Glutaminase
Glutaminases (EC:3.5.1.2) deaminate glutamine to glutamate. In Bacillus subtilis, glutaminase is encoded by glnA, which is part of an operon, glnA-glnT (formerly ybgJ-ybgH), where glnT encodes a glutamine transporter. The glnA-glnT operon is regulated by the 2-component system GlnK-GlnL in response to glutamine [PMID:15995196].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O31465
 (3.5.1.2)
(3.5.1.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1mki
- Crystal Structure of Bacillus Subtilis Probable Glutaminase, APC1040
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.1500.10
 3.40.710.10
3.40.710.10  (see all for 1mki)
(see all for 1mki)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.1.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Lys77 deprotonates Ser74, which initiates a nucleophilic addition onto the carbonyl carbon of the substrate amide group, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the C-N bond and releasing the ammonia product, the nitrogen of which deprotonates Lys77 via a proton relay through Tyr253. Lys77 deprotonates water via a proton relay with Tyr201, which initiates a nucleophilic addition at the carbonyl carbon, forming a new tetrahedral intermediate. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the acyl-enzyme bond and liberating Ser74, which in turn deprotonates the Lys77 via a proton relay with Tyr201.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mki) | ||
| Ser74 | Ser74(77)A | Acts as a nucleophile, forming a covalently attached intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator |
| Ser74 (main-N), Val271 (main-N) | Ser74(77)A (main-N), Val271(274)A (main-N) | Form the oxyanion hole that stabilises the negatively charged intermediates and transition states. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr201 | Tyr201(204)A | Part of a proton relay chain (with Lys77) responsible for protonating the ammonia leaving group. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Tyr253 | Tyr253(256)A | Part of a proton relay chain (with Lys77) responsible for activating the catalytic water molecule. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys77 | Lys77(80)A | Acts as a general acid/base, responsible for activating the catalytic serine. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, proton relay, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Brown G et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 5724-5735. Functional and Structural Characterization of Four Glutaminases from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis†. DOI:10.1021/bi800097h. PMID:18459799.
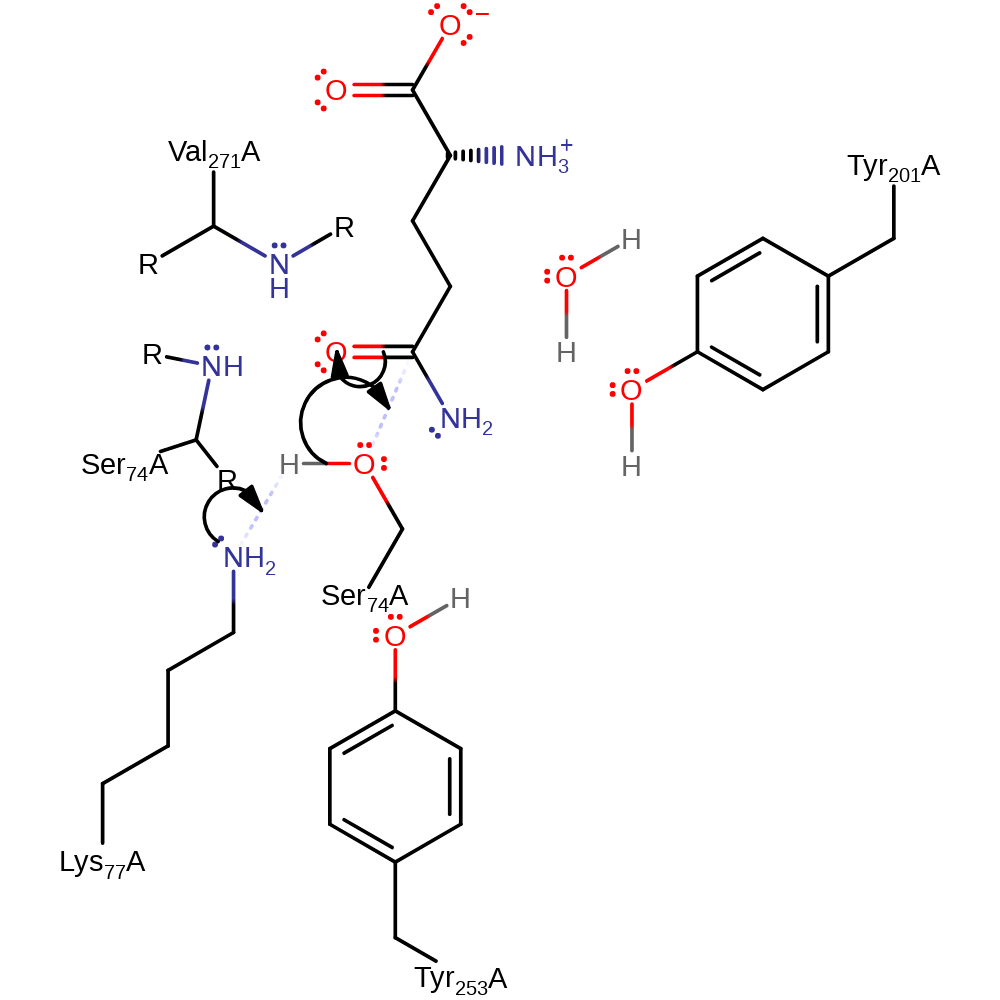
Step 1. Lys77 deprotonates Ser74, which initiates a nucleophilic addition onto the carbonyl carbon of the substrate amide group, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Val271(274)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser74(77)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr253(256)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr201(204)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys77(80)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
| Ser74(77)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the C-N bond and releasing the ammonia product, the nitrogen of which deprotonates Lys77 via a proton relay through Tyr253.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Val271(274)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser74(77)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr253(256)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Tyr201(204)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys77(80)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser74(77)A | covalently attached, activator |
| Lys77(80)A | proton donor |
| Tyr253(256)A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate formation, proton relay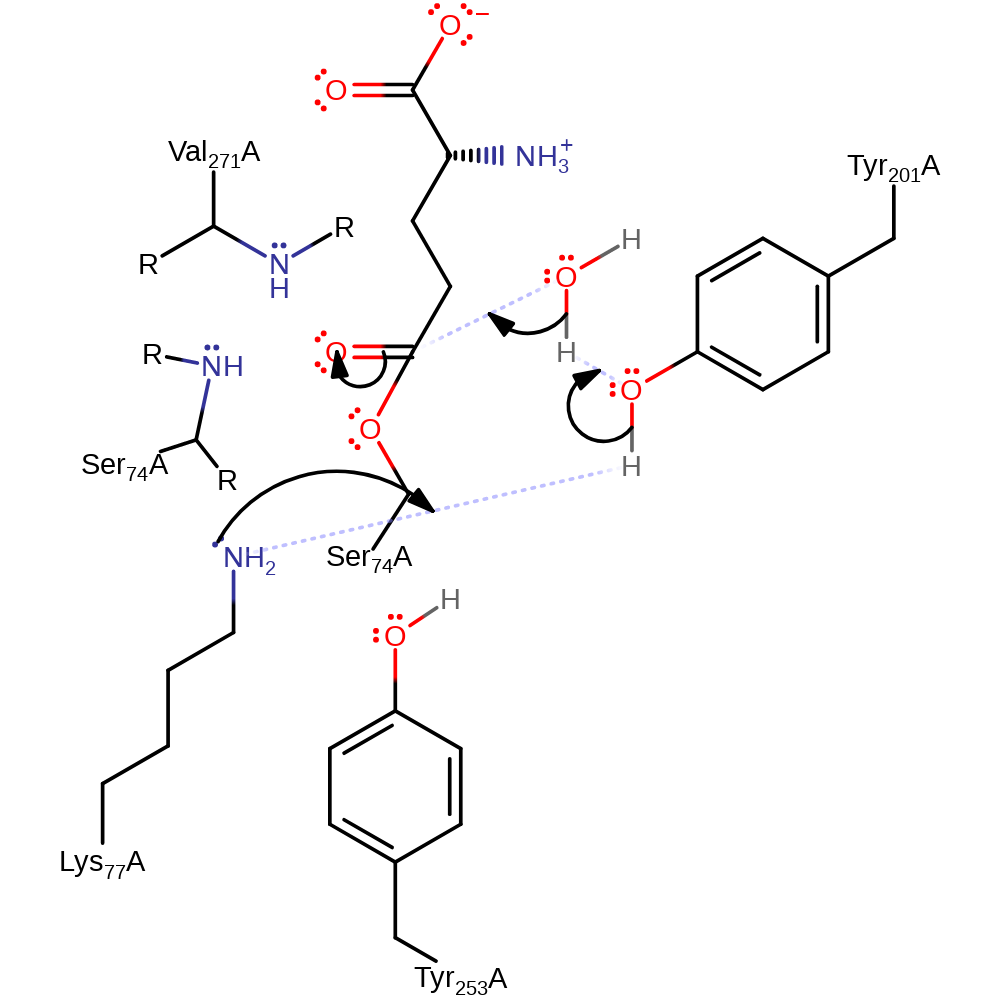
Step 3. Lys77 deprotonates water via a proton relay with Tyr201, which initiates a nucleophilic addition at the carbonyl carbon, forming a new tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Val271(274)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser74(77)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr253(256)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr201(204)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Lys77(80)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser74(77)A | activator, covalently attached |
| Tyr201(204)A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys77(80)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the acyl-enzyme bond and liberating Ser74, which in turn deprotonates the Lys77 via a proton relay with Tyr201.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Val271(274)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser74(77)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr253(256)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr201(204)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Lys77(80)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr201(204)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser74(77)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys77(80)A | proton donor |
| Ser74(77)A | nucleofuge |
| Tyr201(204)A | proton donor |




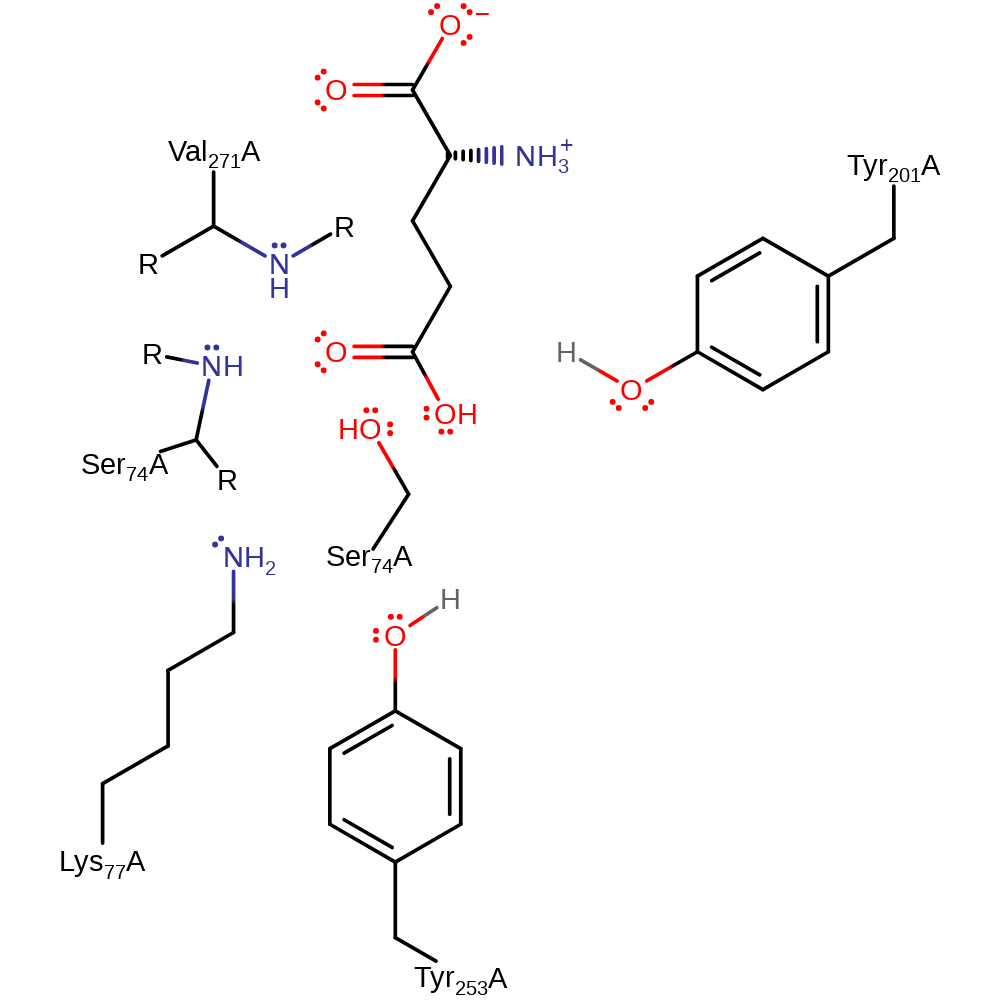 Download:
Download: