Phosphoadenylyl-sulfate reductase (thioredoxin)
Requiring thioredoxin as an electron donor, phosphoadenosine phosphosulphate reductase (CysH) catalyses the reduction of phosphoadenosine phosphosulphate (PAPS) to sulphite and phosphoadenosine phosphate (PAP). It is part of the pathway that synthesises sulfite from sulfate. This pathway for introducing sulfur into biological molecules which utilises phosphoadenylyl reductase is only present in prototrophic organsisms.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P17854
 (1.8.4.8)
(1.8.4.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1sur
- PHOSPHO-ADENYLYL-SULFATE REDUCTASE
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.620
 (see all for 1sur)
(see all for 1sur)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.8.4.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Thioredoxin reduces the active site disulfide bridge. Cys239' deprotonates the thioredoxin intermediate. The free thiol on Cys239 initiates nucleophilic attack at the substrate. The anionic phosphate leaving group accepts a proton from the covalently bound Cys239B. Cys239 attacks Cys239', eliminating sulfite with concomitant regeneration of the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1sur) | ||
| Cys239, Cys239 | Not found, Not found | Act as nucleophiles. In the enzyme's ground state, these cysteine residues are part of a disulfide bridge, which is cleaved during the course of the reaction by thioredoxin. This activates one of them to act as a nucleophile to attack the sulfur group of the substrate. Regeneration of the disulfide bridge eliminates the sulfite product. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton donor, activator, electrofuge, hydride acceptor |
| Trp205, Tyr209, Trp205, Tyr209 | Trp204A, Tyr208A, Trp204A(AA), Tyr208A(AA) | The residues that surround the cross-dimer disulfide bridge act to delocalise the increased electron density in the reaction stage transition state [PMID:7588765]. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, redox reaction, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regenerated, enzyme-substrate complex cleavageReferences
- Berendt U et al. (1995), Eur J Biochem, 233, 347-356. Reaction Mechanism of Thioredoxin: 3'-Phospho-adenylylsulfate Reductase Investigated by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. DOI:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.347_1.x. PMID:7588765.
- Lillig CH et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 22325-22330. Redox Regulation of 3'-Phosphoadenylylsulfate Reductase from Escherichia coli by Glutathione and Glutaredoxins. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m302304200. PMID:12682041.
- Savage H et al. (1997), Structure, 5, 895-906. Crystal structure of phosphoadenylyl sulphate (PAPS) reductase: a new family of adenine nucleotide α hydrolases. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00244-x. PMID:9261082.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys239 | covalently attached |
| Trp204A(AA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp204A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr208A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr208A(AA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys239 | covalently attached, electrofuge |
| Cys239 | nucleofuge |
| Cys239 | hydride acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, redox reaction, overall reactant used, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys239 | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp204A(AA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp204A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr208A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr208A(AA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys239 | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated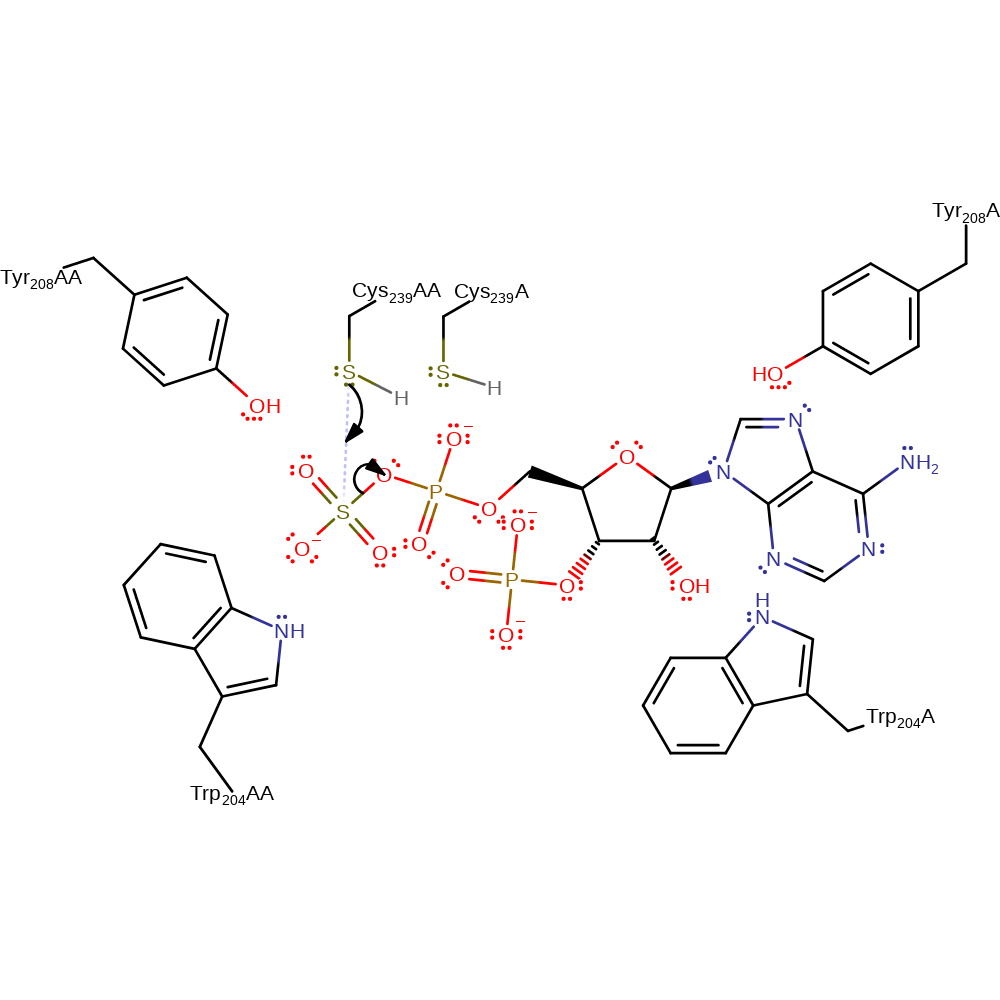
Step 3. The free thiol on Cys239 initiates nucleophilic attack at the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys239 | polar interaction, activator |
| Trp204A(AA) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp204A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr208A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr208A(AA) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys239 | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation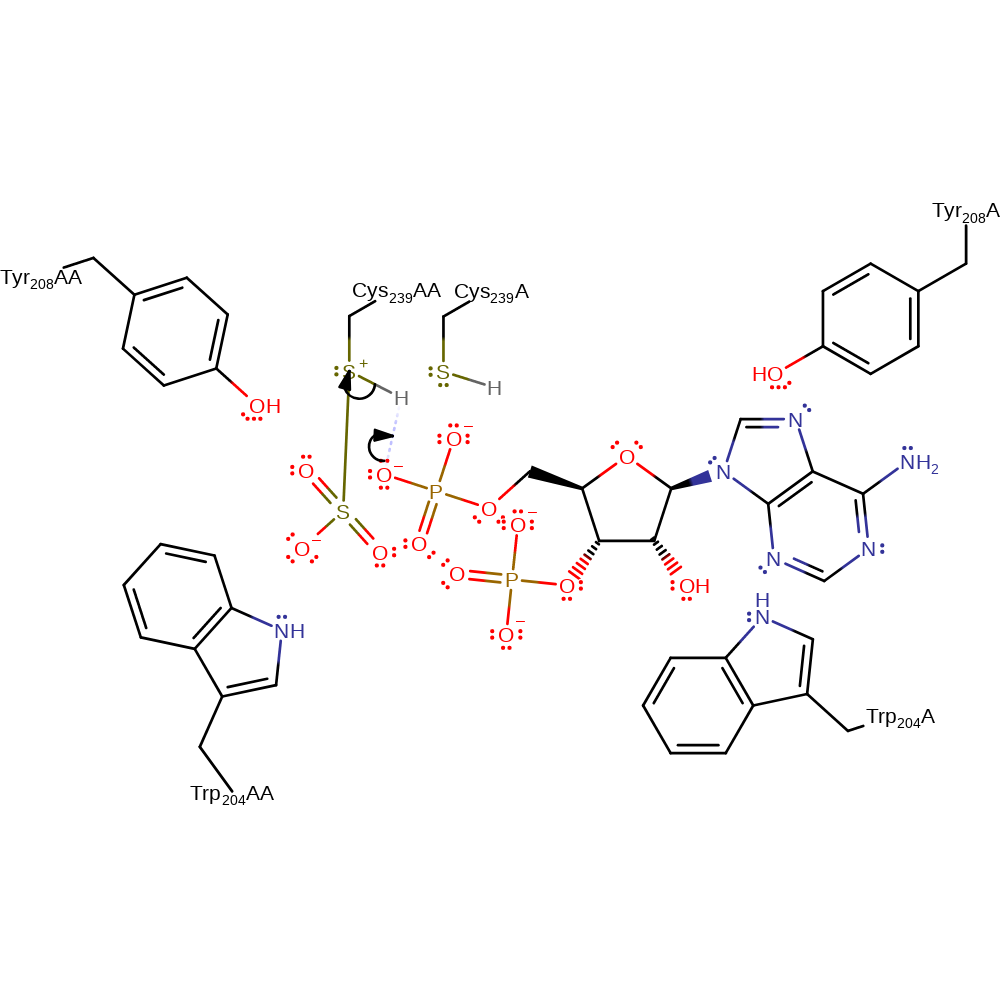
Step 4. The anionic phosphate leaving group accepts a proton from the covalently bound Cys239AA.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys239 | activator, hydrogen bond donor, covalently attached |
| Trp204A(AA) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr208A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr208A(AA) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys239 | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction step
Step 5. Cys239 attacks Cys239AA, eliminating sulfite with concomitant regeneration of the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys239 | activator |
| Cys239 | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys239 | electrophile, electrofuge |
| Cys239 | nucleophile, proton donor |






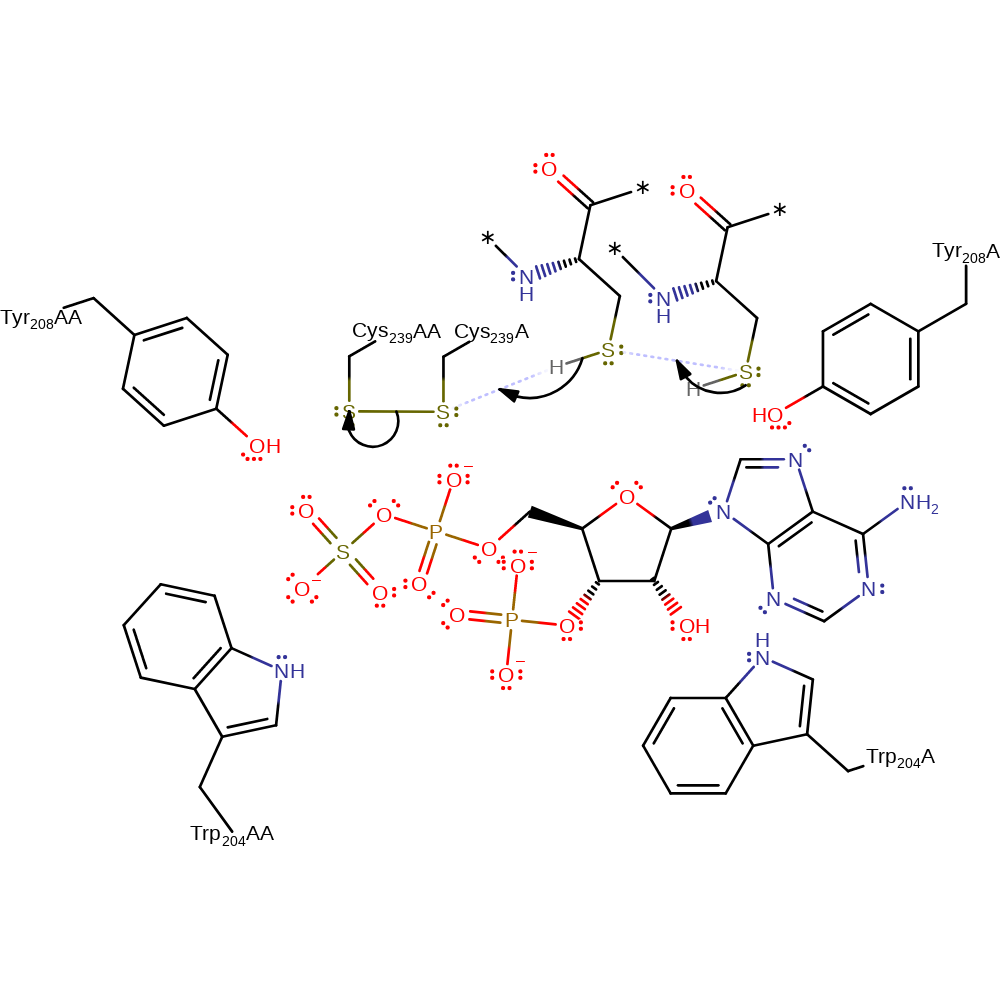

 Download:
Download: