Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase
Converts arachidonate to prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), a committed step in prostanoid synthesis. Constitutively expressed in some tissues in physiological conditions, such as the endothelium, kidney and brain, and in pathological conditions, such as in cancer. PTGS2 is responsible for production of inflammatory prostaglandins. Up-regulation of PTGS2 is also associated with increased cell adhesion, phenotypic changes, resistance to apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis. In cancer cells, PTGS2 is a key step in the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which plays important roles in modulating motility, proliferation and resistance to apoptosis.
Production of prostaglandin hormones in vertebrates depends on this enzyme, which couples the reduction of dangerous hydroperoxides to the generation of a useful oxidised product. The cofactor which makes this possible is a single iron protoporphyrin IX; its interactions with protein ligands are essential for modulating protein function.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q05769
 (1.14.99.1)
(1.14.99.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mus musculus (house mouse)

- PDB
-
5cox
- UNINHIBITED MOUSE CYCLOOXYGENASE-2 (PROSTAGLANDIN SYNTHASE-2)
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.640.10
 (see all for 5cox)
(see all for 5cox)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.14.99.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Mutagenesis studies have identified a number of residues essential for catalysis. The replacement of any one of His207, His309 or His388 (numbering for PGH1) by Gln or Ala abolishes both enzyme activities. His388 is the axial ligand for the haem iron, while His 207 is nearby on the distal side. Puzzlingly, His309 is far away from the active site in the structures which are now available. However, Gln203 has also been implicated in the peroxidase activity, cooperating with His207; while Tyr385 has been shown my mutation to be important for the cyclo-oxygenase activity. Spectroscopic data suggest that a tyrosyl radical formed as a result of peroxide reduction abstracts a hydrogen from arachidonate to start the cyclo-oxygenase reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (5cox) | ||
| His374 | His388(357)A | The axial ligand to the iron ion in heme b. Alters the redox potential of the iron ion. | metal ligand |
| Ser516 | Ser530(499)A | Although not critical for COX activity, it helps to stabilise the reactive intermediates formed on the tyrosine residue. It is a critical residue for the inhibition of COX by NSAIDs (site-directed mutagenesis of Ser-530 to Ala virtually abolished inhibition by diclofenac and piroxicam), along with Tyr385 the residue chelates the NSAIDs carboxylate group. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr371 | Tyr385(354)A | Acts as a hydrogen atom relay. Also an important residue in the inhibition of COX activity by NSAIDs. | hydrogen radical acceptor, hydrogen radical donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Gln189 | Gln203(172)A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His193 | His207(176)A | Acts as a general acid/base | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu370, Gly512 | Leu384(353)A, Gly526(495)A | Help direct the steriochemical outcome of the reaction. Mutation of these residues result in several different isomeric products (15S-, 13R- and 15R-oxygenated diepoxides). | steric role |
Chemical Components
coordination, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, radical formation, redox reaction, overall product formed, radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, atom stereo change, bimolecular homolytic addition, intramolecular homolytic addition, cyclisation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme is not regeneratedReferences
- Marnett LJ (2000), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 4, 545-552. Cyclooxygenase mechanisms. DOI:10.1016/s1367-5931(00)00130-7. PMID:11006543.
- Blobaum AL et al. (2015), J Biol Chem, 290, 12793-12803. Action at a Distance. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m114.635987. PMID:25825493.
- Wu G et al. (2011), J Inorg Biochem, 105, 382-390. Cyclooxygenase reaction mechanism of prostaglandin H synthase from deuterium kinetic isotope effects. DOI:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2010.11.015. PMID:21394223.
- Furse KE et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 3206-3218. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Arachidonic Acid-Derived Pentadienyl Radical Intermediate Complexes with COX-1 and COX-2: Insights into Oxygenation Regio- and Stereoselectivity†. DOI:10.1021/bi052338h. PMID:16519515.
- Schneider C et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 4404-4414. Identification of Two Cyclooxygenase Active Site Residues, Leucine 384 and Glycine 526, That Control Carbon Ring Cyclization in Prostaglandin Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m307431200. PMID:14594816.
- Rowlinson SW et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 45763-45769. A Novel Mechanism of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition Involving Interactions with Ser-530 and Tyr-385. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m305481200. PMID:12925531.
- Seibold SA et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 6616-6624. Peroxidase Activity in Prostaglandin Endoperoxide H Synthase-1 Occurs with a Neutral Histidine Proximal Heme Ligand†. DOI:10.1021/bi0002333. PMID:10828979.
- Kiefer JR et al. (2000), Nature, 405, 97-101. Structural insights into the stereochemistry of the cyclooxygenase reaction. DOI:10.1038/35011103. PMID:10811226.
- Landino LM et al. (1997), J Biol Chem, 272, 21565-21574. Mutational Analysis of the Role of the Distal Histidine and Glutamine Residues of Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase-2 in Peroxidase Catalysis, Hydroperoxide Reduction, and Cyclooxygenase Activation. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.34.21565. PMID:9261177.
- Tang MS et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 7527-7534. Detection of an Fe2+−Protoporphyrin-IX Intermediate during Aspirin-Treated Prostaglandin H2Synthase II Catalysis of Arachidonic Acid to 15-HETE†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi962750k. PMID:9200703.
- Shimokawa T et al. (1991), J Biol Chem, 266, 6168-6173. Essential histidines of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. His-309 is involved in heme binding. PMID:1901057.
- Shimokawa T et al. (1990), J Biol Chem, 265, 20073-20076. Tyrosine 385 of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase is required for cyclooxygenase catalysis. PMID:2122967.

Step 1. His207 deprotonates the alkyl peroxide, which then coordinates to the Fe(III) centre of the haem cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His207(176)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gln203(172)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His388(357)A | metal ligand |
| His207(176)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
coordination, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, proton transfer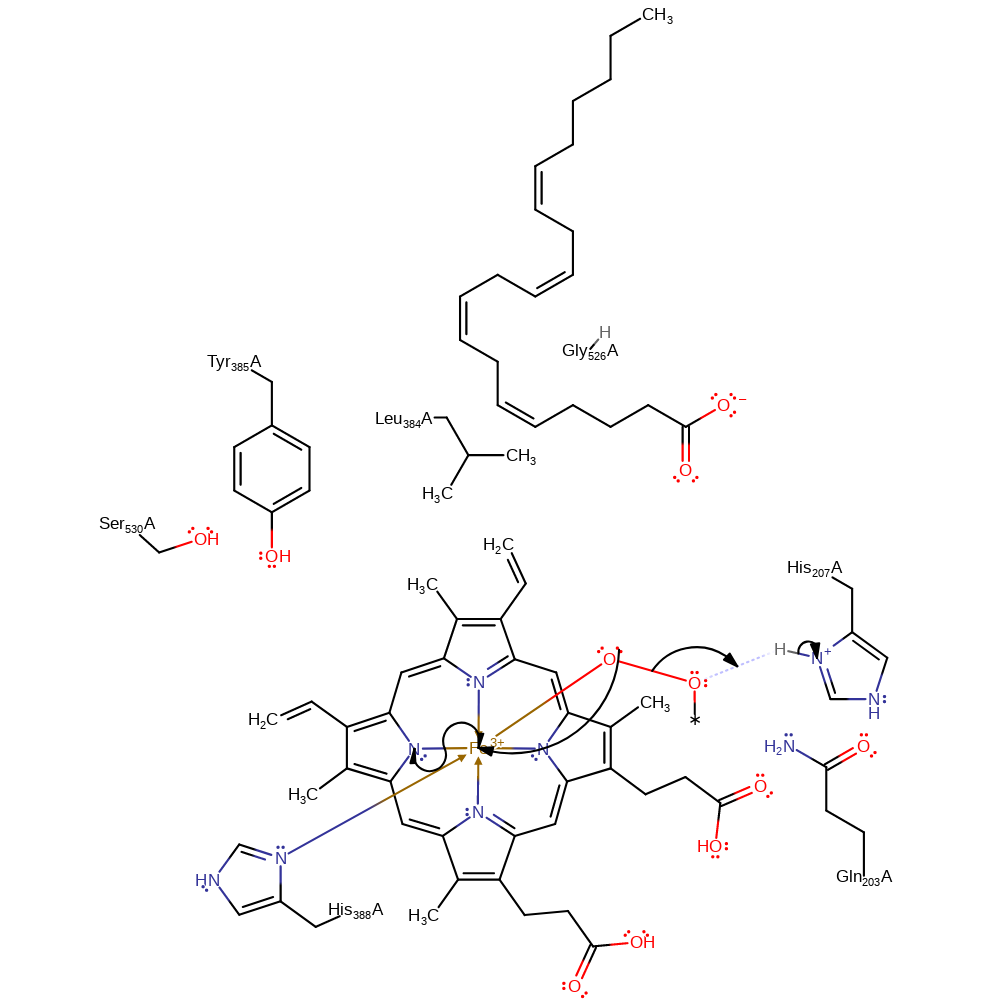
Step 2. The peroxo bond collapses, donating two electrons to the Fe(III) centre, which immediately shuttles one into the porphyrin ring, creating Fe(IV). The liberated alkoxide deprotonates His207
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His207(176)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203(172)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His388(357)A | metal ligand |
| His207(176)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, radical formation, redox reaction, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr385(354)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His388(357)A | metal ligand |
| Tyr385(354)A | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, intermediate formation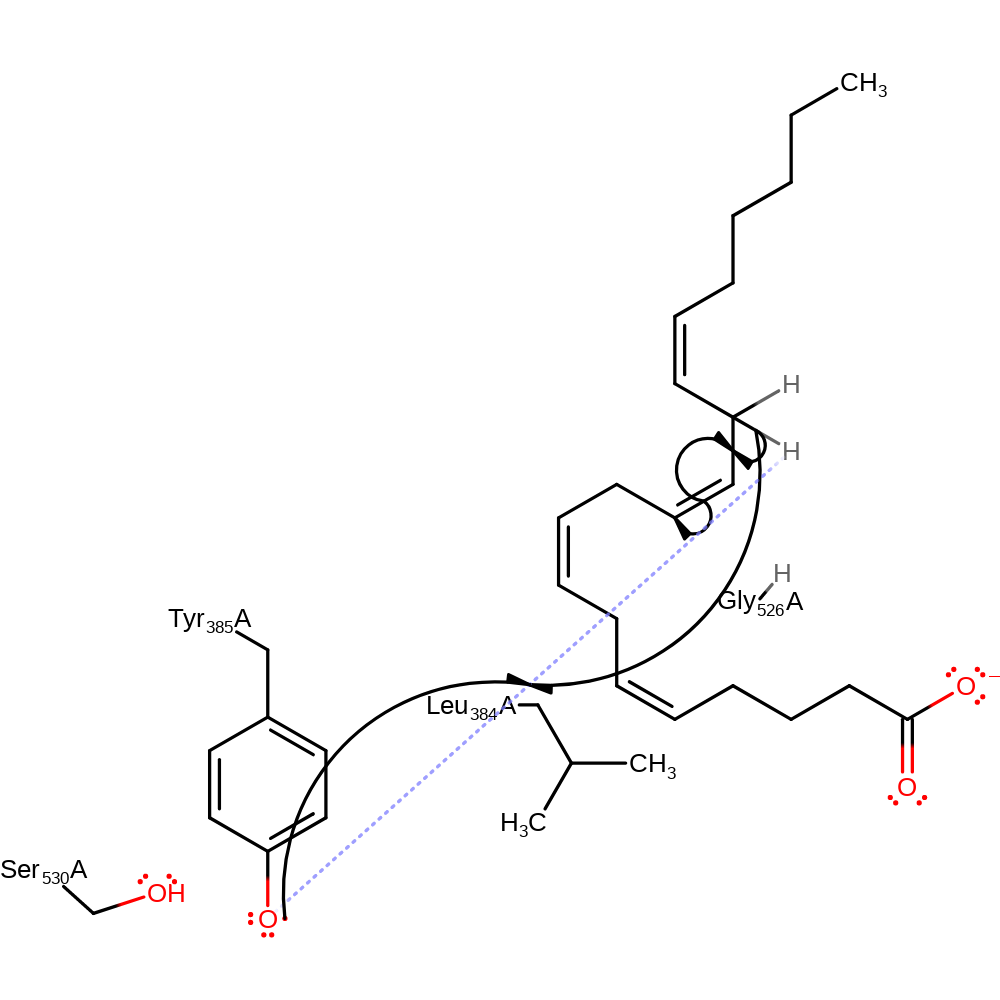
Step 4. Tyr385 abstracts a hydrogen from the arachidonic acid, initiating double bond rearrangement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr385(354)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly526(495)A | steric role |
| Leu384(353)A | steric role |
| Tyr385(354)A | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, atom stereo change, overall reactant used, intermediate formation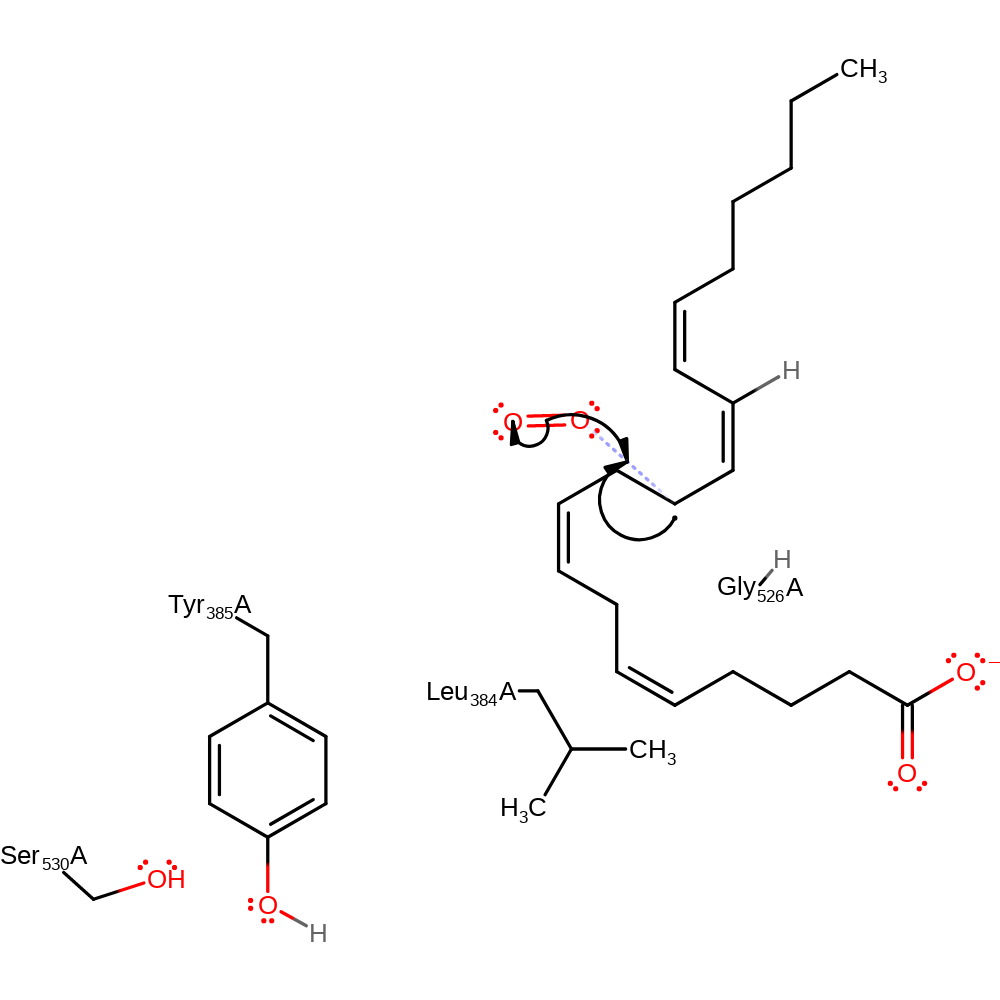
Step 5. The carbon radical initiates a homolytic attack on a dioxygen molecule in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr385(354)A | radical stabiliser |
| Gly526(495)A | steric role |
| Leu384(353)A | steric role |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, atom stereo change, overall reactant used, intermediate formation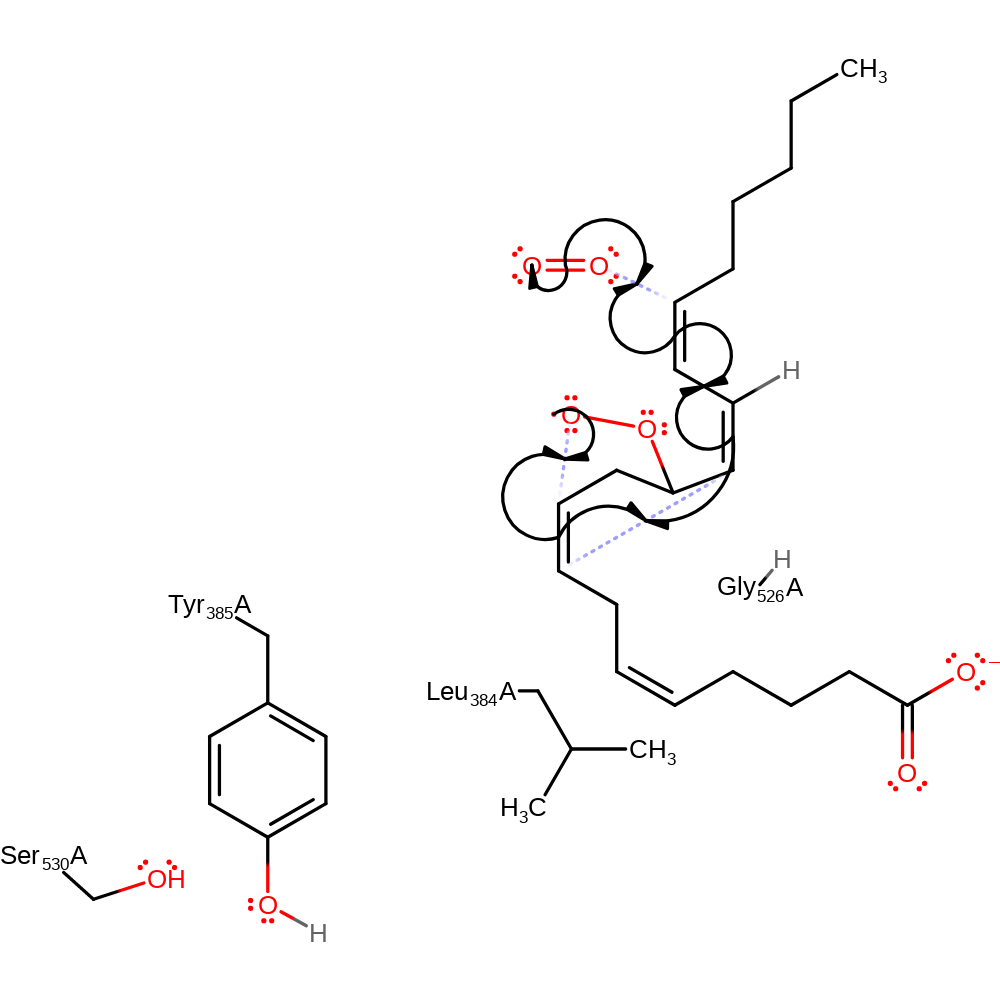
Step 6. The oxygen radical initiates a homolytic attack on the carbon chain, forming a four-membered ring in an addition reaction. This initiates a second homolytic attack, through double bond rearrangement, which causes the formation of a five-membered carbon rind, and initiates homolytic attack on a second dioxygen molecule in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr385(354)A | radical stabiliser |
| Leu384(353)A | steric role |
| Gly526(495)A | steric role |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, ingold: intramolecular homolytic addition, ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, atom stereo change, overall reactant used, cyclisation, intermediate formation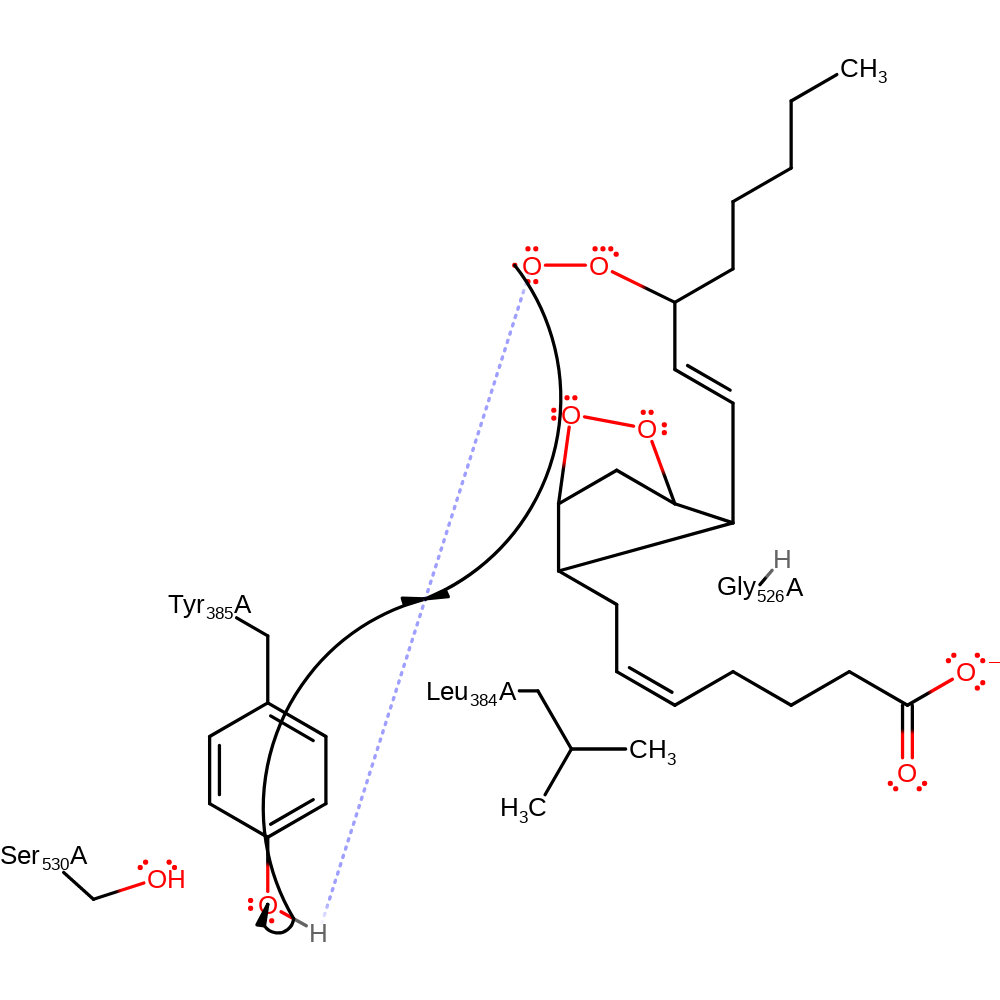
Step 7. The oxygen radical of the peroxo group abstracts a hydrogen from Tyr385.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr385(354)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu384(353)A | steric role |
| Gly526(495)A | steric role |
| Ser530(499)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr385(354)A | hydrogen radical donor |








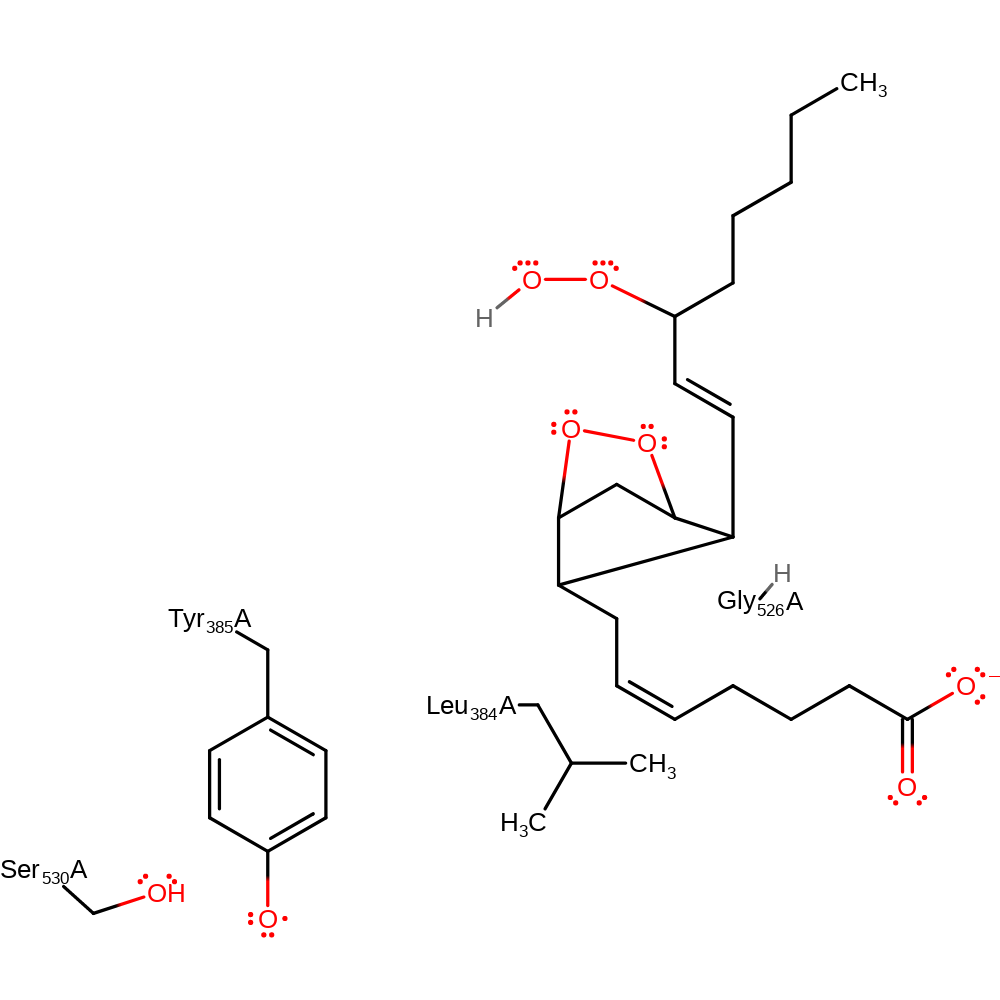 Download:
Download: