L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase
L-ribulose-5-phosphate-4-epimerase catalyses the interconversion of L-ribulose 5-phosphate(L-Ru5P) and D-xylulose 5-phosphate(D-Xu5P). It belongs to a superfamily of epimerases/aldolases that catalyse carbon-carbon bond cleavage reactions via a metal stabilised enolate intermediate. The conversion from L-Ru5P to D-Xu5P allows bacteria to utilise arabinose as an energy source by converting it into an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway(D-Xu5P).
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P08203
 (5.1.3.4)
(5.1.3.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1jdi
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF L-RIBULOSE-5-PHOSPHATE 4-EPIMERASE
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.225.10
 (see all for 1jdi)
(see all for 1jdi)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.1.3.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism involves the initial retroaldol cleavage between C3 and C4 of the substrate after the deprotonation of the C4-OH group by a base. The cleavage generates glycolaldehyde phosphate and metal -bound enolate of dihydroxyactone as intermediates. A subsequent aldol addition of the same face of the enolate to the opposite face of the aldehyde generates the epimeric product. Tyr229 acts as the base for the deprotonation of L-Ru5P while Asp120 acts as the acid to protonate the product to complete the epimerisation. In the reverse reaction, Asp acts as the base to deprotonate D-Xu5P and Tyr229 the acid. Zn2+ acts as an electrophilic catalyst by coordinating to the ketone oxygen at C2 to promote enolate formation.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1jdi) | ||
| His95, His97, His171 | His95A, His97A, His171A | Binds the Zn ion | metal ligand |
| Tyr229 | TyrNone(229)A | Plays a role as acid/base in catalysis. In the conversion from L-Ru5P to D-Xu5P, it acts as a base to deprotonate the substrate, L-Ru5P. In the reverse reaction, it acts as an acid to protonate the product, L-Ru5P. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp120 | Asp120A(AC) | In the conversion from D-Xu5P to L-Ru5P, it acts as a base to deprotonate the substrate, D-Xu5P. In the reverse reaction, it acts as an acid to protonate the product, D-Xu5P. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Samuel J et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 14772-14780. Catalysis and Binding inl-Ribulose-5-Phosphate 4-Epimerase: A Comparison withl-Fuculose-1-Phosphate Aldolase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi011252v. PMID:11732896.
- Luo Y et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 14763-14771. The Structure ofl-Ribulose-5-Phosphate 4-Epimerase: An Aldolase-like Platform for Epimerization†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0112513. PMID:11732895.
- Lee LV et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 4821-4830. Role of Metal Ions in the Reaction Catalyzed byl-Ribulose-5-phosphate 4-Epimerase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9928952. PMID:10769139.
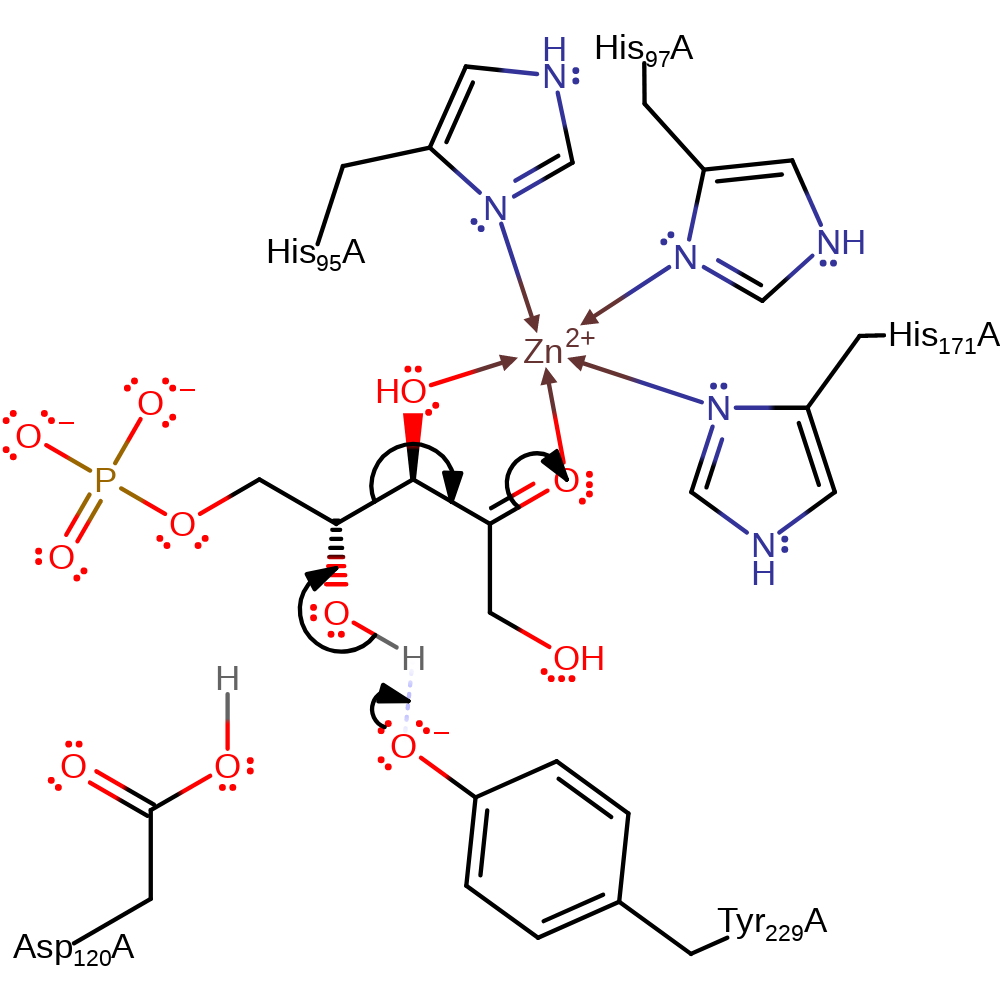
Step 1. Initial retroaldol cleavage between C3 and C4 of the substrate after the deprotonation of the C4-OH group by Tyr229. After the initial cleavege, the glycolaldehyde phosphate intermediate rotates in the active site in order to present the opposite face to the enolate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp120A(AC) | hydrogen bond donor |
| TyrNone(229)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His95A | metal ligand |
| His97A | metal ligand |
| His171A | metal ligand |
| TyrNone(229)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, intermediate formation, overall reactant used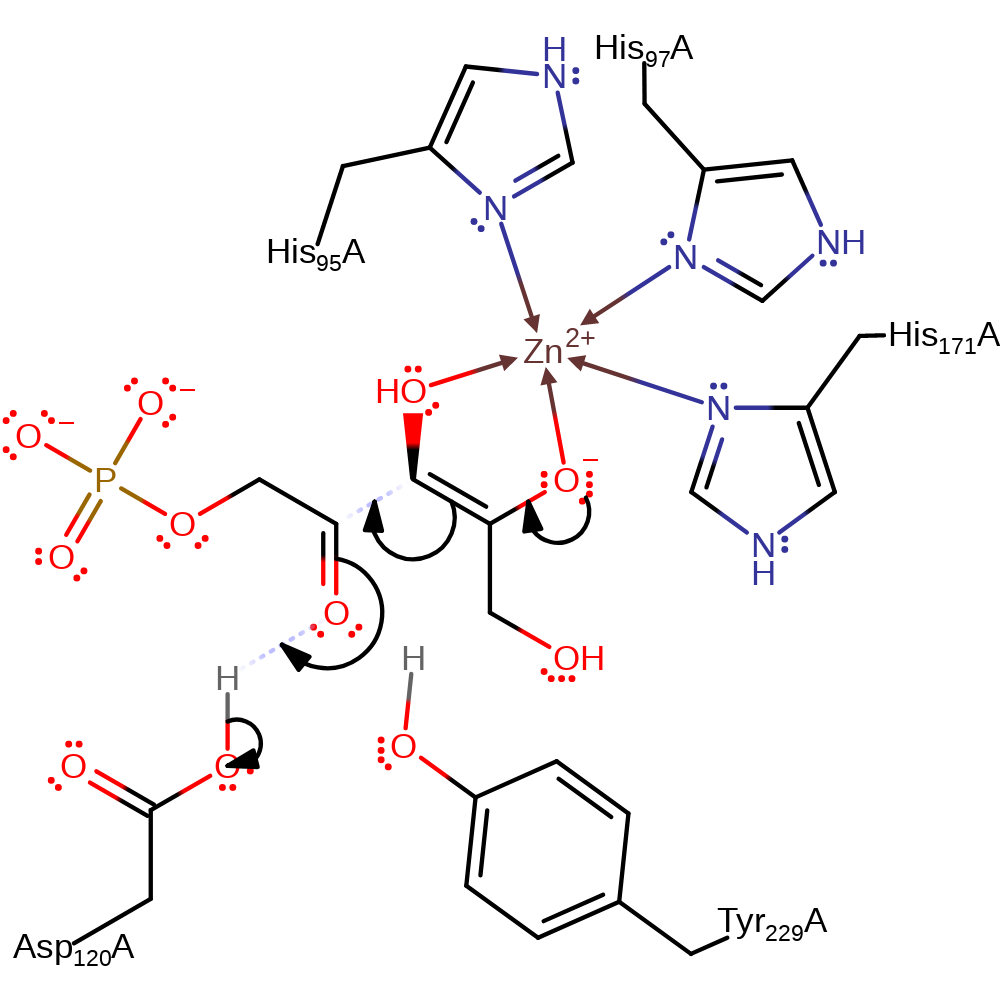
Step 2. Aldol addition of the same face of the enolate intermediate to the opposite face of the glycolaldehyde phosphate intermediate
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp120A(AC) | hydrogen bond donor |
| TyrNone(229)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His95A | metal ligand |
| His97A | metal ligand |
| His171A | metal ligand |
| Asp120A(AC) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed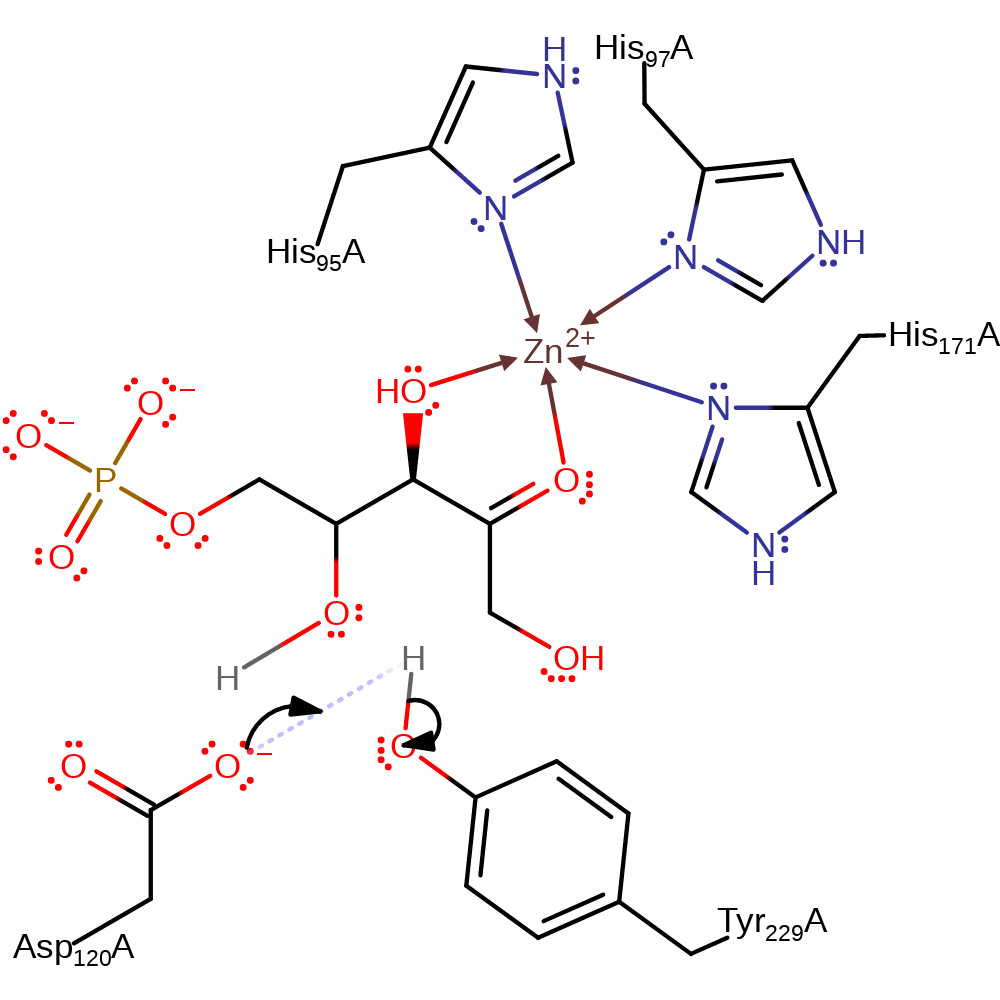
Step 3. Inferred return step. Asp120 deprotonates Tyr229.)ReactiveCentres=(O,H,O
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp120A(AC) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| TyrNone(229)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His95A | metal ligand |
| His97A | metal ligand |
| His171A | metal ligand |
| Asp120A(AC) | proton acceptor |
| TyrNone(229)A | proton donor |


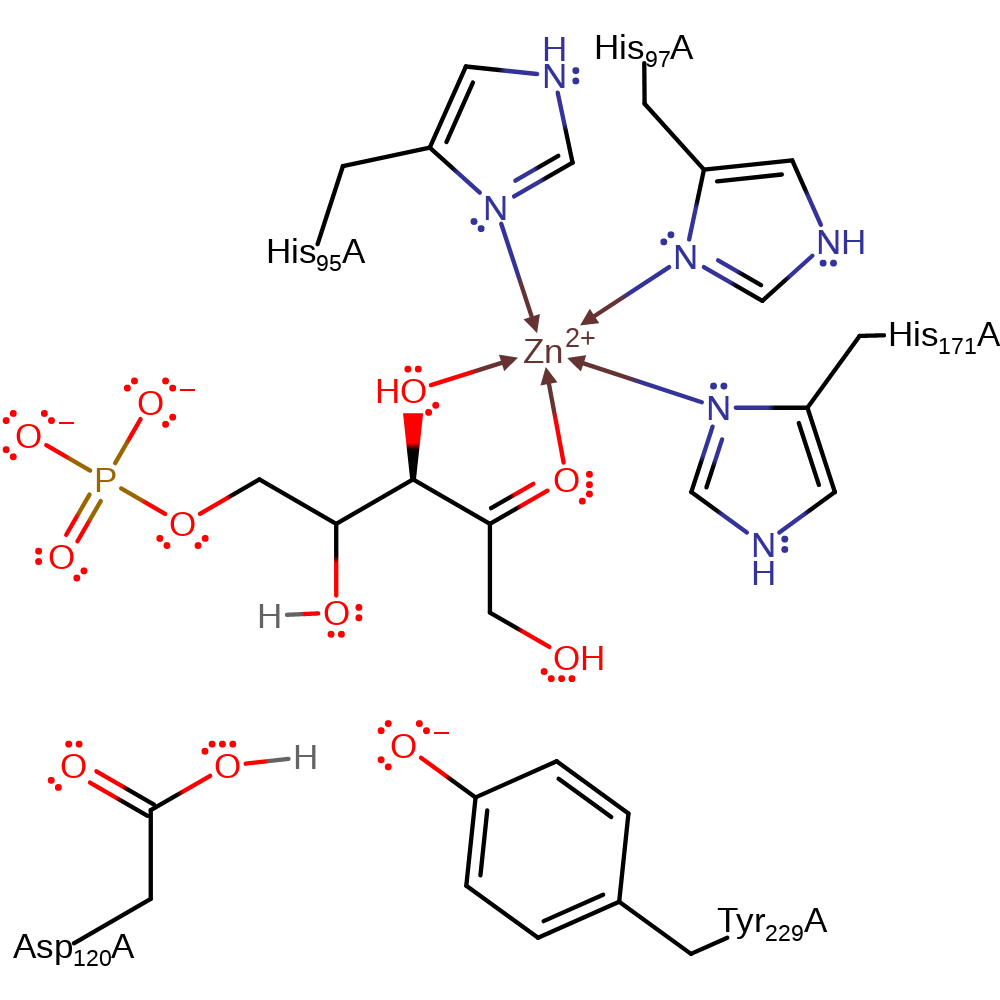 Download:
Download: