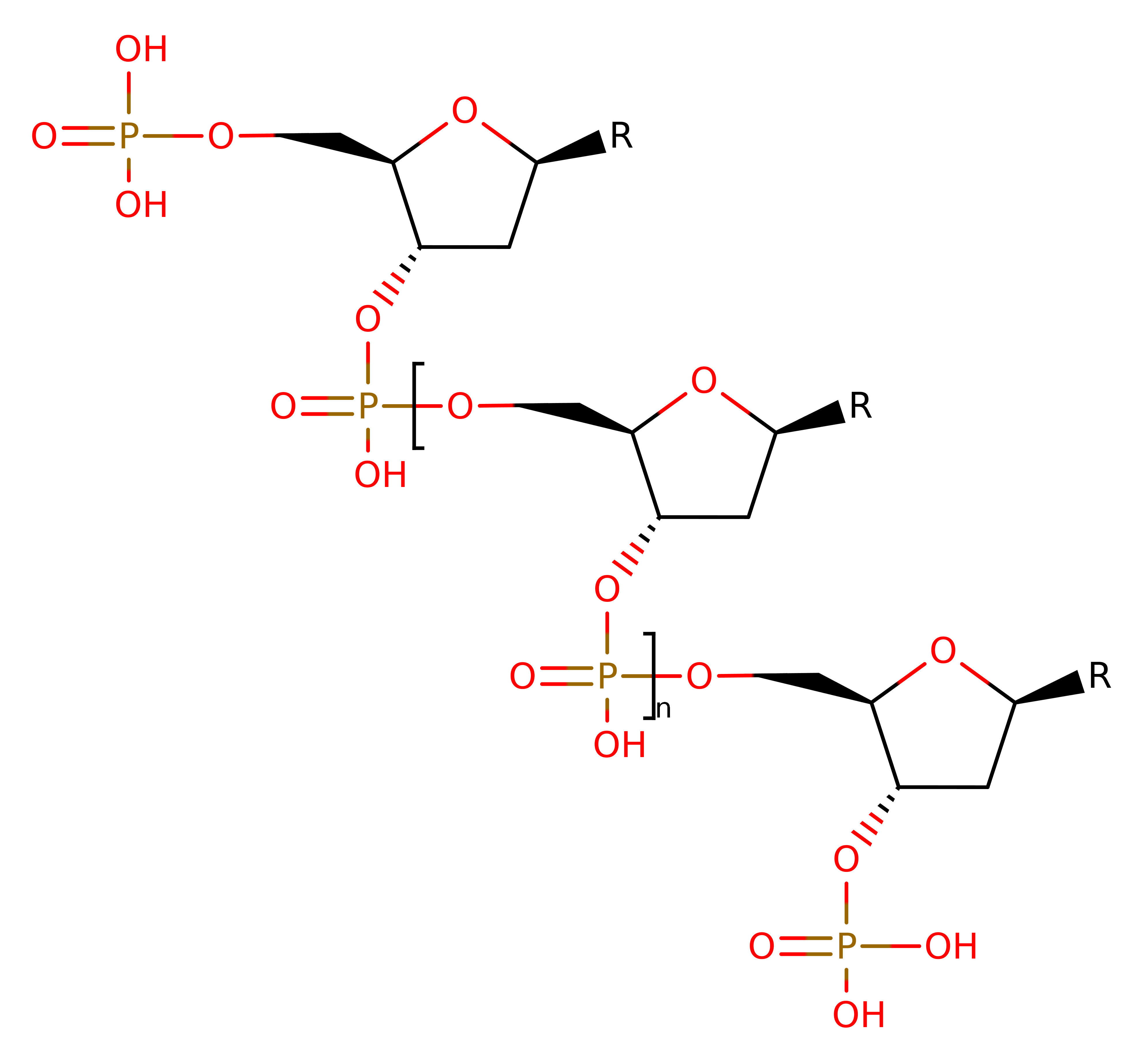
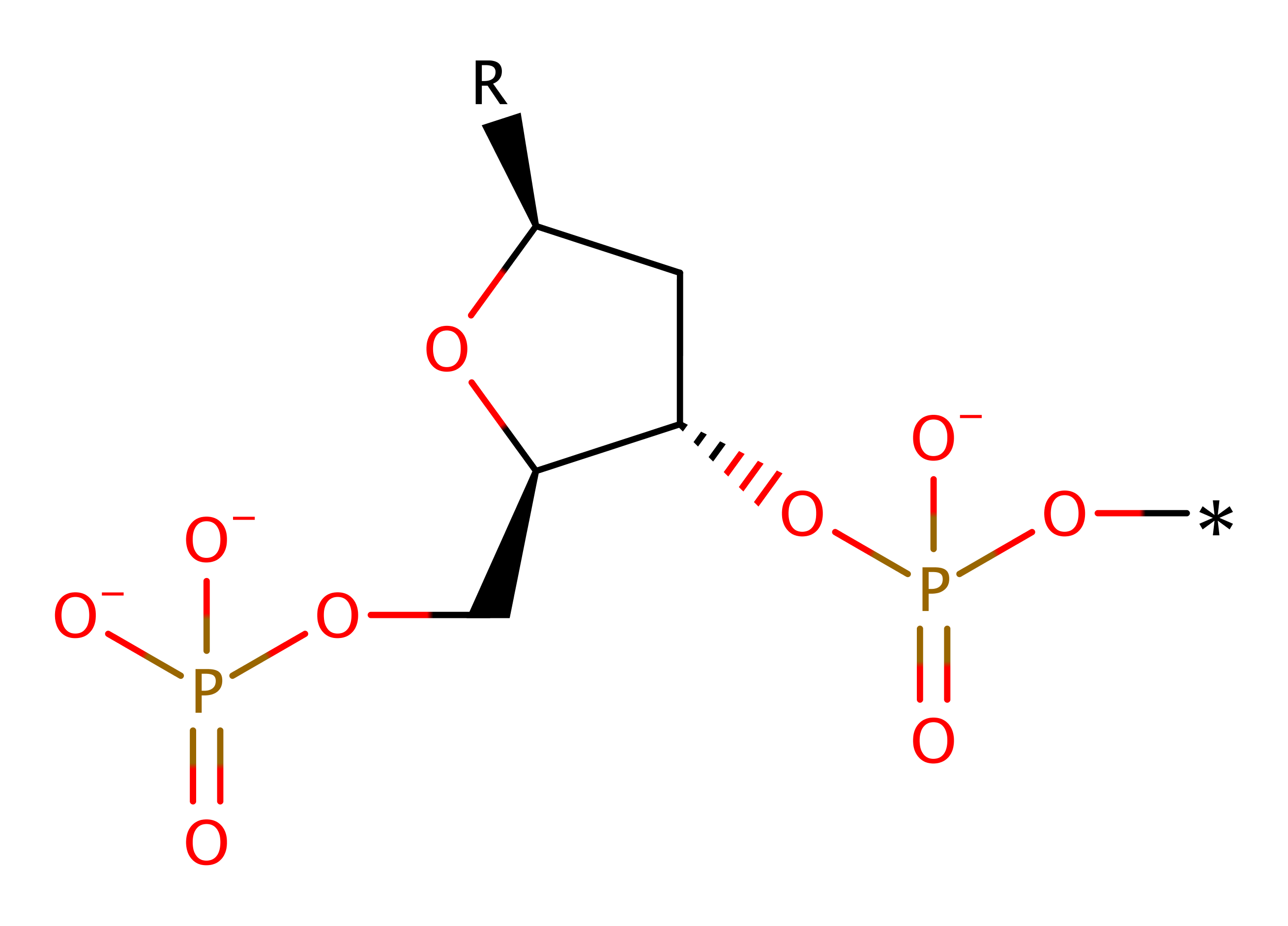
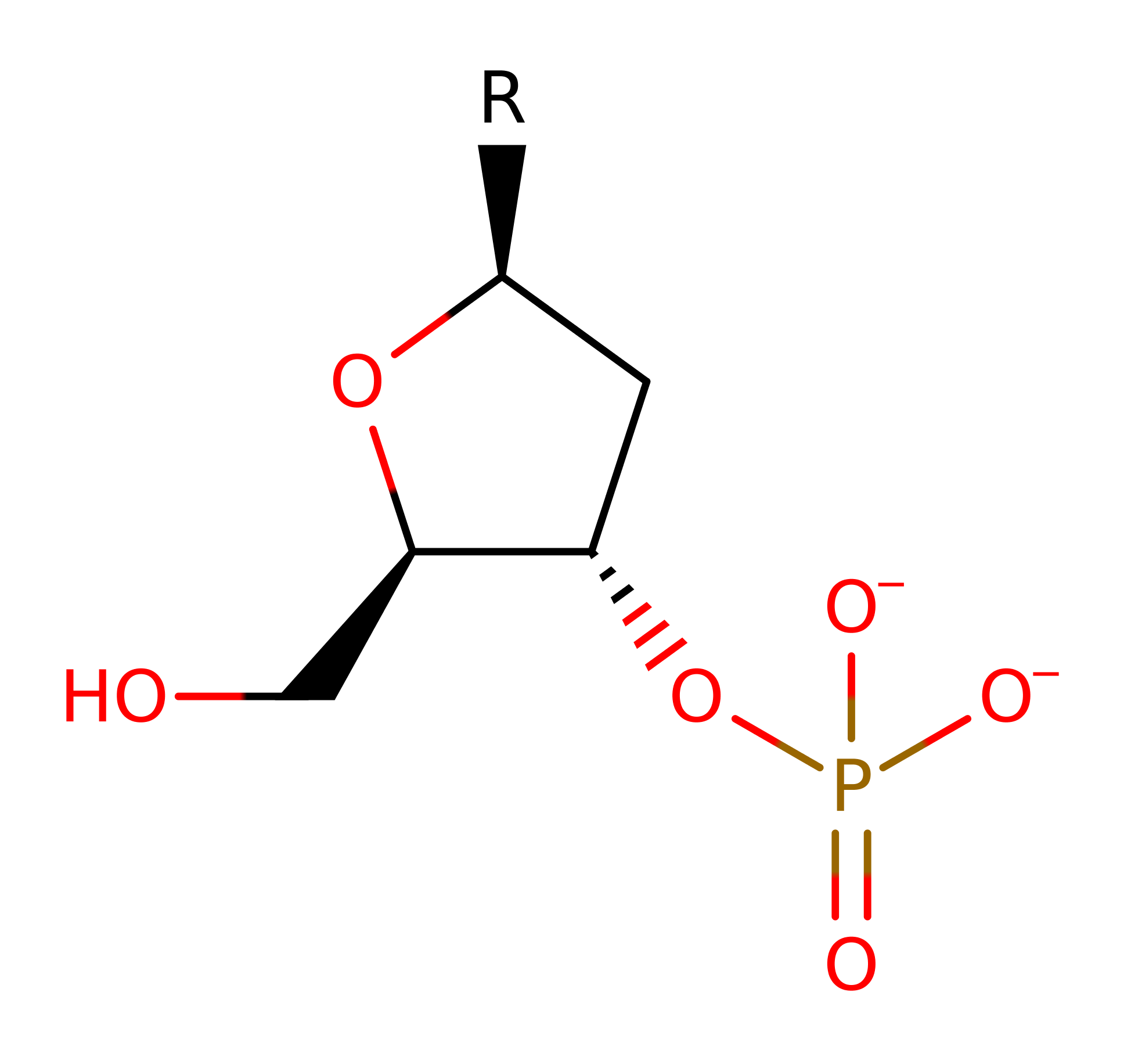
Type II site-specific deoxyribonuclease, BgII
The type-II restriction enzymes catalyse the endonucleolytic cleavage of DNA to give specific double-stranded fragments with terminal 5'-phosphates. This is a large group of enzymes which require only Mg(II) and recognise specific short DNA sequences and cleave either within, or at a short specific distance from, the recognition site. This entry represents the BgII family (IPR011543) which recognises the GCCNNNNNGGC motif and cleaves after N-4.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O68557
 (3.1.21.4)
(3.1.21.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus subtilis (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dmu
- Crystal structure of the restriction endonuclease BglI (e.c.3.1.21.4) bound to its dna recognition sequence
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.600.20
 (see all for 1dmu)
(see all for 1dmu)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Based on the active site structure, one possible mechanism is that the Mg(II) ion at site 1 could help to activate the attacking water molecule, a Mg(II) at site 2 helps to stabilise the negative charge on the 3' oxyanion leaving group, and both ions are involved in stabilising the pentacovalent transition state. The attacking water is activated by Lys144, it is currently unclear if Lys144 also acts as a general acid/base, or simply activates the water.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dmu) | ||
| Asp142 | Asp142A(B) | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site, also activates a second active site water to act as a general acid/base to protonate the O3' leaving atom. | modifies pKa, metal ligand |
| Ile143 (main-C) | Ile143A(B) (main-C) | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp116 | Asp116A(B) | Forms part of both magnesium binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Lys144 | Lys144A(B) | Activates the substrate water to act as a catalytic nulceophile, it is also responsible for stabilising the reactive intermediates. | increase nucleophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Newman M et al. (1998), EMBO J, 17, 5466-5476. Crystal structure of restriction endonuclease BglI bound to its interrupted DNA recognition sequence. DOI:10.1093/emboj/17.18.5466. PMID:9736624.
- Dall'Acqua W et al. (2000), Protein Sci, 9, 1-9. Substrate-assisted catalysis: Molecular basis and biological significance. DOI:10.1110/ps.9.1.1. PMID:10739241.
- Gormley NA et al. (2000), J Biol Chem, 275, 6928-6936. Reactions of BglI and Other Type II Restriction Endonucleases with Discontinuous Recognition Sites. DOI:10.1074/jbc.275.10.6928.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp116A(B) | metal ligand |
| Asp142A(B) | metal ligand |
| Ile143A(B) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Lys144A(B) | increase nucleophilicity |
| Asp142A(B) | modifies pKa |
| Lys144A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |