Thiocyanate hydrolase
Thiocyanate hydrolase is a cobalt-containing metalloenzyme with a cysteine-sulphinic acid ligand that hydrolyses thiocyanate to carbonyl sulphide and ammonia. The enzyme from Thiobacillus thioparus catalyses the first step in the degradation of thiocyanate. Structural studies show all three chains to surround the active site, with positive side chains projecting towards the metal centre from each of them, stabilising the negatively charged substrate and product [PMID:17222425].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
O66188
 (3.5.5.8)
(3.5.5.8)
O66187 (3.5.5.8)
(3.5.5.8)
O66186 (3.5.5.8)
(3.5.5.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thiobacillus thioparus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2dd5
- Thiocyanate hydrolase (SCNase) from Thiobacillus thioparus native holo-enzyme
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.330.10
 1.10.472.20
1.10.472.20  (see all for 2dd5)
(see all for 2dd5)
- Cofactors
- Cobalt(3+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Tyr108 activates a water molecule towards nucleophilic attack on the Co(III) coordinated thiocyanate substrate. A proton is exchanged between the hydrolysis product and Tyr108C. Tautomerisation of the intermediate results in a carbonyl species. An internal proton transfer occurs. The hydroxyl present on Cys133 activates a water molecule to act as a nucleophile towards the thio-acid intermediate. The tetrahedral anion collapses resulting in concomitant release of ammonia and deprotonation of Cys133. An intermolecular elimination of hydroxide occurs, forming carbonyl sulfide.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2dd5) | ||
| Tyr108 | Tyr108B | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys133 (ptm) | Cso133C (ptm) | Forms part of the cobalt binding site, also acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132 (main-N), Cys133 (main-N), Cys128, Ser132, Cys131 (ptm) | Ser132C (main-N), Cso133C (main-N), Cys128C, Ser132C, Csd131C (ptm) | Form part of the cobalt binding site. Also help to activate and stabilise the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, inferred reaction step, keto-enol tautomerisation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Arakawa T et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 366, 1497-1509. Structure of Thiocyanate Hydrolase: A New Nitrile Hydratase Family Protein with a Novel Five-coordinate Cobalt(III) Center. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.011. PMID:17222425.
- Gupta N et al. (2010), J Hazard Mater, 176, 1-13. Enzymatic mechanism and biochemistry for cyanide degradation: A review. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.038. PMID:20004515.
- Arakawa T et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 14838-14843. Structural Basis for Catalytic Activation of Thiocyanate Hydrolase Involving Metal-Ligated Cysteine Modification. DOI:10.1021/ja903979s. PMID:19785438.
- Katayama Y et al. (1998), J Bacteriol, 180, 2583-2589. Cloning of genes coding for the three subunits of thiocyanate hydrolase of Thiobacillus thioparus THI 115 and their evolutionary relationships to nitrile hydratase. PMID:9573140.
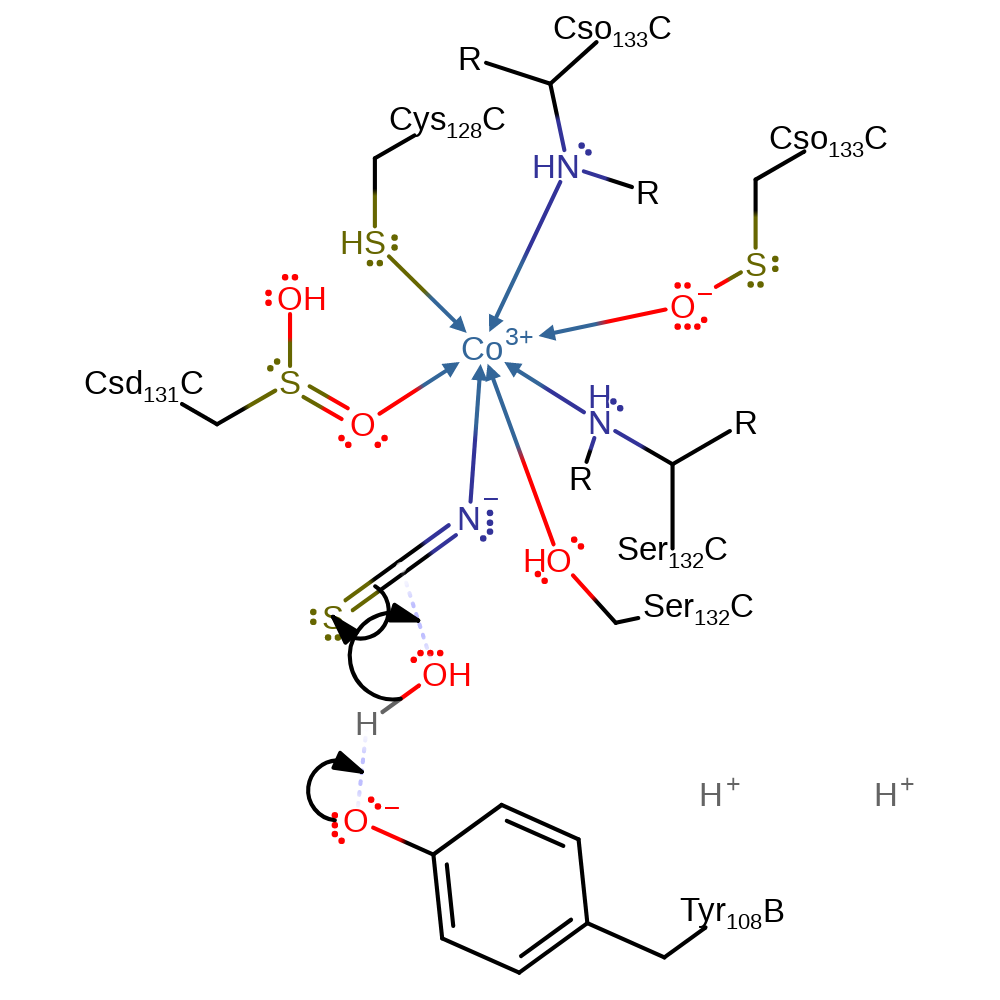
Step 1. Crystallographic data suggests Co(III) forms a pentavalent coordination environment. The distal position is seen not to coordination to water, as is the case for the related enzyme Nitrile hydrolase, but instead binds the thiocyanate substrate via its nitrogen. The metal centre acts as a Lewis acid, increasing the electrophilic character of the bound thiocyanate [PMID:17222425]. Both Tyr108 and Cys133 have been identified as hydrolysis activating residues, although their precise roles are only partially characterised [PMID:17222425]. Tyr108 activates a water molecule towards nucleophilic attack on the Co(III) coordinated thiocyanate substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cso133C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser132C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C | metal ligand |
| Ser132C (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cys128C | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr108B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation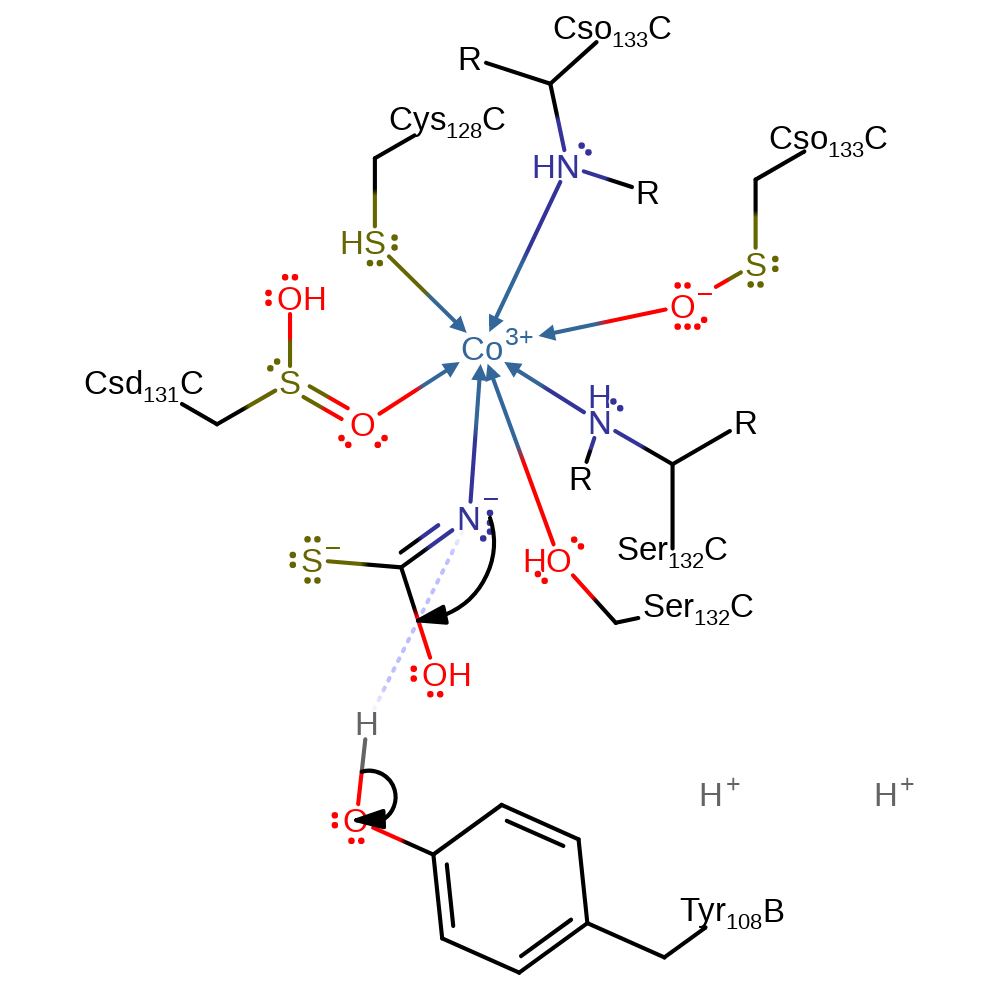
Step 2. A proton is exchanged between the hydrolysis product and Tyr108C.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cso133C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cys128C | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cso133C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C | metal ligand |
| Ser132C (main-N) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr108B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, inferred reaction step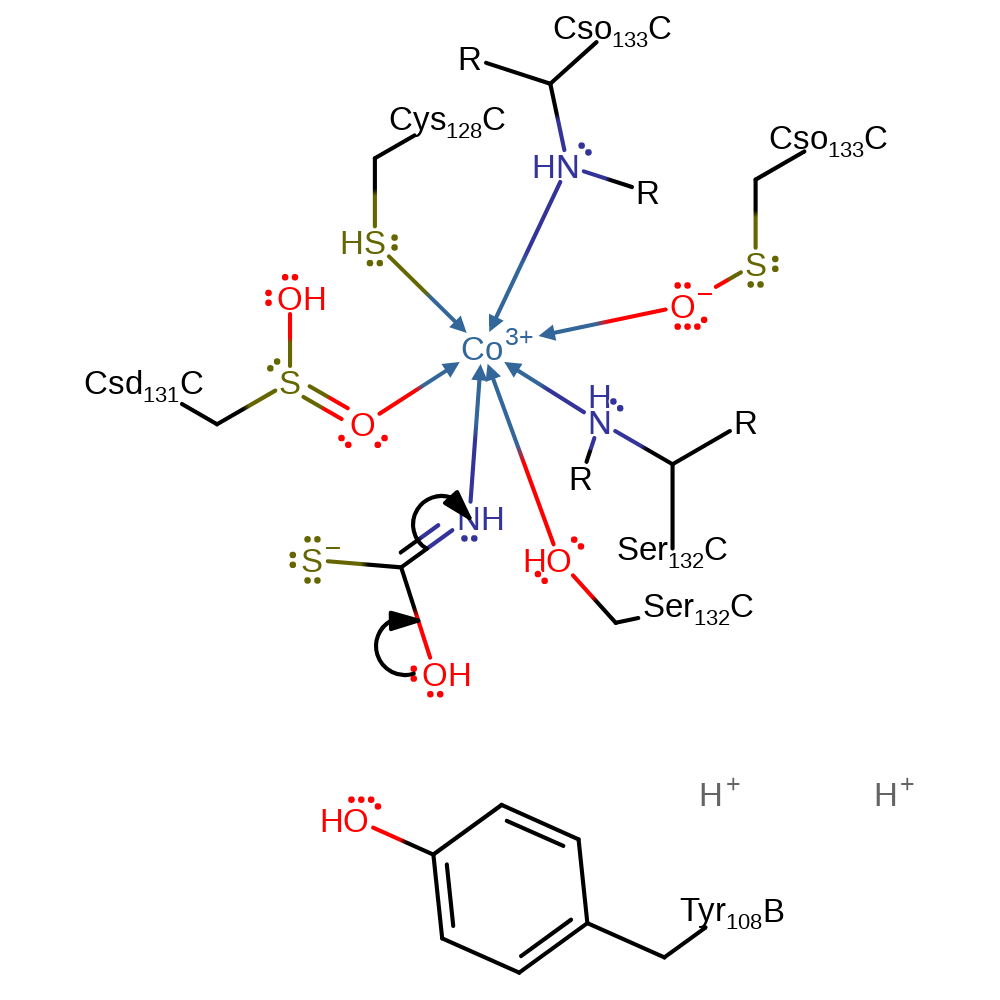
Step 3. Tautomerisation of the intermediate results in a carbonyl species.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser132C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cso133C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C (main-N) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
keto-enol tautomerisation, inferred reaction step, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cso133C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Ser132C (main-N) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, inferred reaction step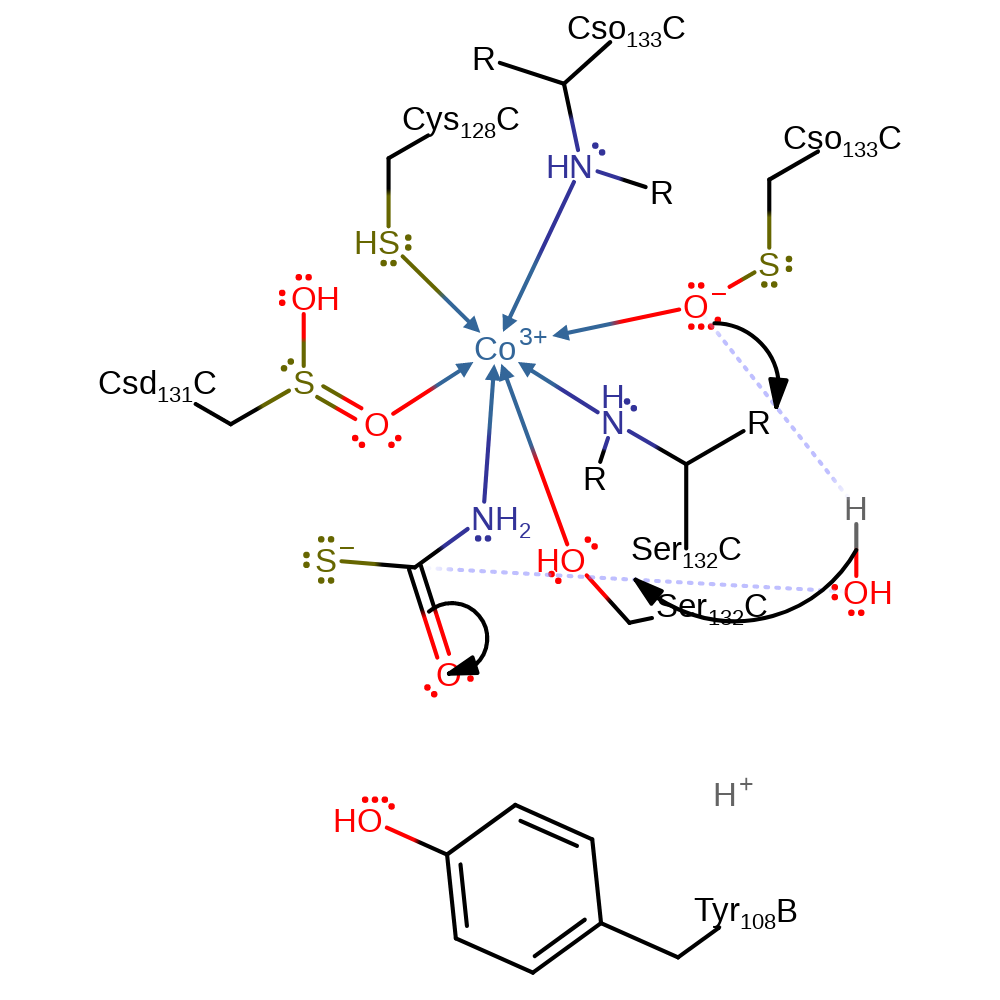
Step 5. The post translation modified hydroxyl group at Cys133 is thought to behave as a general base towards the incoming water molecule. The enzyme is only active once hydroxylation has occurred at this position, and the existence of such a post translational modification has been hypothesised as a regulatory mechanism for enzyme activity [PMID:19785438]. Once activated, water acts as a nucleophile towards the thio-acid intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation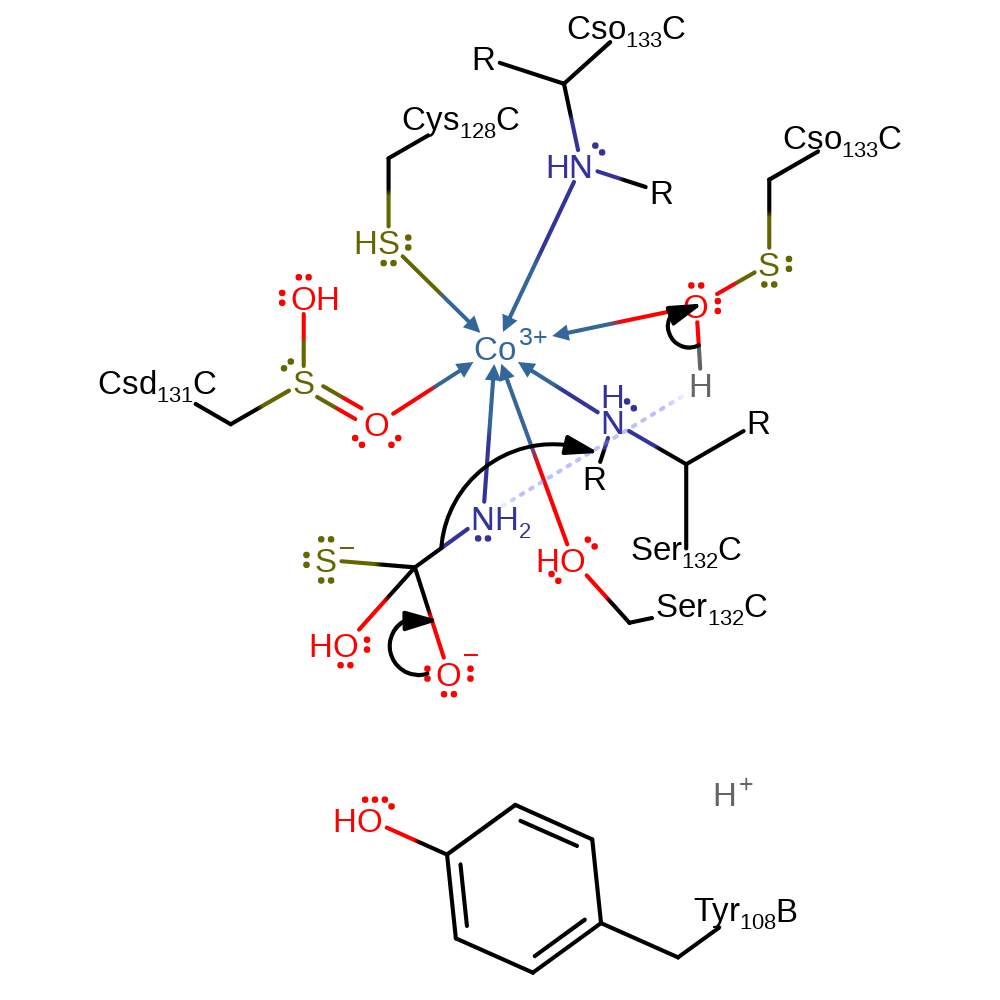
Step 6. The tetrahedral anion collapses resulting in concomitant release of ammonia and deprotonation of Cys133.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate formation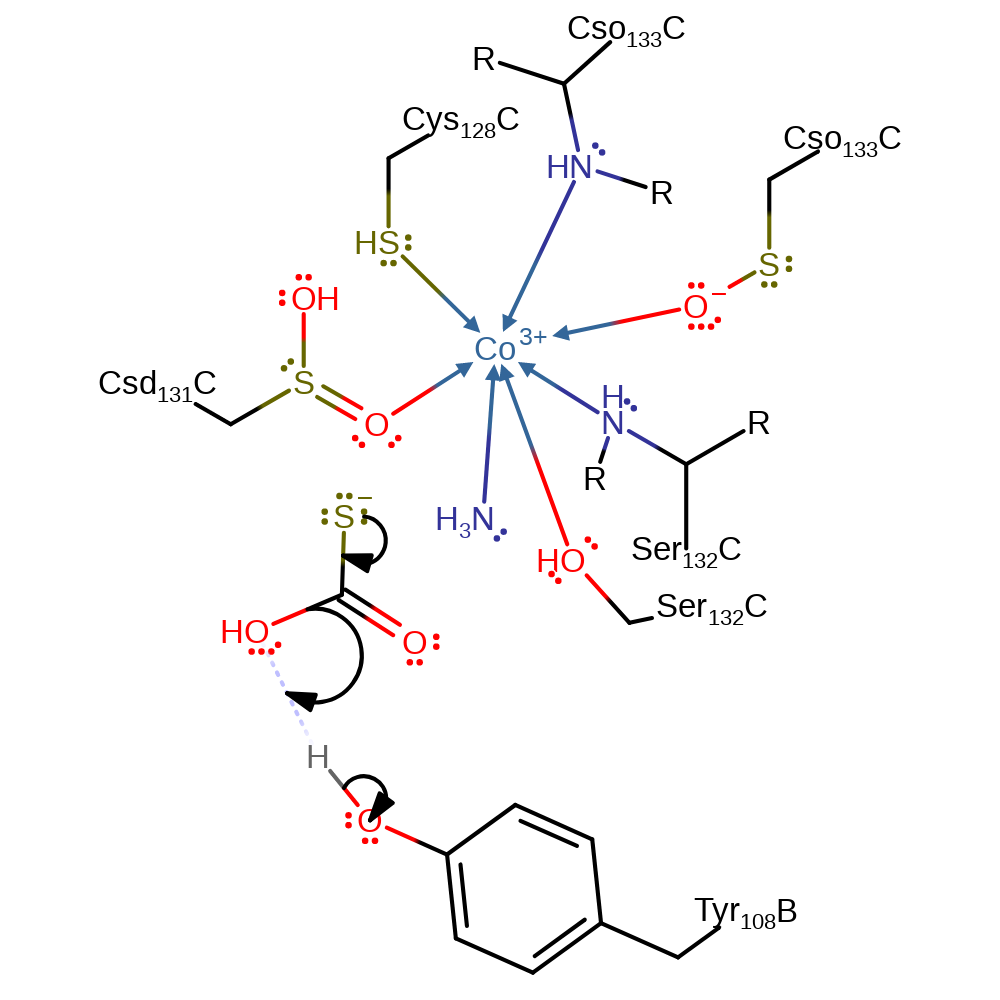
Step 7. An intermolecular elimination of hydroxide occurs, forming carbonyl sulfide. The protonation of the hydroxide by Tyr108 is inferred. Alternatively, these proton exchanges can occur with bulk water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser132C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys128C | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cso133C (main-N) | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Tyr108B | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser132C (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Csd131C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser132C (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cso133C (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Csd131C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Cso133C (ptm) | metal ligand |
| Tyr108B | proton donor |





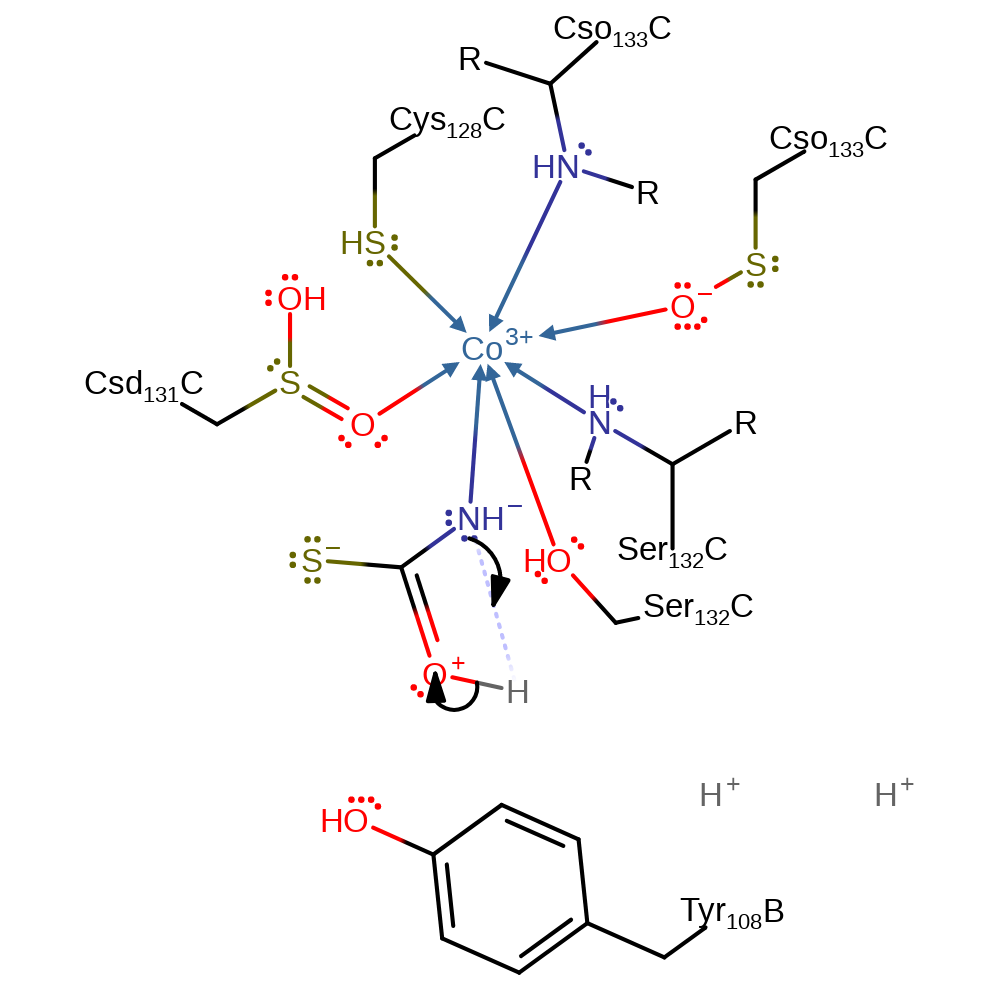
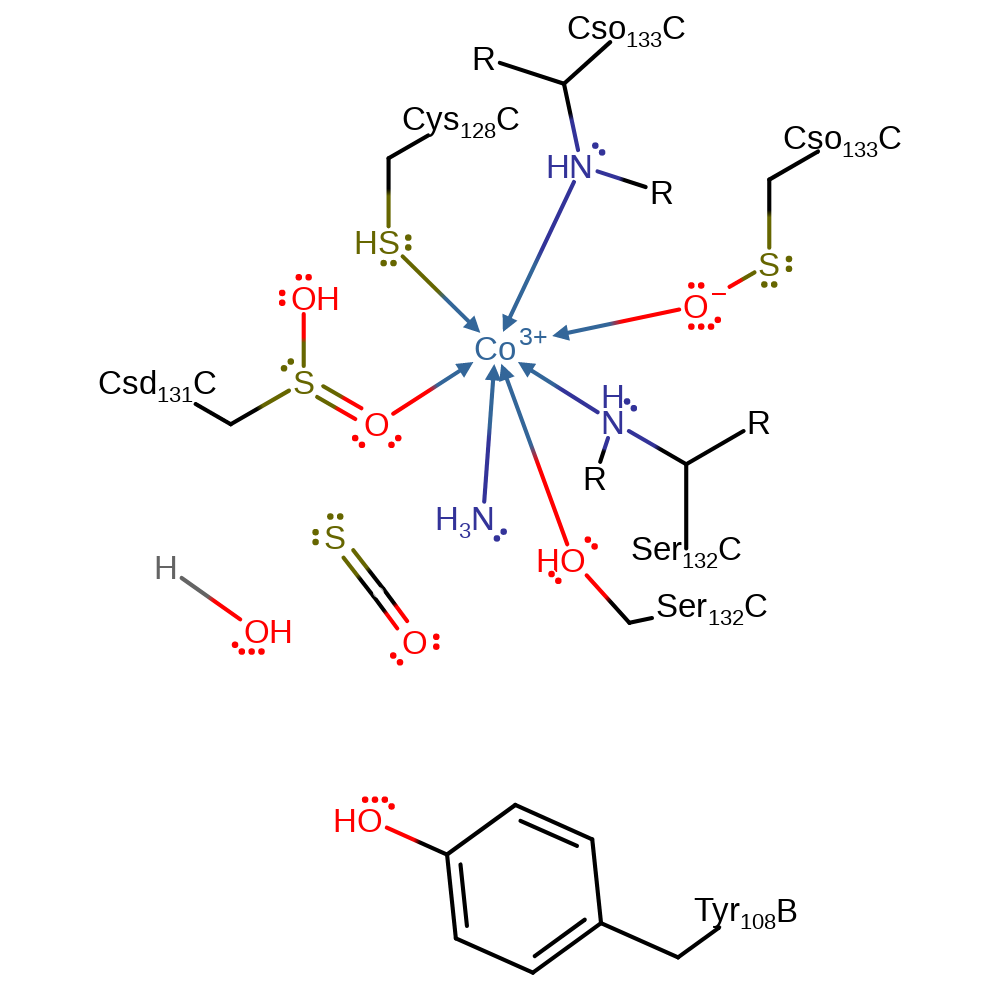 Download:
Download: