Aminodeoxychorismate lyase (class IV)
4-Amino-4-Deoxychorismate Lyase (ADCL), sourced from Escherichia coli is a member of the fold-type IV of PLP dependent enzymes. It converts 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate (ADC) to p-aminobenzoate and pyruvate during the process of tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis. P-aminobenzoate is a precursor of folic acid. ADCL is a homodimer and shows the re-face specific hydrogen transfer typical of a member of the fold-type IV family.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P28305
 (4.1.3.38)
(4.1.3.38)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1et0
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF AMINODEOXYCHORISMATE LYASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.10.10
 3.30.470.10
3.30.470.10  (see all for 1et0)
(see all for 1et0)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.3.38)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Lys159 forms a Schiff base linkage to PLP, attaching it to the active site. The amino group of ADC nucleophilically attacks the C4' of PLP. This forms a PLP-ADC Schiff base linkage and releases Lys159. Lys159 forms a hydrogen bond with Thr38, decreasing the free energy level of the external aldimine form of the enzyme.The hydroxyl of Thr38 makes a van der Waals contact with the methylene group of ADC. The alpha-carbon of the substrate is activated by the protonated Schiff base and the protonated pyridine ring. Lys159 acts as a general base and removes the alpha-proton of the alpha-carbon. This results in a quinonoid intermediate. The quinonoid intermediate is stabilised by the delocalisation of the cofactor-substrate Pi-system and the hydrogen bond between N1-H of the cofactor ring and Glu193. Thr38 acts as a general acid and protonates the olefin moiety, causing electrons to migrate towards the substrate from the cofactor. This results in release of pyruvate with aromatization of the six-membered ring of the substrate. Lys 159 nucleophilically attacks the C4' of PLP. This forms a PLP-Lys 159 Schiff base linkage and releases the substrate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1et0) | ||
| Lys140 | Lys159(140)A | Lys 159 forms a Schiff base linkage to PLP, attaching it to the active site. It also acts as a general base and removes the alpha-proton of the alpha-carbon. Lys 159 releases the substrate from the PLP-ADC Schiff base linkage at the end of the reaction. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Glu173 | Glu193(173)A | Glu 193 hydrogen bonds to the N1-H of the cofactor ring, helping to stabilise the quinonoid intermediate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr28 | Thr38(28)A | Thr 38 acts as a general acid and protonates the olefin moiety. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, proton relay, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Nakai T et al. (2000), J Biochem, 128, 29-38. Three-Dimensional Structure of 4-Amino-4-Deoxychorismate Lyase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022727. PMID:10876155.
- Dai YN et al. (2013), J Biol Chem, 288, 22985-22992. Structure and catalytic mechanism of yeast 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate lyase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.480335. PMID:23818518.

Step 1. The amine of the substrate attacks the PLP cofactor in a nucleophilic addition and the bound Lys159 deprotonates the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used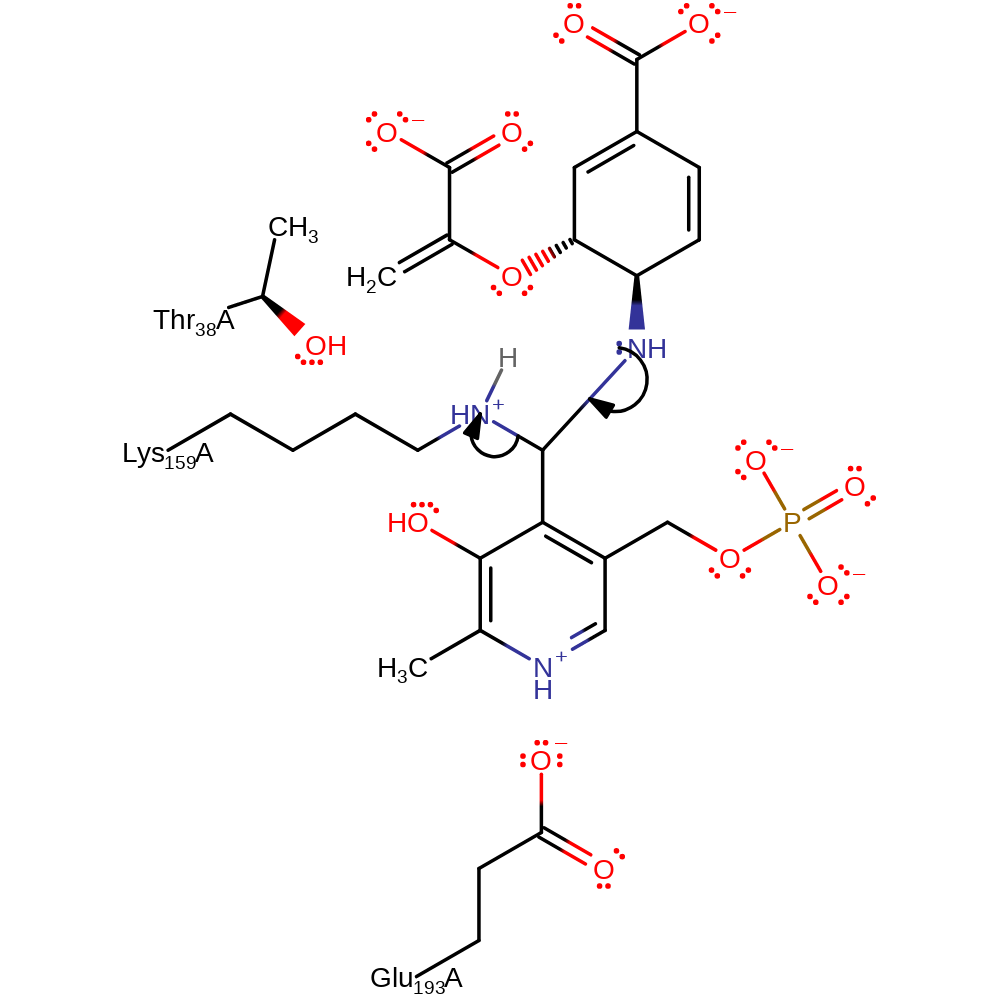
Step 2. The secondary amine initiates an elimination of the covalently bound lysine, forming free PLP and lysine in a neutral state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 3. Lys159 deprotonates the CH adjacent to the bound amine, resulting in double bond rearrangement with the PLP cofactor acting as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 4. The PLP feeds the electrons back, resulting in the cleavage of the C-O attached to the aromatic ring and the C=C of the released substrate deprotonating Lys159.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr38(28)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | proton donor |
| Thr38(28)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 5. The amine of Lys159 attacks the PLP in a nucleophilic addition reaction, the secondary amine of the attached substrate reprotonates from the bound Lys159.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation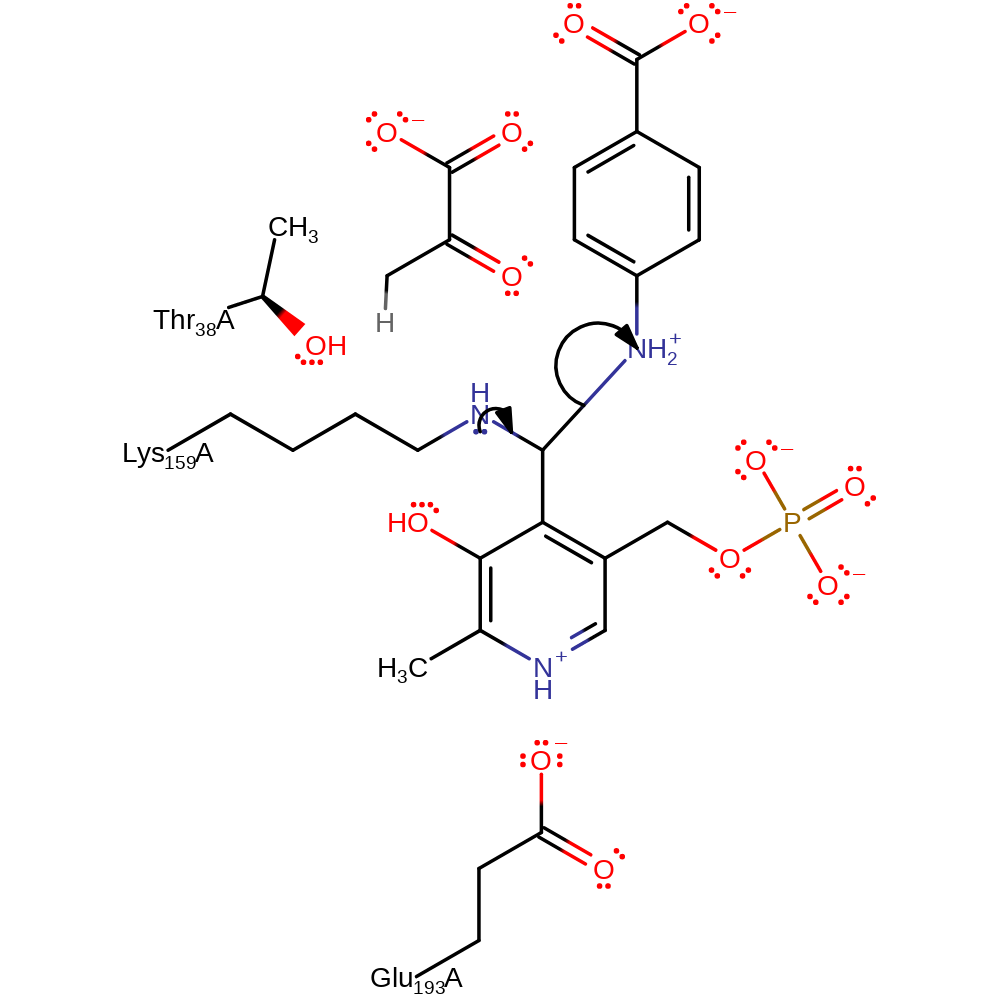
Step 6. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound product, resulting in 4-aminobenzoate and the regenerated PLP cofactor
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
This alternative mechanism follows the same path as the other proposal other than pyruvate being eliminated intramolecularly. However the majority of evidence suggests the other mechanism is correct.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1et0) |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intramolecular elimination, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Culbertson JE et al. (2015), Biochemistry, 54, 2372-2384. Conversion of aminodeoxychorismate synthase into anthranilate synthase with Janus mutations: mechanism of pyruvate elimination catalyzed by chorismate enzymes. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00013. PMID:25710100.

Step 1. The amine of the substrate attacks the PLP cofactor in a nucleophilic addition and the bound Lys159 deprotonates the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used
Step 2. The secondary amine initiates an elimination of the covalently bound lysine, forming free PLP and lysine in a neutral state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage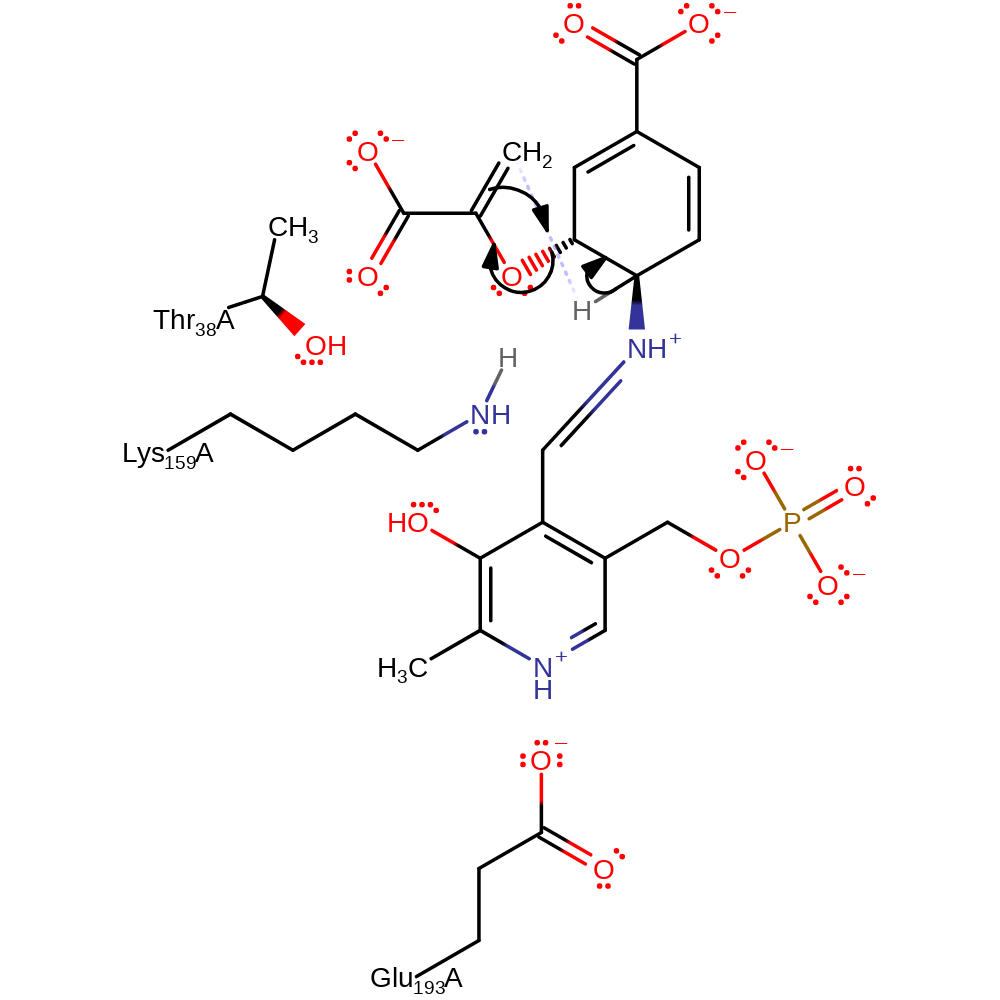
Step 3. Pyruvate is eliminated intramolecularly, generating the aromatic ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu193(173)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, overall product formed
Step 4. The amine of Lys159 attacks the PLP in a nucleophilic addition reaction, the secondary amine of the attached substrate reprotonates from the bound Lys159.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 5. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound product, resulting in 4-aminobenzoate and the regenerated PLP cofactor
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr38(28)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys159(140)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu193(173)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys159(140)A | electron pair donor |




 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: