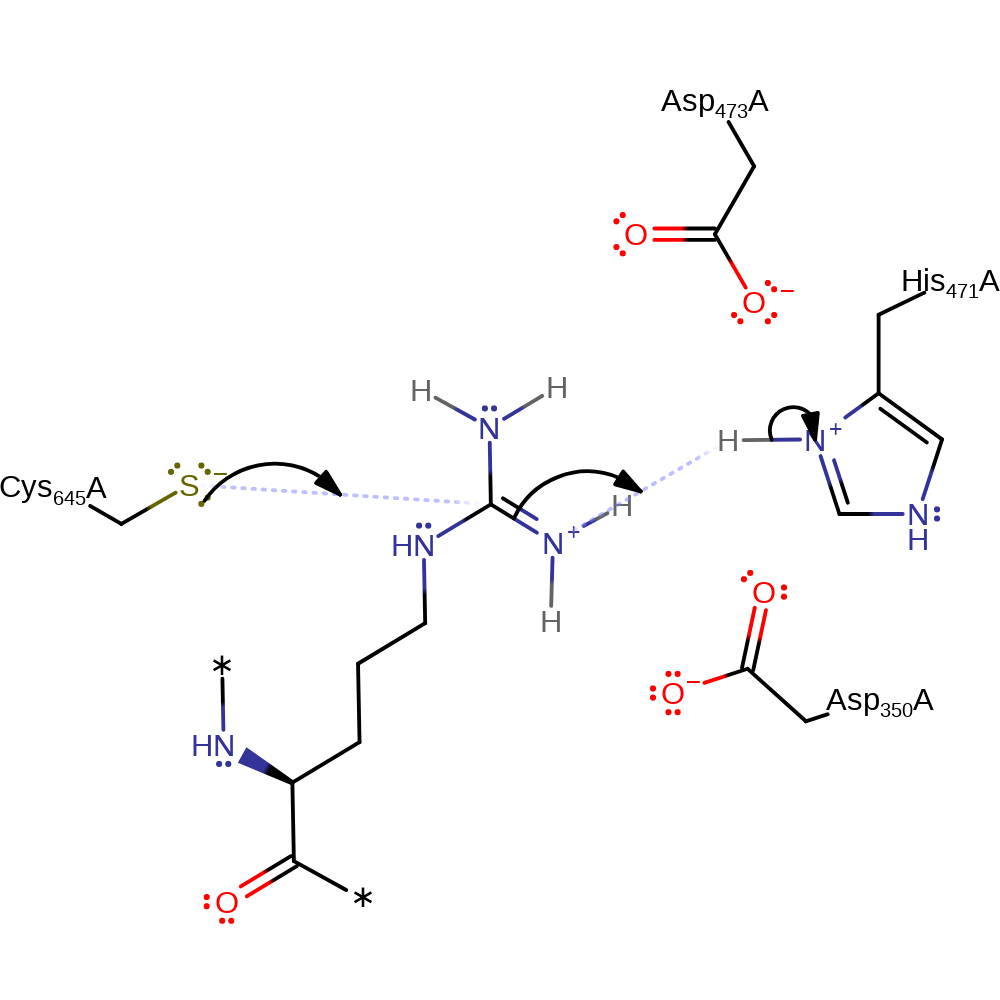
Step 2. Cys647 nucleophilically attacks the guanidinum carbon of arginine. Within this step, His471 acts as a general acid, protonating the guanidinium group
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp350(357)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp473(480)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys645(652)A | nucleophile |
| His471(478)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining stepCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp350(357)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp473(480)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse
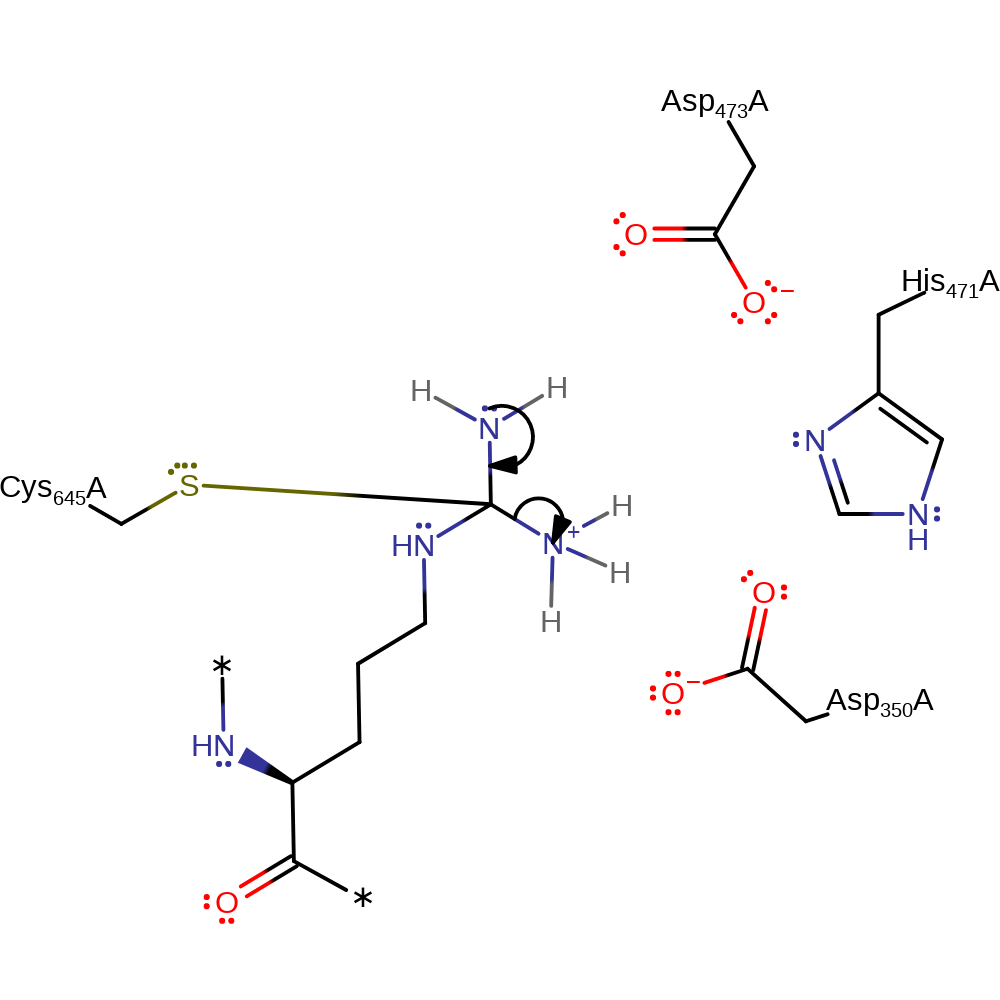
Step 4. His471 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the C=N bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp350(357)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp473(480)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His471(478)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 5. The second tetrahedral intermediate formed protonates Cys645 which initiates the elimination resulting in the cleavage of the acyl-enzyme bond and the release of the citrullinated product.The ammonia released prior can accept a proton from His471 to return the active site to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp350(357)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp473(480)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His471(478)A | proton donor |
| Cys645(652)A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: