Triacylglycerol lipase (EstA)
Lipases catalyse the hydrolysis and synthesis of long-chain triglycerols. They have important industrial applications in resolution of racemic mixtures, ester synthesis and transesterification reactions, as well as additives in washing powders.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P37957
 (3.1.1.3)
(3.1.1.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1r4z
- Bacillus subtilis lipase A with covalently bound Rc-IPG-phosphonate-inhibitor
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1r4z)
(see all for 1r4z)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His 156 activates Ser 77 through general base catalysis to deprotonate Ser 77 allowing it to make a nucleophilic attack on the ester bond. His 156 donates a proton to the leaving group and then activates a water molecule to allow the hydrolysis of the acyl-enzyme intermediate, again by general base catalysis. Asp 133 alters the pKa of the His 156 to activate it and allow it to act as an effective base in the reaction. The Ile 12 and Met 78 backbone amides form the oxyanion hole to stabilise the transition state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1r4z) | ||
| Ile43 (main-N) | Ile12A (main-N) | Forms the oxyanion hole to stabilise the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser108 | Ser77A | Acts as the active site nucleophile in attack of the substrate, to form the acyl-enzyme intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp164 | Asp133A | Alters the pKa of His 156 to allow it to act as a more efficient general base catalyst. | increase basicity, modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His187 | His156A | Acts as a general acid/base catalyst to activate Ser 77 and water for nucleophilic attack by proton abstraction, and to facilitate collapse of intermediates and formation of products by proton donation. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Met109 (main-N) | Met78A (main-N) | Stabilises the transition state by formation of the oxyanion hole. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- van Pouderoyen G et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 309, 215-226. The crystal structure of Bacillus subtilis lipase: a minimal alpha/beta hydrolase fold enzyme. DOI:10.2210/pdb1i6w/pdb. PMID:11491291.
- Kawasaki K et al. (2002), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 58, 1168-1174. Alternate conformations observed in catalytic serine ofBacillus subtilislipase determined at 1.3 Å resolution. DOI:10.1107/s090744490200714x. PMID:12077437.
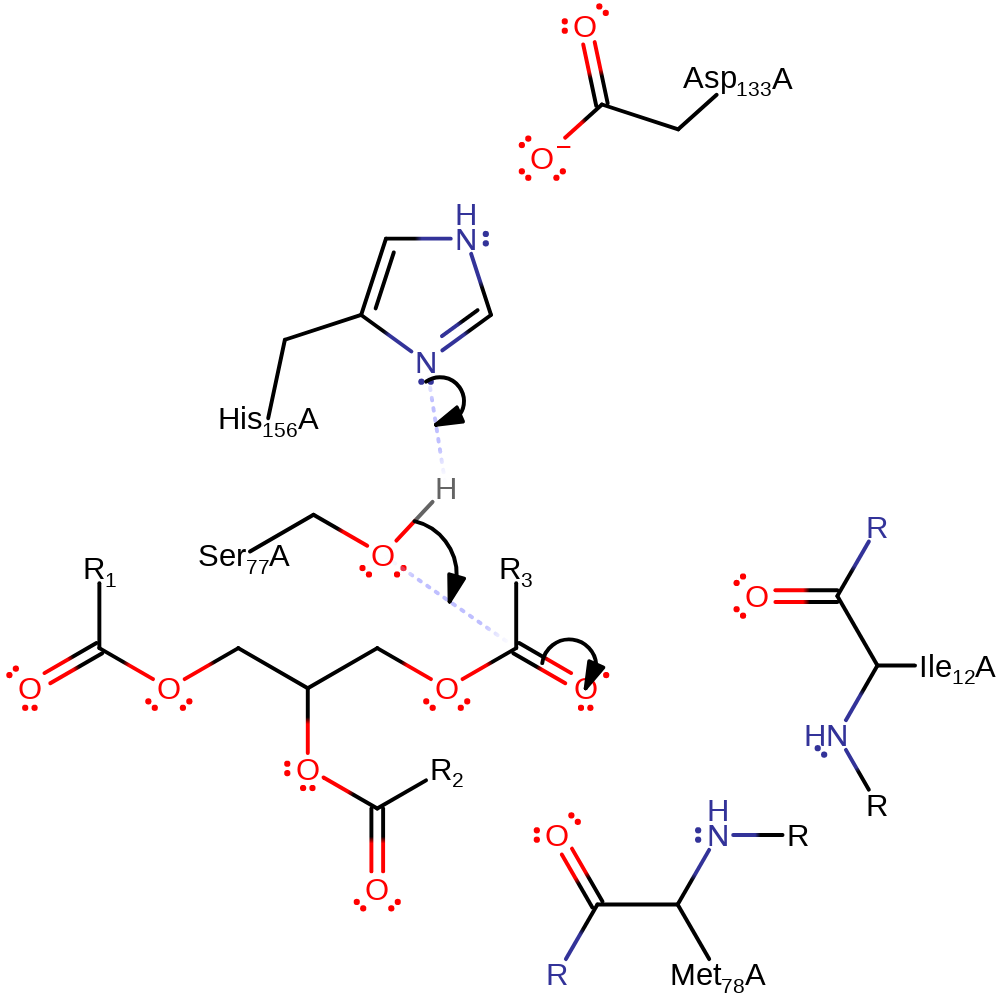
Step 1. His156 acts as a general base activating the Ser77 hydroxyl group for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the ester bond. The third component of this catalytic triad- Asp133 acts to increase the basicity of the histidine. The oxyanion intermediate formed is stabilized by the amide groups of Met78 and Ile12.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp133A | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met78A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile12A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp133A | increase basicity |
| Ser77A | covalently attached, proton donor |
| His156A | proton acceptor |
| Ser77A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer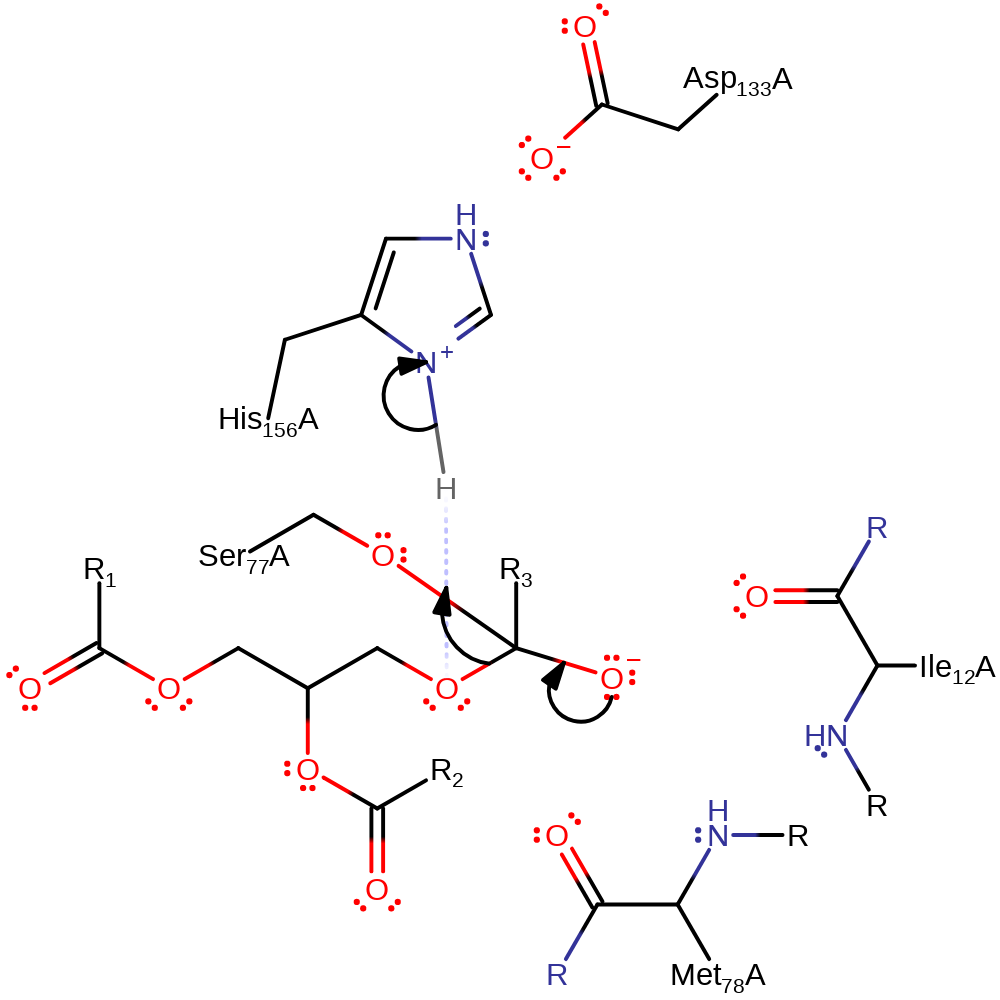
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and diacylglycerol is eliminated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser77A | covalently attached |
| Ile12A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met78A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp133A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His156A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base
Step 3. His156 activates water for nucleophilic attack and another oxyanion intermediate is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser77A | covalently attached |
| Asp133A | increase basicity, modifies pKa |
| Ile12A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met78A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp133A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His156A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
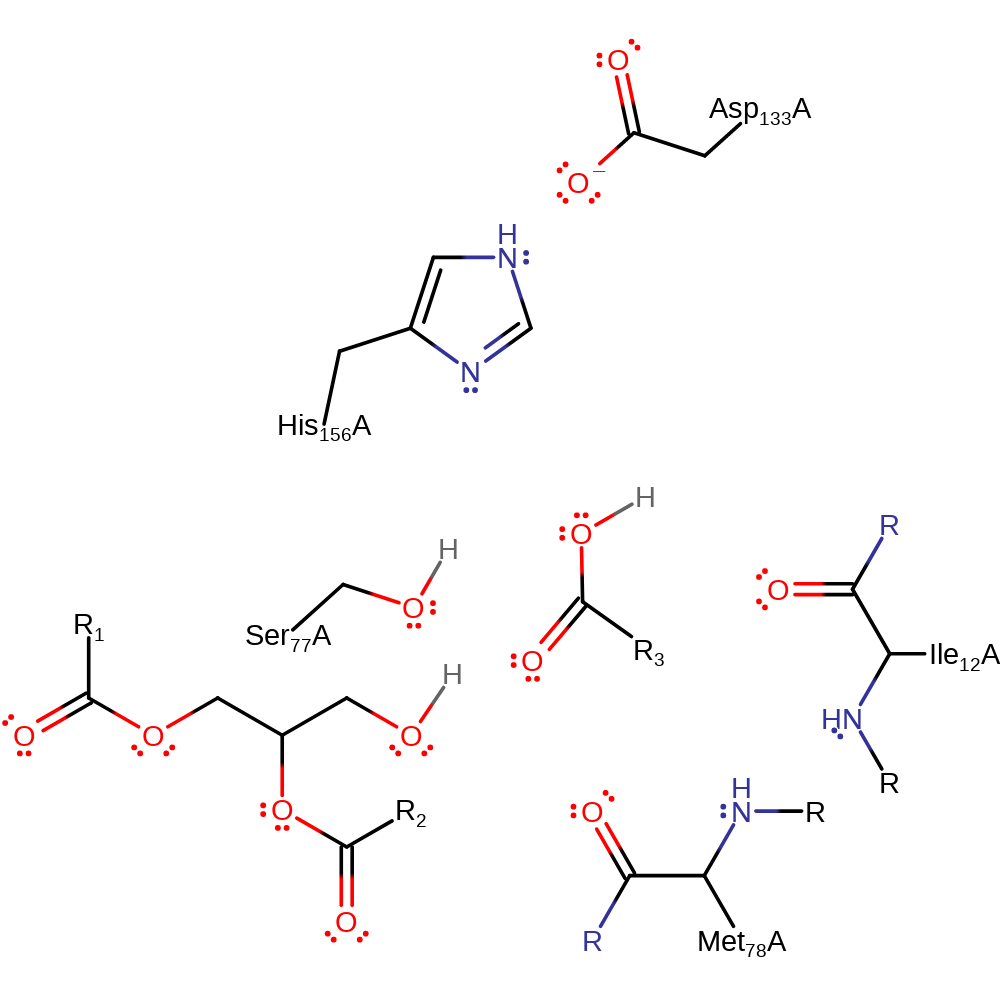
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer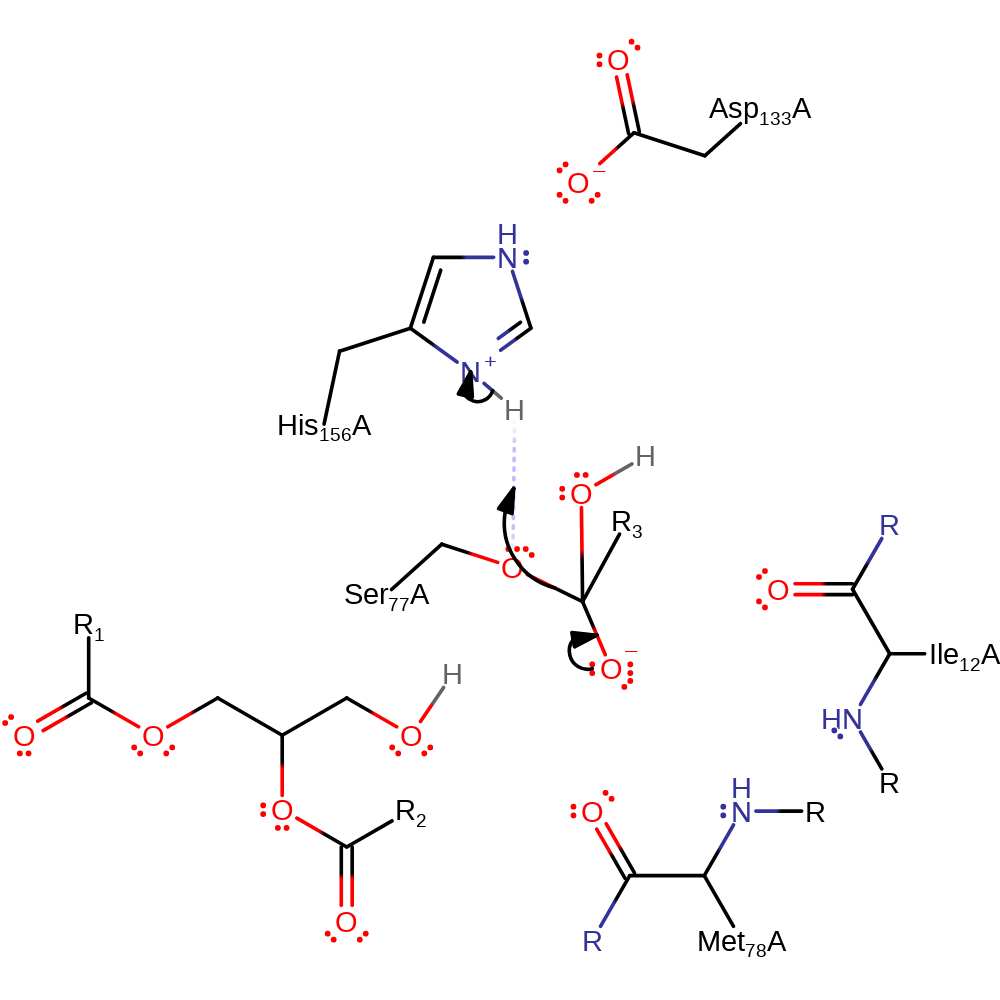
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and Ser77 is eliminated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ile12A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met78A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp133A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser77A | proton acceptor |
| His156A | proton donor |
| Ser77A | nucleofuge |





 Download:
Download: