Xylose isomerase (actinobacterial)
Xylose isomerase catalyses the interconvertion of D-xylose and D-xylulose. It contains two divalent metal ions, preferably magnesium, located at different metal-binding sites within the active site. The enzyme catalyses the interconversion of aldose and ketose sugars with broad substrate specificity. The enzyme binds the closed form of its sugar substrate (in the case of glucose, only the alpha anomer) and catalyses ring opening to generate a form of open-chain conformation that is coordinated to one of the metal sites.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P12070
 (5.3.1.5)
(5.3.1.5)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Arthrobacter sp. NRRL B3728 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1xld
- MECHANISM FOR ALDOSE-KETOSE INTERCONVERSION BY D-XYLOSE ISOMERASE INVOLVING RING OPENING FOLLOWED BY A 1,2-HYDRIDE SHIFT
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.150
 (see all for 1xld)
(see all for 1xld)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2), Water (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.1.5)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
After the enzyme catalysed ring opening reaction (step 1), the substrate undergoes a 1,2-hydride shift which is mediated by the presence of divalent cationic metal cofactors.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xld) | ||
| Met88, Lys183 | Met87A, Lys182A | Act to stabilise the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | steric role, polar interaction |
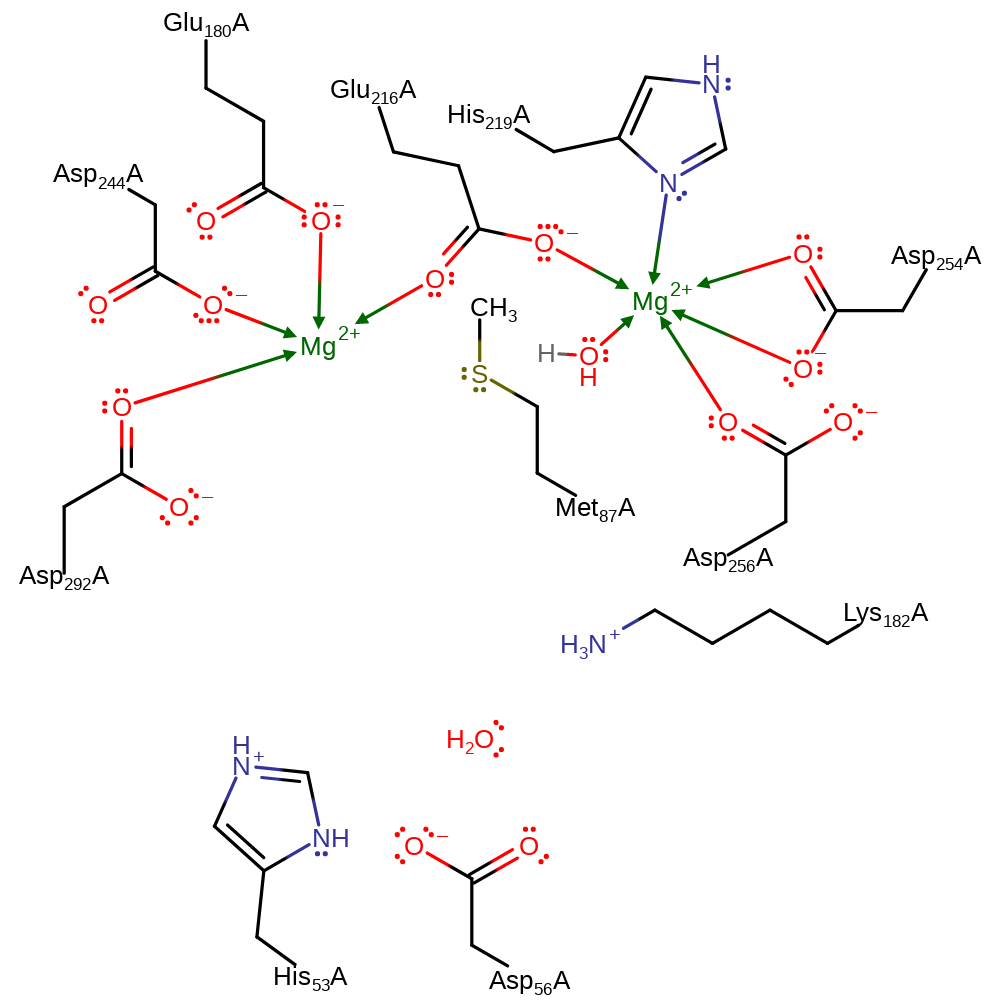
| Asp293 | Asp292A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site, also acts as a general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator |
| His54, Asp57 | His53A, Asp56A | Acts as a general acid/base during the course of the ring opening and closing reactions. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator |
| Glu217 | Glu216A | Acts as a bridging ligand between the two magnesium sites. | metal ligand |
| Glu181, Asp245 | Glu180A, Asp244A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| His220, Asp255, Asp257 | His219A, Asp254A, Asp256A | Forms part of the magnesium 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, proton transfer, decyclisation, proton relay, intermediate formation, hydride transfer, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Kovalevsky AY et al. (2010), Structure, 18, 688-699. Metal Ion Roles and the Movement of Hydrogen during Reaction Catalyzed by D-Xylose Isomerase: A Joint X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction Study. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2010.03.011. PMID:20541506.
- Munshi P et al. (2014), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 70, 414-420. Neutron structure of the cyclic glucose-bound xylose isomerase E186Q mutant. DOI:10.1107/s1399004713029684. PMID:24531475.
- Langan P et al. (2014), Structure, 22, 1287-1300. L-Arabinose Binding, Isomerization, and Epimerization by D-Xylose Isomerase: X-Ray/Neutron Crystallographic and Molecular Simulation Study. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2014.07.002. PMID:25132082.
- Toteva MM et al. (2011), Biochemistry, 50, 10170-10181. Binding Energy and Catalysis byd-Xylose Isomerase: Kinetic, Product, and X-ray Crystallographic Analysis of Enzyme-Catalyzed Isomerization of (R)-Glyceraldehyde. DOI:10.1021/bi201378c. PMID:21995300.
- Kovalevsky AY et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 7595-7597. Hydrogen Location in Stages of an Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction: Time-of-Flight Neutron Structure ofd-Xylose Isomerase with Boundd-Xylulose†‡. DOI:10.1021/bi8005434. PMID:18578508.
- Fenn TD et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 6464-6474. Xylose Isomerase in Substrate and Inhibitor Michaelis States: Atomic Resolution Studies of a Metal-Mediated Hydride Shift†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi049812o. PMID:15157080.
- Hu H et al. (1997), Proteins, 27, 545-555. The reaction pathway of the isomerization of d-xylose catalyzed by the enzyme d-xylose isomerase: A theoretical study. DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(199704)27:4<545::aid-prot7>3.0.co;2-9.
- Allen KN et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 1488-1494. Role of the divalent metal ion in sugar binding, ring opening, and isomerization by D-xylose isomerase: replacement of a catalytic metal by an amino acid. PMID:7906142.
- Whitlow M et al. (1991), Proteins, 9, 153-173. A metal-mediated hydride shift mechanism for xylose isomerase based on the 1.6 ÅStreptomycs rubiginosus structure with xylitol andD-xylose. DOI:10.1002/prot.340090302. PMID:2006134.
- Collyer CA et al. (1990), J Mol Biol, 212, 211-235. Mechanism for aldose-ketose interconversion by d-xylose isomerase involving ring opening followed by a 1,2-hydride shift. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(90)90316-e. PMID:2319597.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp56A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Met87A | steric role, polar interaction |
| His53A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp292A | attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp56A | proton acceptor |
| His53A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, proton transfer, decyclisation, proton relay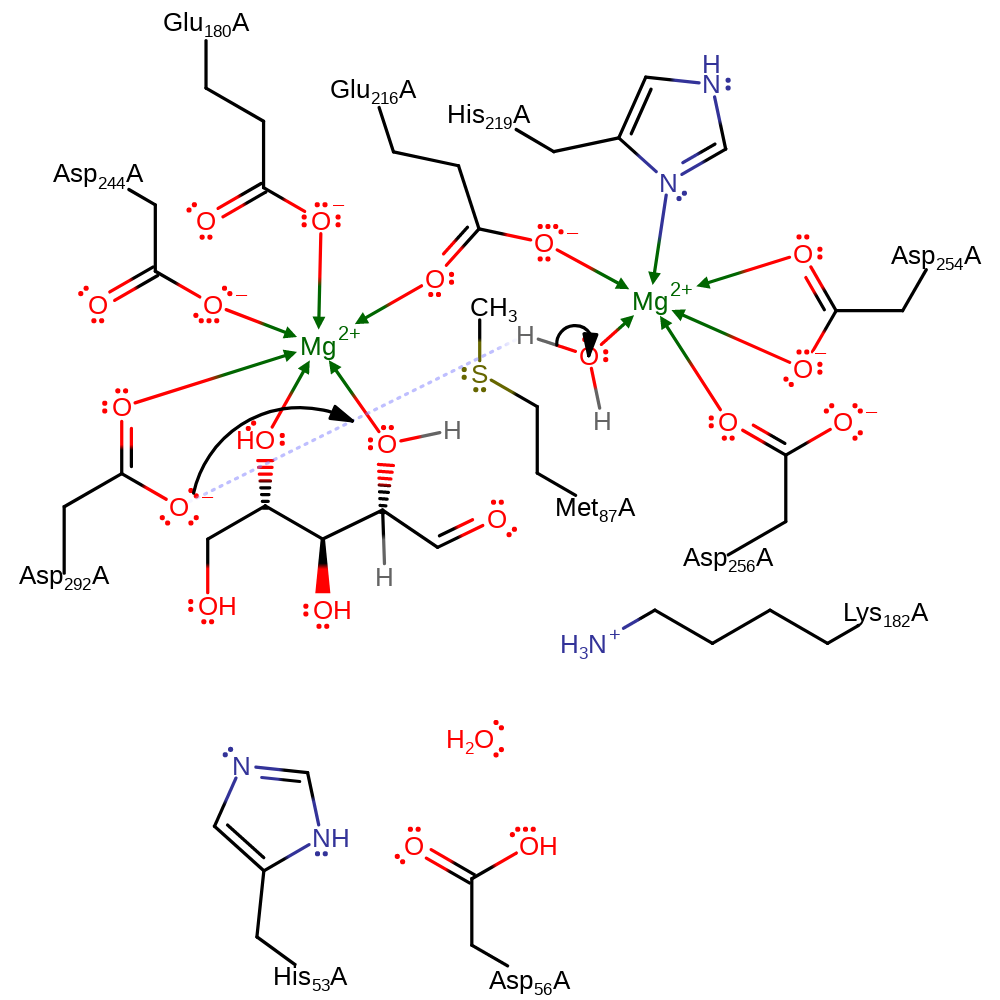
Step 2. Asp292A deprotonates the water coordinated to the second Mg cofactor (MG399A), forming a hydroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp56A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation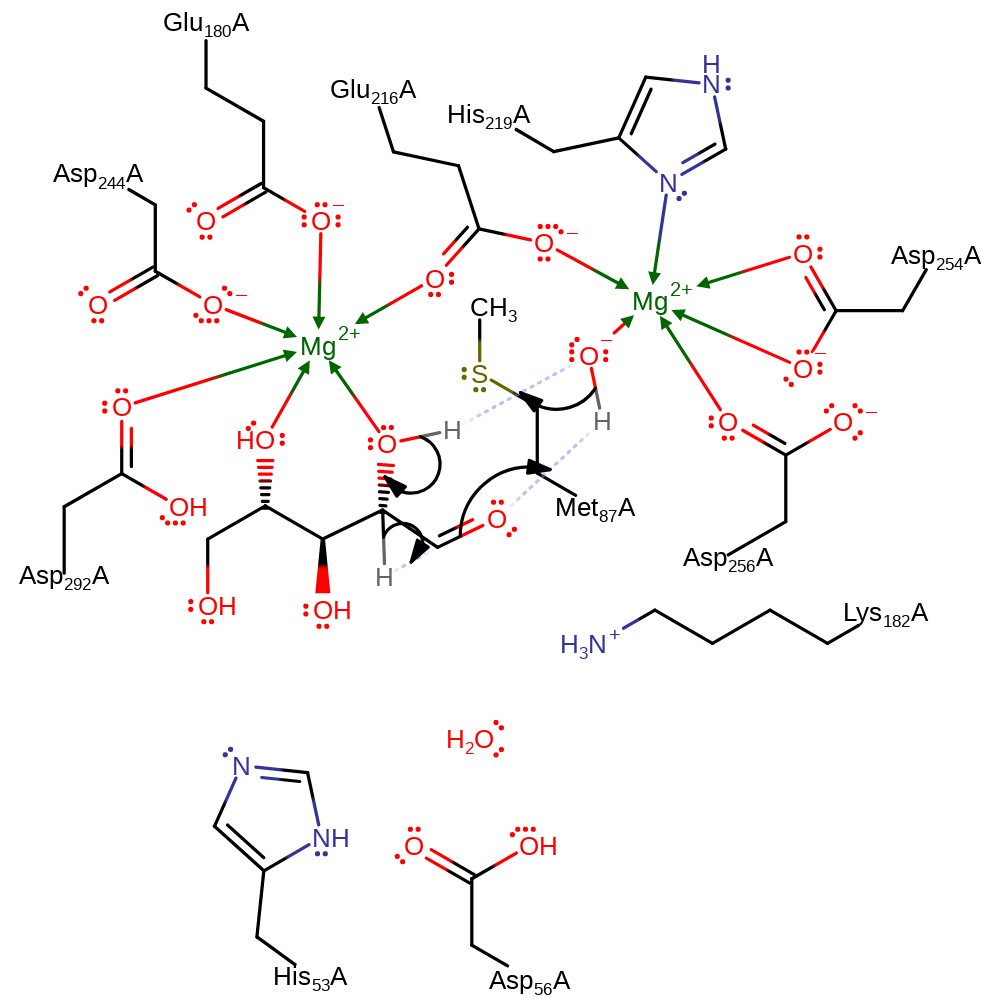
Step 3. An intramolecular 1,2 hydride transfer mechanism occurs, involving a hydroxide anion base and a divalent, cationic metal cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp56A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, proton transfer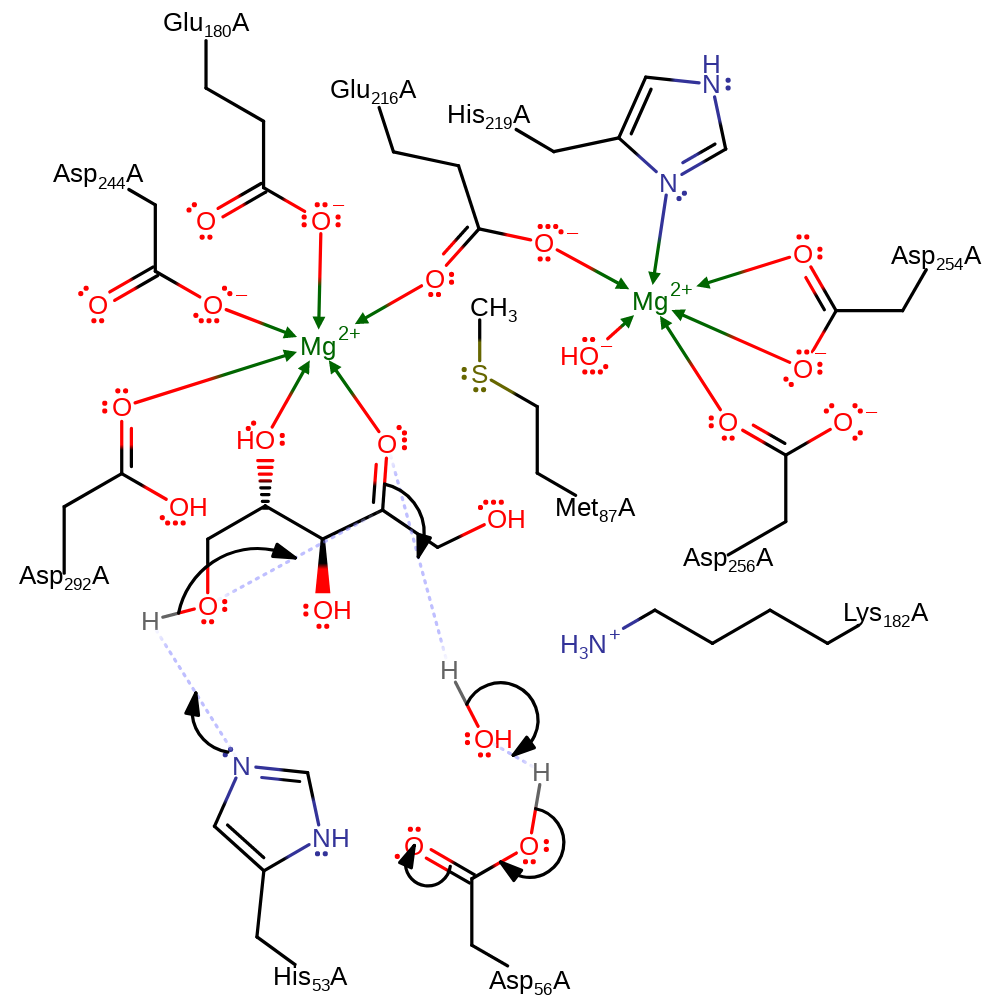
Step 4. The sugar now undergoes catalysed ring closure by the reverse mechanism of ring opening.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp56A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp56A | proton donor |
| His53A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition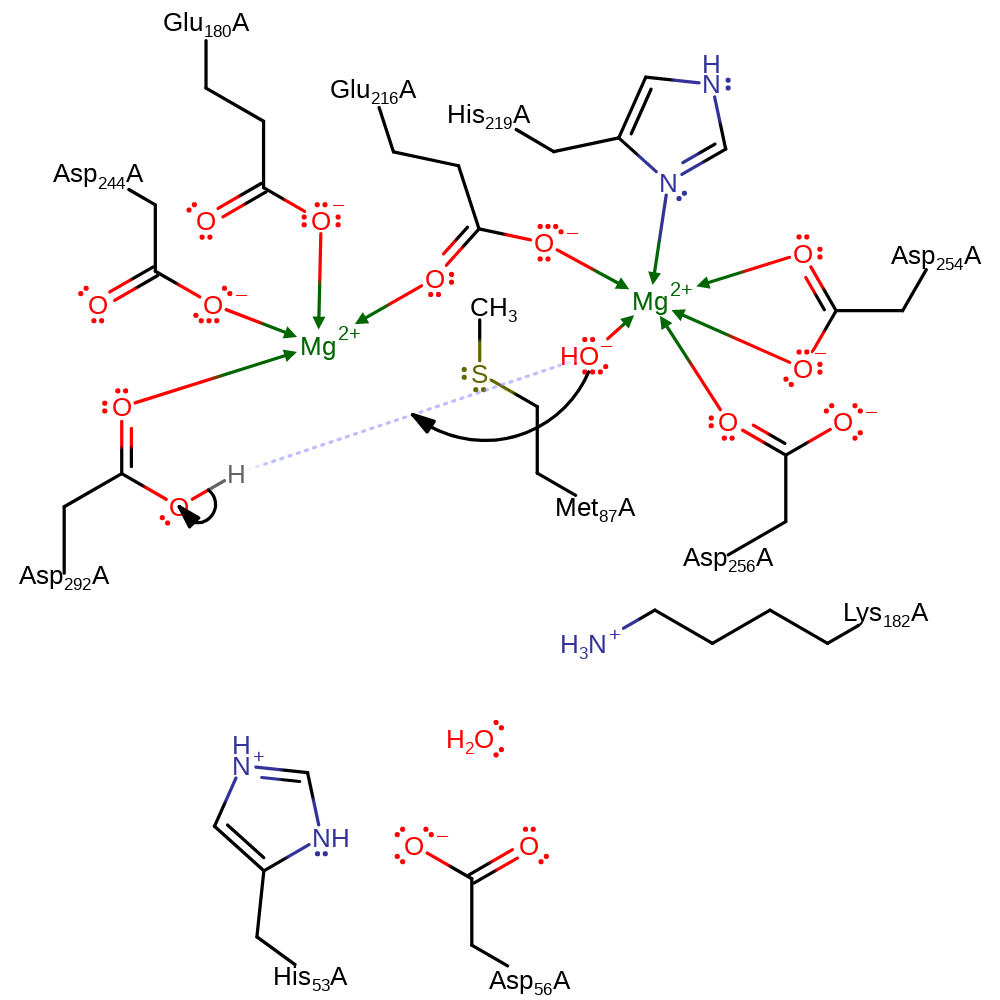
Step 5. The active site is regenerated by reprotonation of the hydroxide ligand to form water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp56A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
After ring opening (step 1) Asp292 abstracts the proton from a carbon atom, causing a bond rearrangement to form the ene-diol intermediate. This collapses, to form the final (linear) product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xld) | ||
| Met88 | Met87A | Acts to stabilise the reactive intermediate. | steric role, polar interaction |
| Asp293 | Asp292A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site, also acts as a general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys183, His54, Asp57 | Lys182A, His53A, Asp56A | Act as general acid/bases during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Glu217 | Glu216A | Acts as a bridging ligand between the two magnesium sites. | metal ligand |
| Glu181, Asp245 | Glu180A, Asp244A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| His220, Asp255, Asp257 | His219A, Asp254A, Asp256A | Forms part of the magnesium 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, proton transfer, decyclisation, proton relay, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Rose IA (1981), Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 293, 131-143. Chemistry of Proton Abstraction by Glycolytic Enzymes (Aldolase, Isomerases and Pyruvate Kinase). DOI:10.1098/rstb.1981.0067.
- Collyer CA et al. (1990), J Mol Biol, 212, 211-235. Mechanism for aldose-ketose interconversion by d-xylose isomerase involving ring opening followed by a 1,2-hydride shift. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(90)90316-e. PMID:2319597.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp56A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Met87A | steric role, polar interaction |
| His53A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp292A | attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Asp56A | proton acceptor |
| His53A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, proton transfer, decyclisation, proton relay
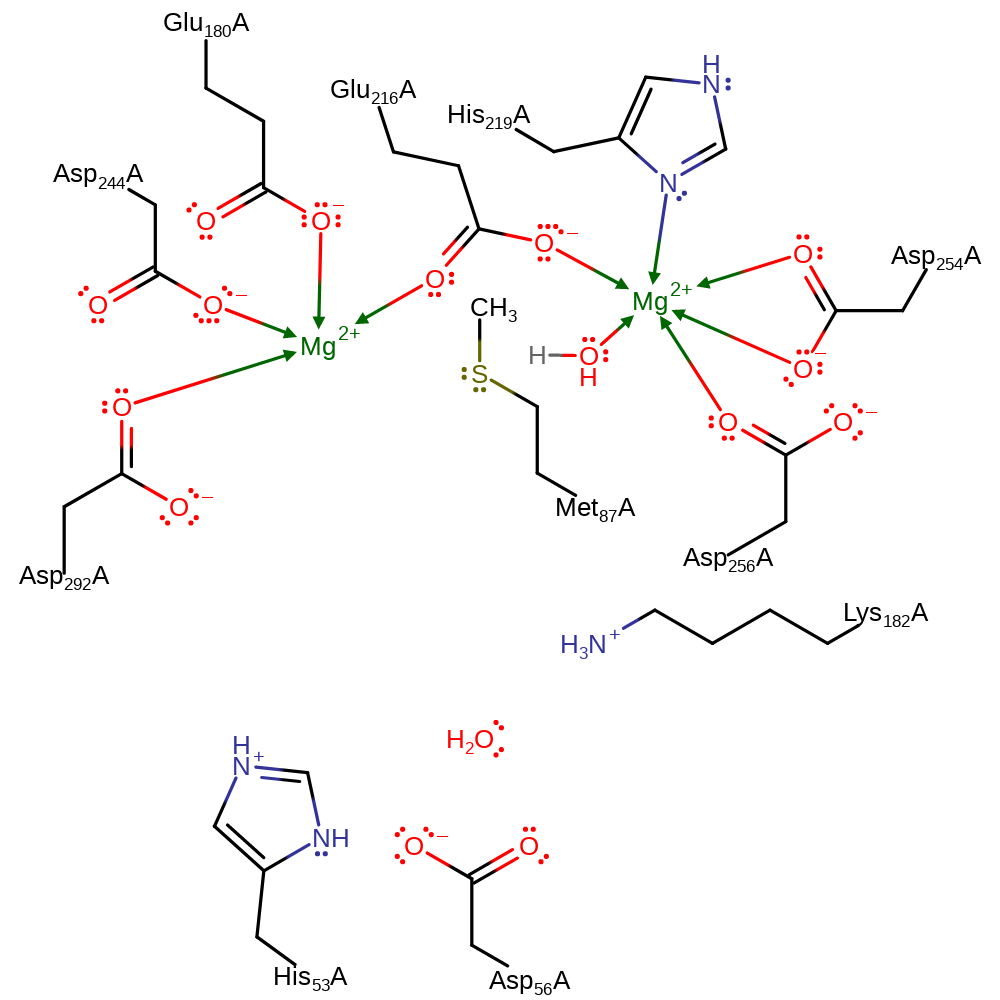
Step 2. Asp292A deprotonates the water coordinated to the second Mg cofactor (MG399A), forming a hydroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp56A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | proton acceptor |
| Lys182A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation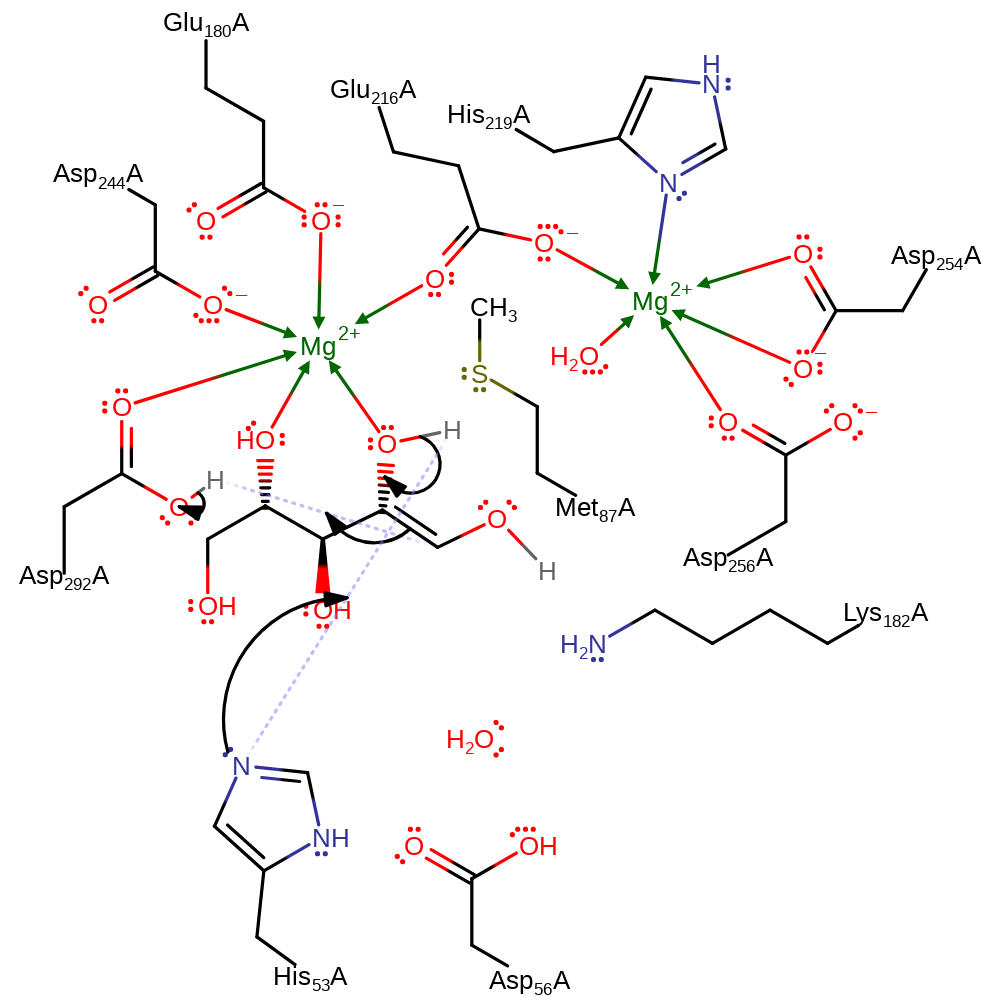
Step 3. His53 deprotonataes the substrate, causing another double bond rearrangement, resulting in the deprotonation of the Asp292.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| His53A | proton acceptor |
| Asp292A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
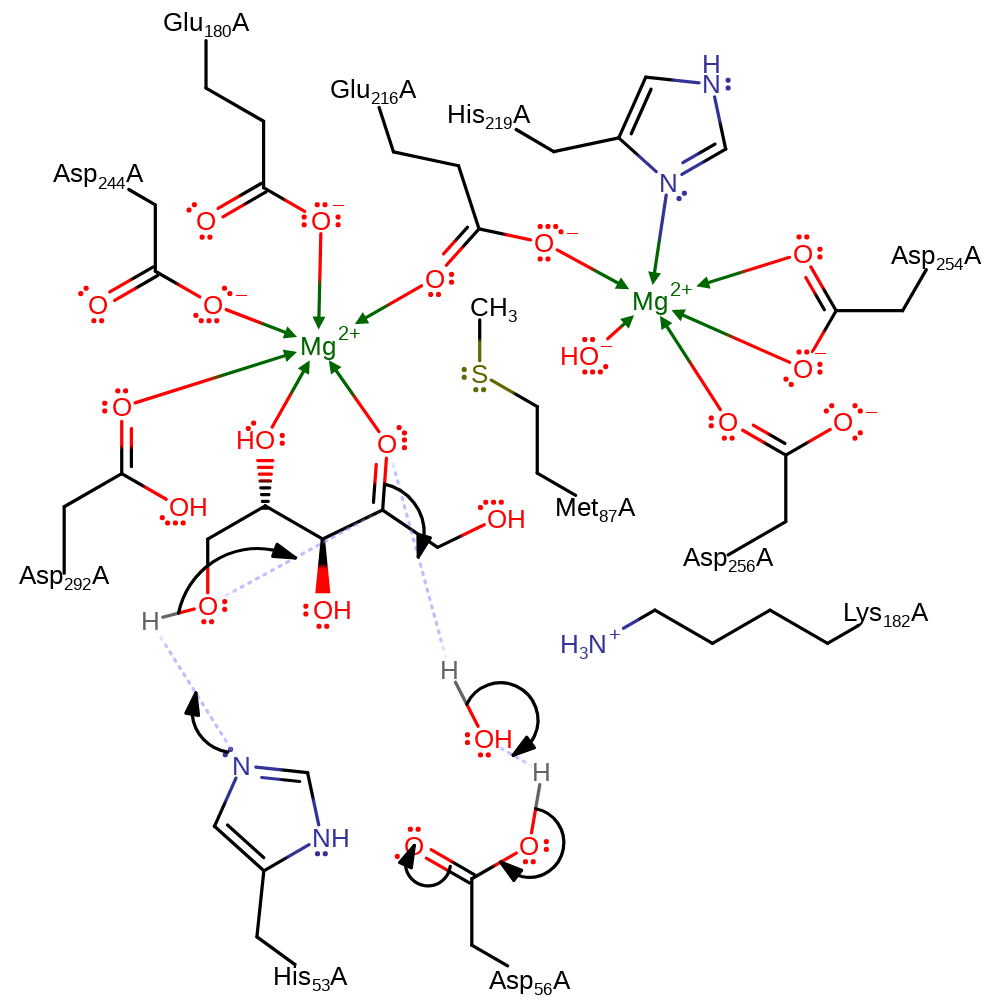
Step 4. The sugar now undergoes catalysed ring closure by the reverse mechanism of ring opening.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp56A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | attractive charge-charge interaction |
| His53A | proton acceptor |
| Asp56A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition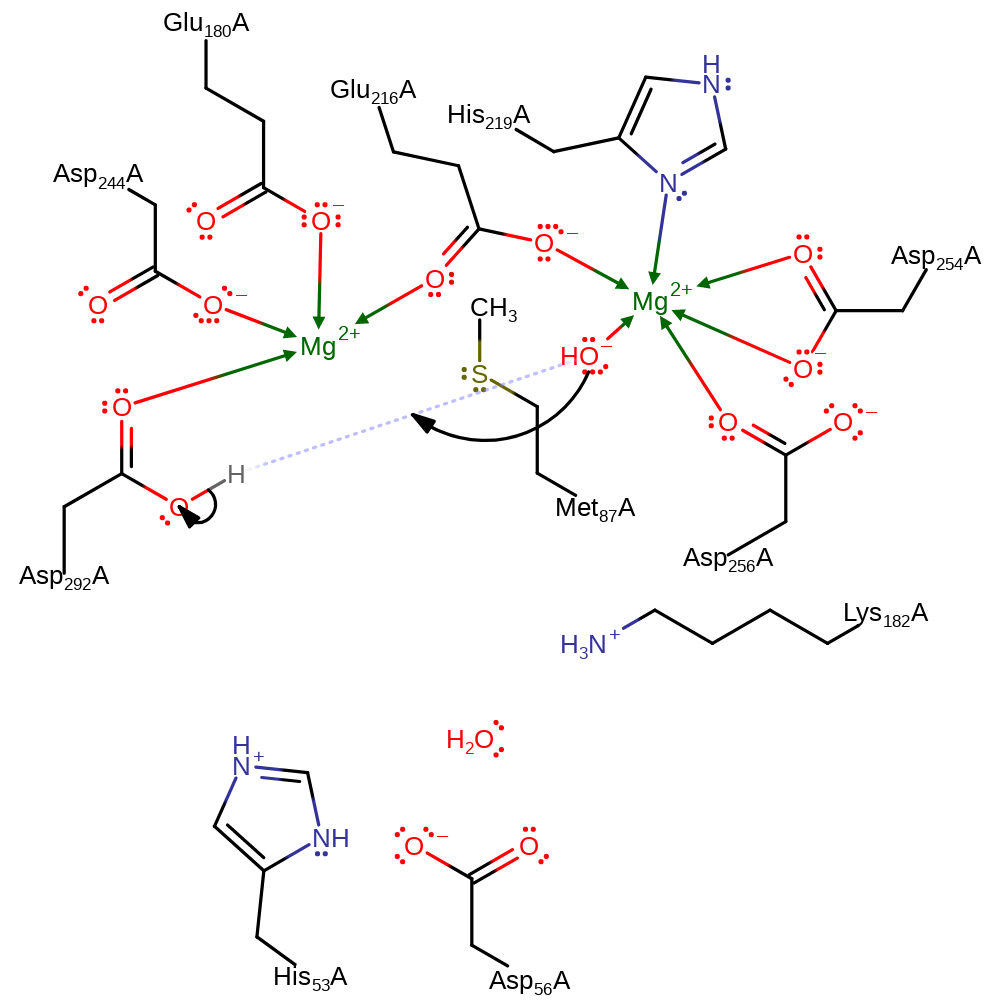
Step 5. The active site is regenerated by reprotonation of the hydroxide ligand to form water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp292A | metal ligand |
| Asp256A | metal ligand |
| Asp254A | metal ligand |
| His219A | metal ligand |
| Glu216A | metal ligand |
| Asp244A | metal ligand |
| Glu180A | metal ligand |
| Lys182A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp56A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His53A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp292A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp292A | proton donor |


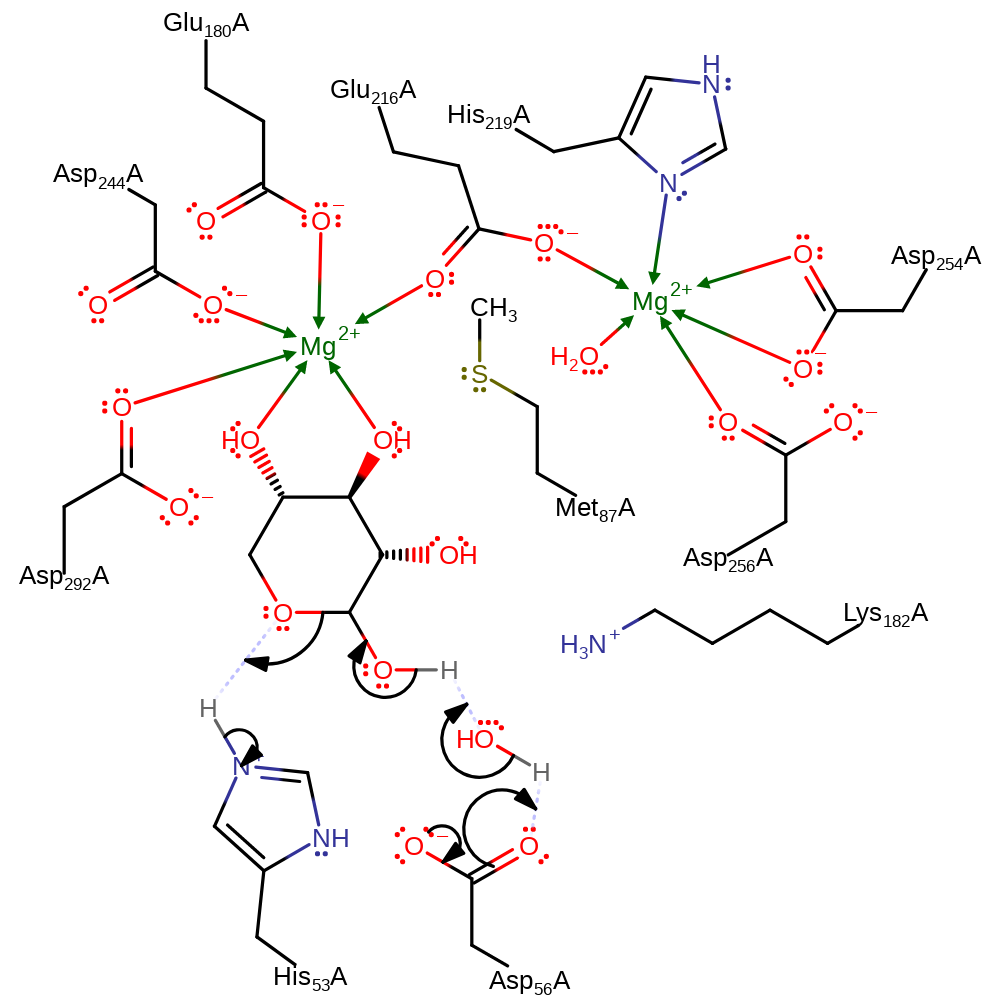
 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: