Glutamate synthase (NADPH)
Binds FMN, FAD, 2 [4Fe-4S] clusters and 1 [3Fe-4S] cluster. The protein is composed of two subunits, alpha and beta. The alpha subunit is composed of two domains, one hydrolysing L-glutamine to ammonia and L-glutamate, the other combining the produced ammonia with 2-oxoglutarate to produce a second molecule of L-glutamate (cf. EC 1.4.1.4, glutamate dehydrogenase [NADP+]). The ammonia is channelled through a 31 Å channel in the active protein. This entry represents the alpha subunit reaction.
Glutamine hydrolysis is absent (or negligible) in the absence of the other substrates. The enzyme also catalyses the oxidation of NADPH, the ammonia-dependent synthesis of glutamate from 2-oxoglutarate and ammonia and the oxidation of L-glutamate in the presence of iodonitrotetrazolium salts, the latter two of which only occur at high pH. There is still much to be determined with respect to the mechanism of this enzyme [PMID:18421771] as well as how the cross-control of the synthase and glutaminase activities occurs with such precision. This enzyme utilises three iron-sulfur clusters (two Fe4S4 and one Fe3S4) as well as FMN and FAD as cofactors.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q05755
 (1.4.1.13)
(1.4.1.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Azospirillum brasilense (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ea0
- Alpha subunit of A. brasilense glutamate synthase
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.20.10
 3.20.20.70
3.20.20.70  (see all for 1ea0)
(see all for 1ea0)
- Cofactors
- Fmnh2(2-) (1), Fadh2(2-) (1), Tri-mu-sulfido-mu3-sulfido-triiron(0) (1), Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.4.1.13)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
NADP reduces the FAD cofactor. A single electron is transferred from FAD, via the iron-sulfur clusters and Met479 to the FMN cofactor. A second single electron is transferred from FAD, via the iron-sulfur clusters and Met479 to the FMN cofactor. The N-terminus of Cys1 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the thiol group of Cys1, initiating a nucleophilic attack on the amide carbon in an addition reaction. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves ammonia from the bound L-glutamine substrate. Ammonia deprotonates water, which deprotonates the N-terminus of Cys1. The N-terminus of Cys1 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the covalently bound intermediate in an addition reaction. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the C-S bond, the thiolate of Cys1 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the N-terminus of Cys1. Ammonia initiates a nucleophilic attack on the C2 of 2-oxoglutarate in an addition reaction. Water is produced through an intramolecular elimination forming the 2-iminoglutarate intermediate. FMN donates a hydride to the 2-iminoglutarate intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ea0) | ||
| Cys37 (N-term) | Cys1A (N-term) | Acts as a general acid/base, activating its own side chain via a water relay. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu922 | Glu886A | It has been suggested that Glu886 acts as a general acid/base in the final protonation step of the reaction. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gly268 (main-N), Asn267 | Gly232A (main-N), Asn231A | Forms the oxyanion hole that stabilises the reactive intermediates and transition states in the glutaminase domain. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys37 | Cys1A | Activated by the N-terminus of the protein, this acts as a catalytic nucleophile in the glutaminase domain of the protein. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, nucleophile, proton donor |
| Met515 | Met479A | Forms part of the electron relay chain that transfers single electrons from the FAD to the FMN cofactor. | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Lys973 | Lys937A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates in the synthase domain. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, redox reaction, proton transfer, electron relay, native state of cofactor regenerated, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, deamination, intermediate collapse, intramolecular elimination, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Vanoni MA et al. (2008), IUBMB Life, 60, 287-300. Structure–function studies of glutamate synthases: A class of self-regulated iron-sulfur flavoenzymes essential for nitrogen assimilation. DOI:10.1002/iub.52. PMID:18421771.
- Vanoni MA et al. (2005), Arch Biochem Biophys, 433, 193-211. Structure–function studies on the iron–sulfur flavoenzyme glutamate synthase: an unexpectedly complex self-regulated enzyme. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.033. PMID:15581577.
- Vanoni MA et al. (2005), Photosynth Res, 83, 219-238. Structure-function studies on the complex iron-sulfur flavoprotein glutamate synthase: the key enzyme of ammonia assimilation. DOI:10.1007/s11120-004-2438-z. PMID:16143853.
- van den Heuvel RH et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 330, 113-128. The Active Conformation of Glutamate Synthase and its Binding to Ferredoxin. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00522-9. PMID:12818206.
- Ravasio S et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 5533-5541. Determination of the Midpoint Potential of the FAD and FMN Flavin Cofactors and of the 3Fe−4S Cluster of Glutamate Synthase†. DOI:10.1021/bi0100889. PMID:11331018.
- Binda C et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 1299-1308. Cross-Talk and Ammonia Channeling between Active Centers in the Unexpected Domain Arrangement of Glutamate Synthase. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00540-2. PMID:11188694.
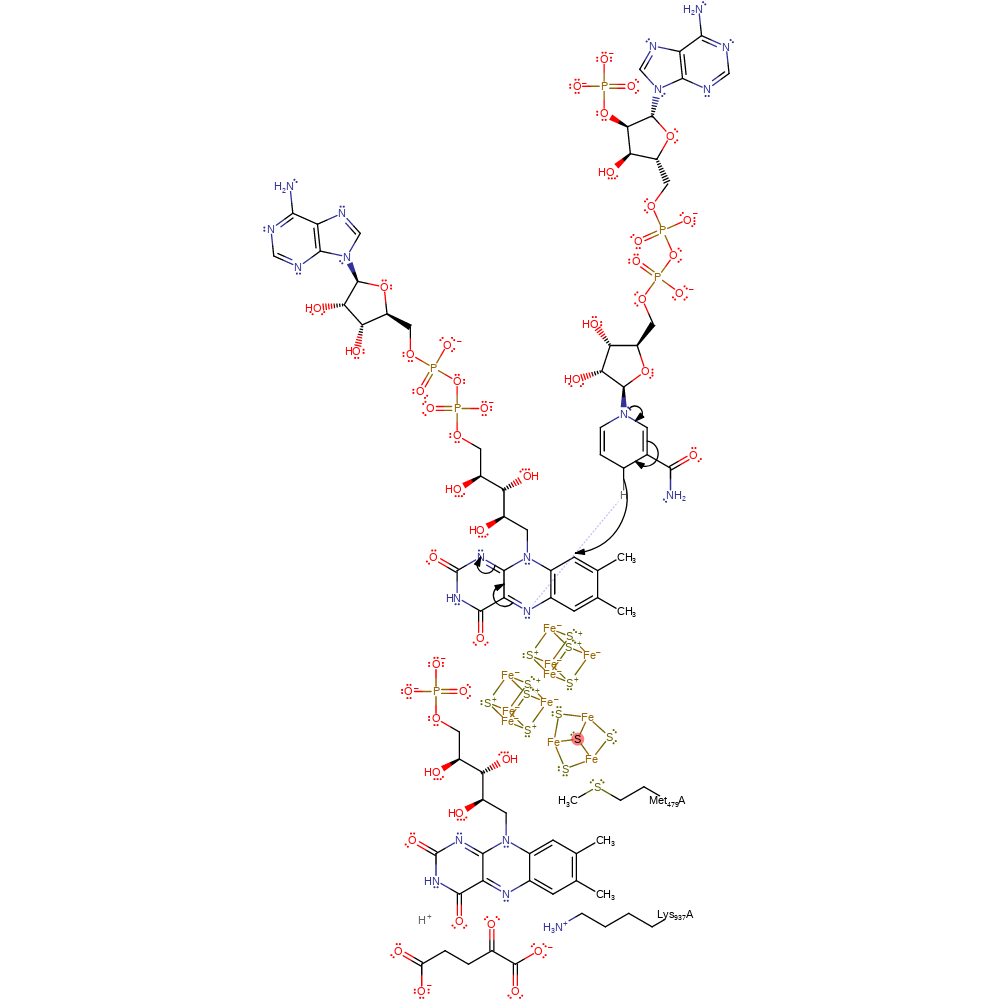
Step 1. NADP reduces the FAD cofactor. It is not yet clear exactly how this step occurs and what residues, if any, are involved
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, overall product formed, intermediate formation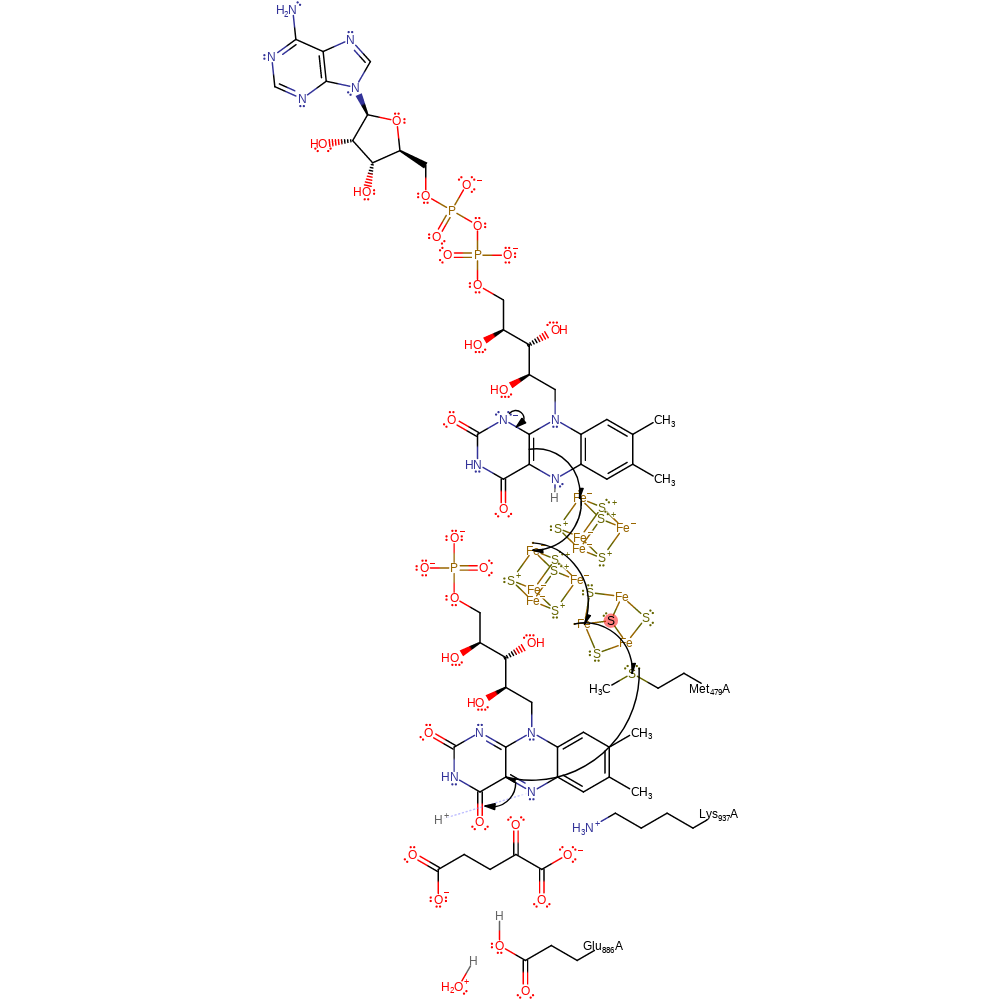
Step 2. The FMN is in the synthase domain. A single electron is transferred from FAD, via the iron-sulfur clusters and Met479 to the FMN cofactor. Studies suggest that the 2-oxoglutarate substrate needs to bind before the electron transfer can occur [PMID:11331018]. This is the first of two single electron transfers. The identity of the proton donors/acceptors is currently unclear.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met479A | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, electron relay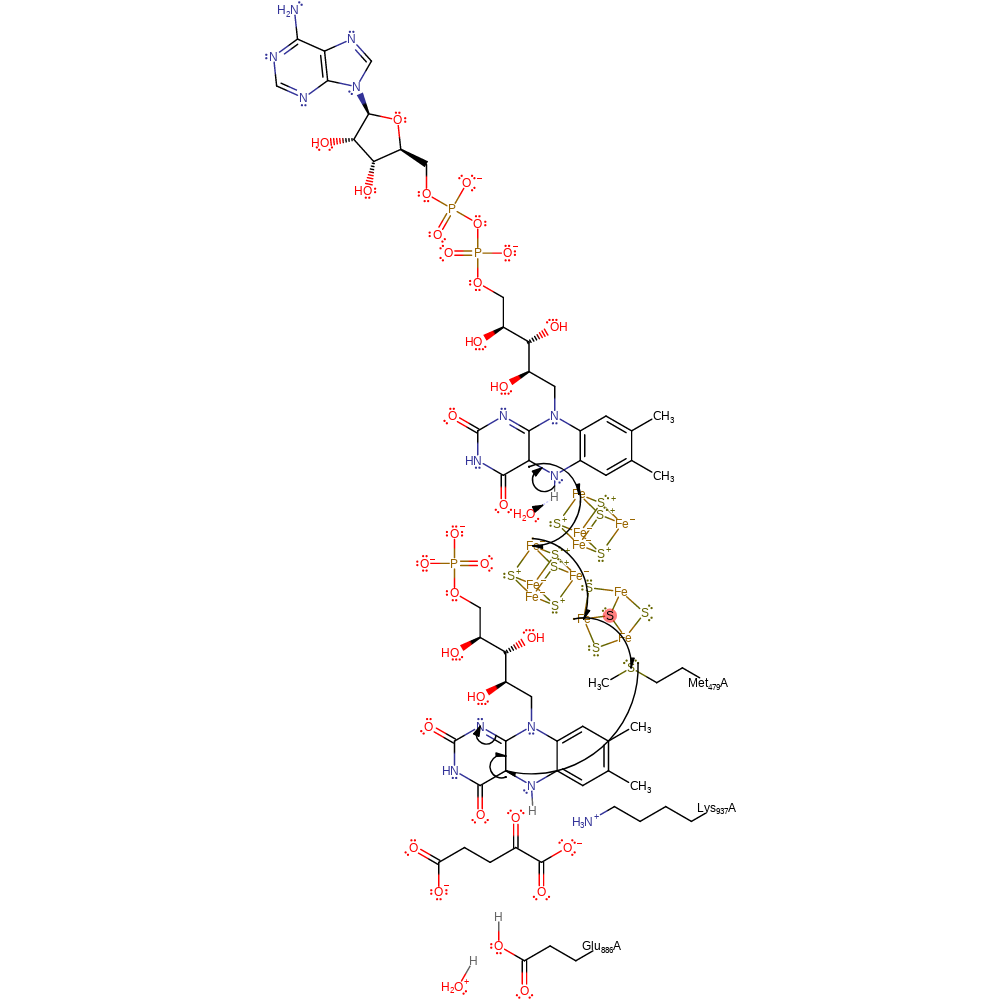
Step 3. The FMN is in the synthase domain. A second single electron is transferred from FAD, via the iron-sulfur clusters and Met479 to the FMN cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met479A | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, proton transfer, intermediate formation, native state of cofactor regenerated, electron relay
Step 4. This reaction occurs in the glutaminase domain. The N-terminus of Cys1 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the thiol group of Cys1, initiating a nucleophilic attack on the amide carbon in an addition reaction. The N-terminus of Cys1 may also directly deprotonate the thiol group of Cys1 and not involve a water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys1A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly232A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn231A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton acceptor |
| Cys1A | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation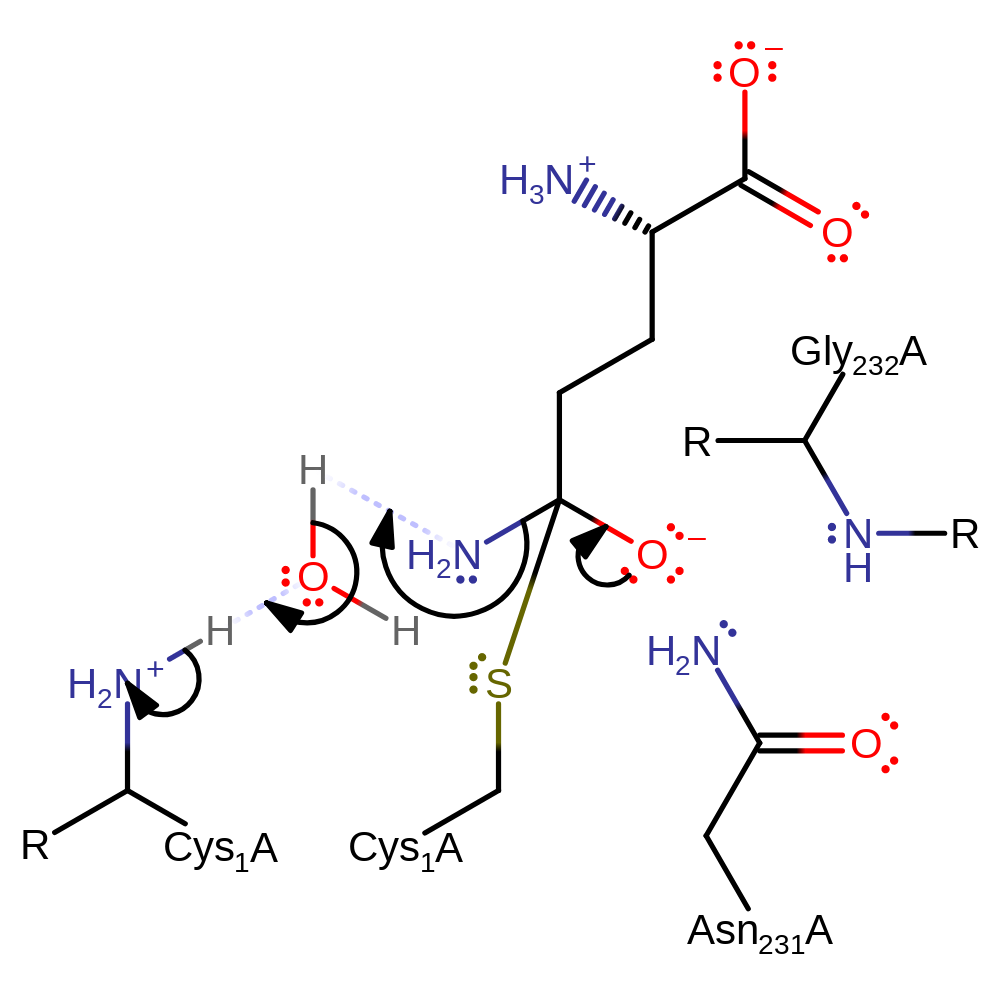
Step 5. This reaction occurs in the glutaminase domain. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves ammonia from the bound L-glutamine substrate. Ammonia deprotonates water, which deprotonates the N-terminus of Cys1.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys1A | covalently attached |
| Gly232A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn231A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton relay, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, deamination
Step 6. This reaction occurs in the glutaminase domain. The N-terminus of Cys1 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the covalently bound intermediate in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys1A | covalently attached |
| Gly232A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn231A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation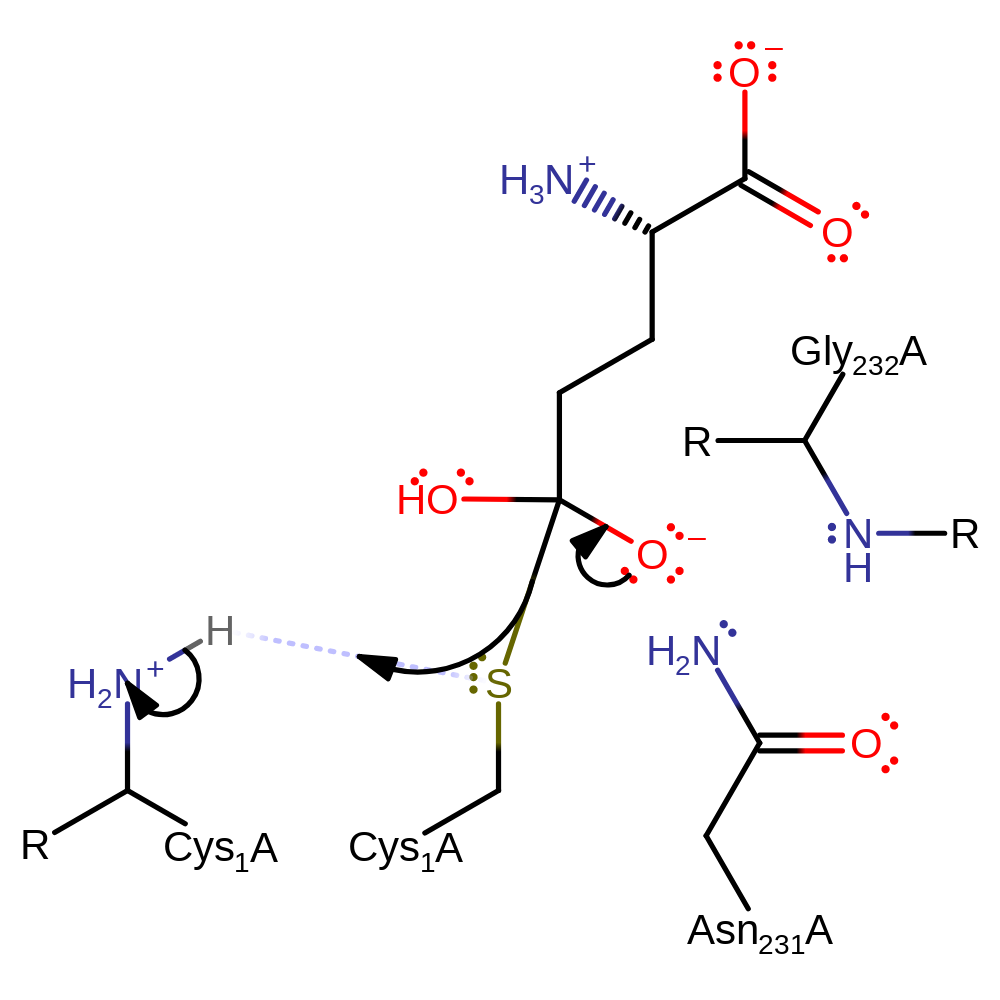
Step 7. This reaction occurs in the glutaminase domain. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the C-S bond, the thiolate of Cys1 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the N-terminus of Cys1.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys1A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly232A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn231A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton relay, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 8. This reaction occurs in the synthase domain. Ammonia initiates a nucleophilic attack on the C2 of 2-oxoglutarate in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys937A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 9. This reaction occurs in the synthase domain. Water is produced through an intramolecular elimination forming the 2-iminoglutarate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys937A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular elimination, intermediate formation, overall reactant used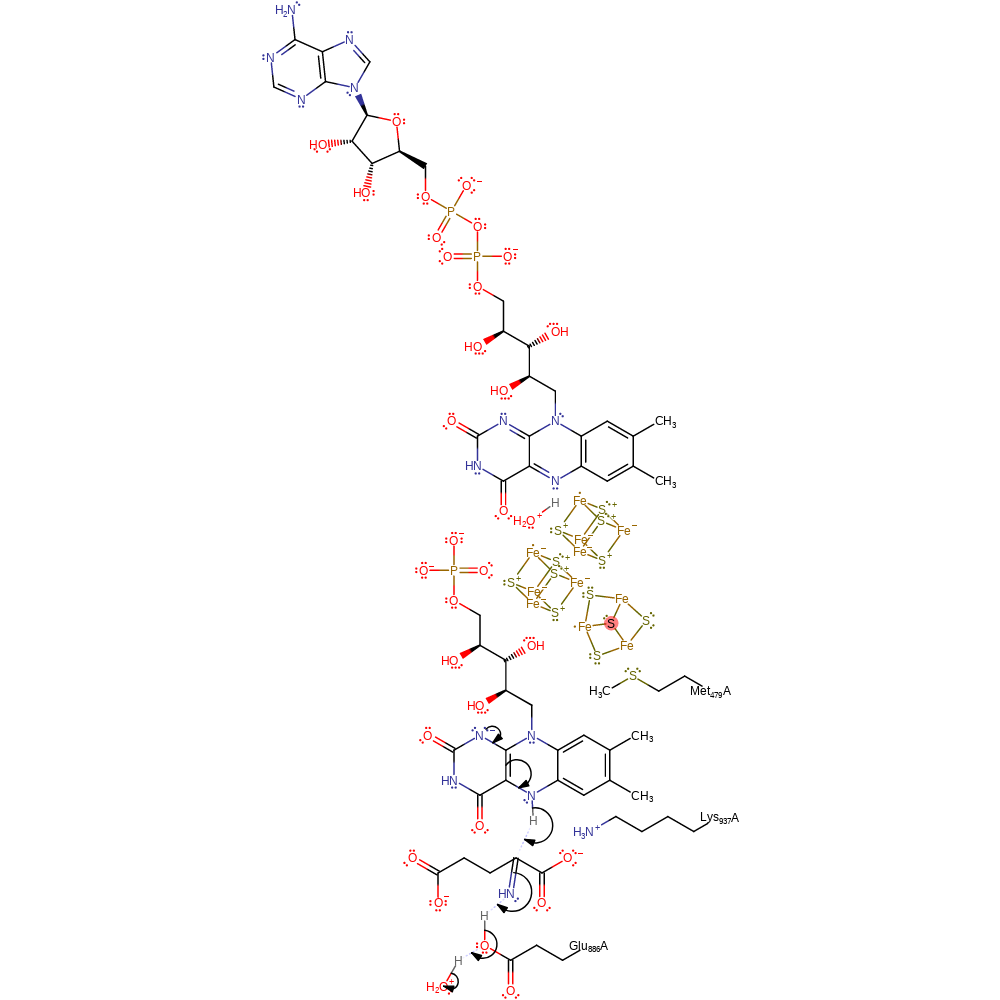
Step 10. This reaction occurs in the synthase domain. FMN donates a hydride to the 2-iminoglutarate intermediate. The observation of reduction of FMN by the L-glutamate product without the formation of a semiquinone species suggests that the 2-iminoglutarate reduction occurs by direct hydride transfer from the reduced FMN cofactor [PMID:18421771]. It is unclear where the proton comes from, one suggestion is Glu886, although it has also been suggested that the ammonia channel is filled by water, and so water could act as the general acid [PMID:18421771].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys937A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu886A | proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |






 Download:
Download: