N-carbamoylsarcosine amidase
Carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase (CSHase) is involved in one of two alternative creatine degradative pathways in micro-organisms. Both pathways start with creatinine and end with glycine, but the CSHase containing pathway proceeds via N-methylhydantoin, N-carbamoylsarcosine, and sarcosine.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P32400
 (3.5.1.59)
(3.5.1.59)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Arthrobacter sp. (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1nba
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS, REFINEMENT AND ENZYMATIC REACTION MECHANISM OF N-CARBAMOYLSARCOSINE AMIDOHYDROLASE FROM ARTHROBACTER SP. AT 2.0 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.850
 (see all for 1nba)
(see all for 1nba)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Cys177 is activated as a nucleophile by the general base Asp51, attacking the carbamoyl group of the substrate. The resulting anionic tretrahedral intermediate is stabilised by the cationic lysine side chain of Lys144. Ammonia is eliminated from the enzyme-substrate adduct intermediate. Hydrolysis eliminates Cys177, producing sarcosine, CO2 and NH3. The release of ammonia is thought to be promoted through electrostatic interactions with Asp51.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1nba) | ||
| Asp51 | Asp51A | Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting a proton from the Cys nucleophile and later the nucleophilic water molecule. In both cases it is returned to its initial protonation state by the leaving group. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ala172 (main-C), Thr173 | Ala172A (main-C), Thr173A | Help stabilise the reactive intermediates. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys144 | Lys144A | Activates the nucleophilic Cys by altering its pKa. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys177 | Cys177A | Acts as the catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, deamination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, reaction occurs outside the enzymeReferences
- Nakai T et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 729-738. Crystal structure of N-carbamyl-d-amino acid amidohydrolase with a novel catalytic framework common to amidohydrolases. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00160-x. PMID:10903946.
- Luo HB et al. (2010), J Struct Biol, 169, 304-311. Crystal structure and molecular modeling study of N-carbamoylsarcosine amidase Ta0454 from Thermoplasma acidophilum. DOI:10.1016/j.jsb.2009.11.008. PMID:19932181.
- Wang WC et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 306, 251-261. Crystal structure and site-directed mutagenesis studies of N-carbamoyl-d-amino-acid amidohydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter reveals a homotetramer and insight into a catalytic cleft11Edited by R. Huber. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4380. PMID:11237598.
- Du X et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 14166-14172. Crystal Structure and Mechanism of Catalysis of a Pyrazinamidase fromPyrococcus horikoshii†. DOI:10.1021/bi0115479. PMID:11714269.
- Zajc A et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 263, 269-283. Crystallographic and Fluorescence Studies of Ligand Binding toN-Carbamoylsarcosine Amidohydrolase fromArthrobactersp. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0574. PMID:8913306.
- Romão MJ et al. (1992), J Mol Biol, 226, 1111-1130. Crystal structure analysis, refinement and enzymatic reaction mechanism of N-carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase from Arthrobacter sp. at 2·0Åresolution. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(92)91056-u. PMID:1381445.

Step 1. Asp51 deprotonates Cys177, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the amide carbon of N-carbamoylsarcosine in an addition reaction forming an oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys177A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp51A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys144A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Thr173A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala172A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys177A | nucleophile |
| Asp51A | proton acceptor |
| Cys177A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer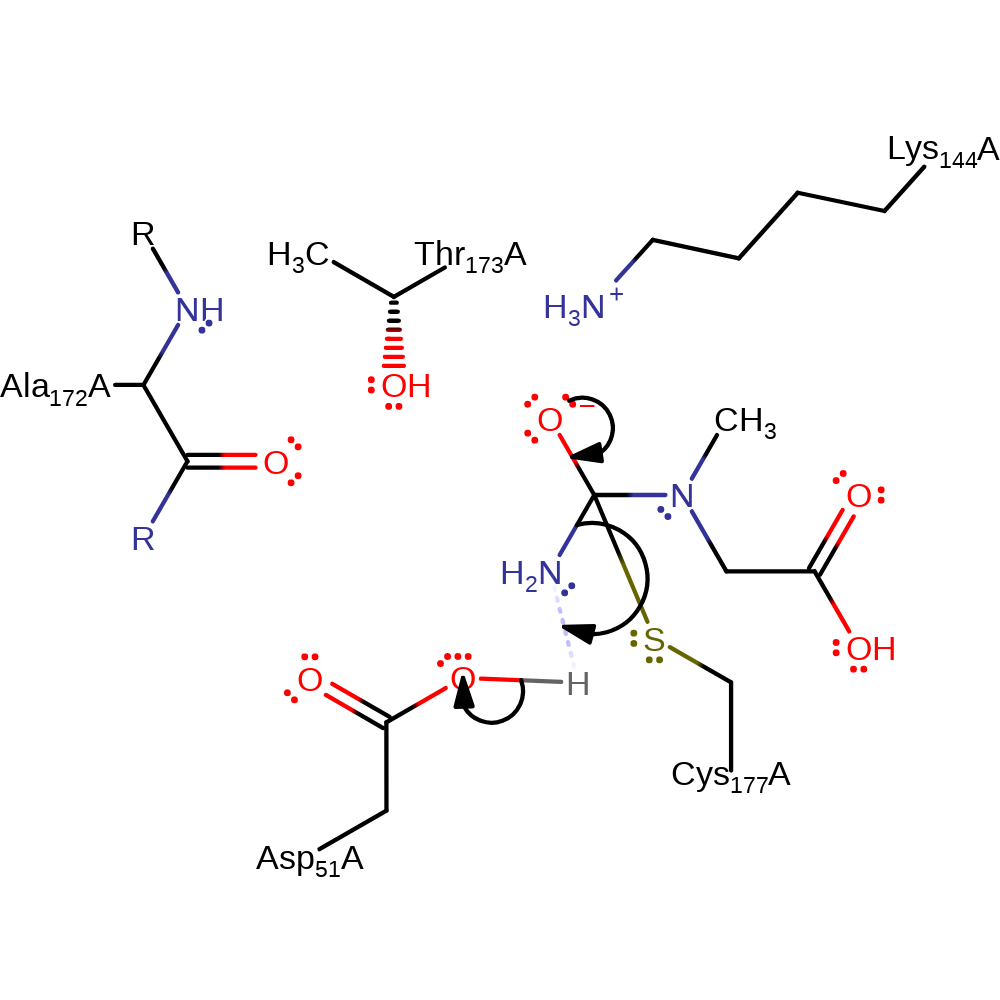
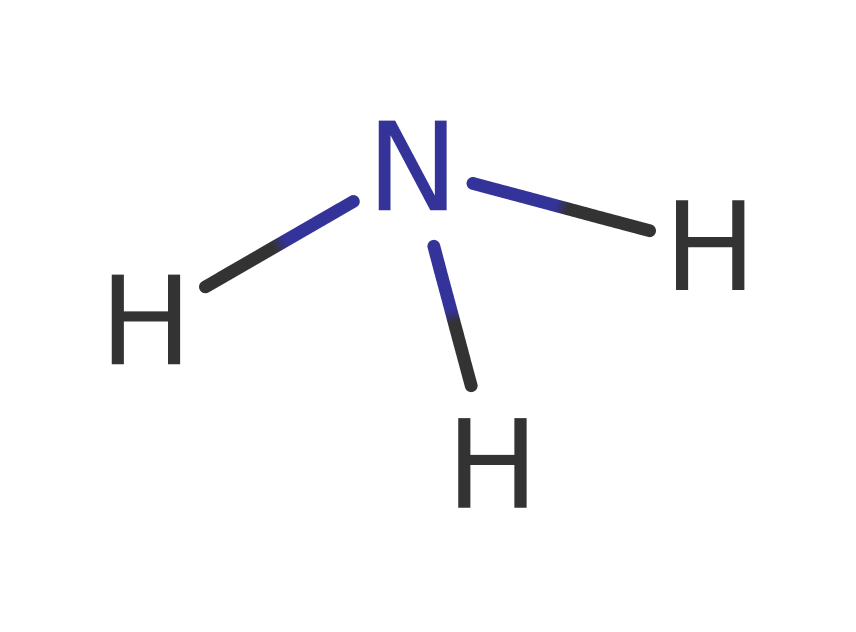
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating ammonia, which deprotonates the Asp51.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys177A | covalently attached |
| Asp51A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys144A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr173A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala172A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp51A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, deamination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, proton transfer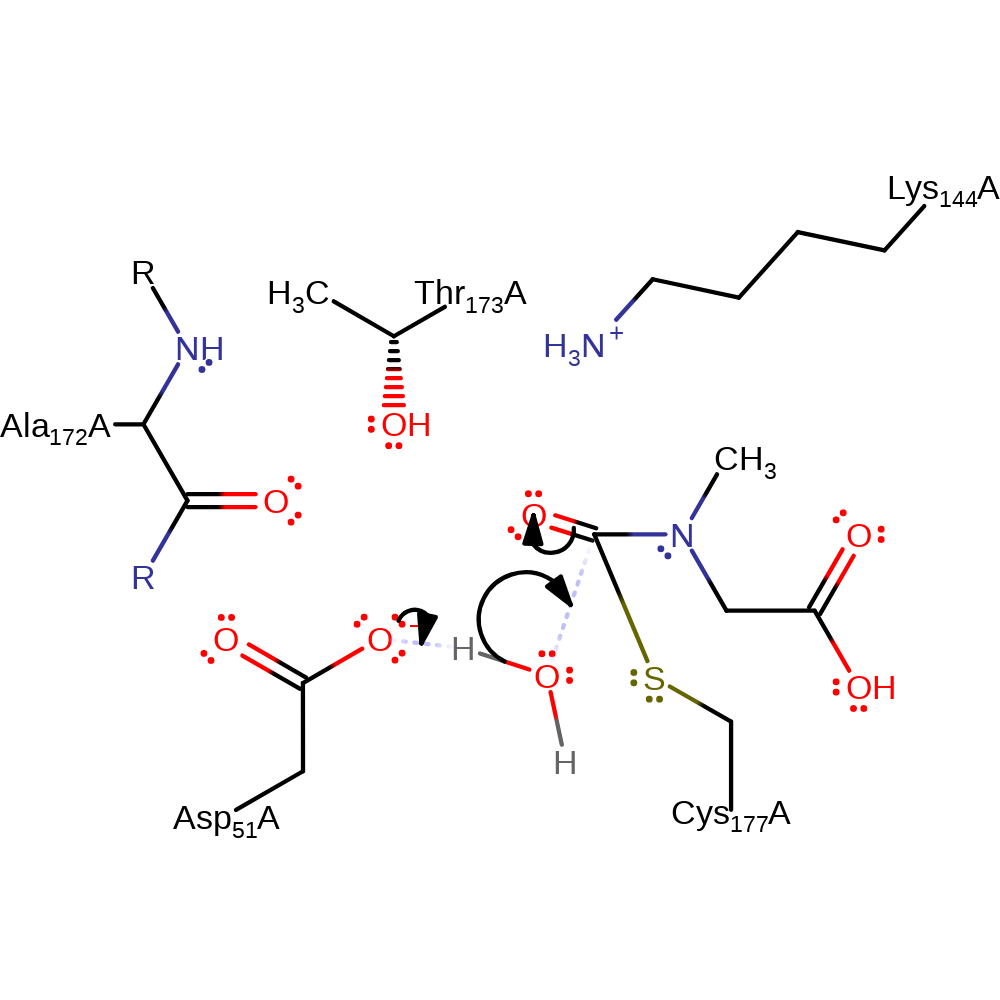
Step 3. Asp51 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the covalently attached intermediate in an addition reaction, forming an oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys177A | covalently attached |
| Asp51A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys144A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr173A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp51A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 4. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating Cys177, which deprotonates the Asp51.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys177A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp51A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys144A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr173A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys177A | proton acceptor |
| Asp51A | proton donor |
| Cys177A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|





 Download:
Download: