Penicillin amidase (peptidase C59 family)
Penicillin V acylase (PVA), isolated from Bacillus sphaericus, catalyses the hydrolysis of penicillin V to 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) and phenoxyacetic acid. This reaction is commercially important because 6-APA is used in the synthesis of semi-synthetic penicillins. The enzyme undergoes post-translational autocatalytic self-cleavage to produce the mature enzyme. A tripeptide of Met-Leu-Gly is removed to expose the catalytic N-terminal cysteine residue. PVA belongs to the N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) superfamily.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P12256
 (3.5.1.11)
(3.5.1.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Lysinibacillus sphaericus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
3pva
- PENICILLIN V ACYLASE FROM B. SPHAERICUS
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.60.10
 (see all for 3pva)
(see all for 3pva)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.1.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The alpha-amine of Cys1 deprotonates the thiol group of the residue. The resulting thiolate attacks the amide carbon of penicillin V, forming a tetrahedral intermediate that can be stabilised by the oxyanion hole (Asn175 and Tyr82). The intermediate collapses and eliminates 6-APA, which is protonated by the Cys1 amine, possibly via water. The alpha-amine then deprotonates water, which acts as the nucleophile for attack on the thiol ester carbon of the intermediate. The resulting tetrahedral intermediate, which is again stabilised by the oxyanion hole, collapses and eliminates the Cys1 thiolate, which is protonated by the alpha-amine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3pva) | ||
| Tyr85 (main-N) | Tyr82A (main-N) | Tyr82 forms part of the oxyanion hole and so can stabilise the tetrahedral intermediates produced during the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg231 | Arg228A | Arg228 is thought to lower the pKa of the alpha-amine of Cys1, thus aiding acid/base catalysis. | hydrogen bond donor, repulsive charge-charge interaction, activator, increase acidity, increase basicity |
| Cys4 (N-term), Cys4 | Cys1A (N-term), Cys1A | The alpha-amine of Cys1 deprotonates the thiol sidechain. The thiolate is then the nucleophile for attack on the amide carbon of the substrate. The amine is responsible for protonating the amine leaving group, possibly via a water molecule. The amine deprotonates water for attack on the intermediate and the Cys1 thiolate is then eliminated. The amine group protonates the thiolate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn178 | Asn175A | Asn175 forms part of the oxyanion hole and so can stabilise the tetrahedral intermediates produced during the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, hydrolysis, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Suresh CG et al. (1999), Nat Struct Biol, 6, 414-416. Penicillin V acylase crystal structure reveals new Ntn-hydrolase family members. DOI:10.1038/8213. PMID:10331865.
- Avinash VS et al. (2016), Crit Rev Biotechnol, 36, 303-316. Penicillin acylases revisited: importance beyond their industrial utility. DOI:10.3109/07388551.2014.960359. PMID:25430891.
- Rathinaswamy P et al. (2005), Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun, 61, 680-683. Cloning, purification, crystallization and preliminary structural studies of penicillin V acylase fromBacillus subtilis. DOI:10.1107/s1744309105017987. PMID:16511127.
- McVey CE et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 313, 139-150. Crystal structures of penicillin acylase enzyme-substrate complexes: structural insights into the catalytic mechanism 1 1Edited by K. Nagai. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5043. PMID:11601852.
- Morillas M et al. (1999), Biochem J, 338, 235-239. The kinetics of acylation and deacylation of penicillin acylase from Escherichia coli ATCC 11105: evidence for lowered pKa values of groups near the catalytic centre. DOI:10.1042/bj3380235. PMID:9931321.
- Duggleby HJ et al. (1995), Nature, 373, 264-268. Penicillin acylase has a single-amino-acid catalytic centre. DOI:10.1038/373264a0. PMID:7816145.
- Brannigan JA et al. (1995), Nature, 378, 416-419. A protein catalytic framework with an N-terminal nucleophile is capable of self-activation. DOI:10.1038/378416a0. PMID:7477383.
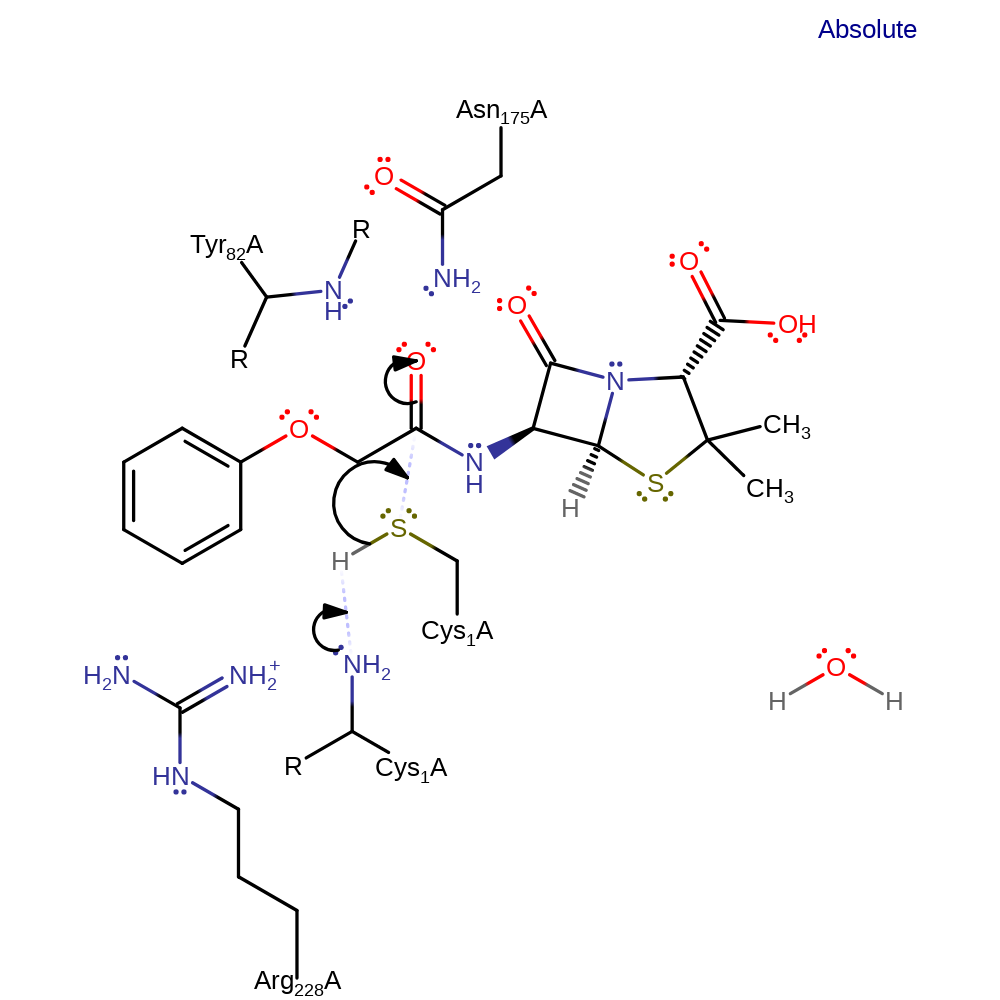
Step 1. The alpha-amine of Cys1 deprotonates the thiol group. The resulting thiolate is the nucleophile for attack on the carbonyl carbon. The tetrahedral intermediate is stabilised by the oxyanion hole.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn175A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg228A | repulsive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor, increase basicity |
| Tyr82A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton acceptor |
| Cys1A | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation
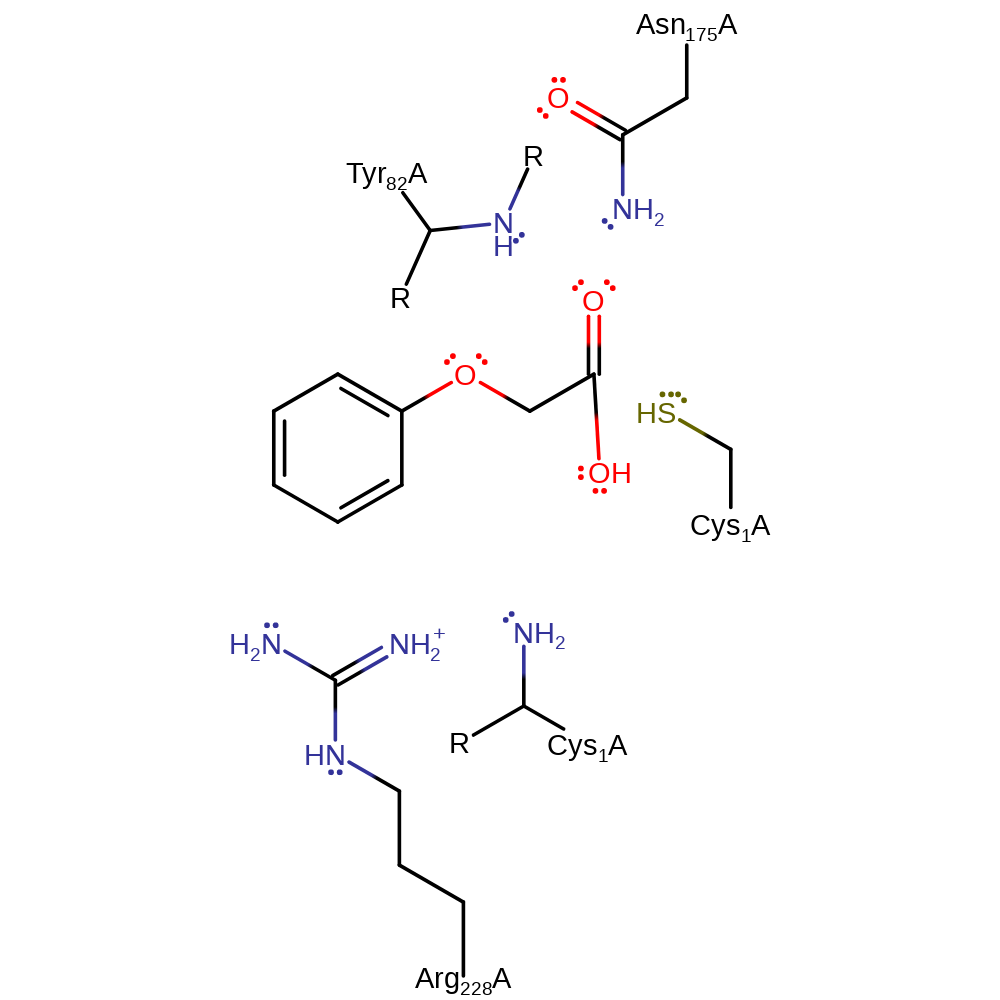
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and eliminates 6-aminopenicillanate, with proton transfer from the alpha amine to the leaving group. Proton transfer between the alpha-amine and the amine leaving group may be mediated by water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr82A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn175A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg228A | activator, repulsive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys1A | covalently attached |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 3. The alpha amine deprotonates water, which then acts as the nucleophile for attack on the carbonyl carbon. The tetrahedral intermediate is stabilised by the oxyanion hole.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys1A | covalently attached |
| Tyr82A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn175A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg228A | repulsive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor, increase basicity |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydrolysis
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and eliminates Cys1 phenoxyacetate. The Cys1 thiolate is protonated by the alpha amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr82A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn175A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg228A | increase acidity, repulsive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys1A | nucleofuge |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton donor |
| Cys1A | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: