L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase
L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase reversibly catalyses the conversion of L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA to the 3-ketoyl acid derivative by proton abstraction and concurrent oxidation by the NAD+ cofactor, the penultimate step in the beta-oxidation spiral, and involved in fatty acid metabolism.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q16836
 (1.1.1.35)
(1.1.1.35)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
2hdh
- BIOCHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND STRUCTURE DETERMINATION OF HUMAN HEART SHORT CHAIN L-3-HYDROXYACYL COA DEHYDROGENASE PROVIDE INSIGHT INTO CATALYTIC MECHANISM
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.720
 (see all for 2hdh)
(see all for 2hdh)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.35)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The Glu-His diad, conserved across all functionally related enzymes, acts in concert to deprotonate the 3-OH of the substrate. The oxyanion intermediate collapses, eliminating a hydride to the C4 position of the NAD cofactor. A proton transfer step has been inferred to allow for active site regeneration.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2hdh) | ||
| Asn220, Ser149 | Asn208(197)A, Ser137(126)A | Acts to stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu182 | Glu170(159)A | Activates the general acid/base histidine as part of a His-Glu catalytic dyad. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His170 | His158(147)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, hydride transfer, intermediate collapse, cofactor used, native state of cofactor is not regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Barycki JJ et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 5786-5798. Biochemical Characterization and Crystal Structure Determination of Human Heart Short Chainl-3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Provide Insights into Catalytic Mechanism†. DOI:10.1021/bi9829027. PMID:10231530.
- Barycki JJ et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 36718-36726. Glutamate 170 of Human L-3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Is Required for Proper Orientation of the Catalytic Histidine and Structural Integrity of the Enzyme. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m104839200. PMID:11451959.
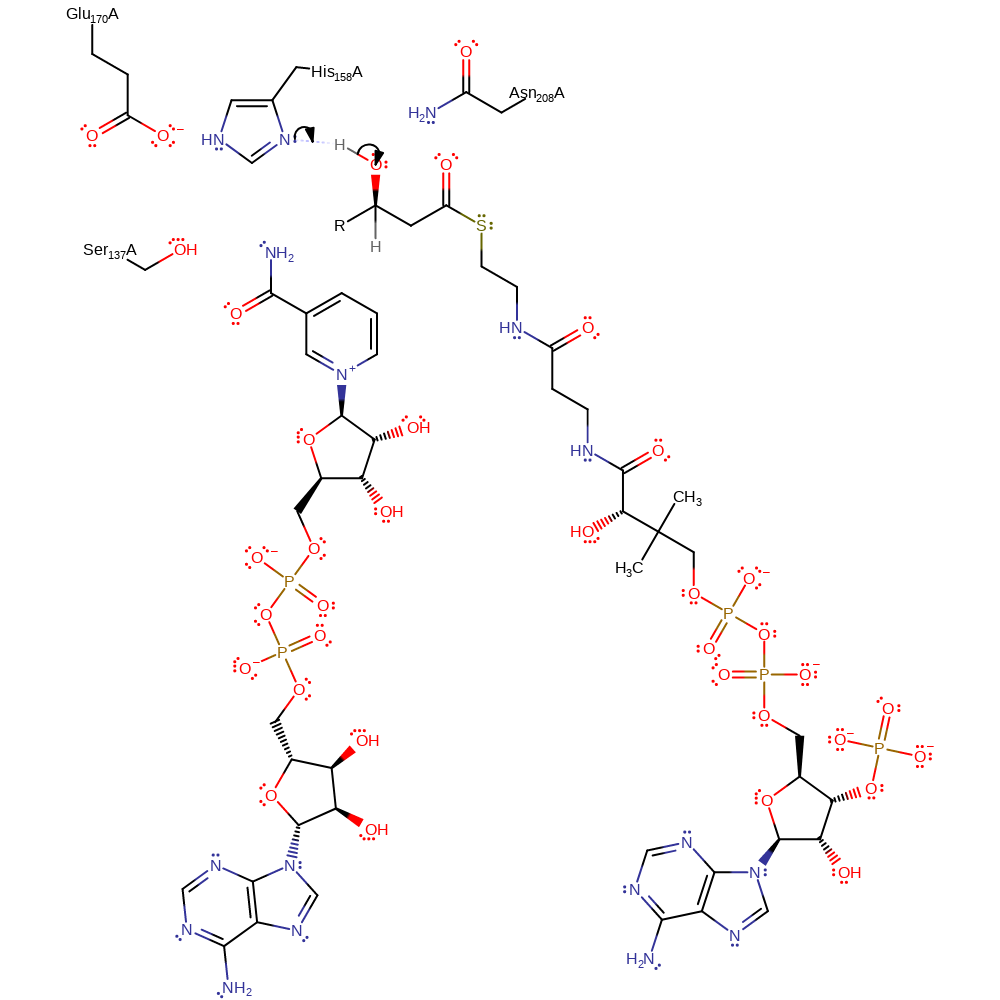
Step 1. The Glu-His diad, conserved across all functionally related enzymes, acts in concert to deprotonate the 3-OH of the substrate. While an initial proton abstraction is shown, there is no direct evidence to suggest that a concerted mechanism, or a hydride transfer followed by proton abstraction do not occur [PMID:10231530].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu170(159)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase basicity |
| Asn208(197)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser137(126)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His158(147)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The oxyanion intermediate collapses, eliminating a hydride to the C4 position of the NAD cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu170(159)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208(197)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser137(126)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate collapse, cofactor used, native state of cofactor is not regenerated
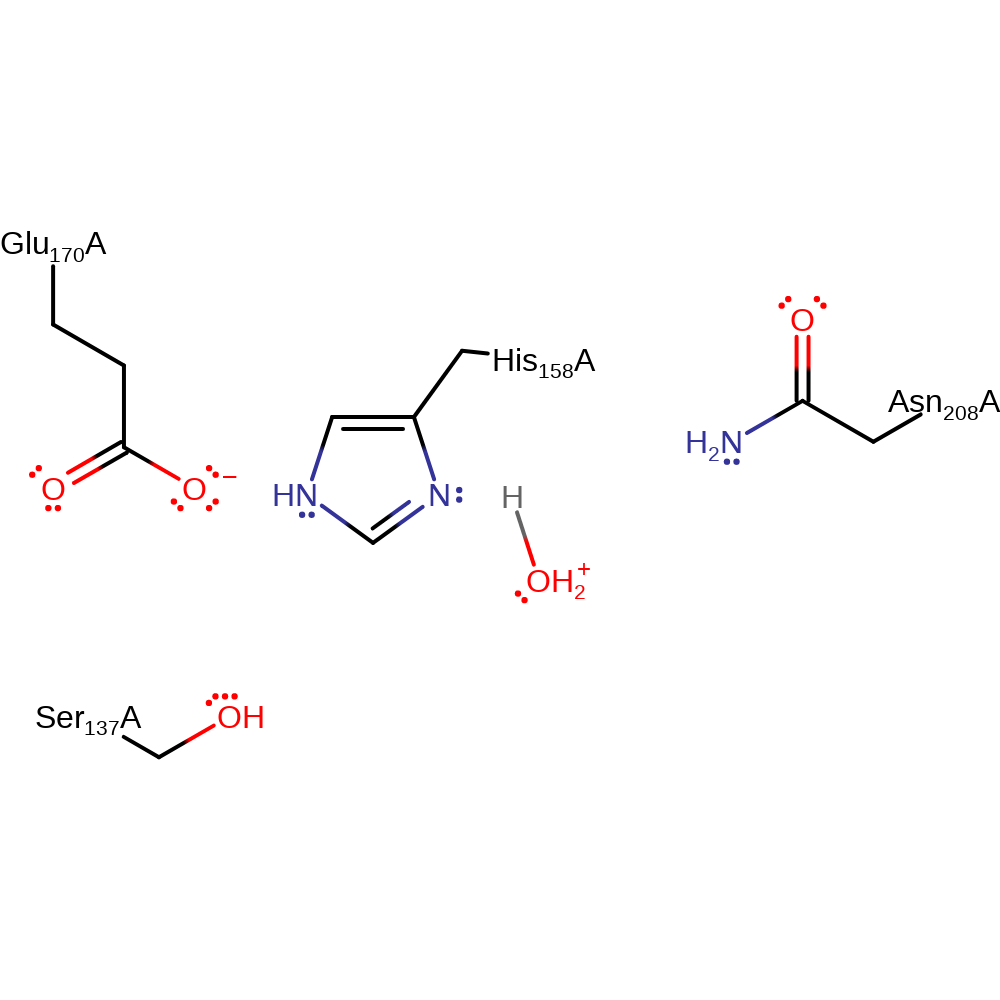
Step 3. A proton transfer step has been inferred to allow for active site regeneration.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu170(159)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208(197)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser137(126)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His158(147)A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: