Alpha-1,3-galactosetransferase
alpha-1,3-galactosetransferase catalyses the transfer of galactose from UDP-alpha-D-galactose into an alpha-1,3 linkage with beta-galactosyl groups in glycoconjugates. It belongs to the family of metal-dependent retaining glycosyltransferase. It is involved in the post translational modification glycosylation of proteins, occurring within the Golgi appararatus.
The enzyme is found in many mammals, including most primates and New World monkeys but is not active in Old World primates. In this group, which also includes humans, the enzyme is inactivated by a frame shift mutation. Therefore, the product, alpha-galactose epitope, is the target of a large fraction of natural antibodies. Many mammals used for xenotranlation of organs express the alpha-galactose epitope product, and without inhibition of alpha-1, 3-galactosetransferase in the donor animal, the presence of antibodies specific to this epitope signal in the recipient human for an immune response towards the organ, resulting in rejection.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P14769
 (2.4.1.87)
(2.4.1.87)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1vzx
- Roles of active site tryptophans in substrate binding and catalysis by ALPHA-1,3 GALACTOSYLTRANSFERASE
(1.97 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.550.10
 (see all for 1vzx)
(see all for 1vzx)
- Cofactors
- Manganese(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.1.87)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism follows a single step SNi reaction, in which hydrolysis of UDP-galactose occurs to form a galactose with an oxycarbenium ion character, which is stabilised by Glu317. The transition state is further stabilised by Arg365, Trp314 and Manganese ion. The galactose is transferred to the acceptor substrate by a nucleophilic attack of the hydroxyl group of its anomeric carbon to the oxycarbenium ion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1vzx) | ||
| Glu317 | Glu317(238)A | Sabilises the cationic transition state with oxocarbenium ion character | activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp314 | Tyr314(235)A | Stabilises the transition state in the galactose transfer | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp356, Gln247, His280, Arg365 | Trp356(277)A, Gln247(168)A, His280(201)A, Arg365(286)A | Stabilises the transition state of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, overall product formed, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, bimolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Zhang Y et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 13512-13521. Roles of Individual Enzyme−Substrate Interactions by α-1,3-Galactosyltransferase in Catalysis and Specificity†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi035430r. PMID:14621997.
- Gómez H et al. (2013), J Am Chem Soc, 135, 7053-7063. Substrate-assisted and nucleophilically assisted catalysis in bovine α1,3-galactosyltransferase. Mechanistic implications for retaining glycosyltransferases. DOI:10.1021/ja4024447. PMID:23578032.
- Jamaluddin H et al. (2009), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 385, 601-604. Crystal structure of α-1,3-galactosyltransferase (α3GT) in a complex with p-nitrophenyl-β-galactoside (pNPβGal). DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.111. PMID:19486884.
- Jamaluddin H et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 369, 1270-1281. Conformational Changes Induced by Binding UDP-2F-galactose to α-1,3 Galactosyltransferase- Implications for Catalysis. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.012. PMID:17493636.
- Zhang Y et al. (2004), Glycobiology, 14, 1295-1302. Roles of active site tryptophans in substrate binding and catalysis by -1,3 galactosyltransferase. DOI:10.1093/glycob/cwh119. PMID:15229192.
- Boix E et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 28310-28318. Structural Basis of Ordered Binding of Donor and Acceptor Substrates to the Retaining Glycosyltransferase, alpha -1,3-Galactosyltransferase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m202631200. PMID:12011052.
- Gastinel LN et al. (2001), EMBO J, 20, 638-649. Bovine alpha1,3-galactosyltransferase catalytic domain structure and its relationship with ABO histo-blood group and glycosphingolipid glycosyltransferases. DOI:10.1093/emboj/20.4.638. PMID:11179209.
- Boix E et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 48608-48614. Structure of UDP Complex of UDP-galactose:β-Galactoside-α-1,3-galactosyltransferase at 1.53-Å Resolution Reveals a Conformational Change in the Catalytically Important C Terminus. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m108828200. PMID:11592969.
- Zhang Y et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 11567-11574. Specificity and Mechanism of Metal Ion Activation in UDP-galactose:beta -Galactoside-alpha -1,3-galactosyltransferase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m006530200. PMID:11133981.
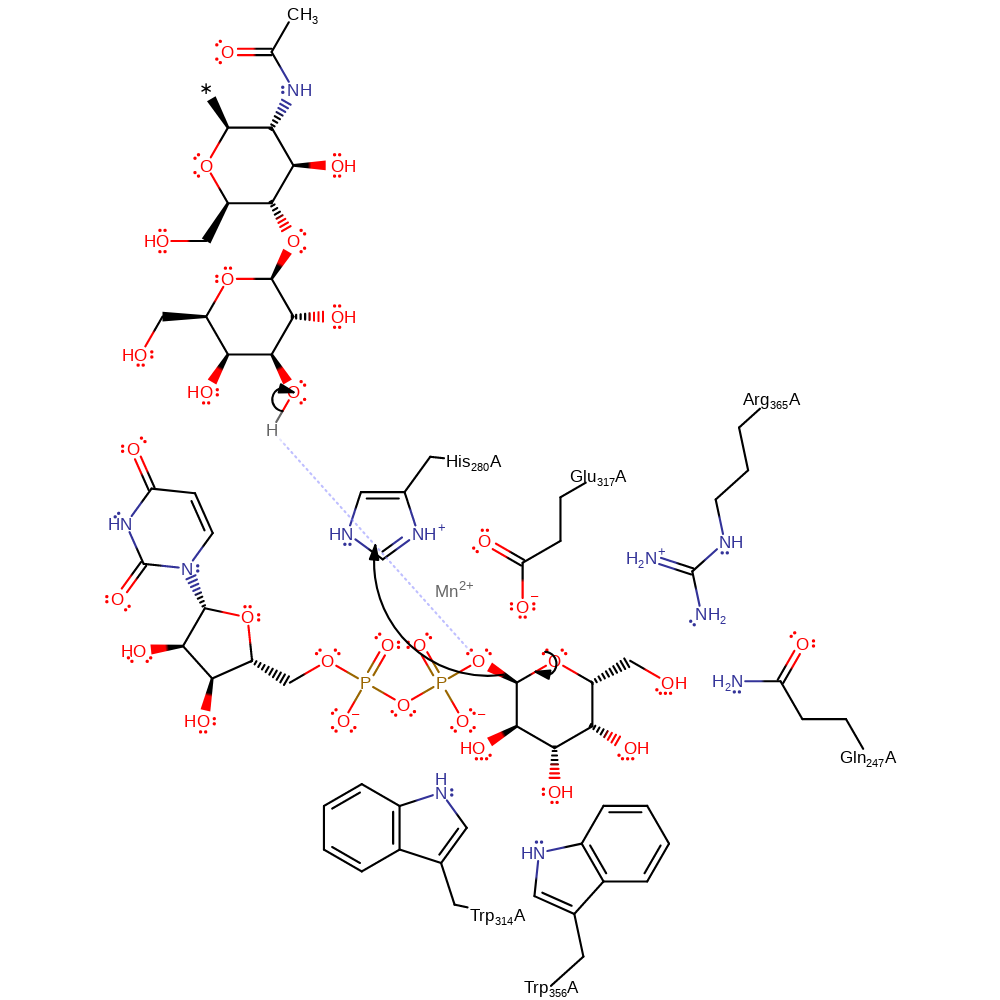
Step 1. UDP is eliminated from the substrate to form an oxycarbenium ion transition state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp356(277)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu317(238)A | activator |
| Tyr314(235)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln247(168)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His280(201)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu317(238)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg365(286)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, overall product formed, proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base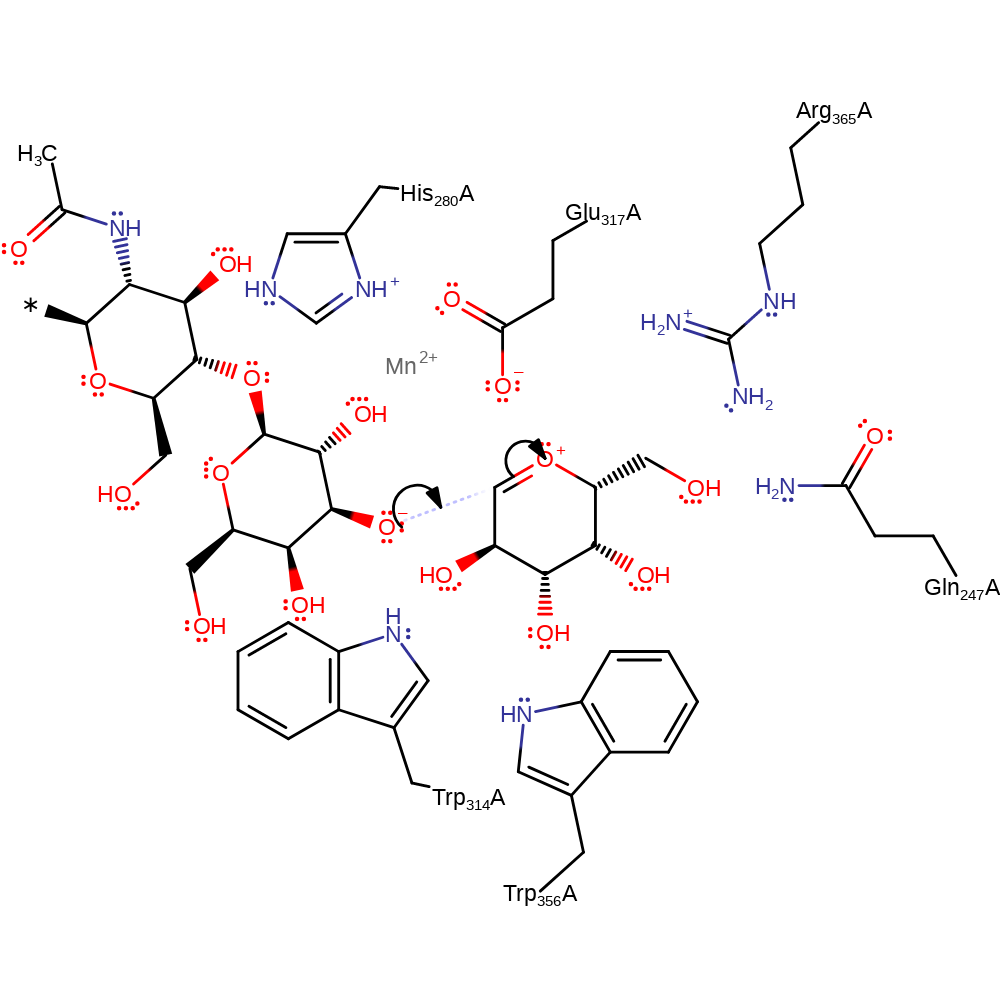
Step 2. The activated polymer then adds to the oxycarbenium transition state to finish the reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln247(168)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His280(201)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr314(235)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu317(238)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp356(277)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg365(286)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionIntroduction
The reaction proceeds via nucleophilic attack on the UDP galactose substrate by the catalytic residue Glu317 to form a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. This allows the galactose to be transferred to the second substrate through nucleophilic attack by the deprotonated sugar oxygen on the anomeric carbon. The double displacement thus results in retention of configuration (alpha). The mechanism whereby the sugar oxygen is deprotonated is unclear, but seems likely to involve direct transfer of the proton to the UDP leaving group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1vzx) | ||
| Glu317 | Glu317(238)A | Attacks the anomeric carbon of UDP galactose to form a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate, allowing transfer of the galactose to the substrate. | activator, covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Trp314 | Tyr314(235)A | Stabilises the transition state in the galactose transfer | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp356, Gln247, His280, Arg365 | Trp356(277)A, Gln247(168)A, His280(201)A, Arg365(286)A | Stabilises the transition state of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, atom stereo change, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Gastinel LN et al. (2001), EMBO J, 20, 638-649. Bovine alpha1,3-galactosyltransferase catalytic domain structure and its relationship with ABO histo-blood group and glycosphingolipid glycosyltransferases. DOI:10.1093/emboj/20.4.638. PMID:11179209.

Step 1. Glu317 displaces UDP from the anomeric carbon, forming an enzyme-substrate adduct.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp356(277)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu317(238)A | activator |
| Tyr314(235)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln247(168)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His280(201)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg365(286)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu317(238)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
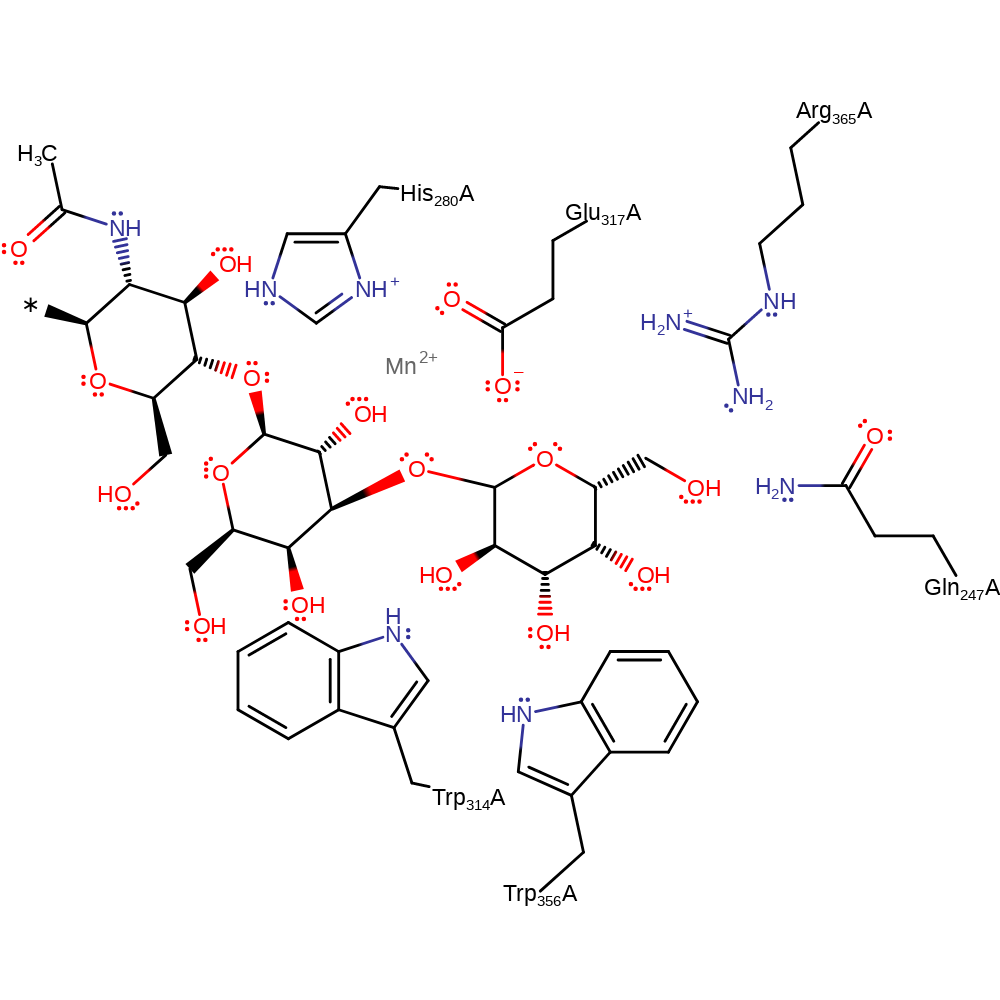
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, atom stereo change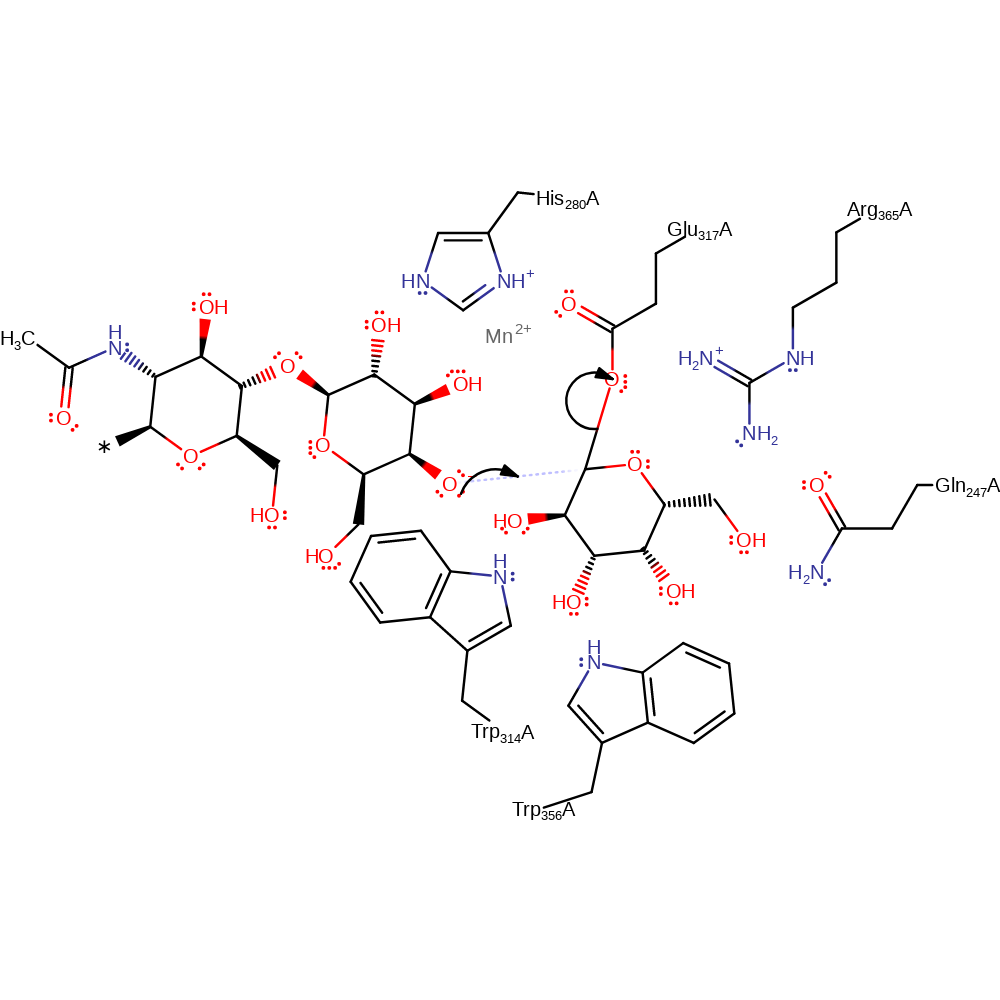
Step 2. The beta-galactosyl acceptor substrate displaces Glu317. This second inversion of stereochemistry at the anomeric centre results in retention of the alpha configuration.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp356(277)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu317(238)A | activator, covalently attached |
| Tyr314(235)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln247(168)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His280(201)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg365(286)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu317(238)A | nucleofuge |





 Download:
Download: 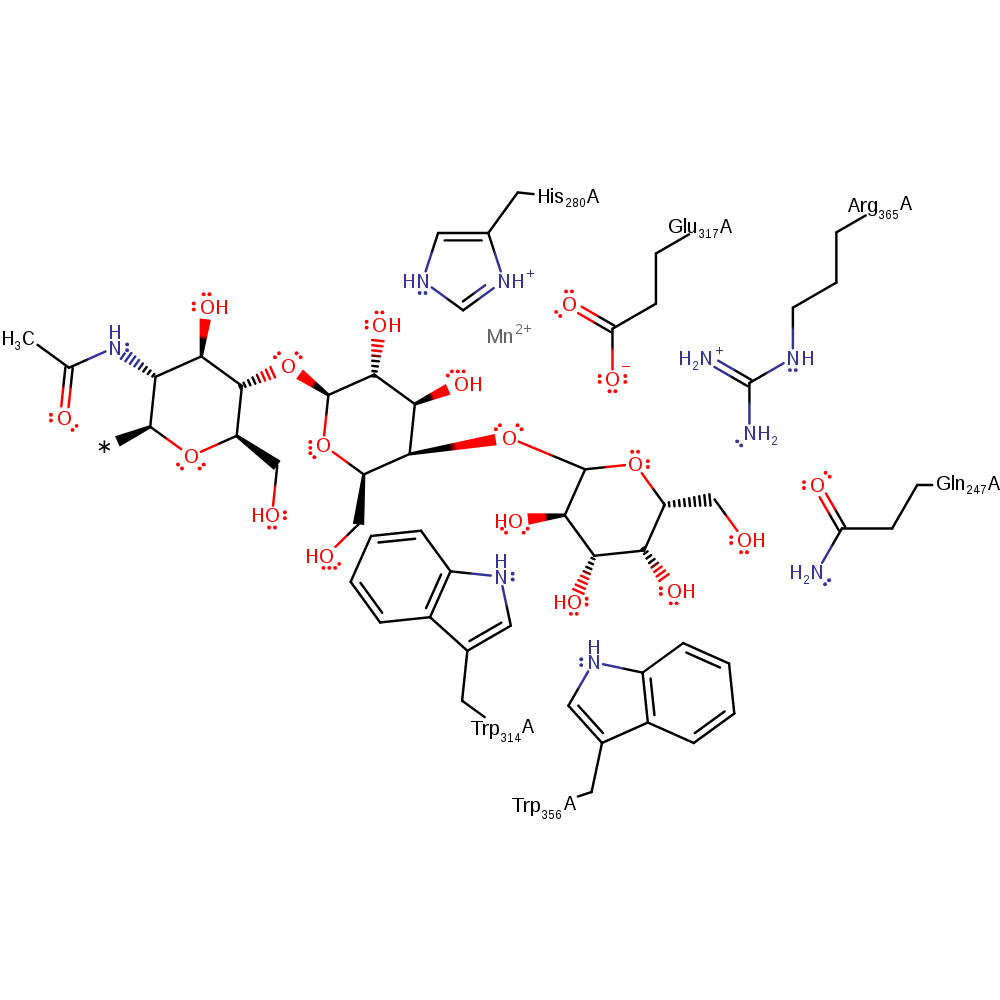 Download:
Download: