Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatases are zinc and magnesium containing metalloenzymes which function optimally at high pH. They are found in all organisms except some plants, in the periplasmic space (E. coli), in vacuoles (fungi) or GPI-anchored to the external cell membrane (mammals). Alkaline phosphatase-type activity is involved in many cell processes, including metabolism of glycerolipids, folate, and xenobiotics. They cleave phosphomonoester bonds from various substrates, such as the end of a DNA molecule.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00634
 (3.1.3.1)
(3.1.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1alk
- REACTION MECHANISM OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE BASED ON CRYSTAL STRUCTURES. TWO METAL ION CATALYSIS
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.720.10
 (see all for 1alk)
(see all for 1alk)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Zinc(2+) (2), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.3.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A metal-activated water molecule deprotonates the nucleophilic serine residue. Serine attacks the phosphomonoester in a substitution reaction which eliminates the alcohol. The alcohol anion deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the covalently bound phosphorus in a substitution reaction which eliminates serine as an anion. Serine then deprotonates water to regenerate the starting state of the enzyme.
There have been suggestions that the magnesium ion in the active site is essential for catalysis (PMID:10873454), but more recent evidence suggests it is not directly involved in the catalytic mechanism (PMID:18851975).
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1alk) | ||
| Arg188 | Arg166A | Stabilises transition states. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp349, His353, His434 | Asp327A, His331A, His412A | Form the zinc 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Ser124 | Ser102A | Serine is the main nucleophile in the reaction, and forms a covalent intermediate with the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge |
| Thr177, Glu344, Asp175, Lys350, Asp73 | Thr155A, Glu322A, Asp153A, Lys328A, Asp51A | Form the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp391, His392, Asp73 | Asp369A, His370A, Asp51A | Form the zinc 2 binding site | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, dephosphorylation, intermediate terminated, hydrolysis, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Stec B et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 299, 1303-1311. A revised mechanism for the alkaline phosphatase reaction involving three metal ions. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3799. PMID:10873454.
- Bobyr E et al. (2012), J Mol Biol, 415, 102-117. High-Resolution Analysis of Zn2+ Coordination in the Alkaline Phosphatase Superfamily by EXAFS and X-ray Crystallography. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.10.040. PMID:22056344.
- Koutsioulis D et al. (2010), Protein Sci, 19, 75-84. Coordination sphere of the third metal site is essential to the activity and metal selectivity of alkaline phosphatases. DOI:10.1002/pro.284. PMID:19916164.
- Zalatan JG et al. (2008), J Mol Biol, 384, 1174-1189. Comparative Enzymology in the Alkaline Phosphatase Superfamily to Determine the Catalytic Role of an Active-Site Metal Ion. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.059. PMID:18851975.
- Wang J et al. (2006), Protein Sci, 15, 2395-2401. Trapping the tetrahedral intermediate in the alkaline phosphatase reaction by substitution of the active site serine with threonine. DOI:10.1110/ps.062351506. PMID:17008720.
- Wang J et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 8378-8386. Metal Specificity Is Correlated with Two Crucial Active Site Residues inEscherichia coliAlkaline Phosphatase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi050155p. PMID:15938627.
- Holtz KM et al. (1999), J Biol Chem, 274, 8351-8354. A Model of the Transition State in the Alkaline Phosphatase Reaction. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.13.8351. PMID:10085061.
- Stec B et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 277, 647-662. Kinetic and X-ray structural studies of three mutant E. coli alkaline phosphatases: insights into the catalytic mechanism without the nucleophile ser102. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.1635. PMID:9533886.
- Murphy JE et al. (1997), Nat Struct Biol, 4, 618-622. Trapping and visualization of a covalent enzyme–phosphate intermediate. DOI:10.1038/nsb0897-618. PMID:9253408.
- Ma L et al. (1994), J Biol Chem, 269, 31614-31619. Mutations at histidine 412 alter zinc binding and eliminate transferase activity in Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. PMID:7989332.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser102A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg166A | activator |
| Ser102A | metal ligand |
| Asp51A | metal ligand |
| Asp369A | metal ligand |
| His370A | metal ligand |
| Asp327A | metal ligand |
| His412A | metal ligand |
| His331A | metal ligand |
| Thr155A | metal ligand |
| Asp153A | metal ligand |
| Lys328A | metal ligand |
| Glu322A | metal ligand |
| Ser102A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer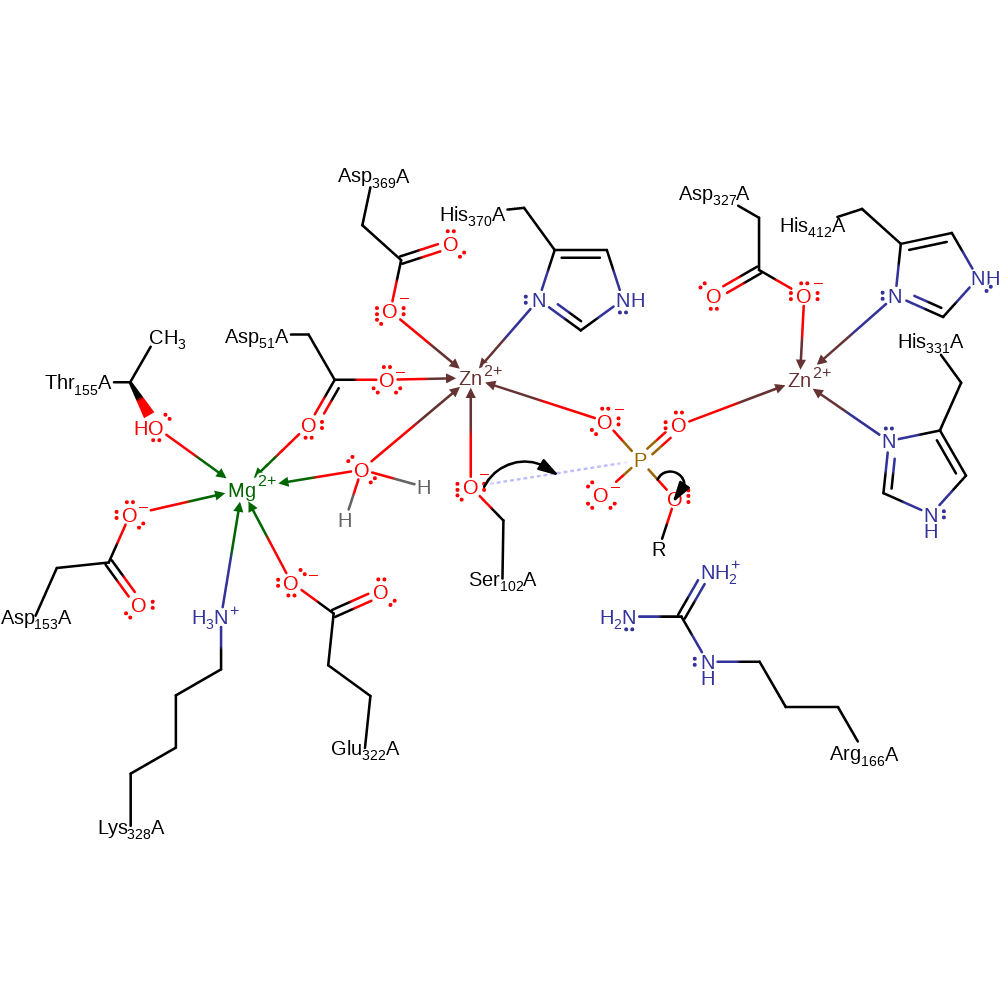
Step 2. Ser102 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphoric monoester in a substitution reaction which eliminates the alcohol as an anionic species.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg166A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser102A | metal ligand |
| Asp51A | metal ligand |
| Asp369A | metal ligand |
| His370A | metal ligand |
| Asp327A | metal ligand |
| His412A | metal ligand |
| His331A | metal ligand |
| Thr155A | metal ligand |
| Asp153A | metal ligand |
| Lys328A | metal ligand |
| Glu322A | metal ligand |
| Ser102A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation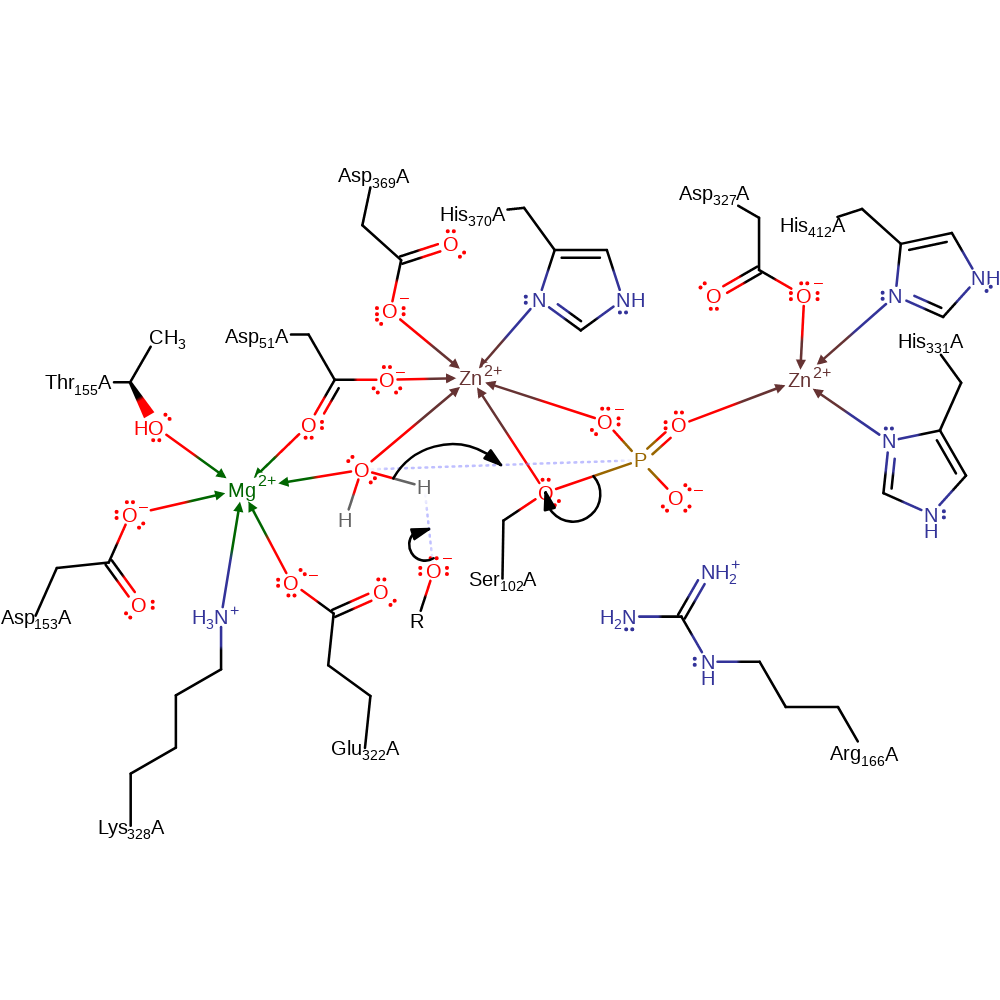
Step 3. The alcohol anion deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the covalently bound phosphorous in a substitution reaction which eliminates serine as an anion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg166A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser102A | metal ligand |
| Asp51A | metal ligand |
| Asp369A | metal ligand |
| His370A | metal ligand |
| Asp327A | metal ligand |
| His412A | metal ligand |
| His331A | metal ligand |
| Thr155A | metal ligand |
| Asp153A | metal ligand |
| Lys328A | metal ligand |
| Glu322A | metal ligand |
| Ser102A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, dephosphorylation, intermediate terminated, hydrolysis, proton transfer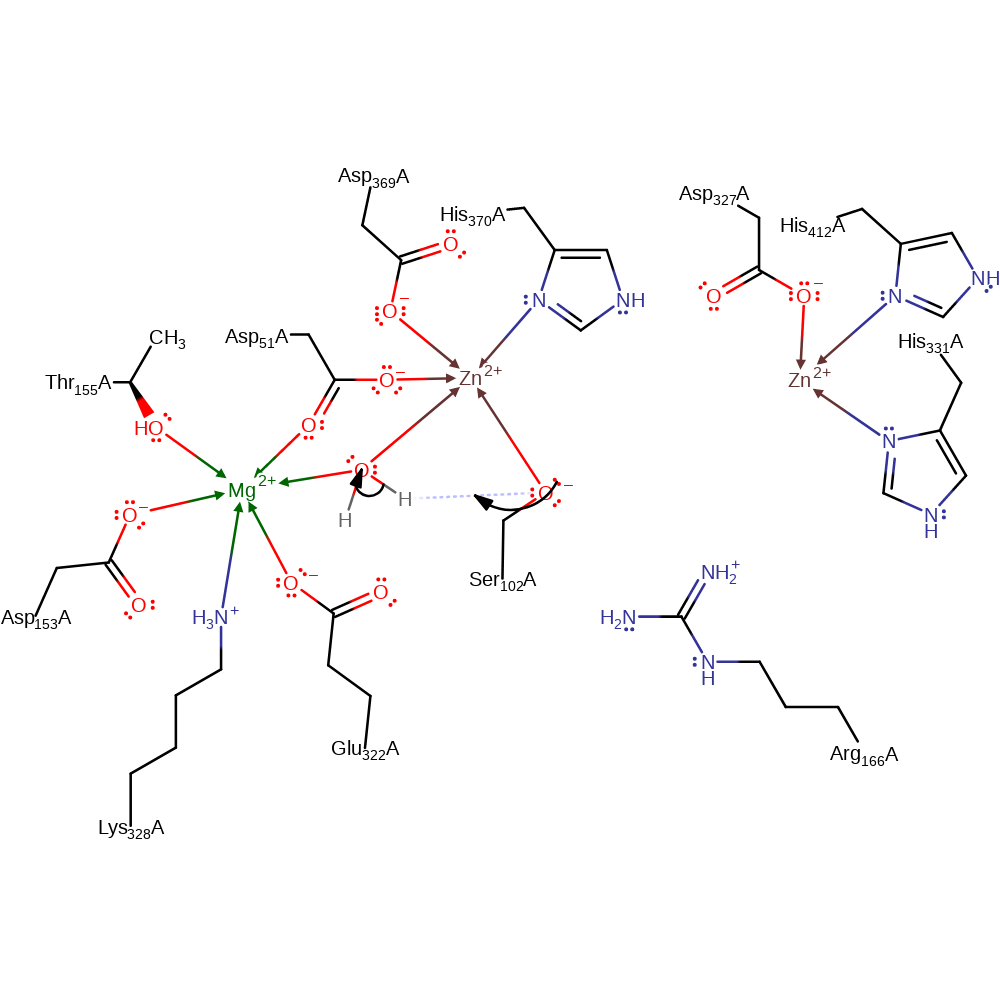
Step 4. Ser102 deprotonates water to regenerate the starting state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser102A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg166A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser102A | metal ligand |
| Asp51A | metal ligand |
| Asp369A | metal ligand |
| His370A | metal ligand |
| Asp327A | metal ligand |
| His412A | metal ligand |
| His331A | metal ligand |
| Thr155A | metal ligand |
| Asp153A | metal ligand |
| Lys328A | metal ligand |
| Glu322A | metal ligand |
| Ser102A | proton acceptor |




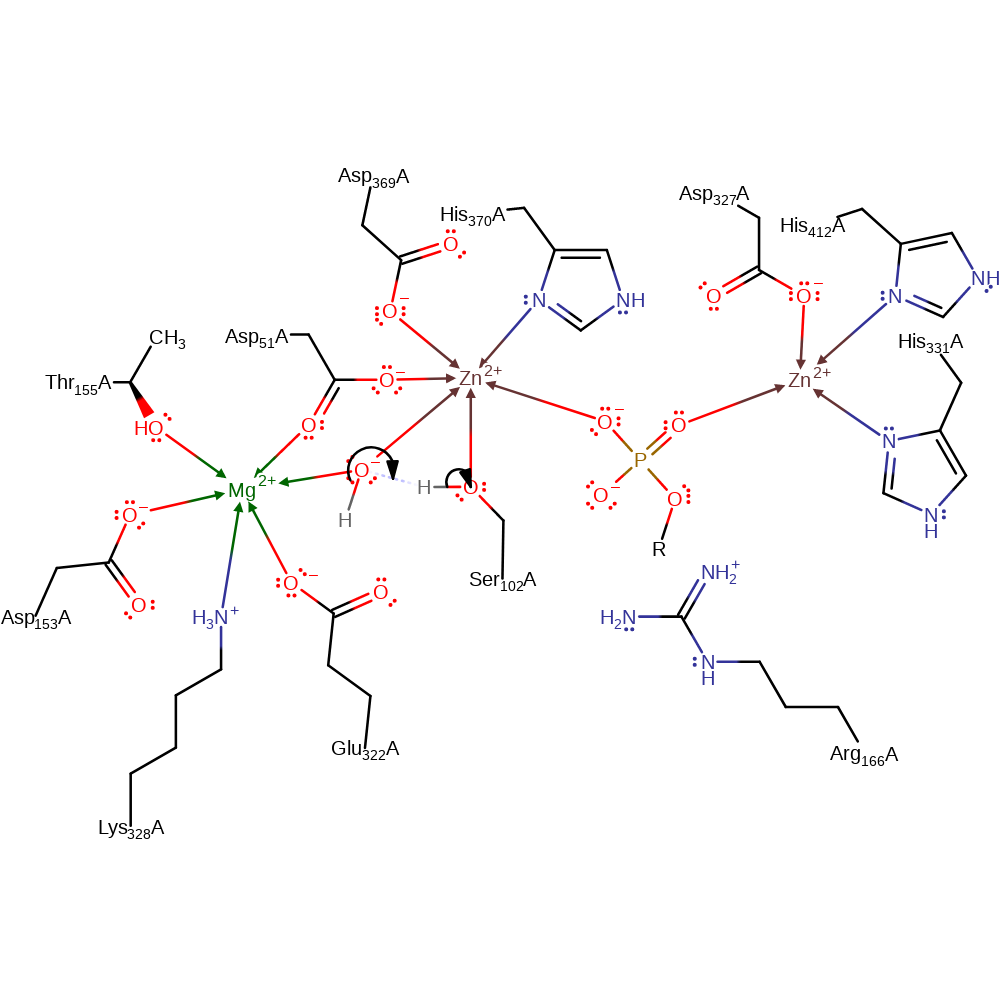
 Download:
Download: