Glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase
Glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase (GRT) catalyses the first two steps of purine biosynthesis: the transfer of formyl from 10-formyltetrahydrofolate to the amino group of glycinamide ribonucleotidem, forming glycinamide ribonucleotide and tetrahydrofolate.
The enzyme’s role in DNA nucleotide biosynthesis makes it an interesting target for anti-neoplastic agents and for developing novel antifolate drugs to be used in cancer chemotherapy. Due to its biological and pharmacological significance, it has been the subject of intensive studies.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P08179
 (2.1.2.2)
(2.1.2.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1grc
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF GLYCINAMIDE RIBONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFORMYLASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI AT 3.0 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION: A TARGET ENZYME FOR CHEMOTHERAPY
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.170
 (see all for 1grc)
(see all for 1grc)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.2.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Folate binding induces active site rearrangements involving Asp144 and His108. Asp144 forms a salt bridge to the imidazolium of His108 and the formyl group is positioned to form hydrogen bonds to Asn106 and the protonated imidazolium group of His108. Asn106 may fine-tune the location of the formyl group.
A low-dielectric active site environment favours the free base form of the amino group of GAR, poised to attack the activated formyl group to form presumably a tetrahedral intermediate in the transfer process. A proton is switched from GAR to the N10 of folate mediated by a catalytic water molecule, followed by breakdown of the tetrahedral intermediate and product release. The positioning of the catalytic water molecule may also be assisted by Asp144.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1grc) | ||
| Ser135 | Ser135A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp144 | Asp144A | Forms a salt bridge with His108. Essential as maintains the correct protonation state of the His108. Asp144 activates a tightly bound water molecule via hydrogen bonding. It is also possible that it acts as a general acid/base (again, via the conserved water molecule) donating a proton to the N10 atom of THF, enabling the formyl group to leave. | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| His108, Asn106 | His108A, Asn106A | The Asn and His residues are both presumed to stabilise the oxyanion group of the GAR-formyl-THF intermediate, supported by the observed conformations of these residues in the structure of the enzyme bound to U89, believed to be a transition state analogue. In addition, the His residue may well rotate substantially to contact Ser135, leaving Asn106 to stabilise the anion. | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall product formedReferences
- Shim JH et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 10024-10031. Catalytic Mechanism ofEscherichia coliGlycinamide Ribonucleotide Transformylase Probed by Site-Directed Mutagenesis and pH-Dependent Studies†. DOI:10.1021/bi9904609. PMID:10433709.
- Warren MS et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 8855-8862. A Rapid Screen of Active Site Mutants in Glycinamide Ribonucleotide Transformylase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9528715. PMID:8688421.
- Almassy RJ et al. (1992), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 89, 6114-6118. Structures of apo and complexed Escherichia coli glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase. DOI:10.1073/pnas.89.13.6114. PMID:1631098.

Step 1. The free base form of glycinamide ribonucleotide attacks the activated formyl group to form an anionic tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His108A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Asn106A | electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Asp144A | hydrogen bond acceptor, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Ser135A | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn106A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation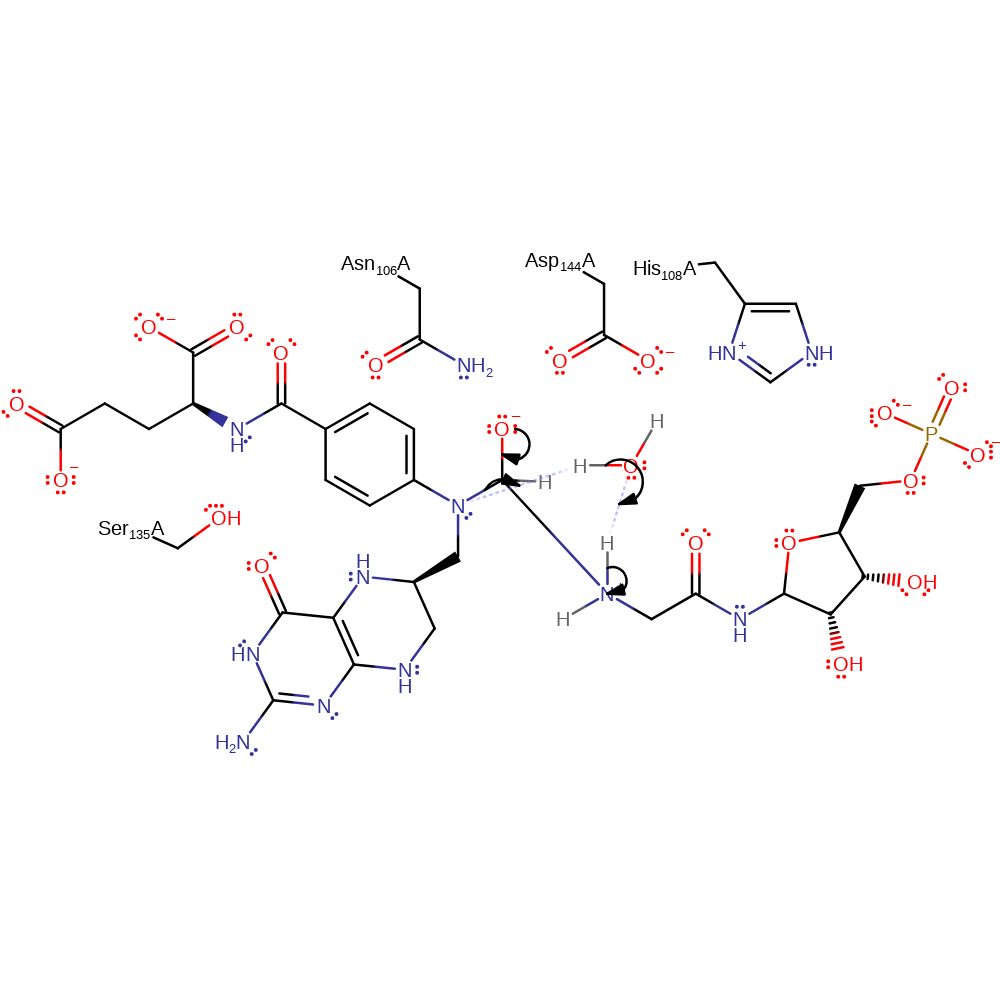
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, to produce the formylated phosphor-ribosyl glycinamide with concomitant reprotonation of the tetrafolate through a conserved water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His108A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Asn106A | electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Asp144A | hydrogen bond acceptor, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Ser135A | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Asn106A | hydrogen bond donor |





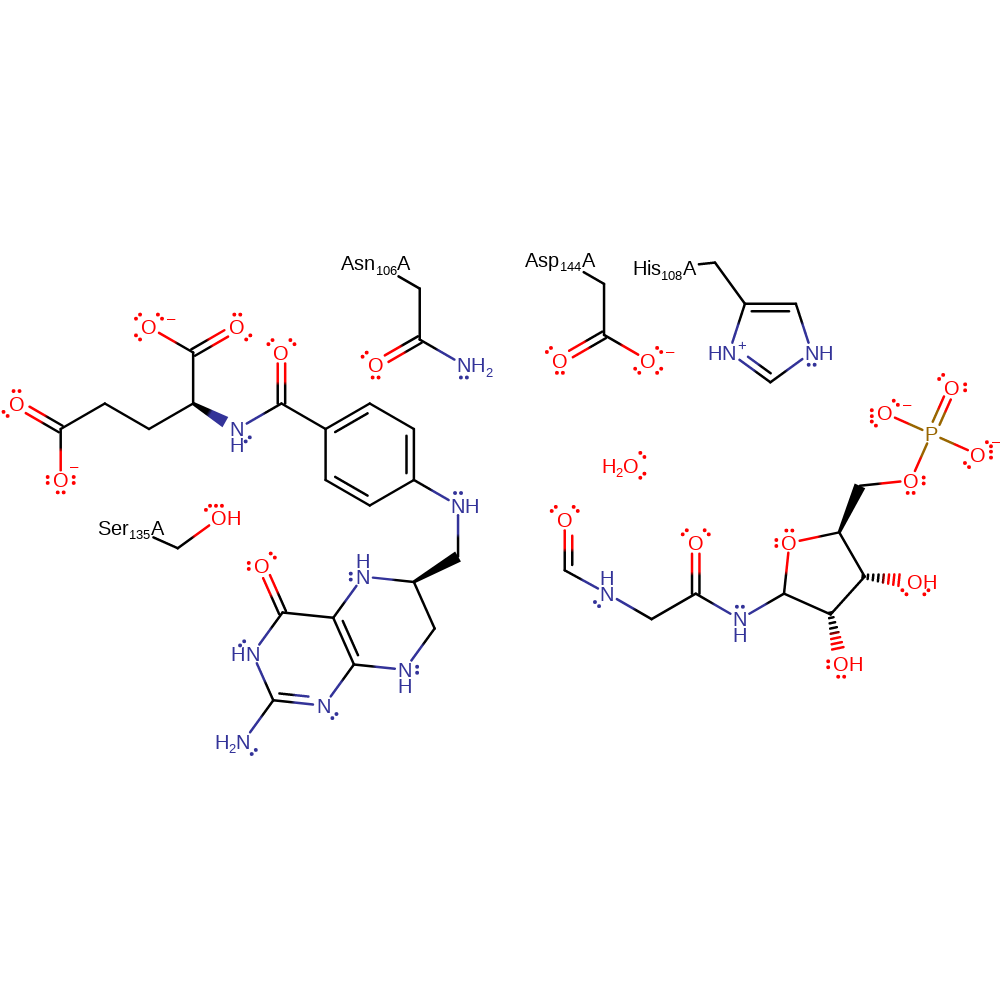 Download:
Download: