Pyruvate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)
Catalyses the formation of acetate and carbon dioxide from pyruvate with the concomittant reduction of ubiquinone. This protein requires thiamine phosphate and FAD for activity. The bacterial enzyme is located on the inner surface of the cytoplasmic membrane and coupled to the respiratory chain via ubiquinone. It does not accept menaquinone as an acceptor. In Escherichia coli this is the primary complex responsible for aerobic growth, pyruvate oxidase (MACiE:274) acts as a backup system.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P07003
 (1.2.5.1)
(1.2.5.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
3ey9
- Structural basis for membrane binding and catalytic activation of the peripheral membrane enzyme pyruvate oxidase from Escherichia coli
(2.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.970
 (see all for 3ey9)
(see all for 3ey9)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), Thiamine(1+) diphosphate(3-) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.2.5.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Products
- All Steps
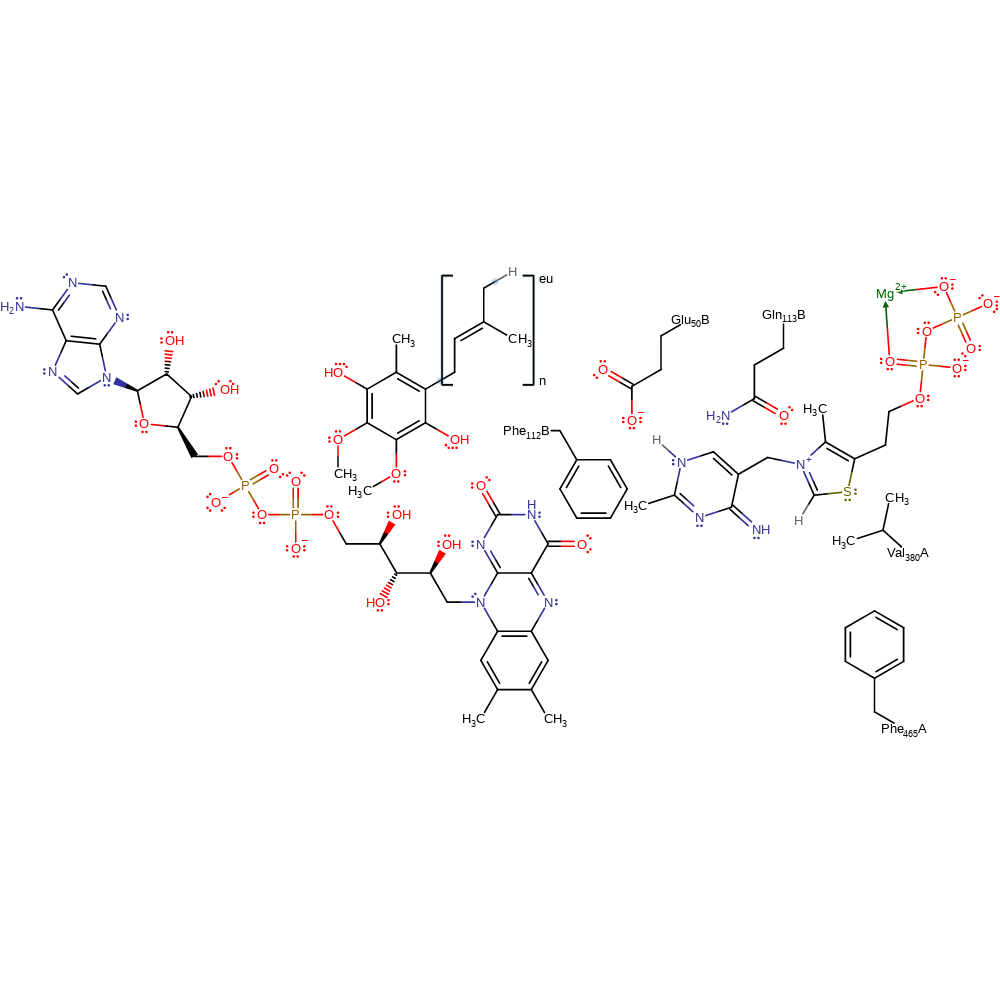
Introduction
Glu50' deprotonates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor at the N1 position. This initiates double bond rearrangement which results in the deprotonation of the N=CH-S group. This activates the cofactor towards electrophilic attack. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of pyruvate in an addition reaction. The conjugated double bond system of the cofactor undergoes rearrangement which results in the deprotonation of Glu50'. The covalently bound pyruvate undergoes decarboxylation. A single electron is transferred from the high energy thamine diphosphate enamine intermediate to the FAD cofactor. This results in bond order rearrangement and deprotonation of the alcohol group present on the intermediate. Tautomerisation of the radical intermediate occurs. The thiamine ring nitrogen acts as an electron sink in the formation of a second radical tautomer. Water acts as a nucleophile towards the neutral radical thiamine diphosphate-pyruvate adduct. The hydrolysis product delivers a second reducing equivalent to the FAD cofactor. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating acetate and regenerating the carbanionic form of thiamine diphosphate. The thiamine diphosphate cofactor is regenerated on deprotonation of the pyruvate product. Ubiquinone receives one reducing equivalent from the reduced FAD cofactor. The second reducing equivalent is transferred to the bound ubiquinone. This forms the electron transport agent ubiquinol and regenerates the FAD cofactor.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3ey9) | ||
| Gln113, Val380 | Gln113B, Val380A | The steric and electrostatic interactions between the intermediate and residues Val380 and Gln133, respectively holds the TPP cofactor in a high energy conformation which also contributes to enhanced reactivity. | promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe465 | Phe465A | Phe465 has been shown by kinetic analysis to be crucial for the efficient transfer of electrons between the thiamine diphosphate and FAD cofactors [PMID:18988747]. | polar/non-polar interaction, electrostatic destabiliser, promote heterolysis, radical stabiliser, steric role |
| Glu50 | Glu50B | Acts as a general acid/base in the activation of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, increase acidity, promote heterolysis |
| Phe112 | Phe112B | Helps stabilise the high energy radical intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | radical stabiliser, promote heterolysis, electrostatic destabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intramolecular elimination, decarboxylation, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, electron transfer, redox reaction, rate-determining step, tautomerisation (not keto-enol), inferred reaction step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Neumann P et al. (2008), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 105, 17390-17395. Structural basis for membrane binding and catalytic activation of the peripheral membrane enzyme pyruvate oxidase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0805027105. PMID:18988747.
- Tittmann K (2009), FEBS J, 276, 2454-2468. Reaction mechanisms of thiamin diphosphate enzymes: redox reactions. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06966.x. PMID:19476487.
- Chang YY et al. (2000), Biochem J, 352, 717-724. Conversion of Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase to an ‘α-ketobutyrate oxidase’. DOI:10.1042/bj3520717. PMID:11104678.
- Tittmann K et al. (1998), J Biol Chem, 273, 12929-12934. Activation of Thiamin Diphosphate and FAD in the Phosphatedependent Pyruvate Oxidase fromLactobacillus plantarum. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.21.12929. PMID:9582325.
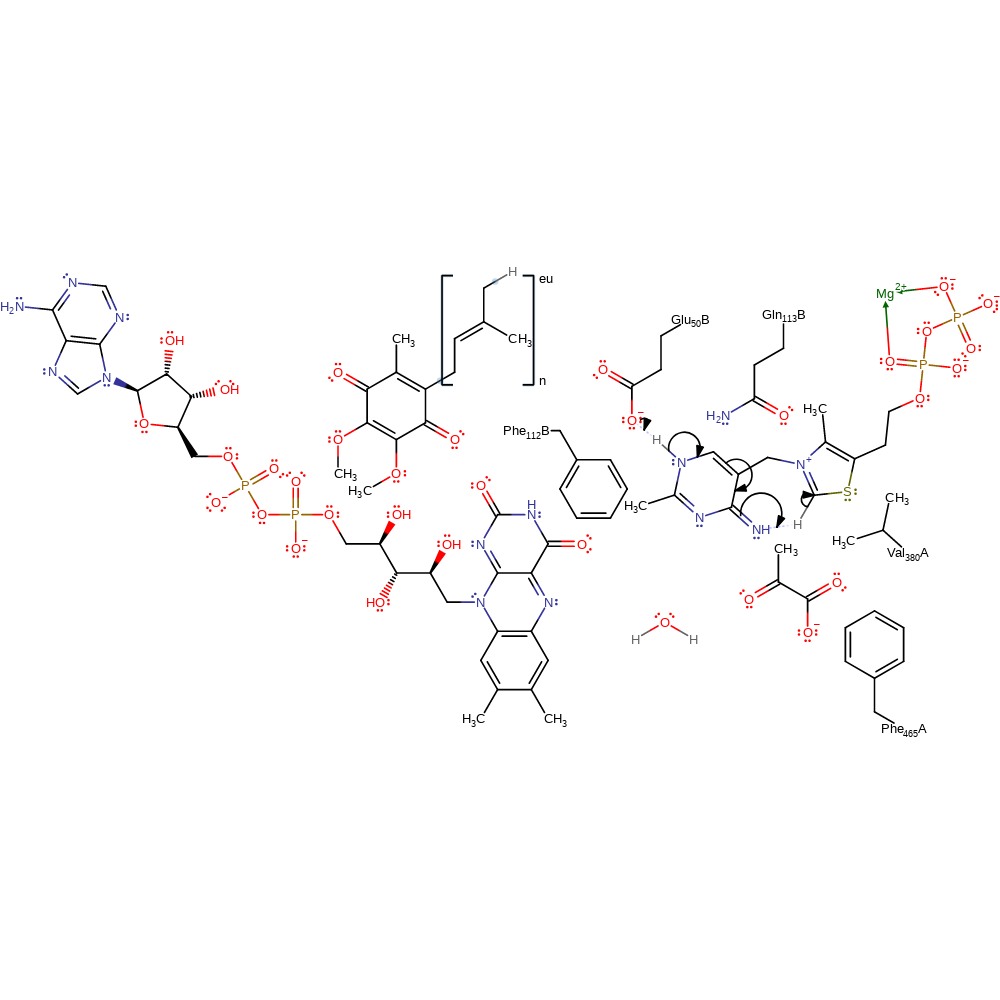
Step 1. Glu50' deprotonates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor at the N1 position. This initiates double bond rearrangement which results in the deprotonation of the N=CH-S group. This activates the cofactor towards electrophilic attack.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Val380A | van der waals interaction |
| Glu50B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, intermediate formation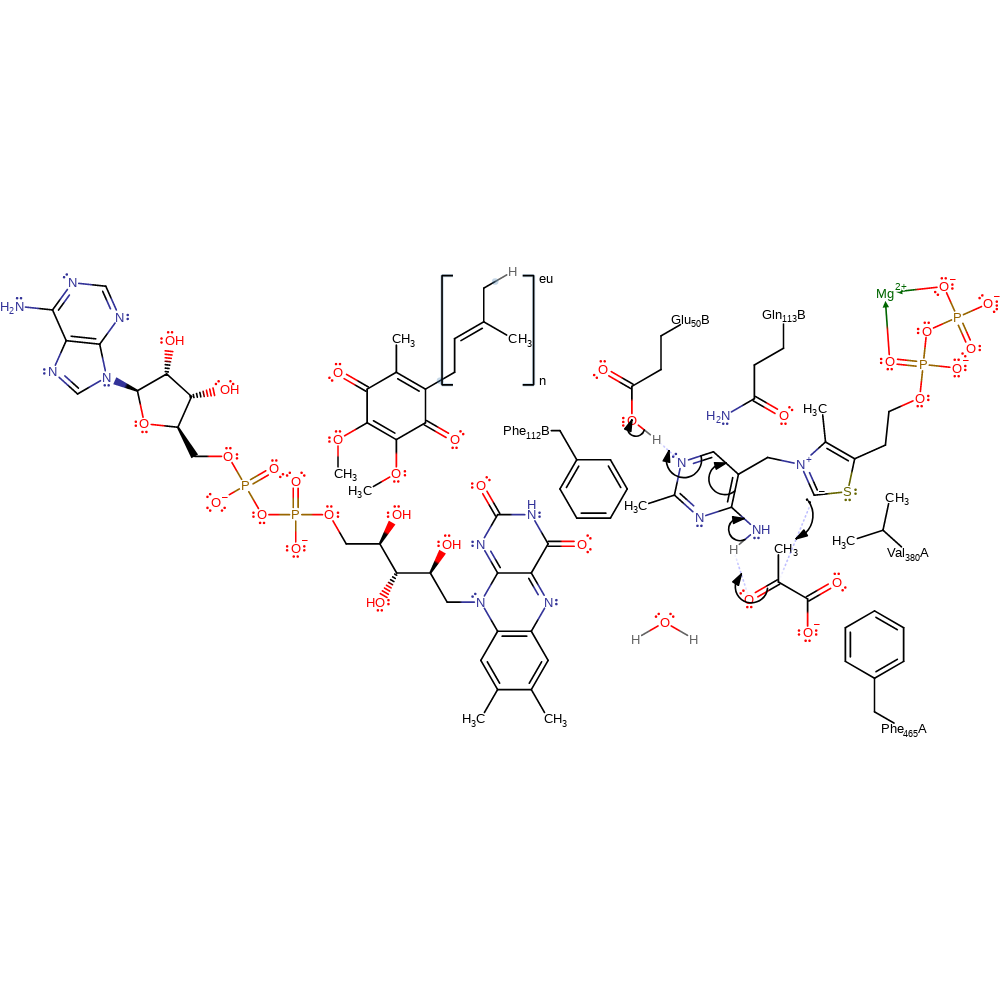
Step 2. The thiamine diphosphate cofactor maintains the canonical V conformation [PMID:18988747]. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of pyruvate in an addition reaction. The conjugated double bond system of the cofactor undergoes rearrangement which results in the deprotonation of Glu50'.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | van der waals interaction |
| Glu50B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation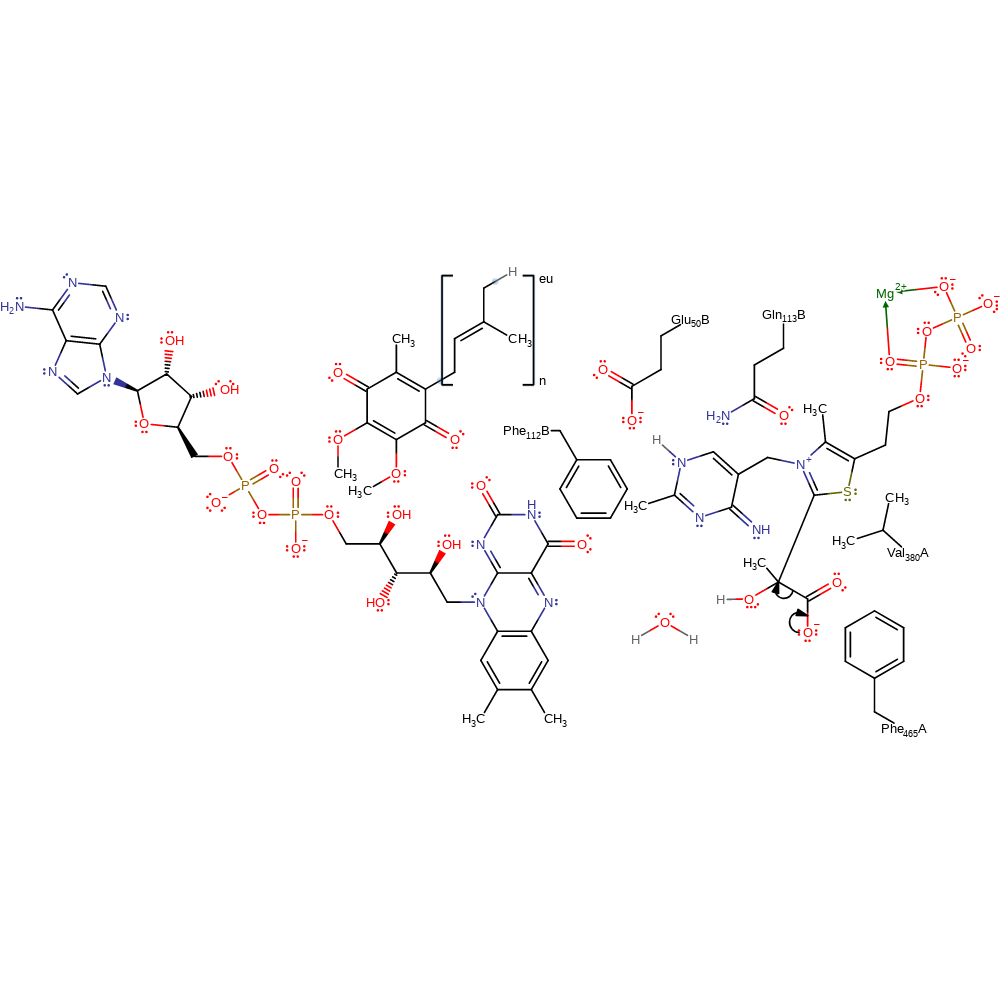
Step 3. The covalently bound pyruvate undergoes decarboxylation. The interactions between the thiamine diphosphate-pyruvate adduct and surrounding residues direct a reactive conformation which lowers the reaction barrier towards decarboxylation [PMID:18988747, PMID:11104678]. This step is not thought to be rate determining [PMID:19476487].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | electrostatic destabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Phe112B | electrostatic destabiliser, promote heterolysis, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, promote heterolysis |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor, promote heterolysis |
| Val380A | steric role, electrostatic destabiliser, promote heterolysis |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, decarboxylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed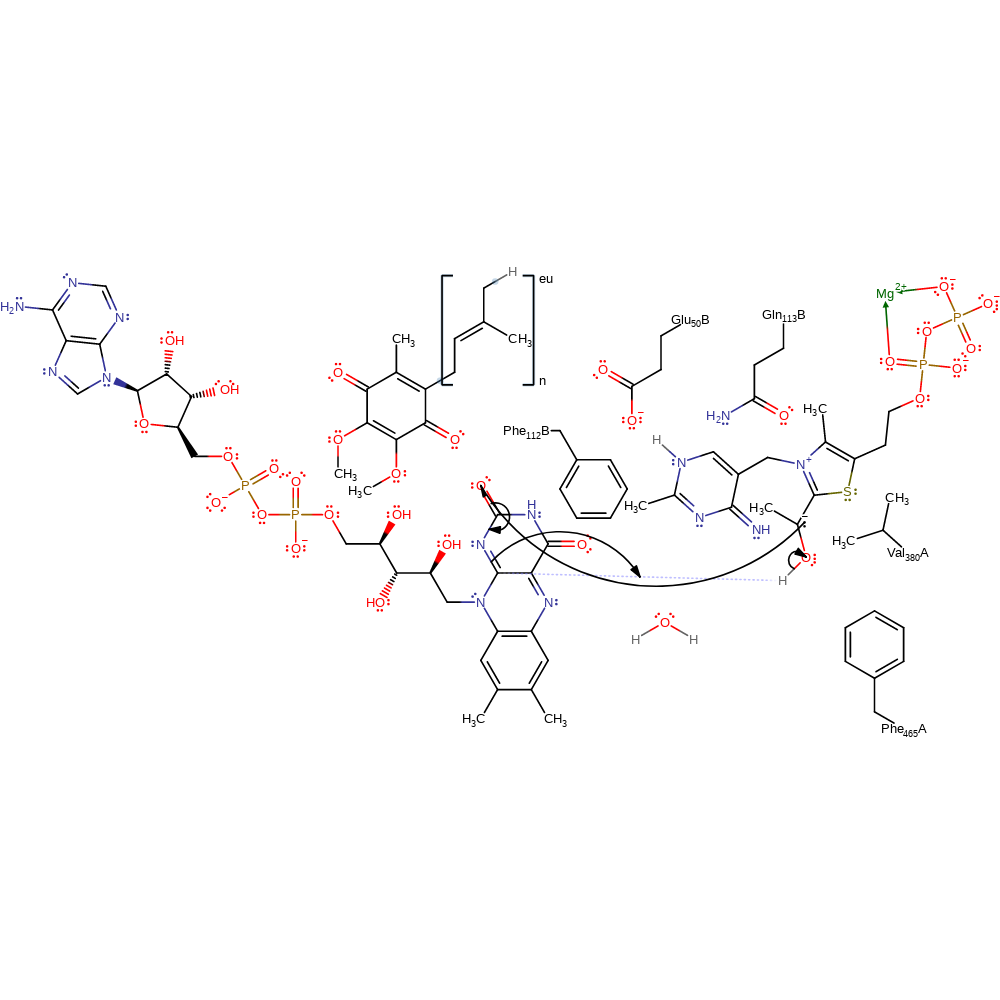
Step 4. A single electron is transferred from the high energy thamine diphosphate enamine intermediate to the FAD cofactor. This results in bond order rearrangement and deprotonation of the alcohol group present on the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, redox reaction, cofactor used, intermediate formation, rate-determining step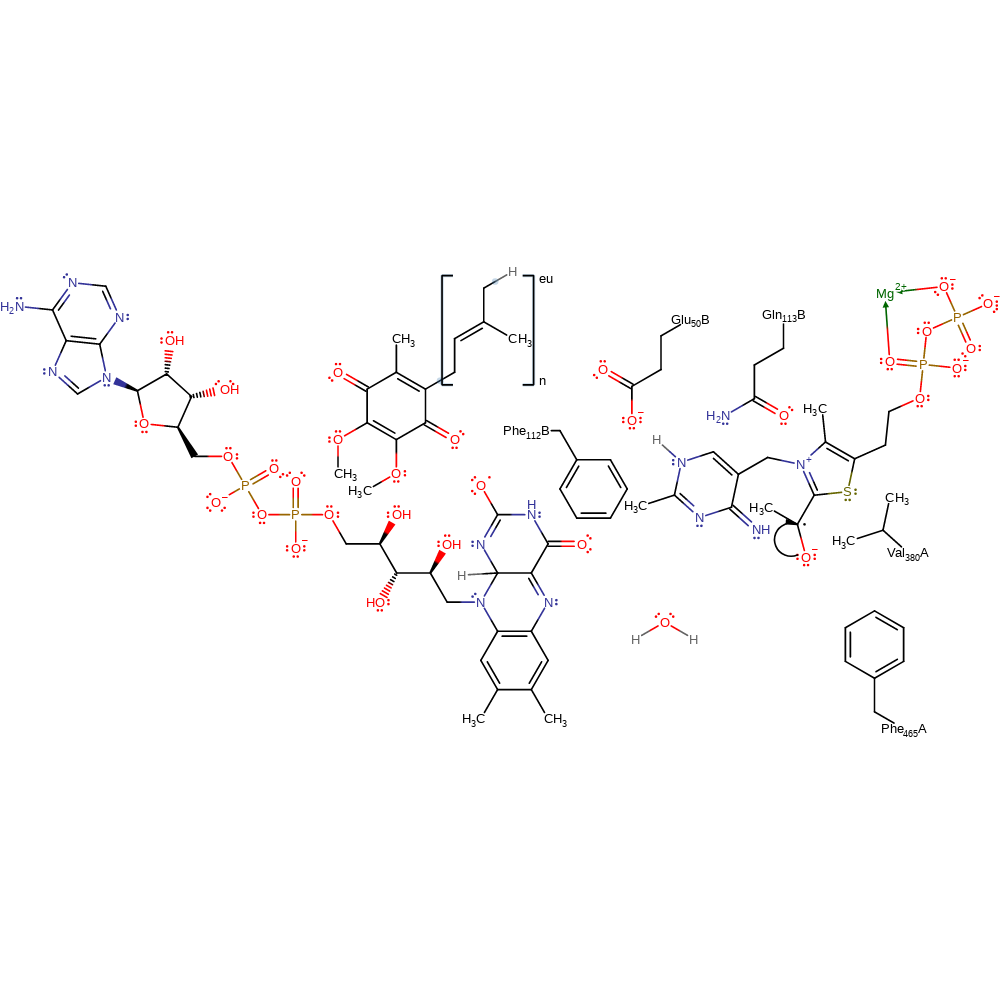
Step 5. Tautomerisation of the radical intermediate occurs. The product of the rearrangement is required in the next reaction step [PMID:19476487].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation, inferred reaction step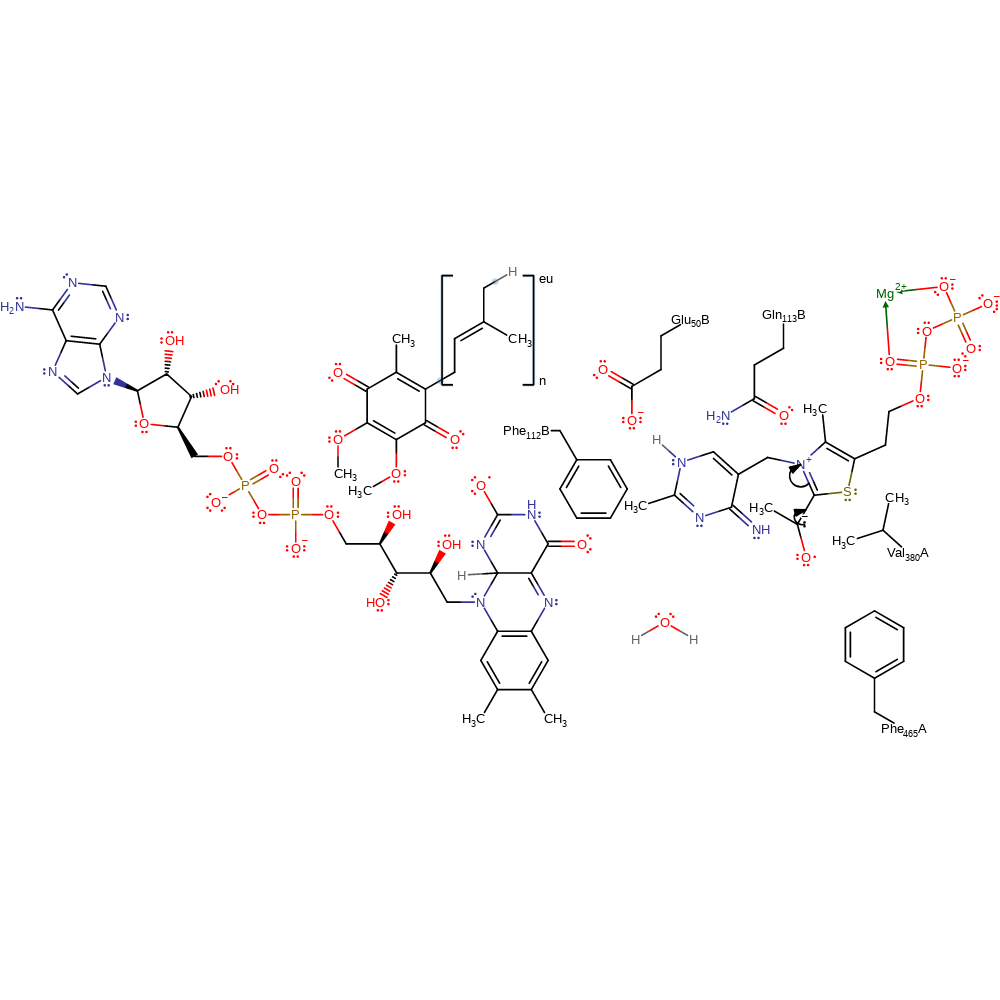
Step 6. The thiamine ring nitrogen acts as an electron sink in the formation of a second radical tautomer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation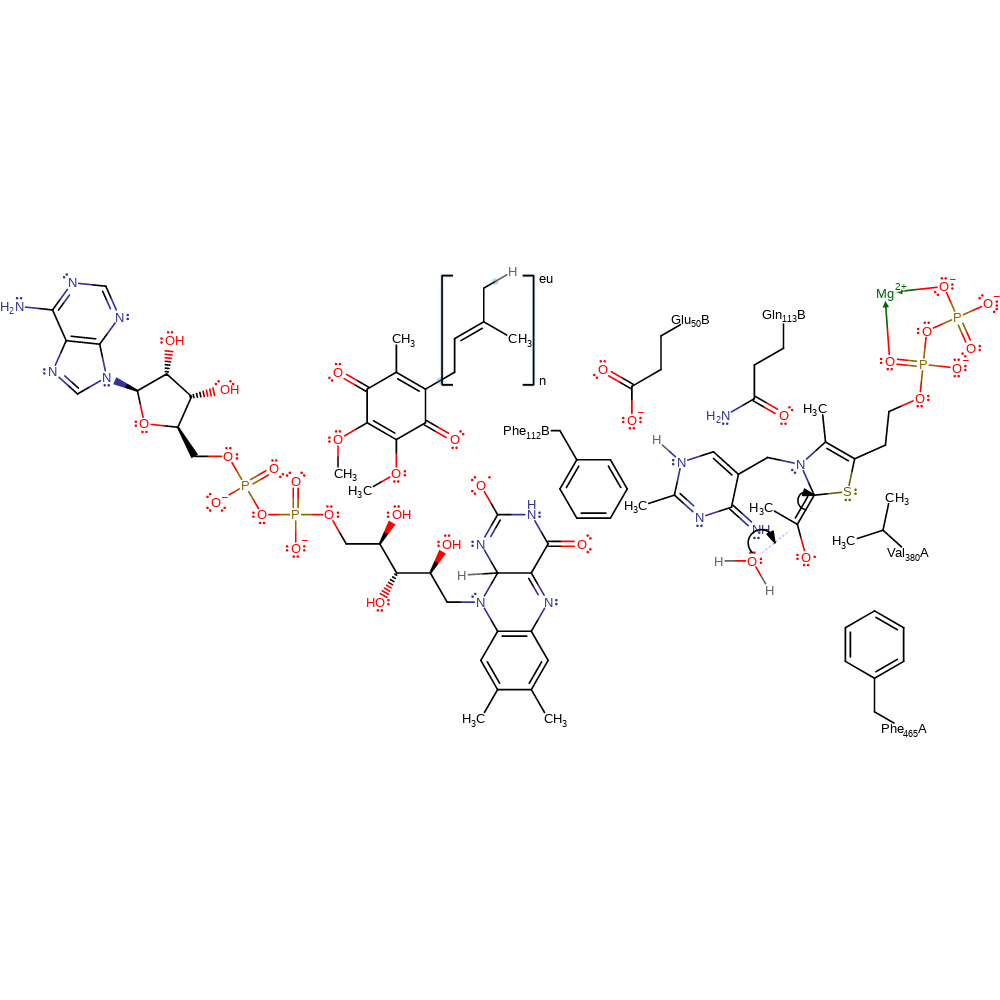
Step 7. Water acts as a nucleophile towards the neutral radical thiamine diphosphate-pyruvate adduct.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation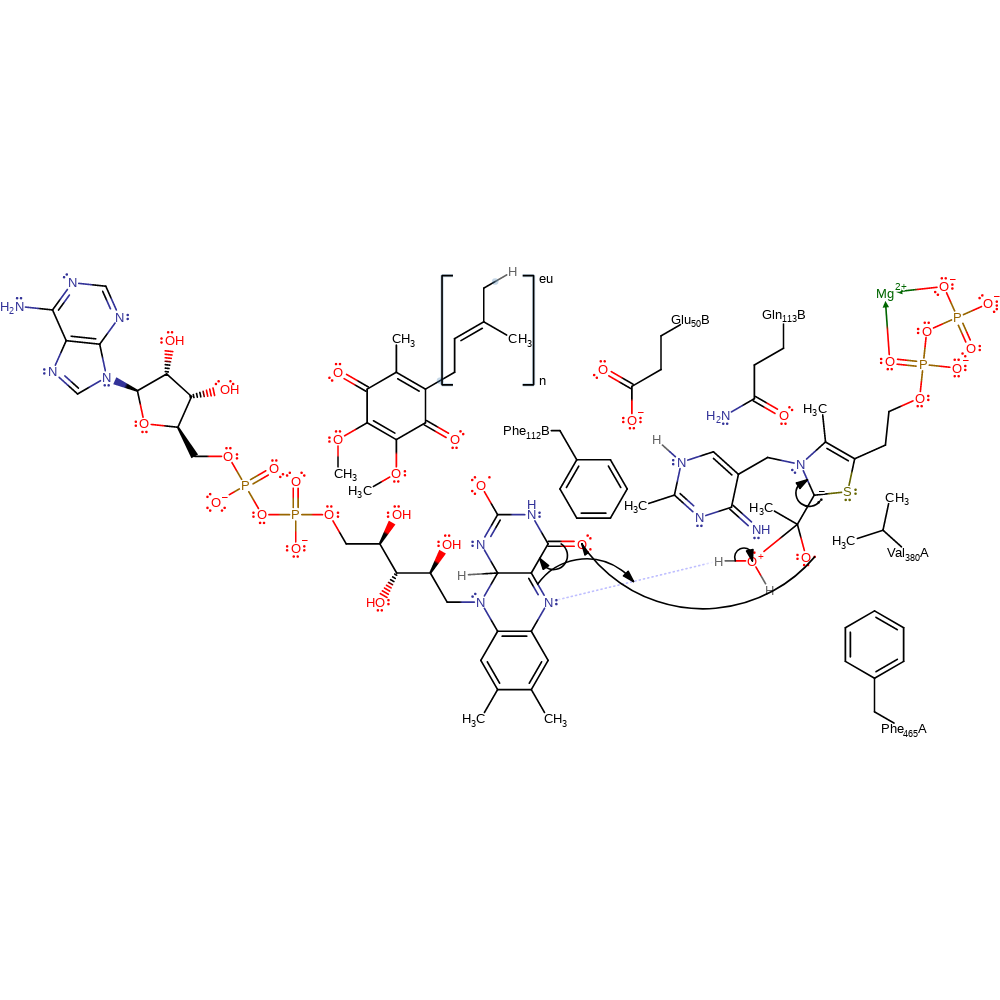
Step 8. The hydrolysis product delivers a second reducing equivalent to the FAD cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, redox reaction, intermediate formation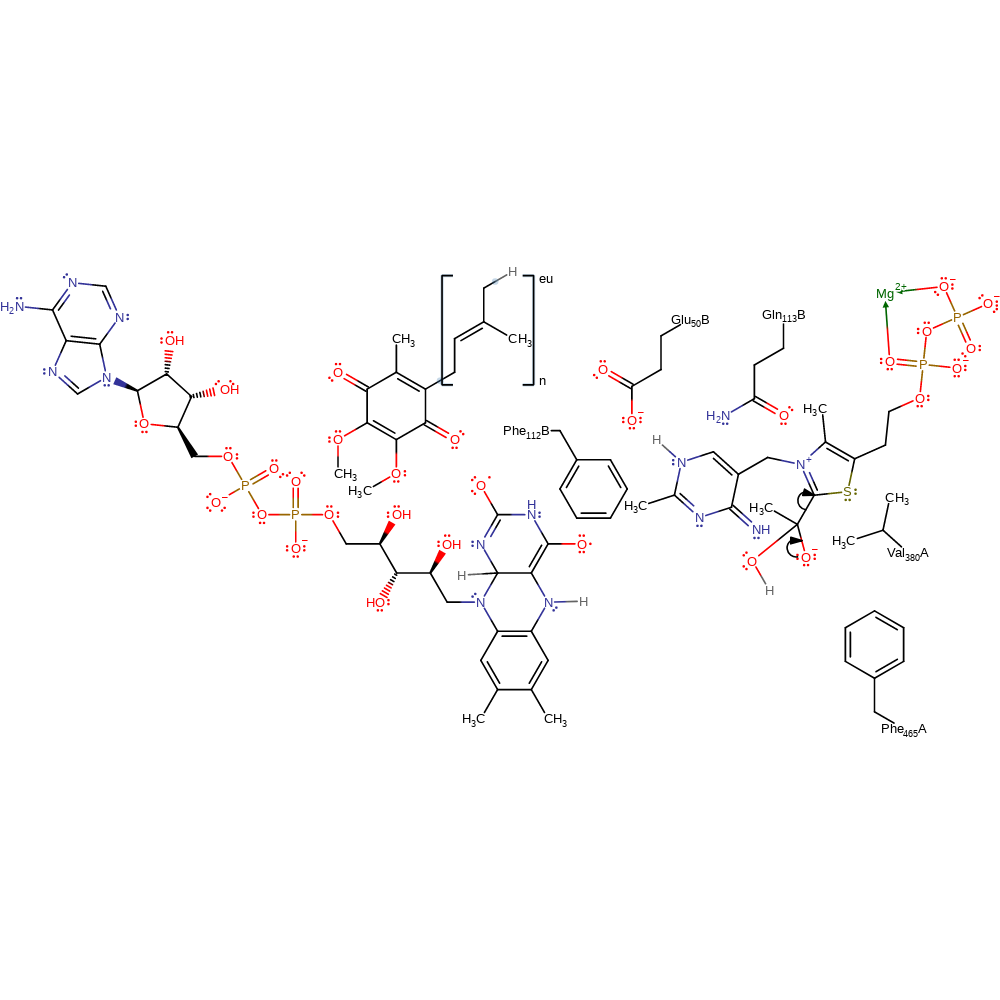
Step 9. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating acetate and regenerating the carbanionic form of thiamine diphosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed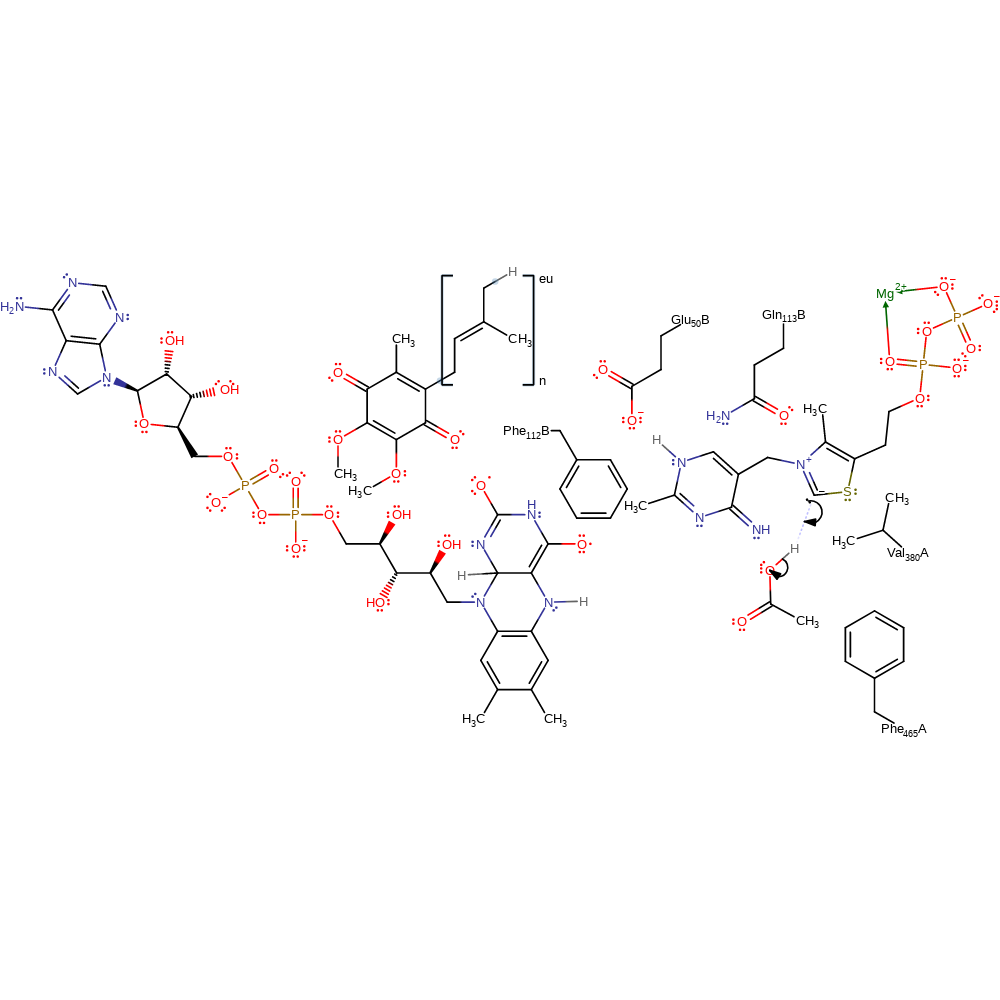
Step 10. The thiamine diphosphate cofactor is regenerated on deprotonation of the pyruvate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe112B | radical stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val380A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, intermediate terminated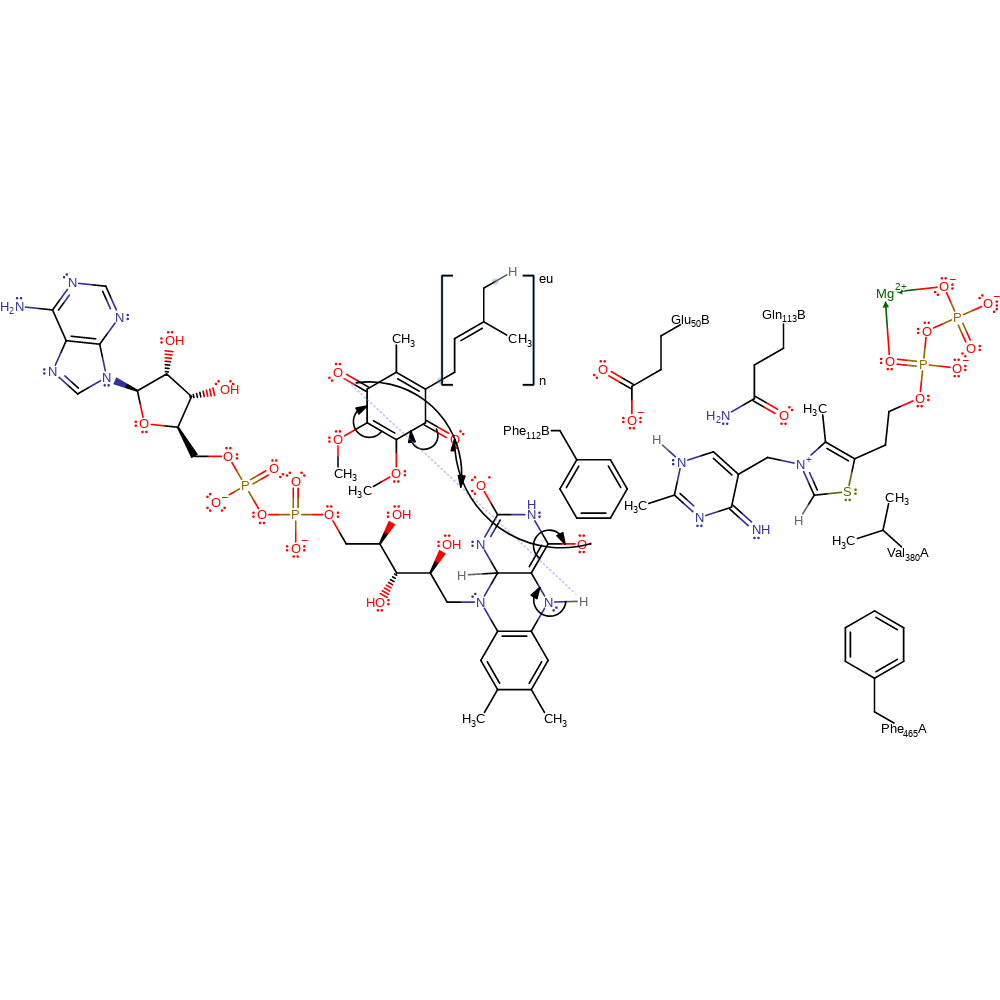
Step 11. The reduction of FAD initiates a conformational rearrangement of the C terminus. This results in the exposure of a high lipid affinity binding site.
Pyruvate oxidase from E. coli does not use molecular oxygen as a final electron acceptor, unlike its Lactobacillus plantarum analogue [PMID:18988747, PMID:11104678]. Once pyruvate has adhered to a biological membrane, the prior structural rearrangement now allows two electrons to be shuttled from reduced flavin to the membrane bound ubiquinone electron carrier [PMID:18988747]. Ubiquinone receives one reducing equivalent from the reduced FAD cofactor.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, redox reaction, overall reactant used, intermediate formation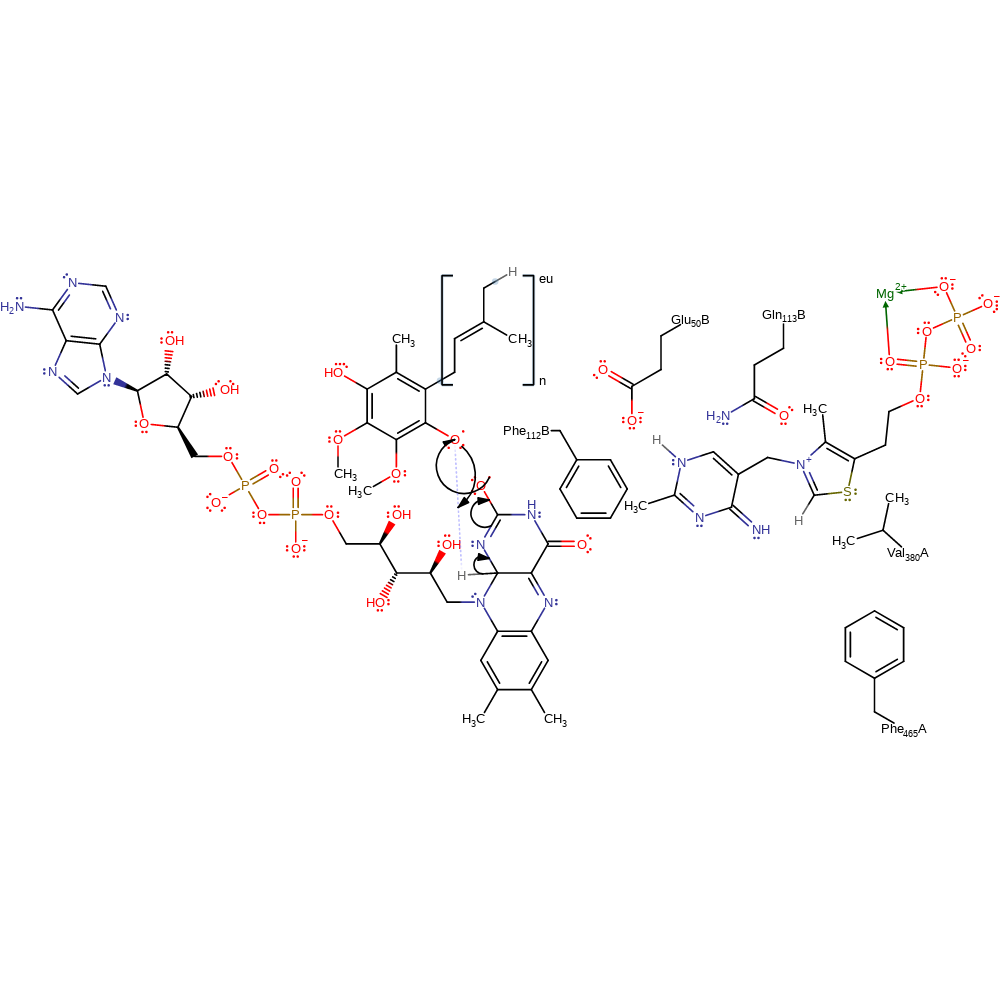
Step 12. The second reducing equivalent is transferred to the bound ubiquinone. This forms the electron transport agent ubiquinol and regenerates the FAD cofactor. Ubiquinol acts as a mobile electron carrier in the electron transport chain [PMID:18988747].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe465A | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond acceptor |






 Download:
Download: