TRNA-(m1-G37)-methyl transferase
In transfer RNA many different modified nucleosides are found, especially in the anticodon region. tRNA (guanine (N1))-methyltransferase (TrmD) is one of several nucleases operating together with the tRNA-modifying enzymes before the formation of the mature tRNA. TrmD catalyses the S-adenosyl-methionine(AdoMet) dependent It methlyation of guanosine(G) to N1-methylguanine (1-methylguanosine (m1G)) at position 37 of tRNAs that read CUN (leucine), CCN(proline), and CGG (arginine) codons. The presence of m1G improves the cellular growth rate and the polypeptide steptime and also prevents the tRNA from shifting the reading frame.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P43912
 (2.1.1.228)
(2.1.1.228)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Haemophilus influenzae Rd KW20 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1uam
- Crystal structure of tRNA(m1G37)methyltransferase: Insight into tRNA recognition
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1280.10
 (see all for 1uam)
(see all for 1uam)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.1.228)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism follows a general base catalysis. Asp169 deprotonates the N1 group of guanosine to allow it to nucleophilically attack the methyl group of AdoMet to yield the product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1uam) | ||
| Pro89 | Pro89(109)A | Ensures that the SAM substrate takes the correct orientation to transfer the methyl group to the tRNA. | increase nucleophilicity, steric role |
| Glu116 | Glu116(136)A | Binds and orients the guanine base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg154 | Arg154(174)A(AA) | Acts to stabilise and activate the catalytic base. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp169 | Asp169(189)A(AA) | Acts as a base to deprotonate N1 group of guanosine to allow its nucleophilic attack on methyl group of AdoMet. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, increase nucleophilicity |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, cofactor used, rate-determining step, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Elkins PA et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 333, 931-949. Insights into Catalysis by a Knotted TrmD tRNA Methyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.09.011. PMID:14583191.
- Swinehart WE et al. (2015), RNA Biol, 12, 398-411. Diversity in mechanism and function of tRNA methyltransferases. DOI:10.1080/15476286.2015.1008358. PMID:25626150.
- Christian T et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 7463-7473. Catalysis by the Second Class of tRNA(m1G37) Methyl Transferase Requires A Conserved Proline†. DOI:10.1021/bi0602314. PMID:16768442.
- Ahn HJ et al. (2003), EMBO J, 22, 2593-2603. Crystal structure of tRNA(m1G37)methyltransferase: insights into tRNA recognition. DOI:10.1093/emboj/cdg269. PMID:12773376.
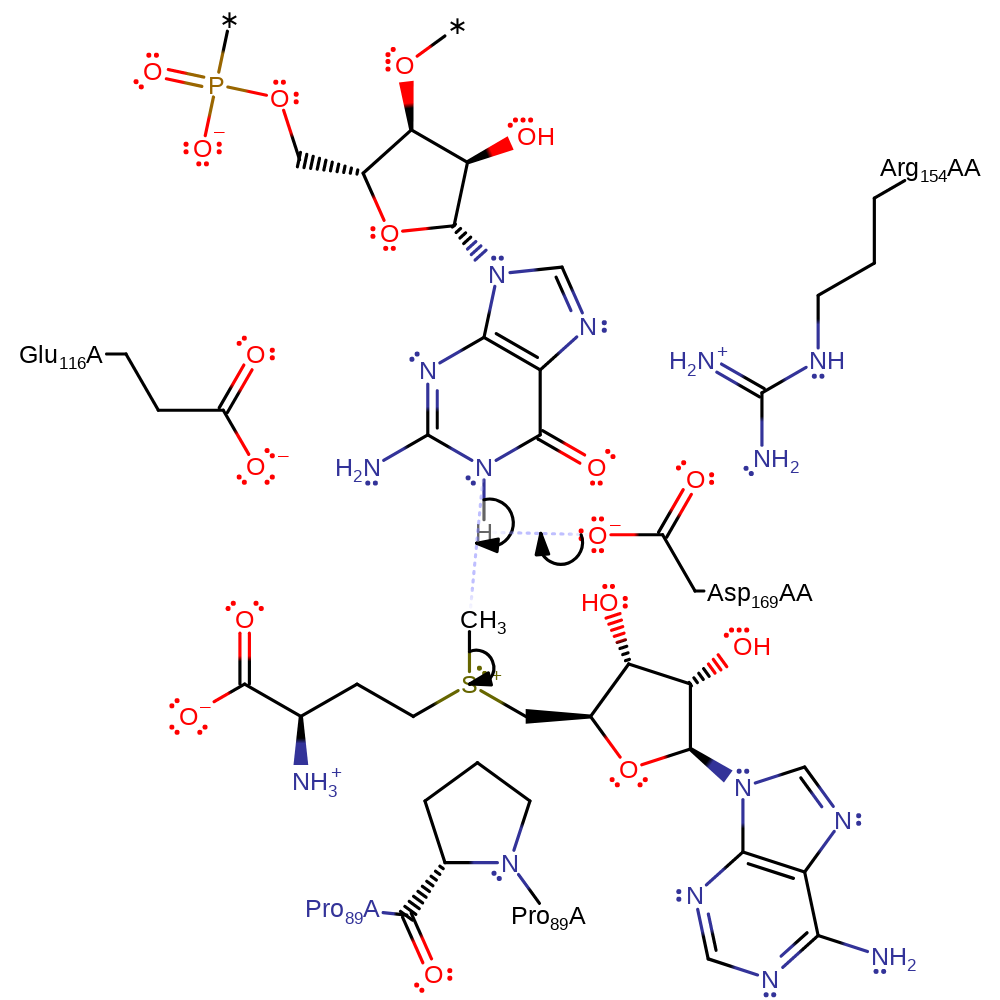
Step 1. Asp169B abstracts a proton from the N1 position of guanine, enhancing its nucleophilicity towards the methyl group of S-adenosyl methionine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu116(136)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg154(174)A(AA) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp169(189)A(AA) | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, increase nucleophilicity |
| Pro89(109)A | steric role, increase nucleophilicity |
| Glu116(136)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg154(174)A(AA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg154(174)A(AA) | activator |
| Asp169(189)A(AA) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, cofactor used, rate-determining step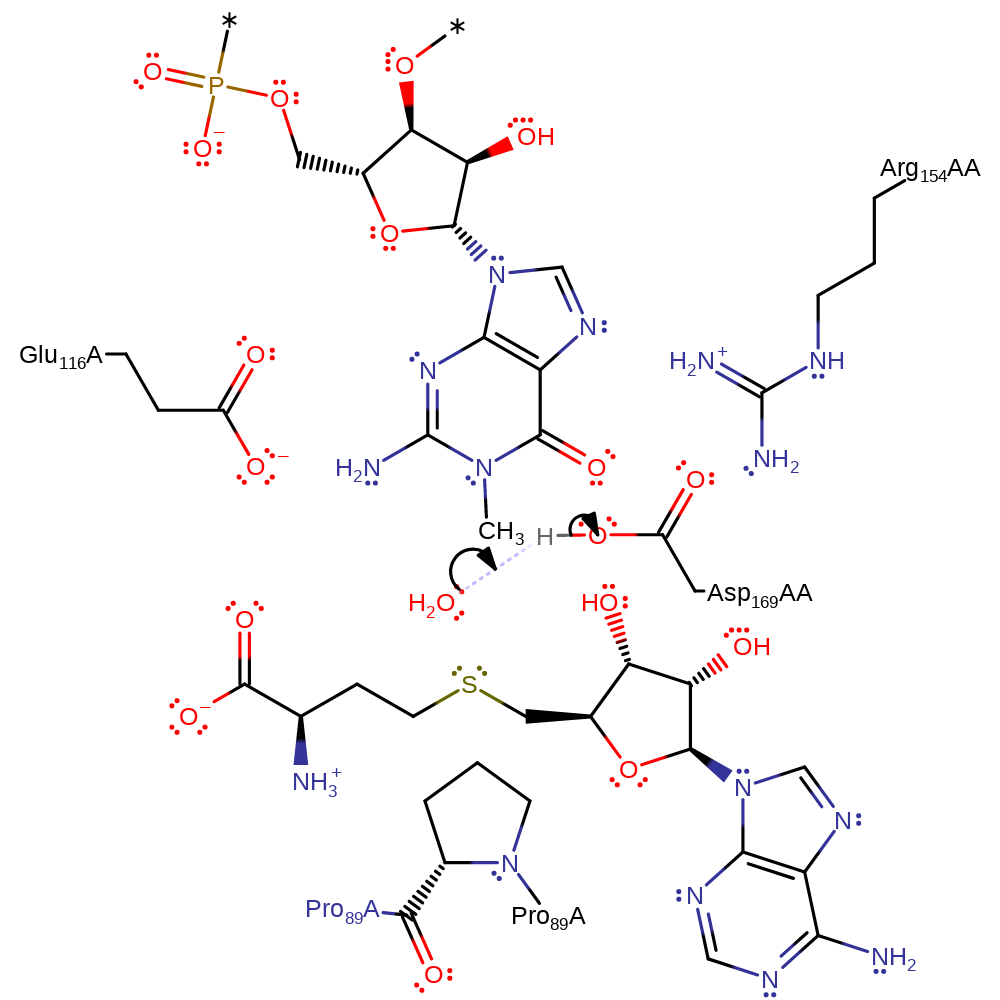
Step 2. The active site is regenerated by the deprotonation of Asp169B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp169(189)A(AA) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg154(174)A(AA) | activator |
| Asp169(189)A(AA) | proton donor |





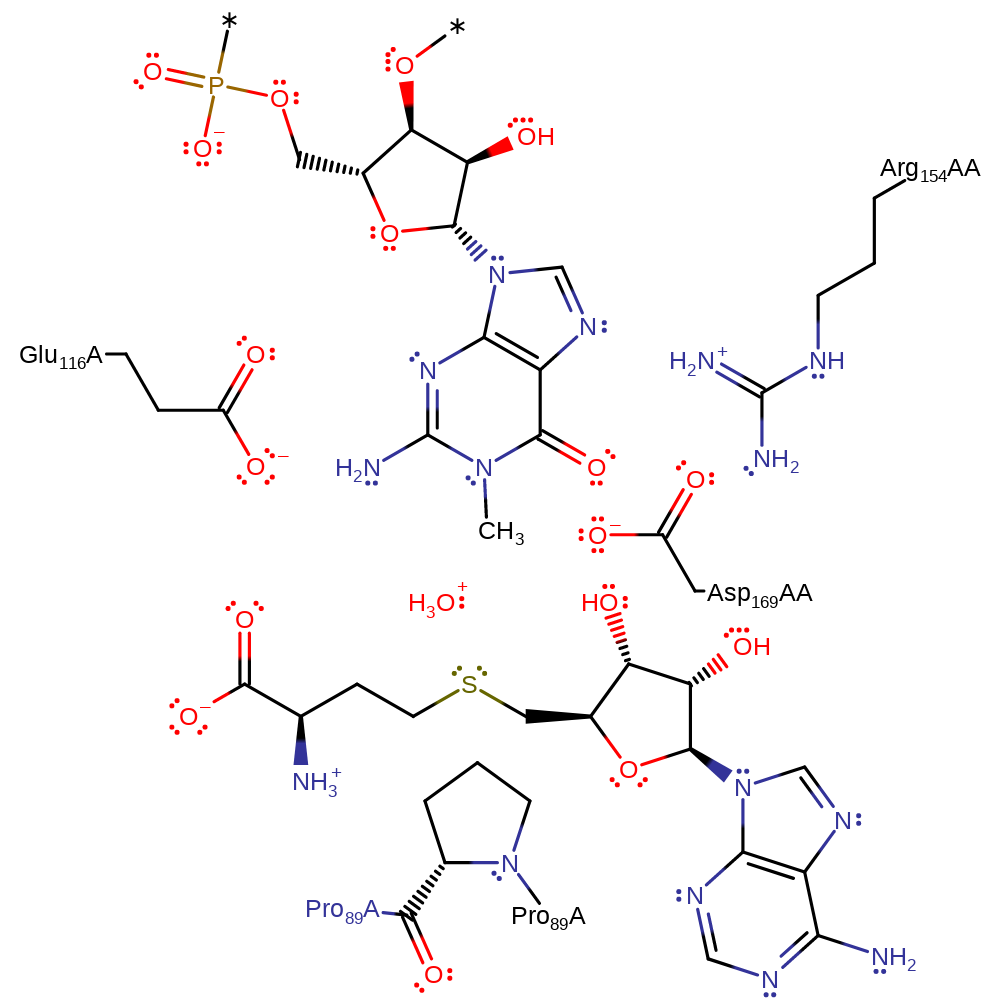 Download:
Download: