1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme which catalyses a cyclopropane ring-opening reaction, the irreversible conversion of ACC to ammonia and alpha-ketobutyrate. In plants, the latter is a precursor of the ripening hormone ethylene. Some plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria can produce 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase to enhance plant growth.
ACC deaminase is unique amongst PLP-dependent enzymes, since the ring cleavage catalysed by ACC deaminase cannot proceed through an α-carbanionic intermediate due to the lack of an abstractable alpha-hydrogen atom from the substrate ACC.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q7M523
 (3.5.99.7)
(3.5.99.7)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Cyberlindnera saturnus (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1f2d
- 1-AMINOCYCLOPROPANE-1-CARBOXYLATE DEAMINASE
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1100
 (see all for 1f2d)
(see all for 1f2d)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.99.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The substrate ACC reacts with the PLP cofactor and with the enzyme ACC deaminase to first produce an internal aldimine between the PLP and the Lys residue of the protein. This is followed by an aminyl intermediate which produces the external aldimine. This is followed by nucleophilic attack by a basic residue on the pro-S beta-carbon of ACC. Ring opening is initiated, aided by a nearby second basic residue located on the protein which removes a proton from the pro-R beta-carbon. This results in the formation of a quinonoid. The quinonoid undergoes electronic rearrangement to form another quinonoid. This is followed by deprotonation of a nearby residue regaining its nucleophilic capacity (basic activity) on the protein backbone. This eventually produces an aminocrotonate and a quinoid. These products reversibly undergo hydrolysis to form α-ketobutyrate and ammonium, regenerating the internal aldimine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1f2d) | ||
| Tyr269 | Tyr269A | The residue is implicated in a proton relay from the surrounding solvent to the active site. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295 | Tyr295A | The residue has been proposed to act as a nucleophile towards the pro-S carbon of the ACC substrate. The close interaction between the residue and the carboxylate group of ACC is thought to lower the pKa of the residue's hydroxyl group, increasing its nucleophilicity. In addition, Tyr 295 may interact with Tyr 268 to form a charge relay system that further enhances the reactivity of Tyr 295. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Lys51 | Lys51A | The residue acts as a nucleophile towards the PLP cofactor. The pKa of the residue is thought to be modified by the hydrophobic protein environment, making the residue less basic than in free solution. The residue is also thought to abstract the beta proton, forming the aldimine intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, schiff base formed, enzyme-substrate complex formation, decyclisation, bimolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, overall product formed, intramolecular eliminationReferences
- Hontzeas N et al. (2006), Biotechnol Adv, 24, 420-426. Reaction mechanisms of the bacterial enzyme 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.01.006. PMID:16524684.
- Karthikeyan S et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 13328-13339. Structural Analysis ofPseudomonas1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate Deaminase Complexes: Insight into the Mechanism of a Unique Pyridoxal-5‘-phosphate Dependent Cyclopropane Ring-Opening Reaction†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi048878g. PMID:15491139.
- Ose T et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 41069-41076. Reaction intermediate structures of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase: insight into PLP-dependent cyclopropane ring-opening reaction. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M305865200. PMID:12882962.

Step 1. The substrate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the covalently bound PLP-Lys Schiff base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr295A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys51A | covalently attached |
| Lys51A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used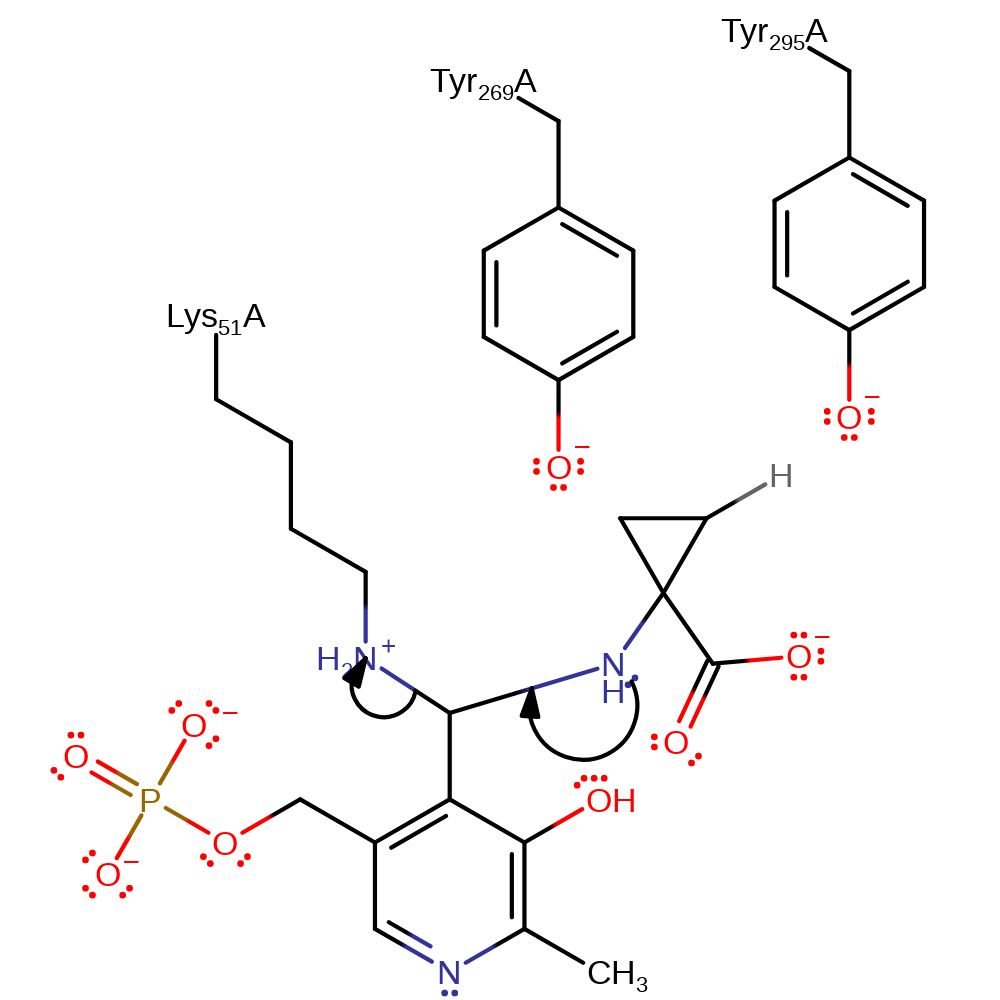
Step 2. Lys51 is eliminated from the PLP-cofactor to form the PLP-substrate Schiff base intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys51A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, schiff base formed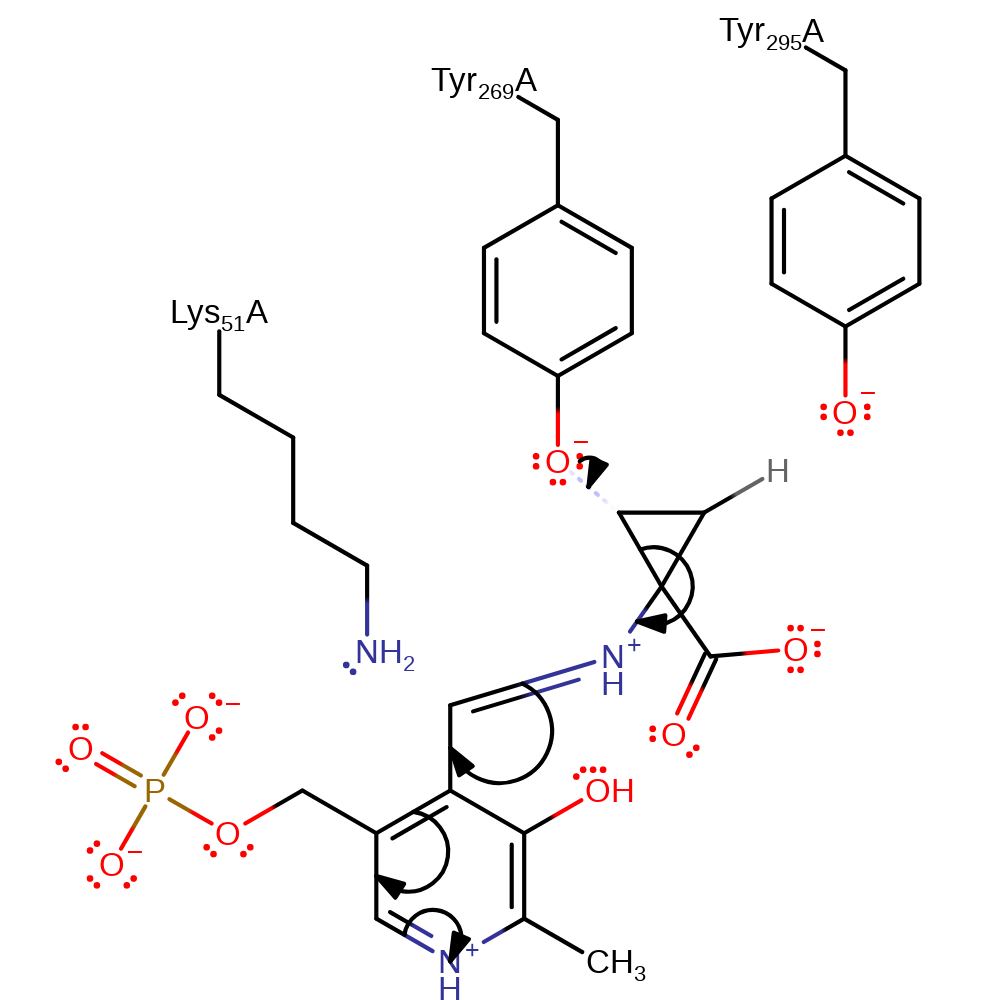
Step 3. Tyr269 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the propane ring of the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr295A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr269A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, decyclisation
Step 4. Tyr295 abstracts a proton from the intermediate, eliminating the Tyr269.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | covalently attached |
| Tyr295A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr269A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 5. The PLP cofactor undergoes rearrangement to abstract a proton from Tyr295.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 6. Lys51 initiates the nucleophilic attack that is the first step in the transaldimination reaction to release the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys51A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 7. In the final step of the transaldimination reaction, the PLP-Lys cofactor is regenerated and the enzyme's final product released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys51A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, schiff base formed
Step 8. The enzyme product undergoes hydrolysis to produce the final products. It is likely that this process occurs outside the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
reaction occurs outside the enzyme, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
overall product formed, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, ingold: intramolecular eliminationIntroduction
The substrate ACC reacts with the PLP cofactor and with the enzyme ACC deaminase to first produce an internal aldimine between the PLP and the Lys residue of the protein. This is followed by an aminyl intermediate which produces the external aldimine. Then there is an initial direct beta-proton abstraction, performed by a basic residue on the protein leading to a quinonoid. The quinonoid undergoes electronic rearrangement to form another quinonoid. This is followed by deprotonation of a nearby residue regaining its nucleophilic capacity (basic activity) on the protein backbone. This eventually produces an aminocrotonate and a quinoid. These products reversibly undergo hydrolysis to form alpha-ketobutyrate and ammonium, regenerating the internal aldimine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1f2d) | ||
| Tyr269 | Tyr269A | The residue is implicated in a proton relay from the surrounding solvent to the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295 | Tyr295A | Tyr 295 may interact with Tyr 268 to form a charge relay system that further enhances the reactivity of the residues in the active site. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Lys51 | Lys51A | The residue acts as a nucleophile towards the PLP cofactor. The pKa of the residue is thought to be modified by the hydrophobic protein environment, making the residue less basic than in free solution. The residue is also thought to abstract the beta proton, forming the aldimine intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, schiff base formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, decyclisation, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, intramolecular elimination, overall product formedReferences
- Hontzeas N et al. (2006), Biotechnol Adv, 24, 420-426. Reaction mechanisms of the bacterial enzyme 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.01.006. PMID:16524684.
- Ose T et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 41069-41076. Reaction intermediate structures of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase: insight into PLP-dependent cyclopropane ring-opening reaction. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M305865200. PMID:12882962.

Step 1. The substrate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the covalently bound PLP-Lys Schiff base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys51A | covalently attached |
| Lys51A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 2. Lys51 is eliminated from the PLP-cofactor to form the PLP-substrate Schiff base intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys51A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, schiff base formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 3. Tyr295 abstracts a proton from the intermediate. The PLP cofactor acts as an electron sink to stabilise the reactive intermediate formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisation
Step 4. The intermediate undergoes double bond rearrangement that results in the terminal ene group bring reduced.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr295A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 5. Lys51 initiates the nucleophilic attack that is the first step in the transaldimination reaction to release the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys51A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 6. In the final step of the transaldimination reaction, the PLP-Lys cofactor is regenerated and the enzyme's final product released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys51A | covalently attached, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
schiff base formed, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated
Step 7. The enzyme product undergoes hydrolysis to produce the final products. It is likely that this process occurs outside the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
reaction occurs outside the enzyme, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|





 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: