Ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase (cytoplasmic)
Ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase (EC:5.1.3.1) (also known as RPE, pentose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase or PPE) is the enzyme that converts D-ribulose 5-phosphate (Ru5P) into D-xylulose 5-phosphate in Calvin's reductive pentose phosphate cycle. RPE has been found in a wide range of bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi and plants. All the proteins have from 209 to 241 amino acid residues and have a TIM barrel structure.
This enzyme participates in both the oxidative and reductive pentose phosphate pathways and is thus an amphibolic enzyme [PMID:12547196]. There is some discussion as to whether this enzyme is zinc dependent or not. No zinc dependence has been reported [PMID:12547196]. The zinc independent (in which a water molecule is bound in place of a zinc ion to the two histidine residues that are seen as the zinc binding ligands as well as the two catalytic aspartate residues) mechanism has issues relating to how the intermediate formed is stabilised, and it has been suggested that the three strictly conserved methionines (Met40, Met71 and Met144) act as a transient 'electrostatic cushion' [PMID:10191144]. However, the alternative in which the zinc ion stabilises the oxyanion formed is more attractive [PMID:12547196] with the methionine residues aiding in this process and ensuring a hydrophobic and thus proton free environment. The actual mechanisms (with respect to the bonds formed and cleaved) are identical between the two proposals, the only difference lies in how the intermediate is stabilised [PMID:10191144, PMID:12547196, PMID:15333955].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9SE42
 (5.1.3.1)
(5.1.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryza sativa Japonica Group (Japanese rice)

- PDB
-
1h1z
- The structure of the cytosolic D-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase from rice complexed with sulfate and zinc
(3.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 1h1z)
(see all for 1h1z)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.1.3.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Asp38 deprotonates the C3 of the substrate molecule, causing a rearrangement of the double bonds and the formation of the enolate form. The enolate then collapses back to the keto form with concomitant deprotonation of Asp178, forming the xylulose product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1h1z) | ||
| Asp179 | Asp178(179)A | Forms part of the zinc binding site. Also acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp39 | Asp38(39)A | Forms part of the zinc binding site and acts as a general acid/base. Upon protonation, it leaves the Zn(II) ligand sphere leaving room for the negatively charged intermediate to be stabilised as a zinc ligand [PMID:12547196]. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser12 | Ser11(12)A | Activates and stabilises Asp38. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Met145, Met72, Met41 | Met144(145)A, Met71(72)A, Met40(41)A | These methionine residues aid catalysis by ensuring a hydrophobic and thus proton free environment. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His37, His70 | His36(37)A, His69(70)A | Forms part of the divalent metal binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Jelakovic S et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 326, 127-135. Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of the Cytosolic d-Ribulose-5-phosphate 3-Epimerase from Rice. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01374-8. PMID:12547196.
- Liang W et al. (2011), FASEB J, 25, 497-504. Conversion of D-ribulose 5-phosphate to D-xylulose 5-phosphate: new insights from structural and biochemical studies on human RPE. DOI:10.1096/fj.10-171207. PMID:20923965.
- Akana J et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 2493-2503. D-Ribulose 5-phosphate 3-epimerase: functional and structural relationships to members of the ribulose-phosphate binding (beta/alpha)8-barrel superfamily. DOI:10.1021/bi052474m. PMID:16489742.
- Wise EL et al. (2004), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 60, 1687-1690. Structure ofD-ribulose 5-phosphate 3-epimerase fromSynechocystisto 1.6 Å resolution. DOI:10.1107/s0907444904015896. PMID:15333955.
- Kopp J et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 287, 761-771. Structure and mechanism of the amphibolic enzyme d-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase from potato chloroplasts. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2643. PMID:10191144.

Step 1. Asp38 deprotonates the C3 of the substrate molecule, causing a rearrangement of the double bonds and the formation of the enolate form. Upon protonation, Asp38 leaves the Zn(II) ligand sphere leaving room for the negatively charged intermediate to be stabilised as a zinc ligand [PMID:12547196]. Three conserved methionines are essential for maintaining a proton free environment to ensure that the epimerisation (and not isomerisation) occurs [PMID:12547196].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp178(179)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp38(39)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser11(12)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp178(179)A | metal ligand |
| Asp38(39)A | metal ligand |
| His36(37)A | metal ligand |
| His69(70)A | metal ligand |
| Met40(41)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met71(72)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met144(145)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp38(39)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used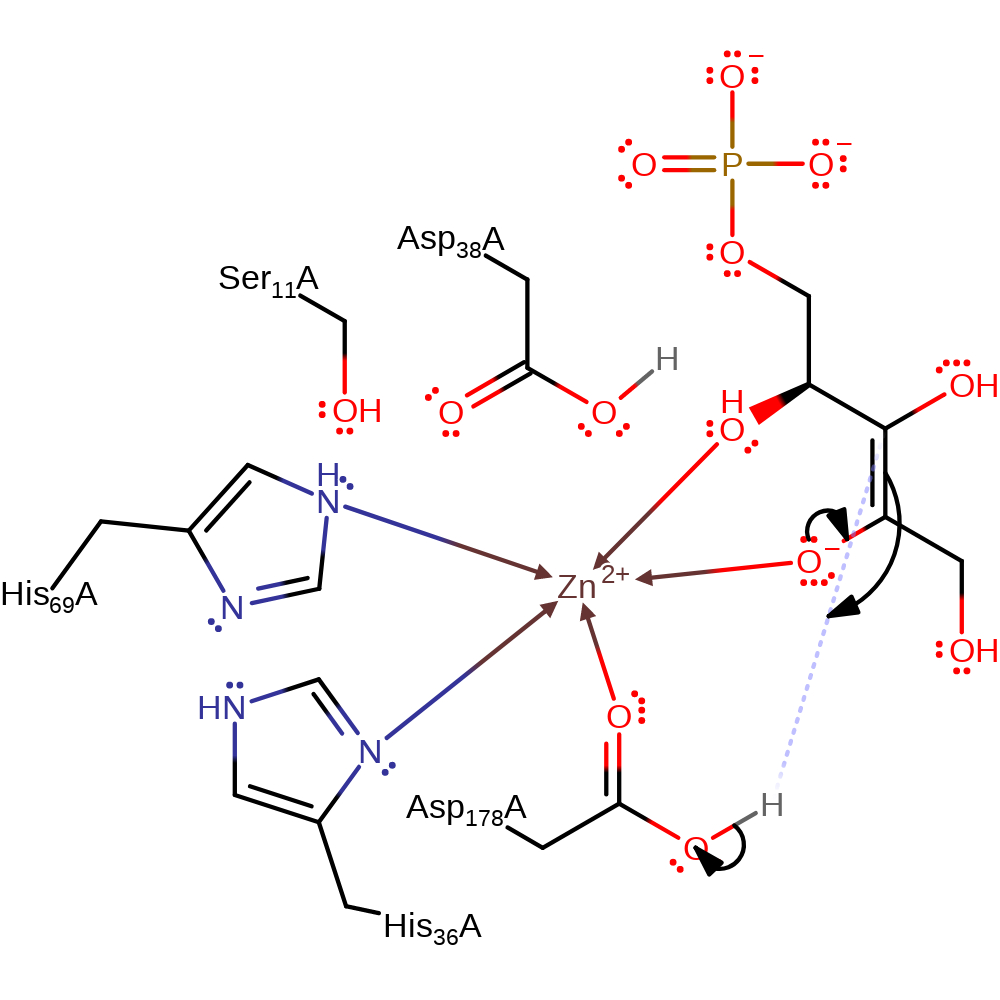
Step 2. The enolate collapses back to the keto form with concomitant deprotonation of Asp178, forming the xylulose product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp178(179)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp38(39)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser11(12)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp178(179)A | metal ligand |
| His36(37)A | metal ligand |
| His69(70)A | metal ligand |
| Met40(41)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met71(72)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met144(145)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp178(179)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall product formed
Step 3. Once the product has left the active site the two catalytic aspartates are open to bulk solvent and it is expected that the return to the correct protonation states is thus from bulk solvent [PMID:10191144, PMID:12547196]. This step is only necessary if the enzyme is to perform the reaction again in the same direction as described here. The enzyme catalyses the epimerisation in both directions, however.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp178(179)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp38(39)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser11(12)A | hydrogen bond donor, increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp178(179)A | metal ligand |
| Asp38(39)A | metal ligand |
| His36(37)A | metal ligand |
| His69(70)A | metal ligand |
| Asp38(39)A | proton donor |
| Asp178(179)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
The zinc-independent proposal in which the conserved methionines are responsible for the stabilisation of the reactive intermediates and transition states. The mechanism itself is identical to the primary proposal in which Asp38 deprotonates the C3 of the substrate molecule, causing a rearrangement of the double bonds and the formation of the enolate form. The enolate then collapses back to the keto form with concomitant deprotonation of Asp178, forming the xylulose product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1h1z) | ||
| Asp179, Asp39 | Asp178(179)A, Asp38(39)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser12 | Ser11(12)A | Activates and stabilises Asp38. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Met145, Met72, Met41 | Met144(145)A, Met71(72)A, Met40(41)A | These three methionine residues are highly conserved and thought to act as a transient 'electrostatic cushion' [PMID:10191144] that stabilises the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. These methionine residues also aid catalysis by ensuring a hydrophobic and thus proton free environment. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Kopp J et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 287, 761-771. Structure and mechanism of the amphibolic enzyme d-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase from potato chloroplasts. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2643. PMID:10191144.
- Jelakovic S et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 326, 127-135. Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of the Cytosolic d-Ribulose-5-phosphate 3-Epimerase from Rice. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01374-8. PMID:12547196.

Step 1. Asp38 deprotonates the C3 of the substrate molecule, causing a rearrangement of the double bonds and the formation of the enolate form. Three conserved methionines are essential for maintaining a proton free environment to ensure that the epimerisation (and not isomerisation) occurs [PMID:12547196].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp178(179)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp38(39)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser11(12)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met40(41)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met71(72)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met144(145)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp38(39)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The enolate collapses back to the keto form with concomitant deprotonation of Asp178, forming the xylulose product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser11(12)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met40(41)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met71(72)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met144(145)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp178(179)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall product formed
Step 3. Once the product has left the active site the two catalytic aspartates are open to bulk solvent and it is expected that the return to the correct protonation states is thus from bulk solvent [PMID:10191144, PMID:12547196]. This step is only necessary if the enzyme is to perform the reaction again in the same direction as described here. The enzyme catalyses the epimerisation in both directions, however.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp178(179)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp38(39)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser11(12)A | hydrogen bond donor, increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp38(39)A | proton donor |
| Asp178(179)A | proton acceptor |


 Download:
Download: 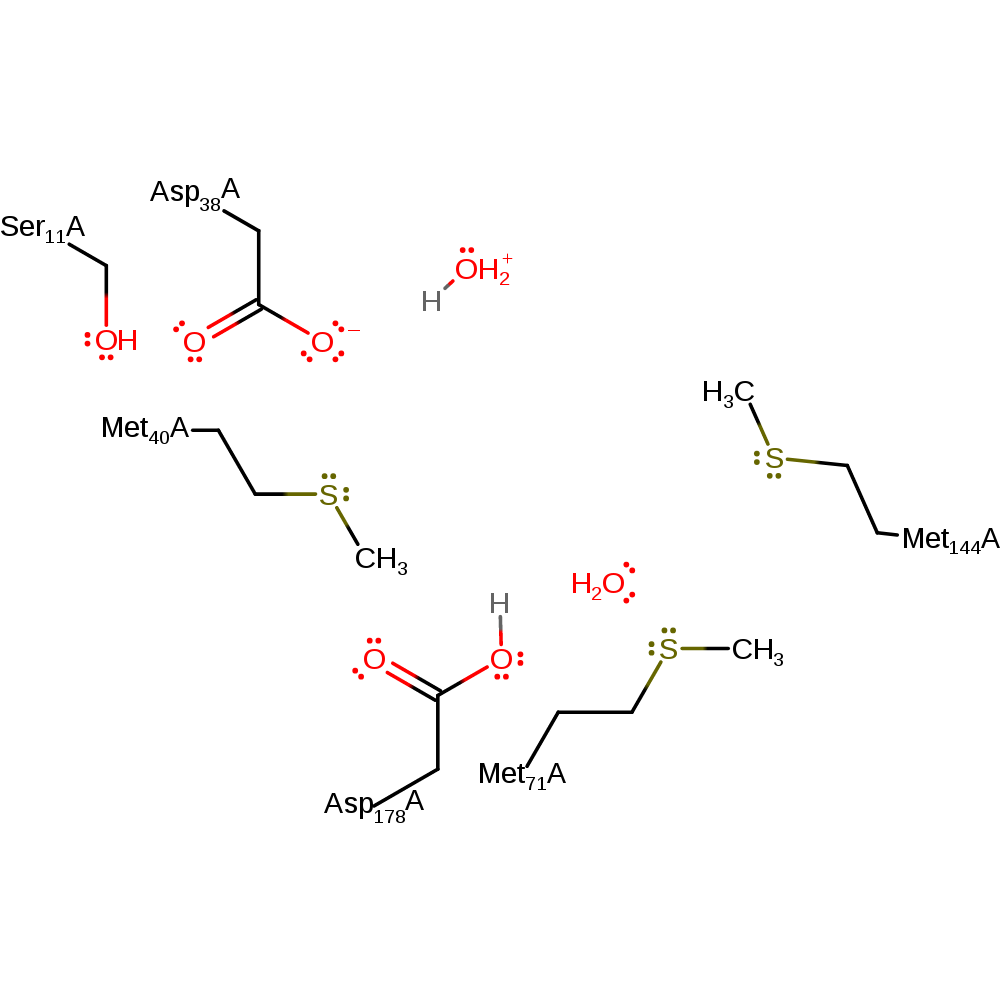 Download:
Download: