Serine racemase
Serine racemase (SRR) catalyses the PLP-dependent synthesis of D-serine from L-serine (and vice versa. SRR also has dehydratase activity towards both L-serine and D-serine, resulting in pyruvate and ammonia. It is allosterically activated by ATP, by magnesium, and possibly also by other divalent metal cations. The magnesium ion present in the crystal structure is thought to be essential for the structural integrity of the enzymes, and not directly involved in catalysis [PMID:20564571].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O59791
 (4.3.1.17, 4.3.1.18, 5.1.1.18)
(4.3.1.17, 4.3.1.18, 5.1.1.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe 972h- (Fission yeast)

- PDB
-
2zr8
- Crystal Structure of Modified Serine Racemase complexed with Serine
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1100
 (see all for 2zr8)
(see all for 2zr8)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
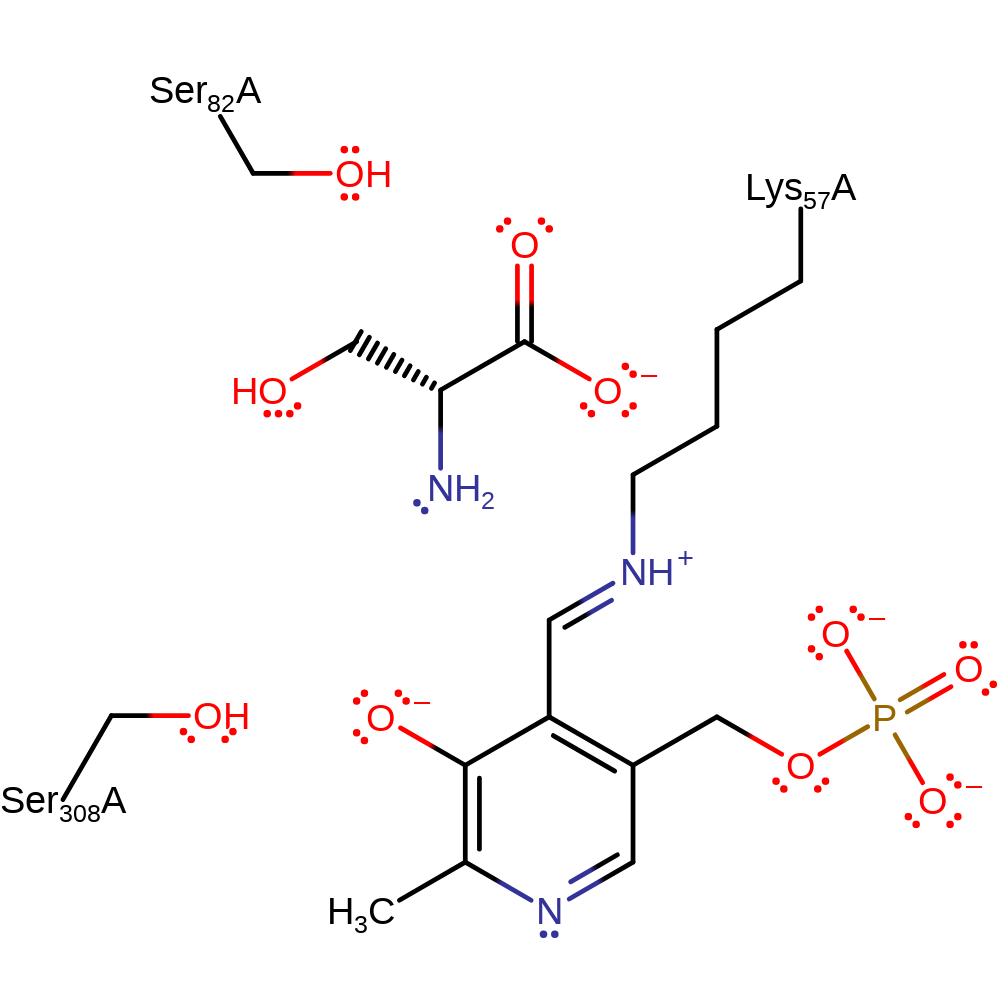
The neutral amine group of L-serine attacks the imine functionality of the pyridoxal-5-phosphate cofactor, forming a Schiff base precursor. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, generating the external aldimine, PDD-substrate complex. Lys57 acts as a general base towards the C-alpha of the covalently bound serine, forming a planar sterocentre. Ser82 returns a proton to the serine C-alpha position from the alternative face of the molecule, reversing the previous stereochemistry. The deprotonated Lys57 acts as a nucleophile towards the PDD-serine complex, forming a precursor to the regeneration of the internal aldimine. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses releasing L/D-serine, inverted at the c-alpha relative to the starting material, and the internal aldimine is regenerated.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2zr8) | ||
| Glu208, Gly212 (main-C), Asp214 | Glu208A, Gly212A (main-C), Asp214A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Ser308 | Ser308A | Acts to stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states during the course of the reaction. | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82 | Ser82A | Suggested to act as a general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Lys57 | Lys57A | Lys57 is covalently attached to the PLP cofactor in the ground state of the reaction. It is thought to act as a general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge, activator, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, schiff base formed, cofactor used, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Gogami Y et al. (2010), Chem Biodivers, 7, 1579-1590. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Rice Serine Racemase: Evidence That Glu219 and Asp225 Mediate the Effects of Mg2+ on the Activity. DOI:10.1002/cbdv.200900257. PMID:20564571.
- Nitoker N et al. (2015), Biochemistry, 54, 516-527. Understanding the reaction mechanism and intermediate stabilization in mammalian serine racemase using multiscale quantum-classical simulations. DOI:10.1021/bi500984m. PMID:25493718.
- Goto M et al. (2009), J Biol Chem, 284, 25944-25952. Crystal Structure of a Homolog of Mammalian Serine Racemase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m109.010470. PMID:19640845.
- Yamauchi T et al. (2009), J Biochem, 145, 421-424. Serine Racemase with Catalytically Active Lysinoalanyl Residue*. DOI:10.1093/jb/mvp010. PMID:19155267.
Step 1. The neutral amine group of L-serine attacks the imine functionality of the pyridoxal-5-phosphate cofactor, forming a Schiff base precursor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser308A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys57A | covalently attached, activator |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu208A | metal ligand |
| Gly212A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp214A | metal ligand |
| Lys57A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, schiff base formed, cofactor used
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, generating the external aldimine, PDD-substrate complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser308A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys57A | activator |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu208A | metal ligand |
| Gly212A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp214A | metal ligand |
| Lys57A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, schiff base formed, cofactor used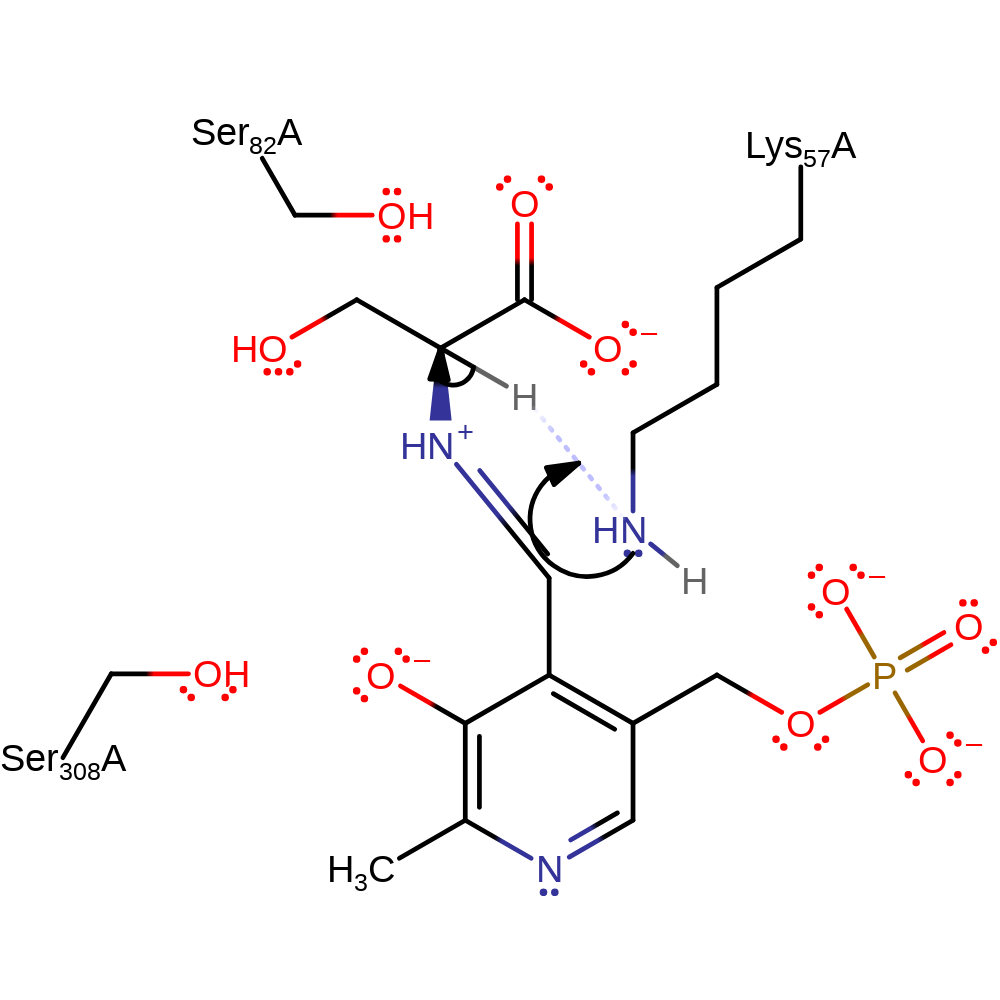
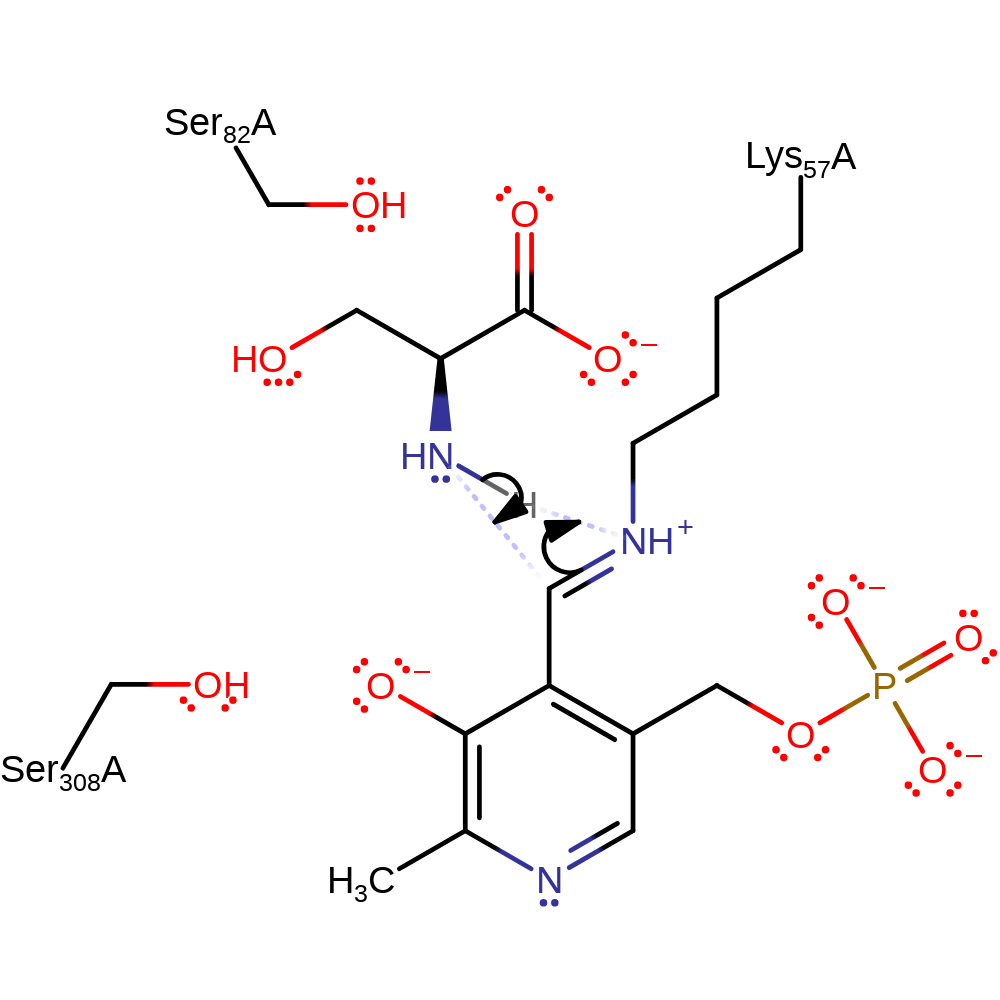
Step 3. Either Lys57 or Ser82 acts as a general base towards the C-alpha of the covalently bound serine, forming a planar sterocentre [PMID:19640845]. Lys57 shown here in analogy to other PLP-dependent enzymes.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser308A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu208A | metal ligand |
| Gly212A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp214A | metal ligand |
| Lys57A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation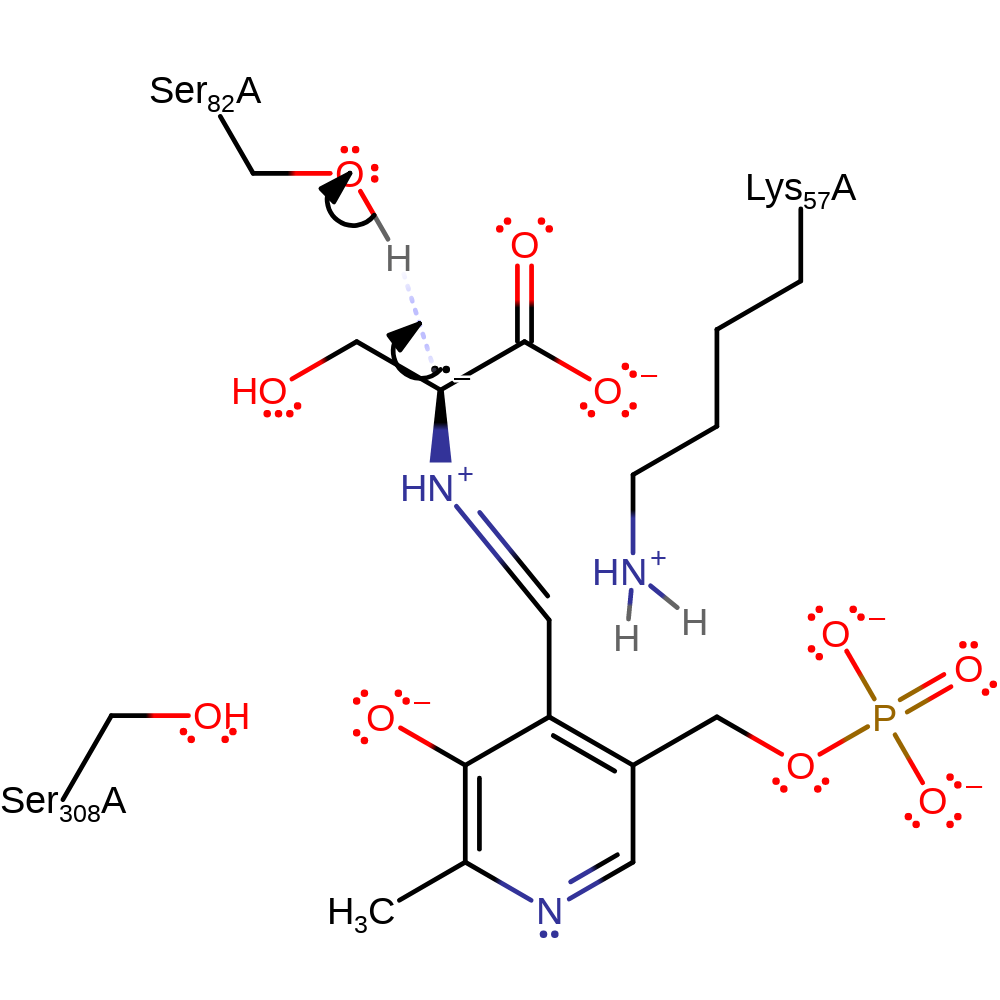
Step 4. Either Lys57 or Ser82 returns a proton to the serine C-alpha position from the alternative face of the molecule, reversing the previous stereochemistry. Ser82 shown as this reaction results in a different steroisomer to the original molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser308A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys57A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu208A | metal ligand |
| Gly212A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp214A | metal ligand |
| Ser82A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 5. Ser82 abstracts a proton from Lys57. The deprotonated Lys57 acts as a nucleophile towards the PLP-serine complex, forming a precursor to the regeneration of the internal aldimine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser308A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys57A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, covalently attached |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu208A | metal ligand |
| Gly212A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp214A | metal ligand |
| Lys57A | nucleophile, proton donor |
| Ser82A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used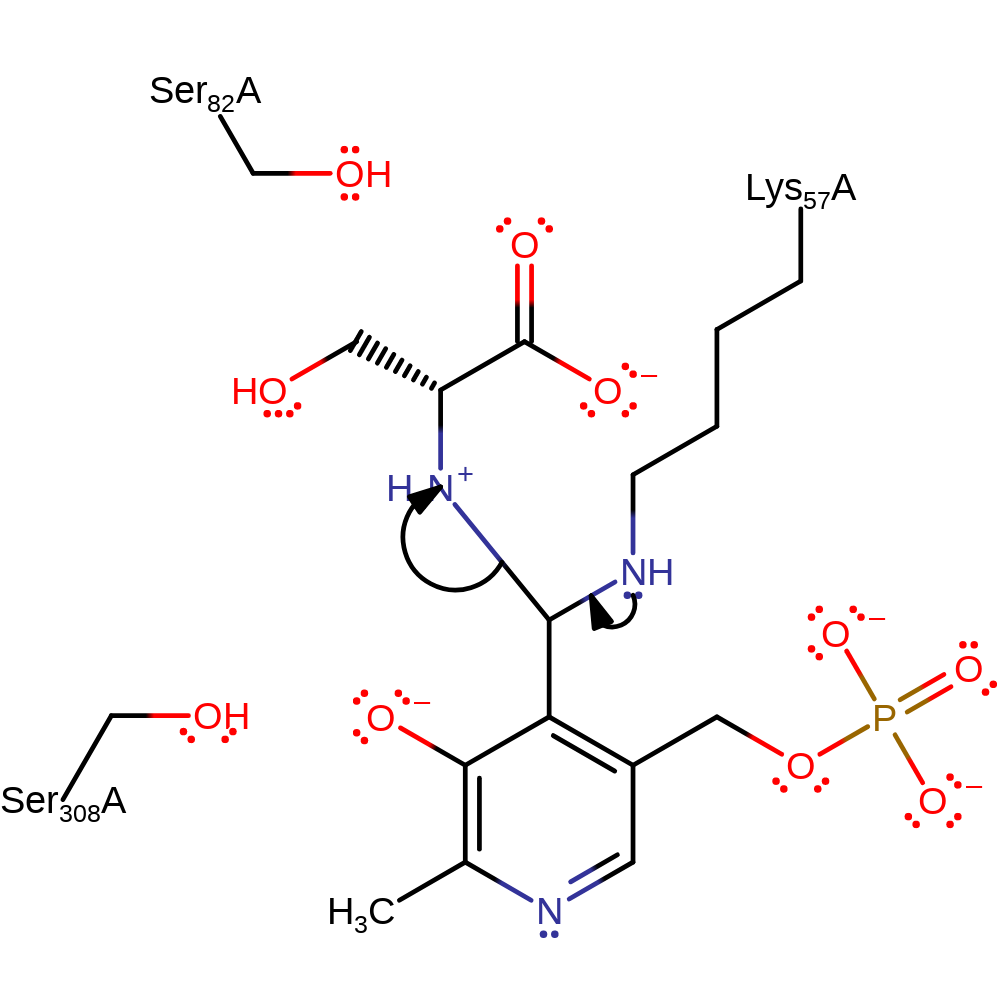
Step 6. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses releasing L/D-serine, inverted at the c-alpha relative to the starting material, and the internal aldimine is regenerated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser308A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys57A | covalently attached, activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu208A | metal ligand |
| Gly212A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp214A | metal ligand |
| Lys57A | electron pair donor |


 Download:
Download: