Nuclease
Serratia endonuclease is of particular interest because of its broad specificity, high activity and chemical stability. In addition antiviral and anti-tumour properties have been attributed to this enzyme.
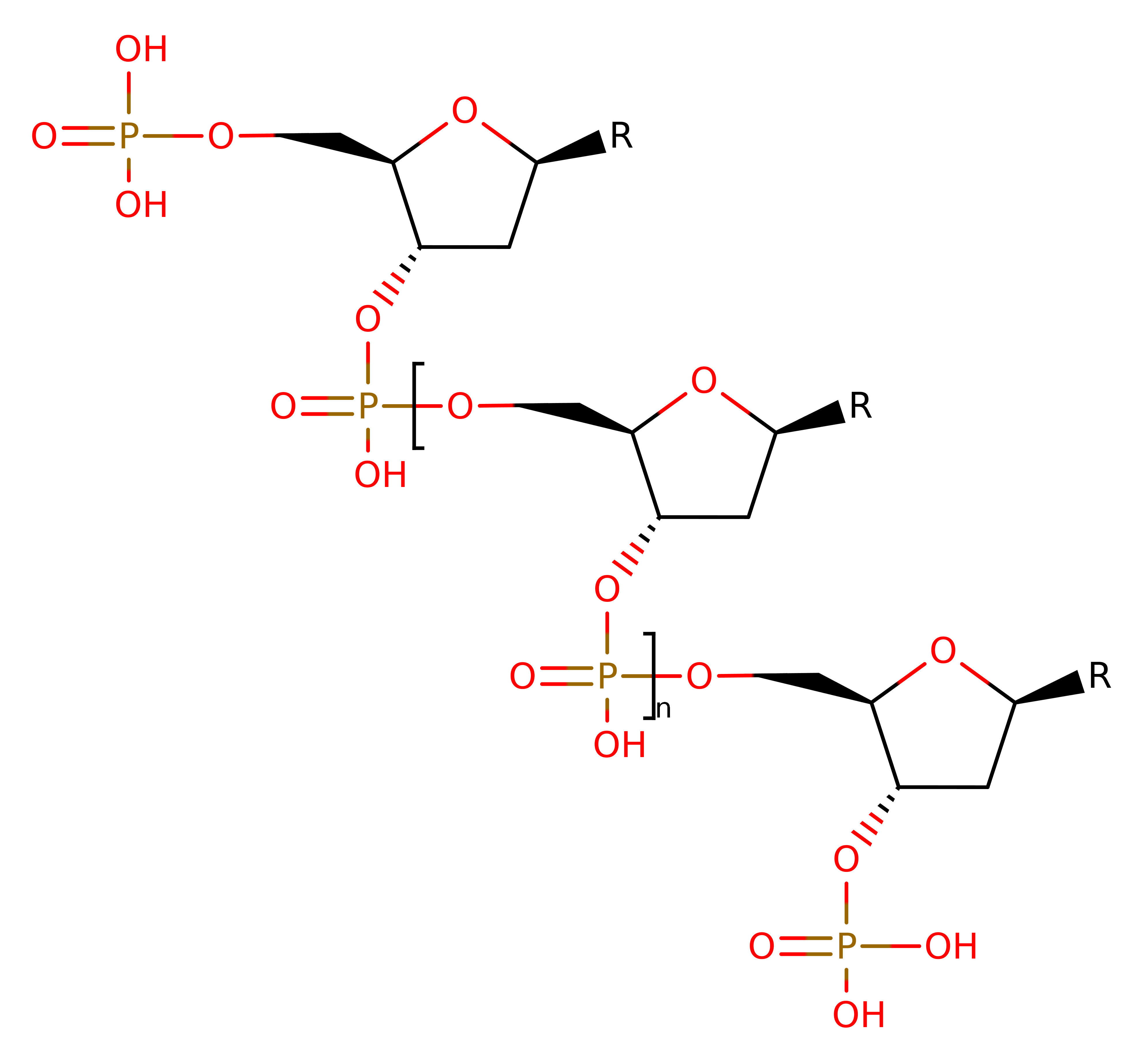
It acts without any apparent base preference and cleaves both single- and double - stranded DNA and RNA. Functionally, the enzyme is similar to DNase I as they are both magnesium-dependent endonucleases that catalyse the cleavage of 3'O-P bond. Although functional similarities exist, Serratia nuclease structure contrasts sharply with the protein fold observed in DNase I.
Magnesium is important for activity, absence of magnesium significantly reduces the activity of the nuclease. The nuclease DNA-binding site is located between two main amino and carboxy-terminal structural domains of the protein, the DNA binding cleft is flanked by two rows of positively charged amino acids that could interact with about one full turn of DNA B-form. This cleft contains among other cationic amino acids, the invariant catalytic residues of ARG 87 and ARG 131, and also contains HIS 89 and GLU 127.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P13717
 (3.1.30.2)
(3.1.30.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Serratia marcescens (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ql0
- Sm Endonuclease from Seratia marcenscens at atomic resolution
(1.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.570.10
 (see all for 1ql0)
(see all for 1ql0)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.30.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
HIS 89 and GLU 127 are both potential participants in the nuclease reaction. It has been postulated that HIS 89 serves as a general acid and GLU 127 serves as either a nucleophile or a general base. Phosphodiesters are hydrolysed via nucleophilic attack by a water molecule forming a penta-coordinated trigonal bipyramid intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ql0) | ||
| His110 | His89(85)A | Acts as a general acid/base, deprotonates the nucleophilic water | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn140 | Asn119(115)A | Binds the Mg(II) ion and helps stabilise the negatively charged transition state. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand |
| Glu148 | Glu127(123)A | Part of the Mg(II) binding site and acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg78 | Arg57(53)A | Stabilizes the transition state and the leaving group as well | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn131 | Asn110(106)A | Activates and stabilises the general acid/base His89 in the DNA bound state. In the apo enzyme, Asn110 is replaced with Arg87 | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, proton relay, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Shlyapnikov SV et al. (2000), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 56, 567-572. Atomic structure of theSerratia marcescensendonuclease at 1.1 Å resolution and the enzyme reaction mechanism. DOI:10.1107/s090744490000322x. PMID:10771425.
- Chen C et al. (2009), J Phys Chem B, 113, 511-521. Advantage of Being a Dimer for Serratia marcescens Endonuclease. DOI:10.1021/jp8057838. PMID:19053714.
- Koziołkiewicz M et al. (2001), Bioorg Med Chem, 9, 2403-2409. Stereochemistry of cleavage of internucleotide bonds by Serratia marcescens endonuclease. PMID:11553482.
- Miller MD et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 288, 975-987. The active site of Serratia endonuclease contains a conserved magnesium-water cluster. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2729. PMID:10329193.
- Lunin VY et al. (1997), FEBS Lett, 412, 217-222. Three-dimensional structure ofSerratiamarcescensnuclease at 1.7 Å resolution and mechanism of its action. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00512-7. PMID:9257723.
- Klabunde T et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 259, 737-748. Mechanism of Fe(III) – Zn(II) Purple Acid Phosphatase Based on Crystal Structures. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0354. PMID:8683579.
- Miller MD et al. (1994), Nat Struct Biol, 1, 461-468. 2.1 Å structure of Serratia endonuclease suggests a mechanism for binding to double-stranded DNA. DOI:10.1038/nsb0794-461. PMID:7664065.

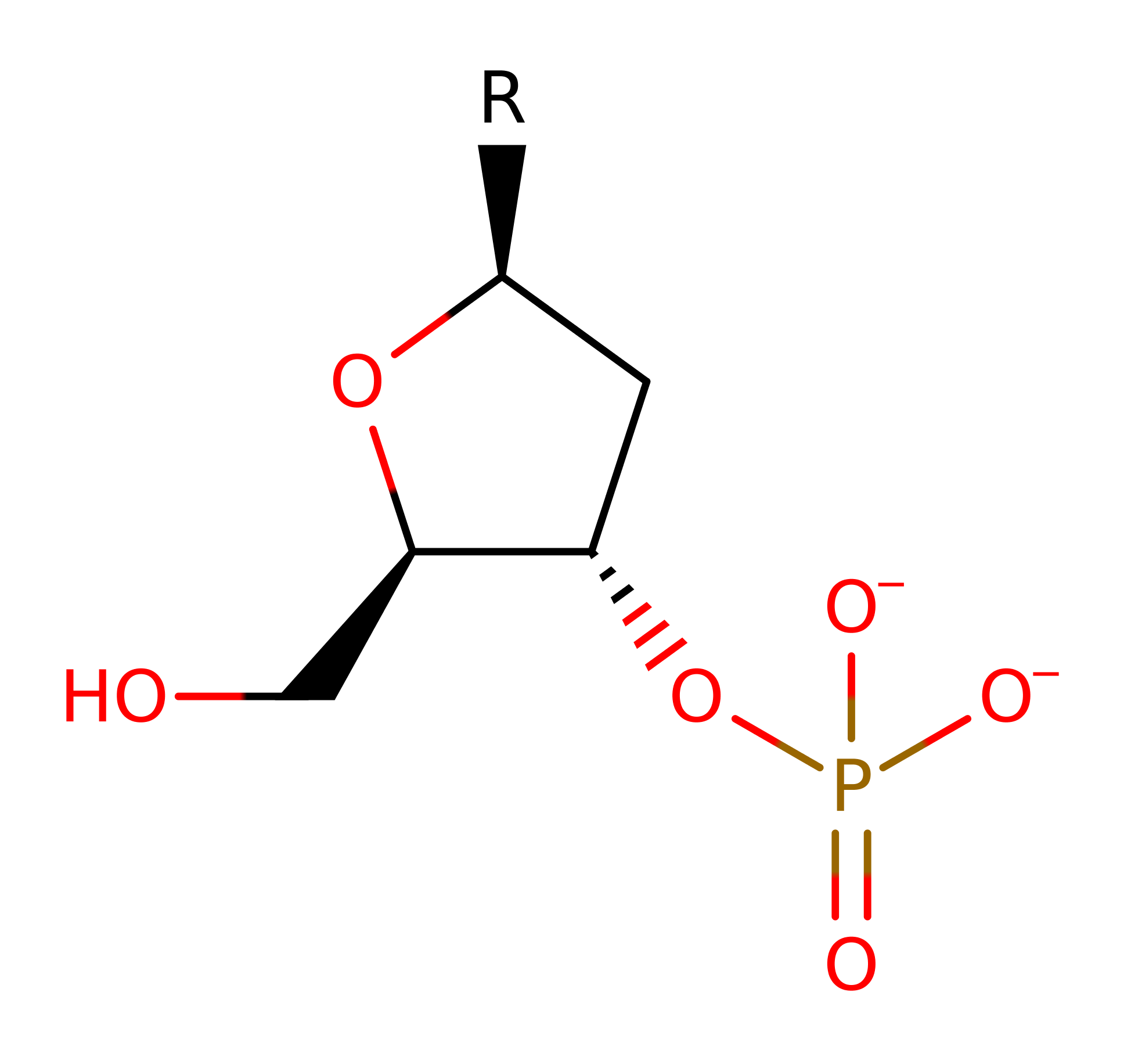
Step 1. His89 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate of the DNA, forming a pentavalent intermediate in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu127(123)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn119(115)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| His89(85)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn110(106)A | increase basicity |
| Arg57(53)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn119(115)A | metal ligand |
| Glu127(123)A | metal ligand |
| His89(85)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, rate-determining step
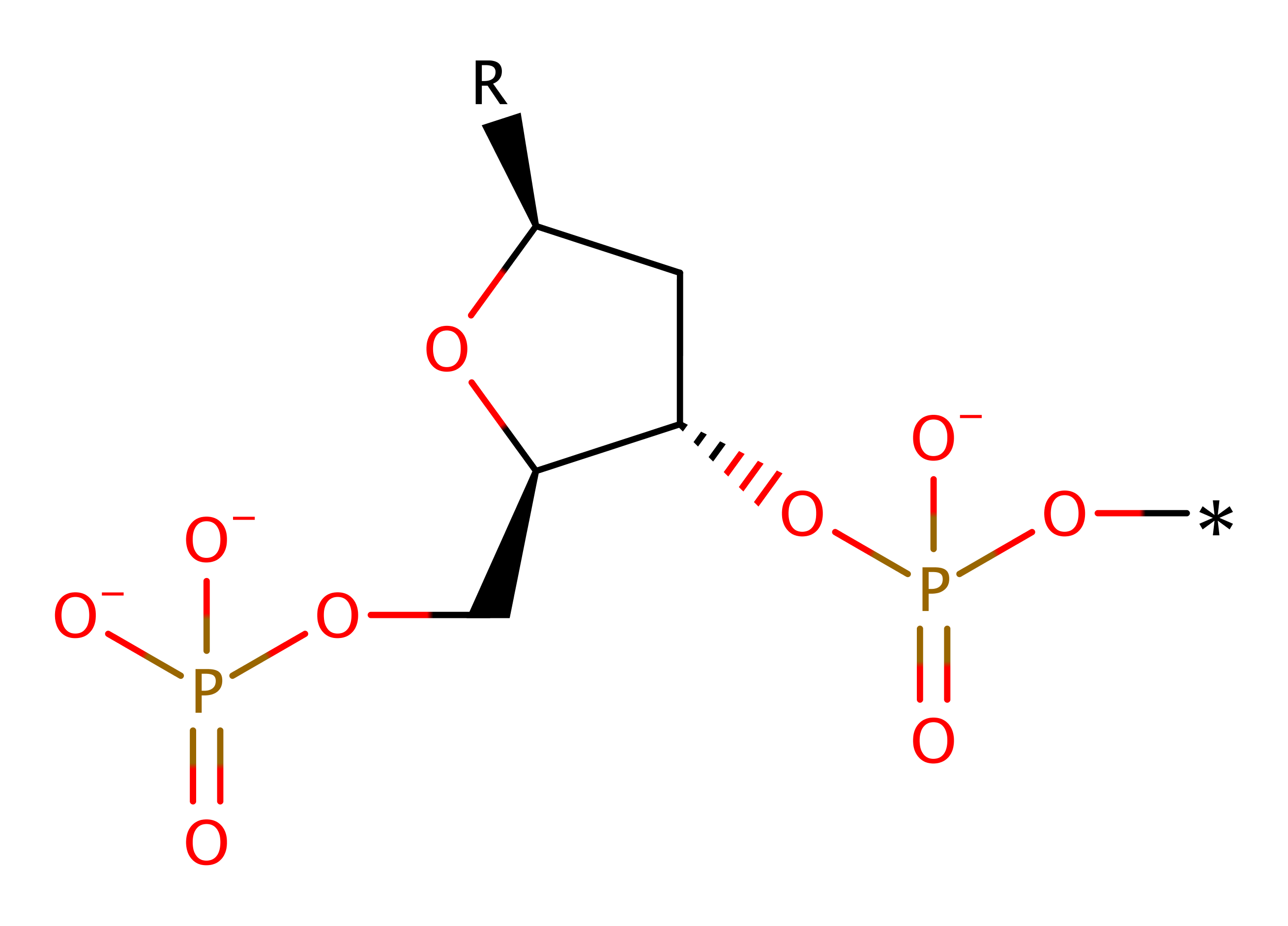
Step 2. The pentavalent intermediate collapses, eliminating the 3'-hydroxyl of the DNA, which deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates Glu127.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu127(123)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn119(115)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His89(85)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn119(115)A | metal ligand |
| Glu127(123)A | metal ligand |
| Asn110(106)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg57(53)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu127(123)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, proton relay, native state of enzyme regenerated
Step 3. Inferred return step in which Glu abstracts a proton from water, and water abstracts a proton from His.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn119(115)A | metal ligand |
| Glu127(123)A | metal ligand |
| Asn110(106)A | increase acidity |
| His89(85)A | proton donor |
| Glu127(123)A | proton acceptor |


 Download:
Download: