Aminodeoxychorismate synthase
The enzyme is composed of two parts, PabA and PabB. In the absence of PabA and glutamine, PabB will still convert ammonia and chorismate into 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate. PabA, a 21kDa subunit, converts glutamine into glutamate only in the presence of stoichiometric amounts of PabB and provides the nucleophile (ammonia) via hydrolysis of glutamine to the PabA subunit. The crystal structure used here is only of PabB, there doesn't appear to be a structure available of both components together. Of the two domains present, the Chlorismate Superfamily Fold is thought to be the site of catalysis, but the second domain, situated in the N-terminus is thought to be involved in regulating an inhibitory feedback mechanism involving tryptophan.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P05041
 (2.6.1.85)
(2.6.1.85)
P00903 (2.6.1.85)
(2.6.1.85)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1k0g
- THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF AMINODEOXYCHORISMATE SYNTHASE FROM PHOSPHATE GROWN CRYSTALS
(2.05 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.120.10
 (see all for 1k0g)
(see all for 1k0g)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.6.1.85)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Chorismate is attacked at C(2) by the nucleophilic Lys274, resulting in the conjugate elimination of water from C(4). Glu258 acts as a general acid to the departing water. The imidazol of His168 is proposed to act as a general base towards Cys79, activating the thiol towards nucleophilic attack at the glutamine carbonyl. The anionic tetrahedral intermediate collapses. This generates the ammonia which is subsequently transferred to the aminodeoxychorismate synthase catalytic centre in the PapB subunit through a specific channel. Ammonia formed from the hydrolysis of glutamine attacks at the C(4) position of the chorismate-enzyme adduct, eliminating Lys274. Glu258 acts as a general base, abstracting a proton from the C(4) amino group and regenerating the synthase catalytic site. His168 deprotonates the water, which attacks the enzyme-glutamine complex, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating Cys79, which deprotonates His168.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1k0g) | ||
| Glu170 | Not found | Present in the PapA subunit. Activates His168. Part of a Cys-His-Glu catalytic triad. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity, increase basicity, steric role |
| Lys274 | Lys274A | Present in the PapB subunit. Acts as a catalytic nucleophile. | hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, polar/non-polar interaction, activator |
| Cys79 | Not found | Present in the PapA subunit. Acts as a catalytic nucleophile. Part of a Cys-His-Glu catalytic triad. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge, activator, increase electrophilicity |
| His168 | Not found | Present in the PapA subunit. Acts as a general acid/base. Part of a Cys-His-Glu catalytic triad. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, increase nucleophilicity |
| Glu258 | Glu258A | Present in the PapB subunit. Acts as a general acid/base | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Parsons JF et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 2198-2208. Structure ofEscherichia coliAminodeoxychorismate Synthase: Architectural Conservation and Diversity in Chorismate-Utilizing Enzymes†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi015791b. PMID:11841211.
- Bera AK et al. (2012), Biochemistry, 51, 10208-10217. Structure of aminodeoxychorismate synthase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. DOI:10.1021/bi301243v. PMID:23230967.
- Ziebart KT et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 2851-2859. Nucleophile Specificity in Anthranilate Synthase, Aminodeoxychorismate Synthase, Isochorismate Synthase, and Salicylate Synthase. DOI:10.1021/bi100021x. PMID:20170126.
- He Z et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 5019-5028. Direct Detection and Kinetic Analysis of Covalent Intermediate Formation in the 4-Amino-4-deoxychorismate Synthase Catalyzed Reaction. DOI:10.1021/bi052216p. PMID:16605270.
- He Z et al. (2004), J Am Chem Soc, 126, 2378-2385. Conservation of Mechanism in Three Chorismate-Utilizing Enzymes. DOI:10.1021/ja0389927. PMID:14982443.
- Massière F et al. (1998), Cell Mol Life Sci, 54, 205-222. The mechanism of glutamine-dependent amidotransferases. DOI:10.1007/s000180050145. PMID:9575335.
- Roux B et al. (1993), Biochemistry, 32, 3763-3768. p-Aminobenzoate synthesis in Escherichia coli: Mutational analysis of three conserved amino acid residues of the amidotransferase PabA. DOI:10.1021/bi00065a031. PMID:8096767.
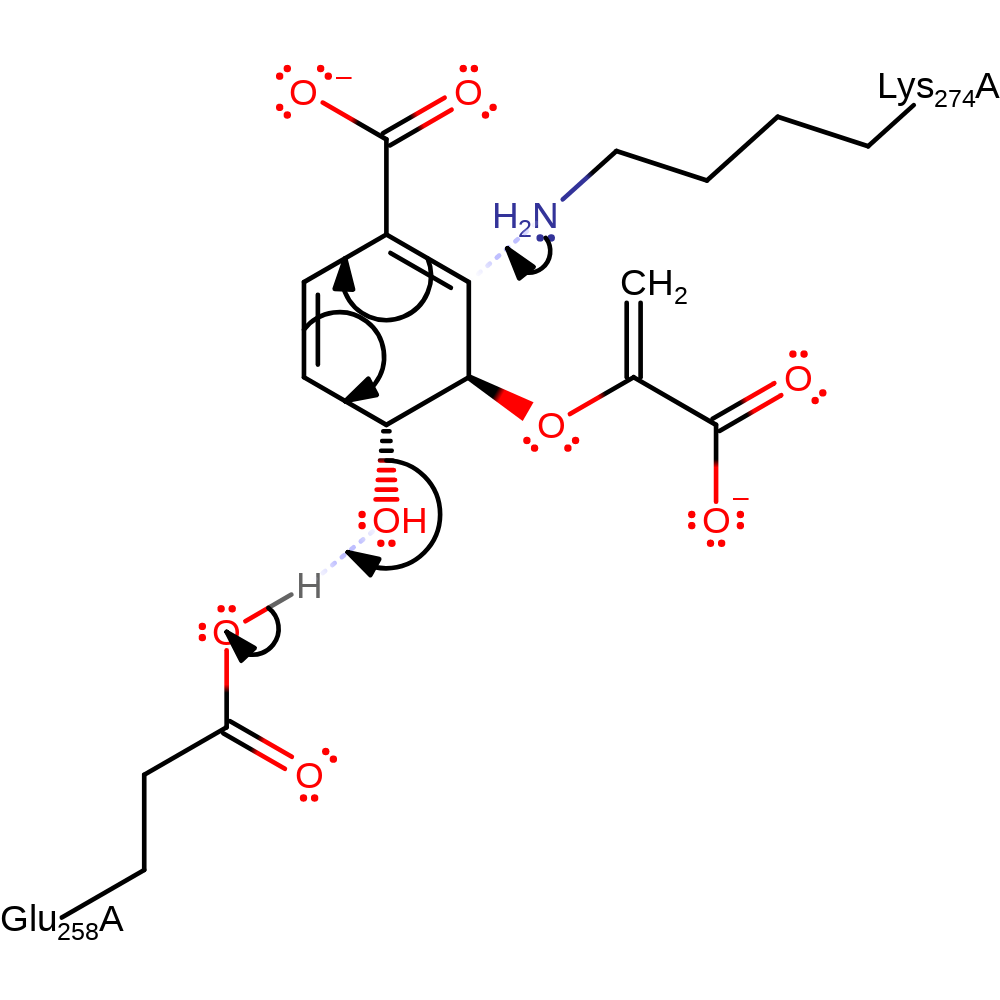
Step 1. The chlorismate substrate binds in the synthase domain before glutamine is present [PMID:9575335].. Chorismate is attacked at C(2) by the nucleophilic Lys274, resulting in the conjugate elimination of water from C(4). Glu258 acts as a general acid to the departing water. The reaction proceeds via a Sn2" which maintains the stereochemistry at C(4). A single displacement mechanism would result in stereochemical inversion [PMID:14982443].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu258A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys274A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Glu258A | proton donor |
| Lys274A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation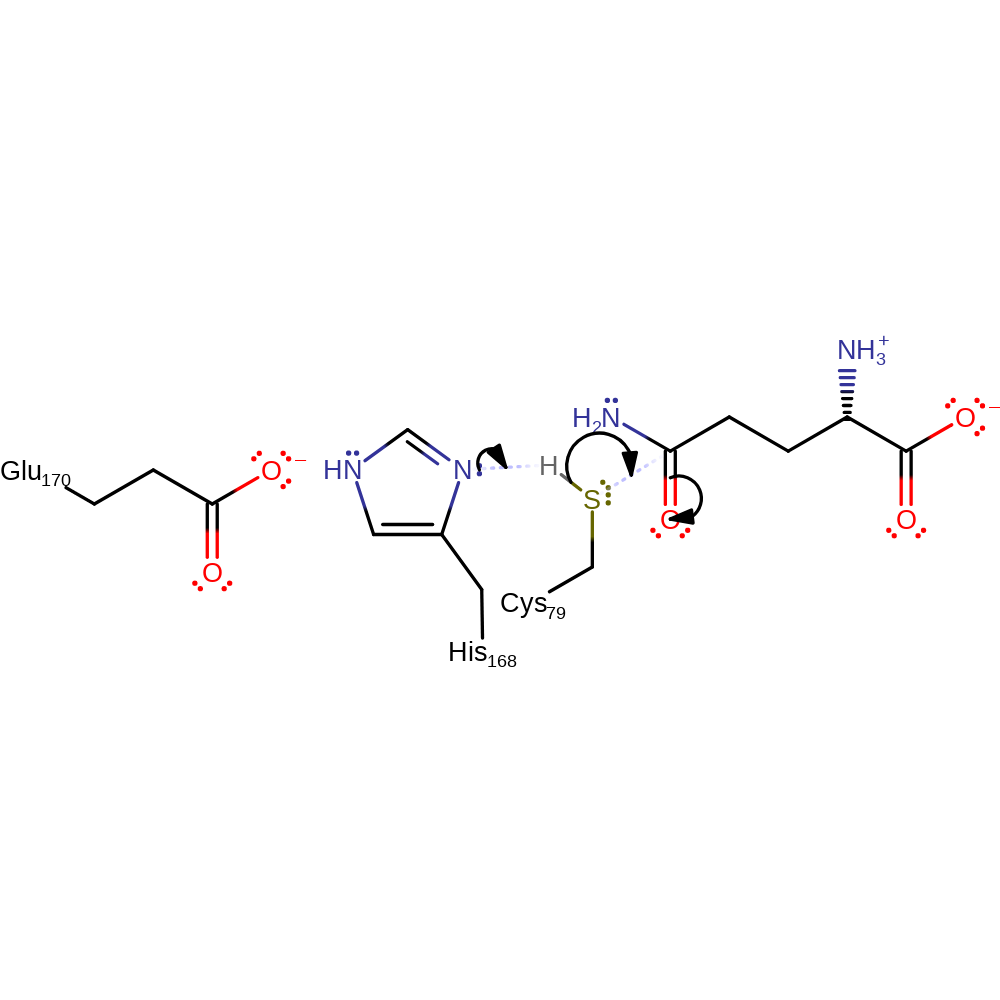
Step 2. The imidazol of His168 is proposed to act as a general base towards Cys79, activating the thiol towards nucleophilic attack at the glutamine carbonyl.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys79 | hydrogen bond donor |
| His168 | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase nucleophilicity |
| Glu170 | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, increase basicity |
| Cys79 | nucleophile |
| His168 | proton acceptor |
| Cys79 | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used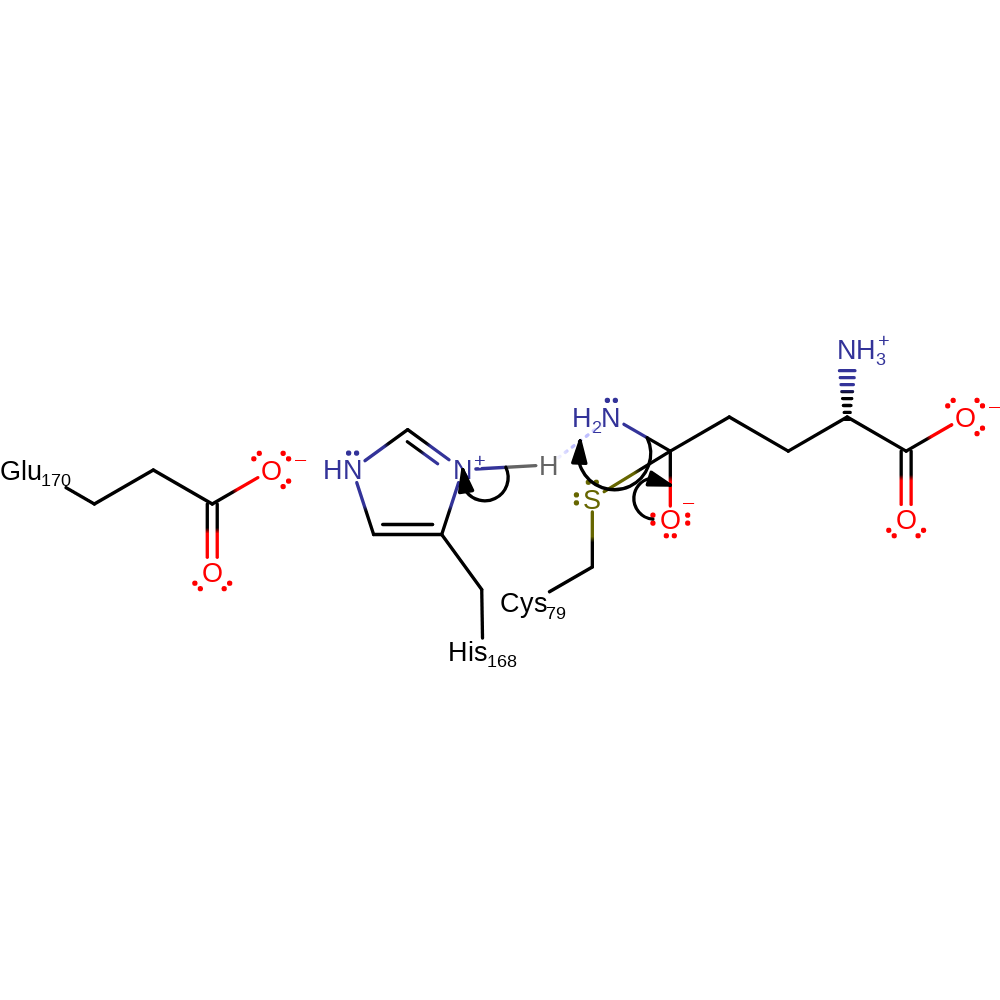
Step 3. The anionic tetrahedral intermediate collapses. This generates the ammonia. The ammonia produced in this step is then relayed to the active site contained in PapB (where the 4-amino 4-deoxychorismate is formed) through a channel; similar to the reactions of GMP and CTP synthetase [PMID:11841211].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys79 | activator, covalently attached |
| His168 | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu170 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His168 | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation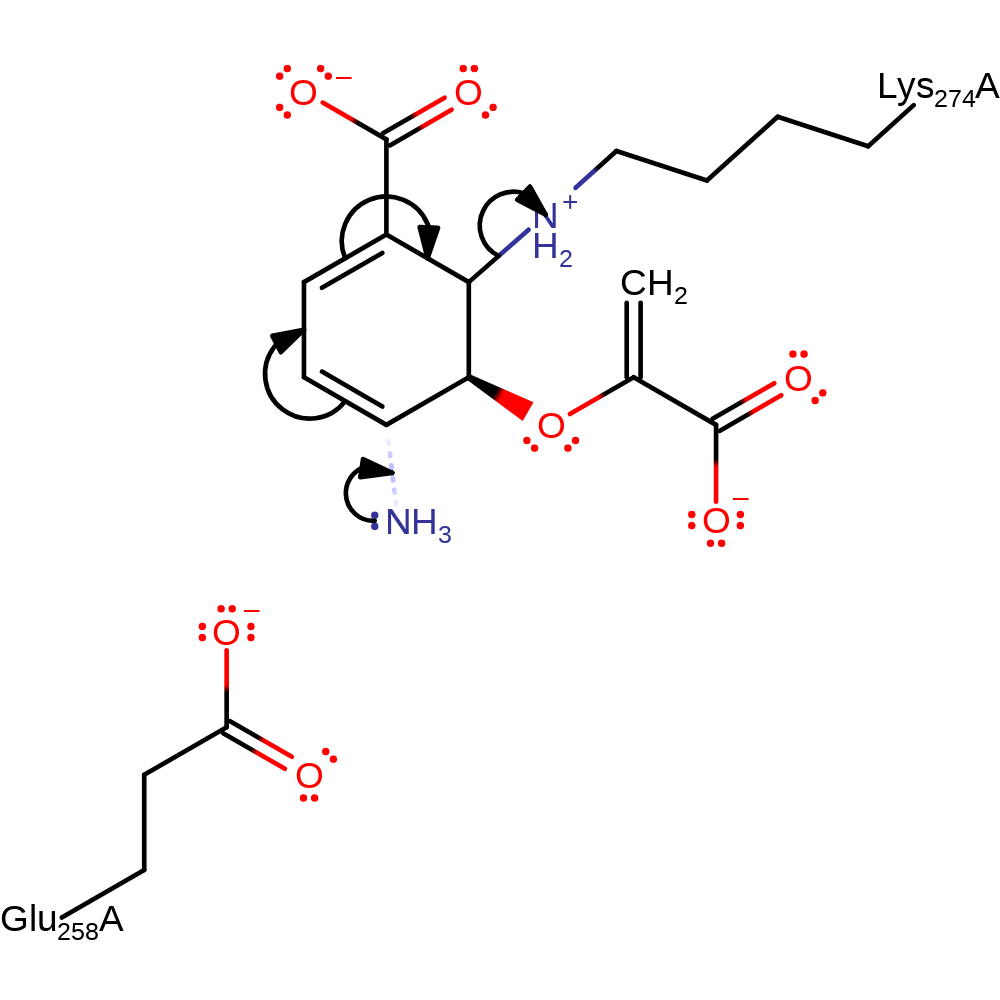
Step 4. Ammonia formed from the hydrolysis of glutamine attacks at the C(4) position of the chorismate-enzyme adduct, eliminating Lys274.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu258A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Lys274A | activator, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage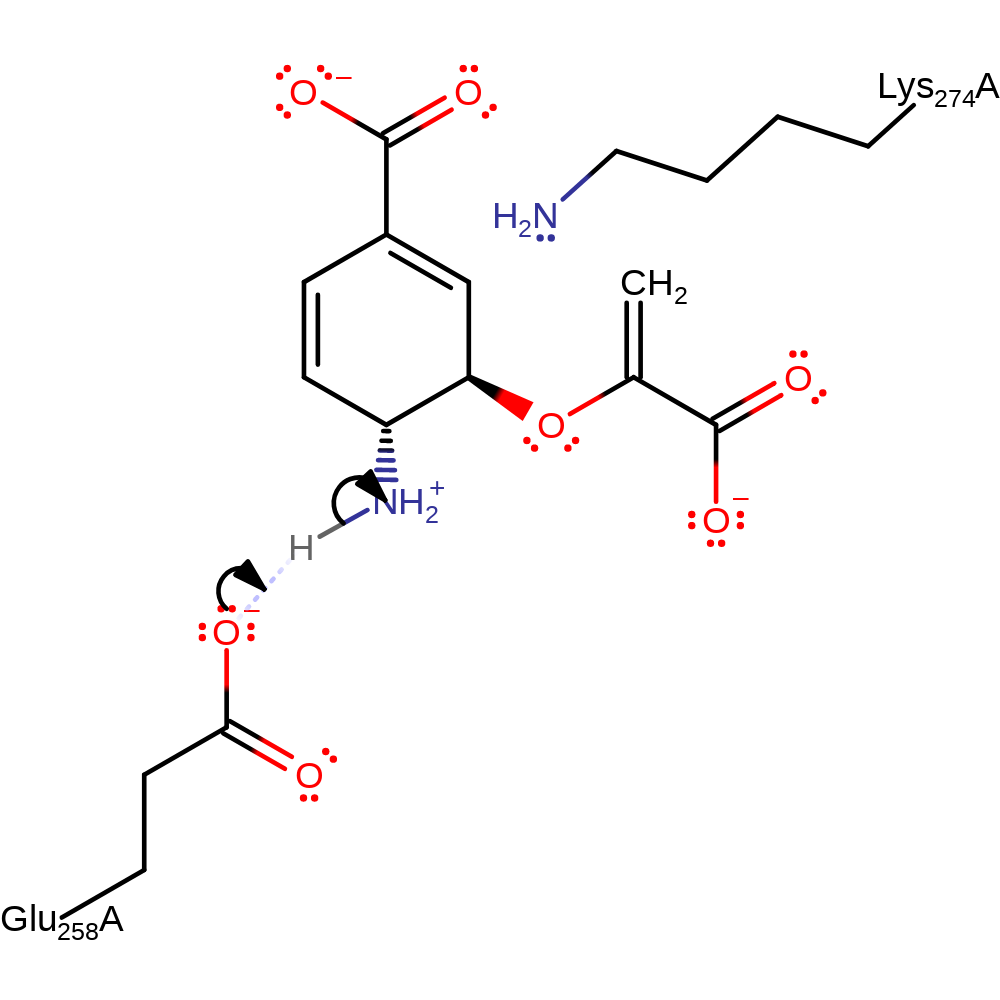
Step 5. Glu258 acts as a general base, abstracting a proton from the C(4) amino group and regenerating the synthase catalytic site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu258A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Lys274A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu258A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer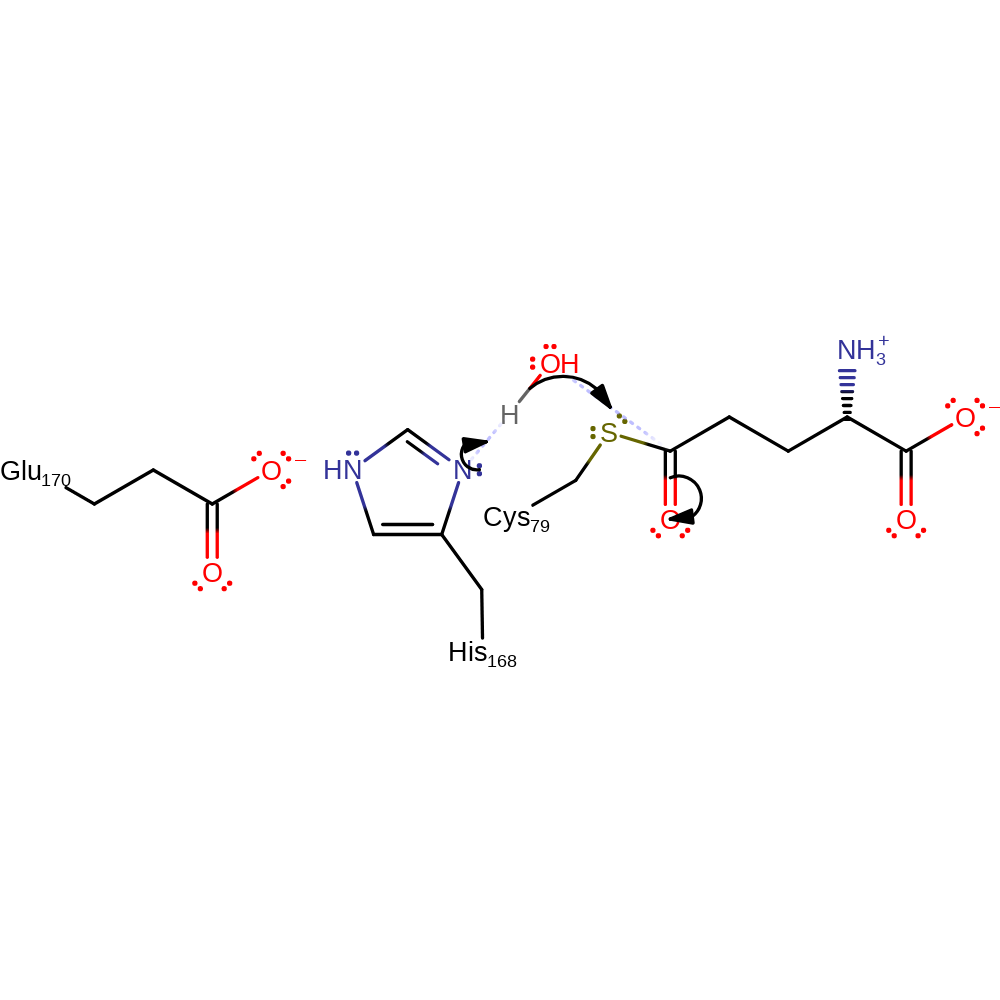
Step 6. His168 deprotonates the water, which attacks the enzyme-glutamine complex, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys79 | activator, covalently attached, increase electrophilicity |
| Glu170 | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| His168 | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, inferred reaction step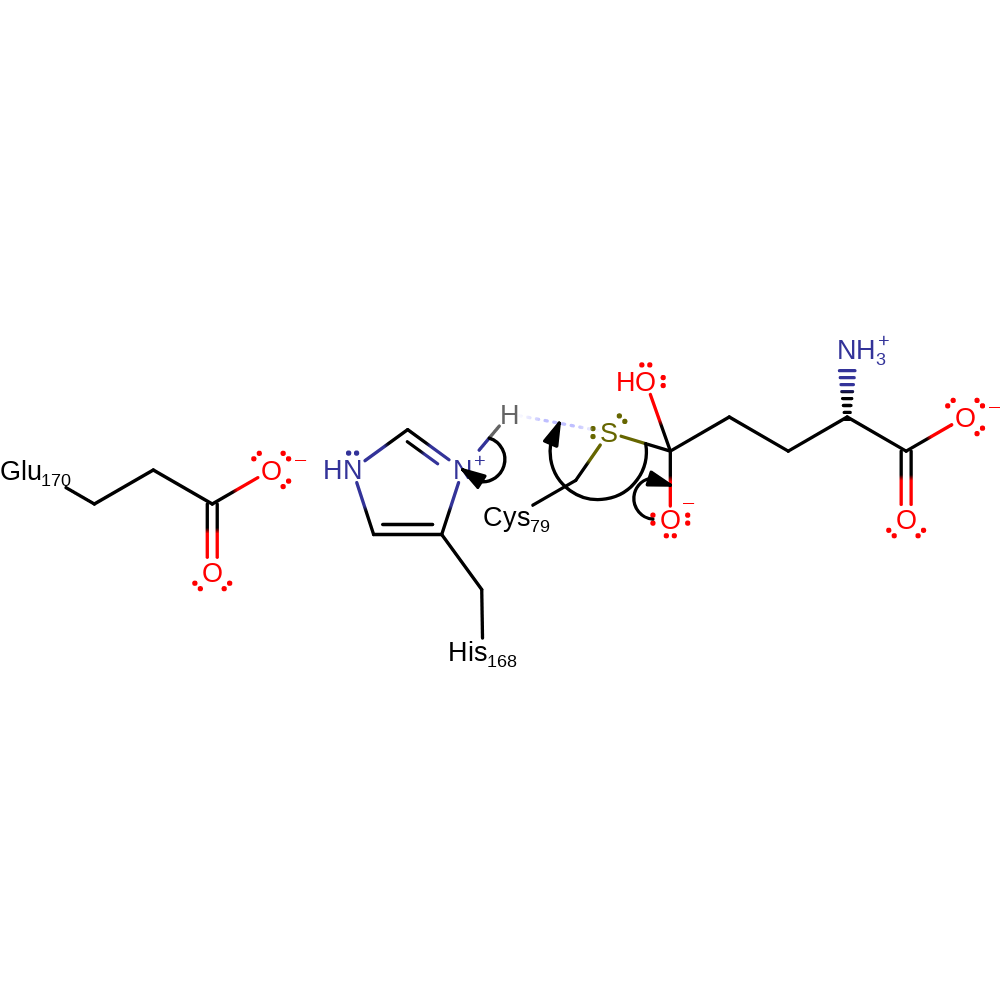
Step 7. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating Cys79, which deprotonates His168.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys79 | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu170 | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His168 | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys79 | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |
| His168 | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: