Pteridine reductase
Pteridine reductase (TbPTR1), isolated from Trypanosoma brucei, is an NADPH-dependent short-chain reductase. TbPTR1 has broad specificity and can catalyse the reduction of biopterin to 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (THB) and folate to tetrahydrofolate. Both these reactants can be reduced from the oxidised or dihydro-state since the mechanism is a two step reduction by two molecules of NADPH. These reactions are important for the salvage of pteridines from the host and so TbPTR1 is a potential drug target for the treatment of African trypanosomiasis.
TbPTR1 is a member of the Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) superfamily.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O76290

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Trypanosoma brucei brucei (Trypanosome)

- PDB
-
2c7v
- Structure of Trypanosoma brucei pteridine reductase (PTR1) in ternary complex with cofactor and the antifolate methotrexate
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.720
 (see all for 2c7v)
(see all for 2c7v)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
NADPH binds first, followed by biopterin. NADPH transfers a hydride to C7 of biopterin. The N8 position is then protonated by Tyr174, which is part of a proton shuffling system also involving Asp161. The dihydrobiopterin intermediate dissociates, followed by NADP+. A second molecule of NADPH can then bind, followed by the intermediate. The 4-keto function of the intermediate enolises, with Arg14 stabilising the resulting hydroxyl and the phosphate of NADPH acting as a temporary proton acceptor for the N3 proton. NADPH then transfers a hydride to the C6 position and the N5 position is protonated by a water molecule. The latter is activated by interactions with the 4-hydroxyl group and is reprotonated by the 4-hydroxyl, leading to tautomerisation of THB to the keto-form.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2c7v) | ||
| Arg14 | Arg14A | Arg14 stabilises the enol tautomer of the intermediate, which is better suited for water activation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr174 | Tyr174A | Tyr174 is part of a proton shuffling system during the first reaction step. It transfers a proton from Asp161 to the N8 position of the pterin. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp161 | Asp161A | Asp161 is part of a proton shuffling system during the first reduction step. It transfers a proton from the solvent to Tyr194. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay, overall reactant used, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, bond polarisation, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Dawson A et al. (2006), Mol Microbiol, 61, 1457-1468. Structure and reactivity of Trypanosoma brucei pteridine reductase: inhibition by the archetypal antifolate methotrexate. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05332.x. PMID:16968221.
- Gourley DG et al. (2001), Nat Struct Biol, 8, 521-525. Pteridine reductase mechanism correlates pterin metabolism with drug resistance in trypanosomatid parasites. DOI:10.1038/88584. PMID:11373620.
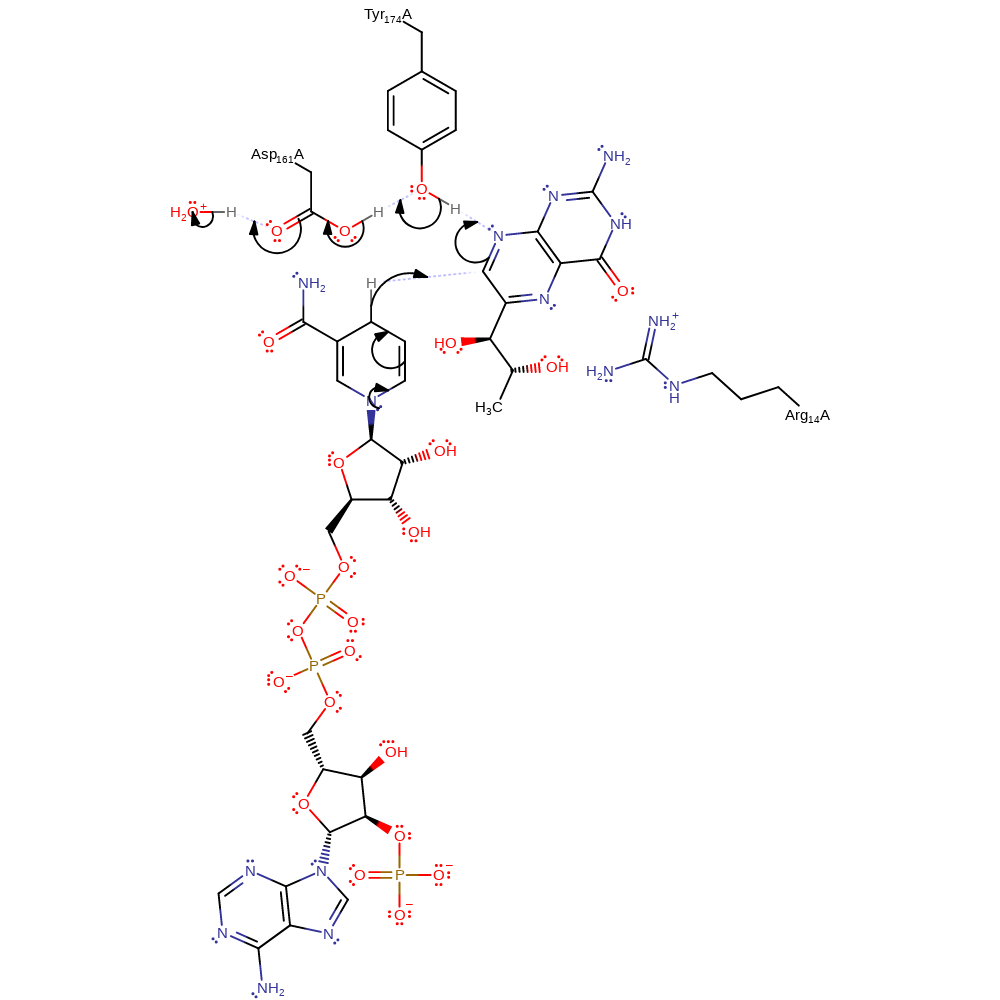
Step 1. NADPH transfers a hydride to the C7 position of biopterin. The N8 position is protonated by Tyr174, which in turn is protonated by Asp161. Since Asp161 is exposed to the bulk solvent it is then protonated by water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg14A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp161A | proton relay, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr174A | proton relay, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp161A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr174A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay, overall reactant used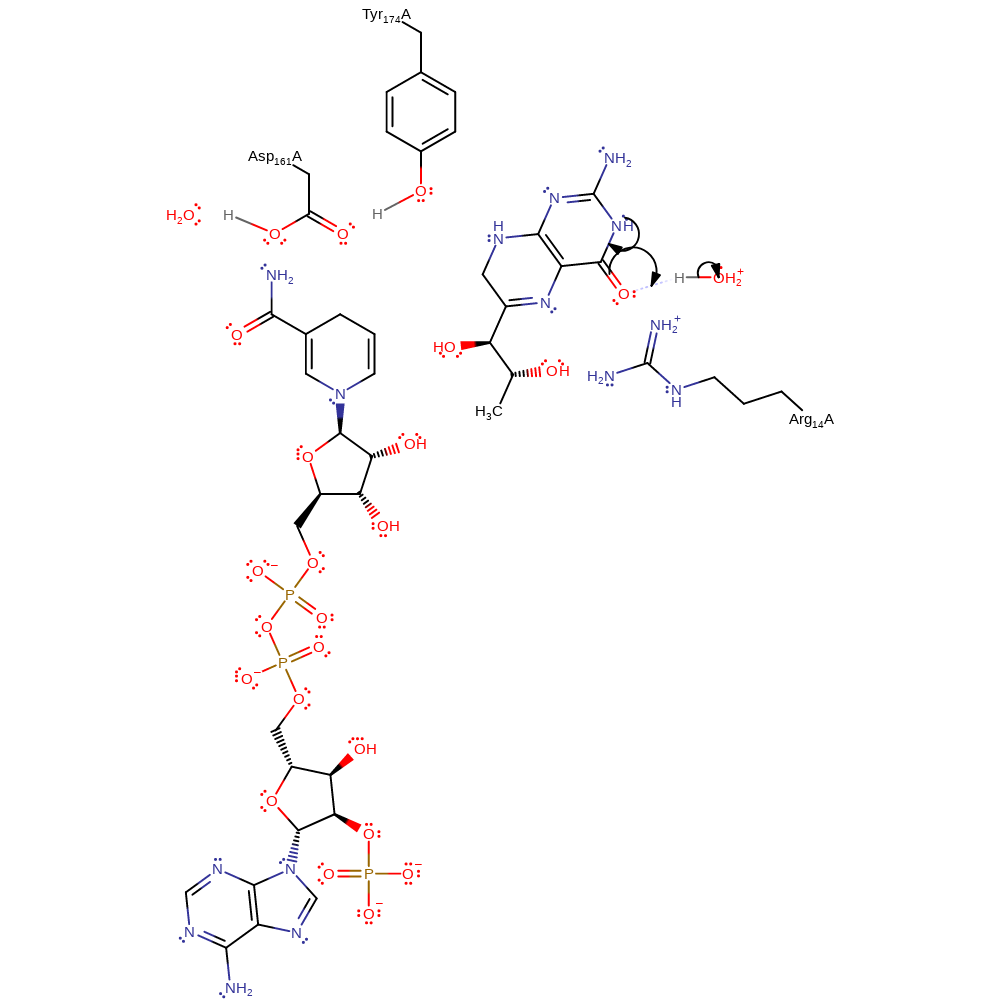
Step 2. Before this step (tautomerisation of the dihydrobiopterin) occurs the dihydrobiopterin must dissociate from the active site, followed by NADP+. A second molecule of NADPH can then bind to the active site, followed by dihydrobiopterin. It is unclear whether the dihydrobiopterin is deprotonated (the base most likely to be the phosphate of the NADPH) or whether it retains the proton, with the intermediate stabilised by the negative charge of the NADPH phosphates.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg14A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp161A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr174A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, bond polarisation, intermediate formation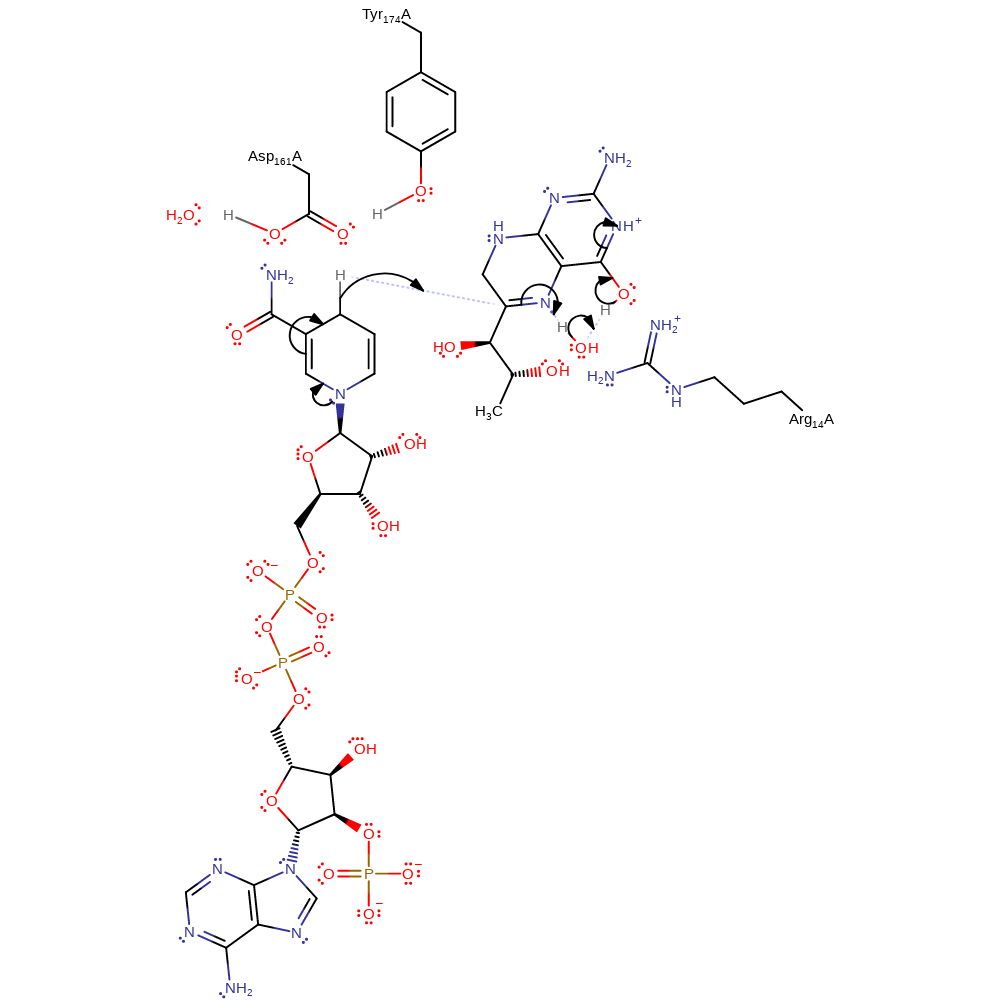
Step 3. NADPH transfers a hydride to the C6 position of the dihydrobiopterin intermediate. The N5 position is protonated by an activated water. This water then deprotonates the 4-hydroxyl group and causes tautomerisation back to the keto-form.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg14A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Asp161A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr174A | hydrogen bond donor |





 Download:
Download: