Deoxyribonuclease I
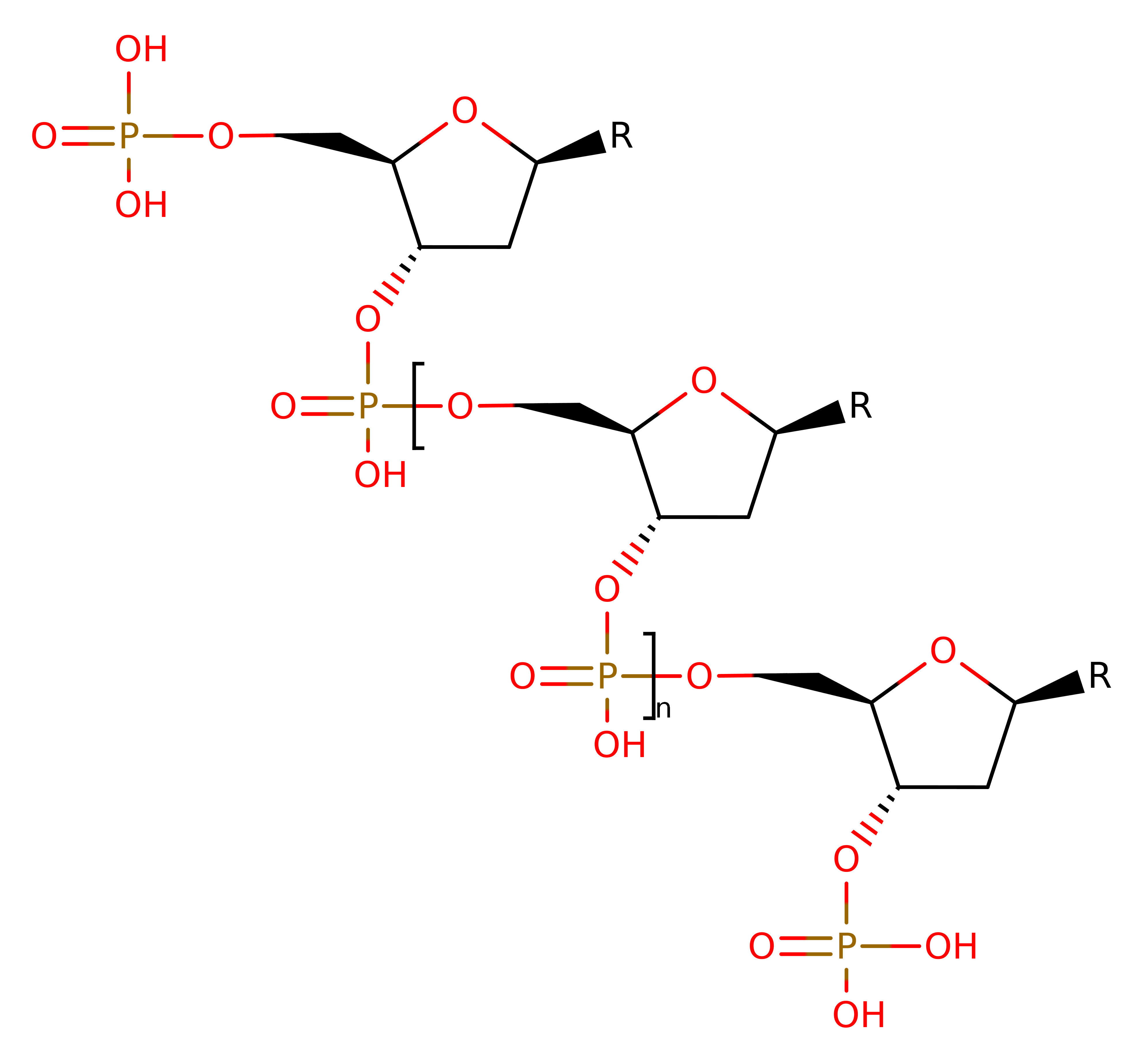
DNase I is a vertebrate enzyme that cleaves double stranded DNA to 5'-phosphodinucleotide and 5'-phospho-oligonucletide end-products. DNase I requires calcium and magnesium for full activity. It is a glycoprotein that causes single-stranded nicks on double-stranded DNA. DNase I shares structural homology to the Human Apurinic/Apyrimidinic endonuclease and Exonuclease III. These three enzymes also share similar mechanisms of DNA cleavage.
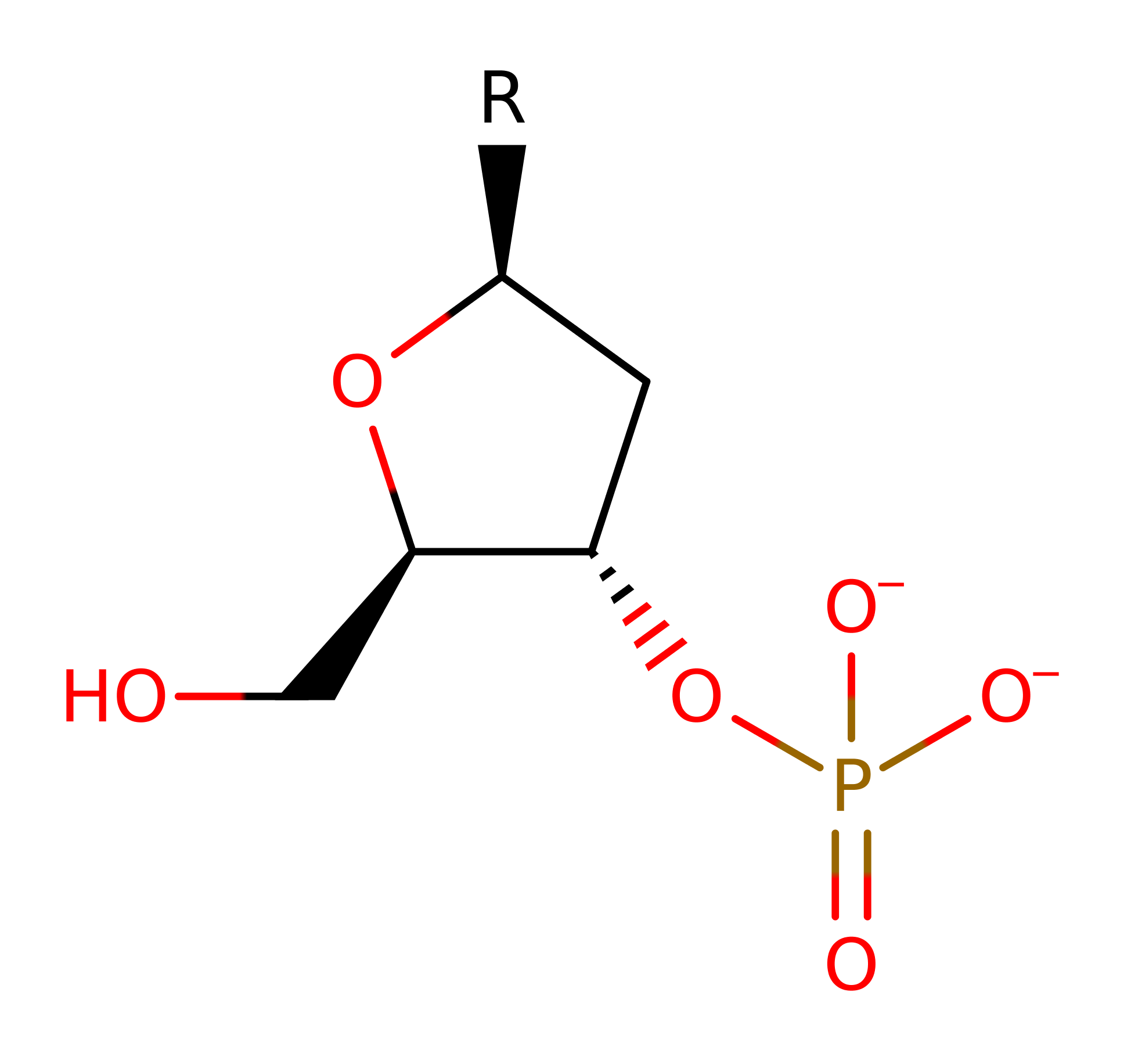
The overall reaction has been created using poly dAMP to show the chemical reaction.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00639
 (3.1.21.1)
(3.1.21.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1dnk
- THE X-RAY STRUCTURE OF THE DNASE I-D(GGTATACC)2 COMPLEX AT 2.3 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.10.10
 (see all for 1dnk)
(see all for 1dnk)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.21.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction involves an in-line attack at the DNA phosphorus group by a water molecule. His252 may act as a general base to abstract a proton from a water molecule opposite the O3' atom. Subsequent attack at the phosphorus group with inversion of its configuration gives rise to a penta-covalent state that may be stabilised by the metal ion. His134 is in an ideal position to protonate the leaving O3'. The metal ion may also be important for the correct positioning of the phosphate group.
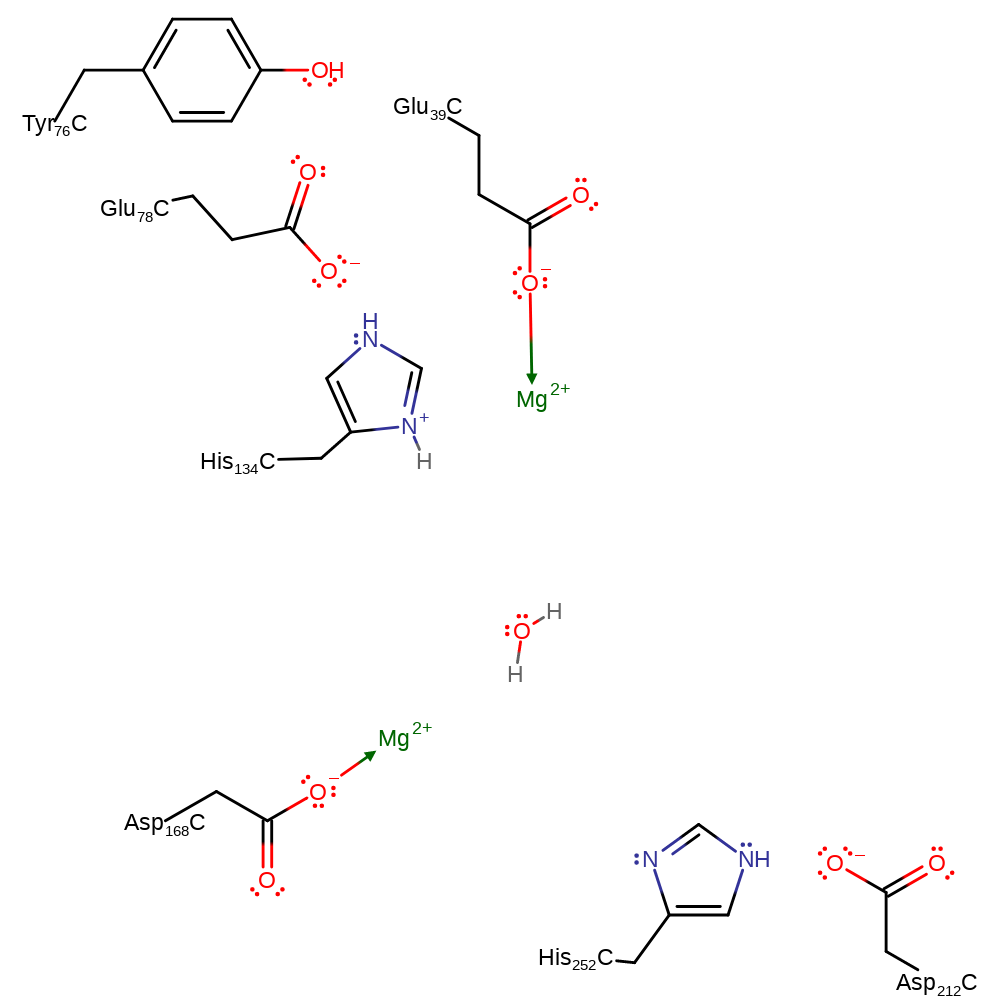
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dnk) | ||
| Asp234 | Asp212A(C) | Activates His252 to act as the general base. | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Tyr98, Glu100 | Tyr76A(C), Glu78A(C) | Part of the His-Glu-Tyr triad that activates His134 as a general acid. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His156, His274 | His134A(C), His252A(C) | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu61, Asp190 | Glu39A(C), Asp168A(C) | Binds one of the Mg(II) ions. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysis, proton transfer, rate-determining step, native state of enzyme regenerated, proton relay, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Jones SJ et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 264, 1154-1163. Site-directed Mutagenesis of the Catalytic Residues of Bovine Pancreatic Deoxyribonuclease I. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0703. PMID:9000637.
- Chen WJ et al. (2007), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 352, 689-696. Probing the catalytic mechanism of bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease I by chemical rescue. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.11.078. PMID:17141190.
- Kabsch W et al. (1990), Nature, 347, 37-44. Atomic structure of the actin: DNase I complex. DOI:10.1038/347037a0. PMID:2395459.
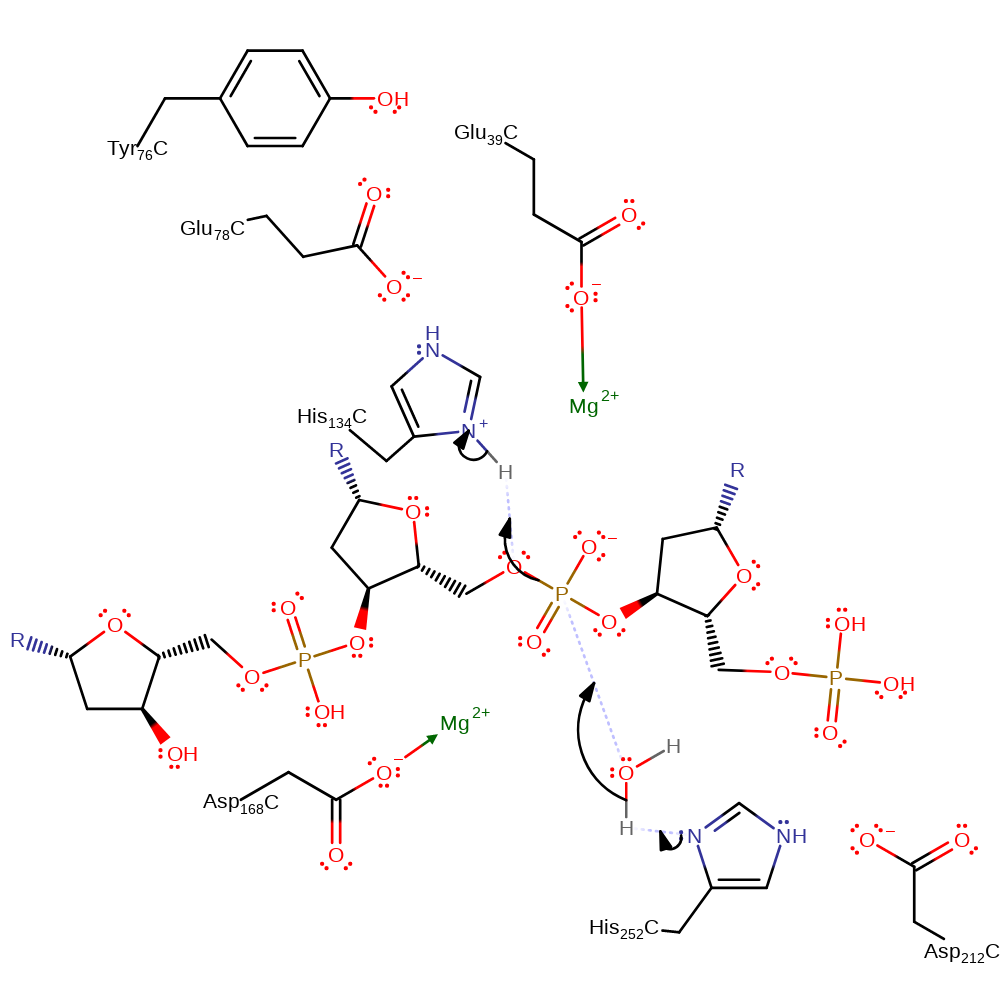
Step 1. His252 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate of the DNA in a substitution reaction which eliminates the 5' end of the DNA, with concomitant deprotonation of His134.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu39A(C) | metal ligand |
| Asp168A(C) | metal ligand |
| Tyr76A(C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu78A(C) | increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp212A(C) | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His252A(C) | proton acceptor |
| His134A(C) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysis, proton transfer, rate-determining step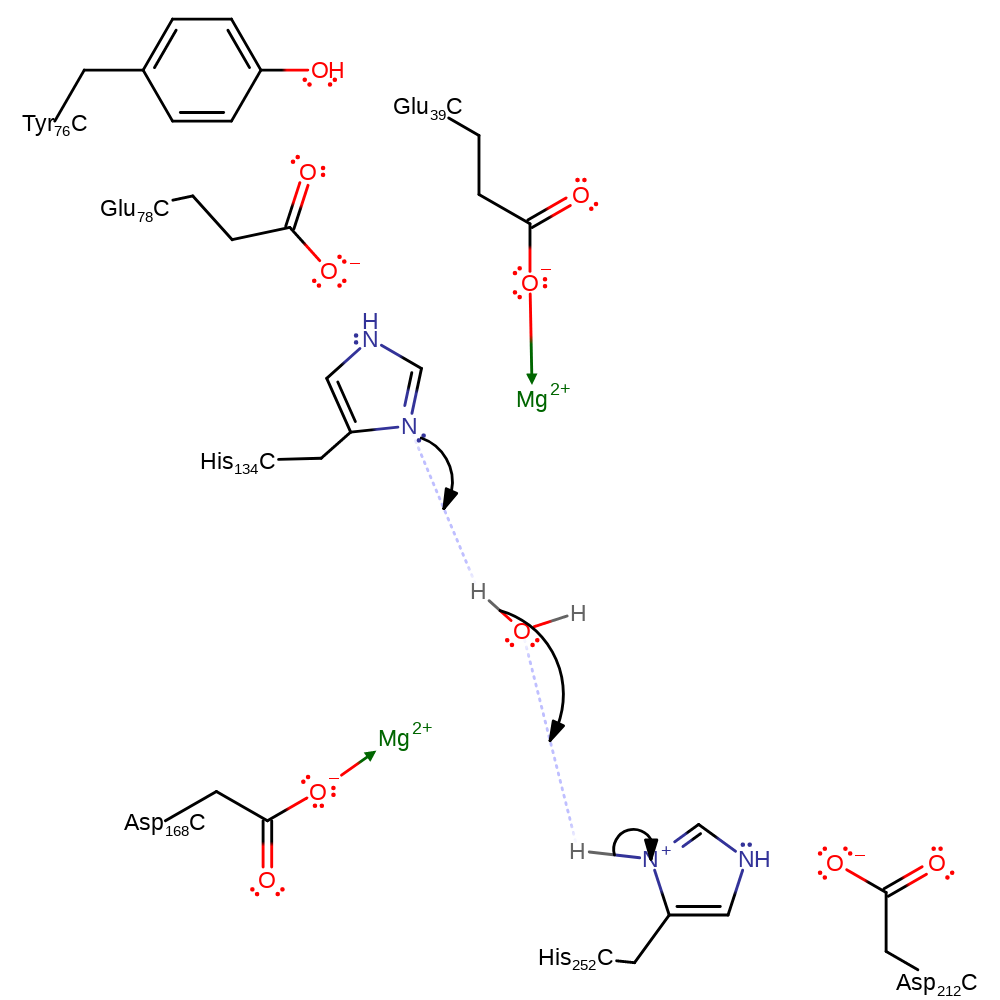
Step 2. His134 deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates His252 in an inferred return step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu39A(C) | metal ligand |
| Asp168A(C) | metal ligand |
| Tyr76A(C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu78A(C) | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp212A(C) | increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His252A(C) | proton donor |
| His134A(C) | proton acceptor |

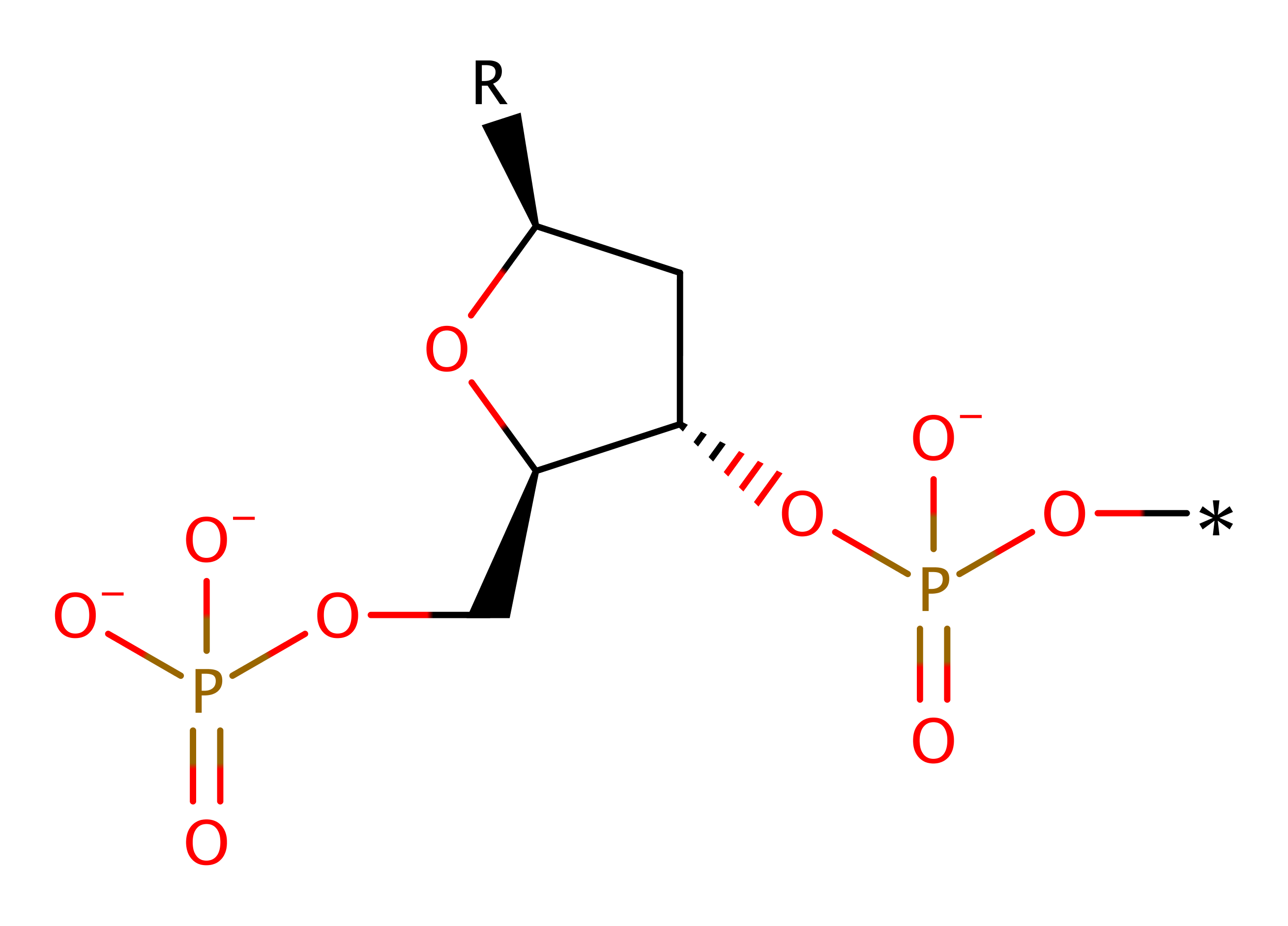

 Download:
Download: