GMP synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing)
The Class I glutamine amidotransferase an example of a single enzymatic reaction being catalysed by two modules, each responsible for a distinct component of the reaction. It catalyses the amination of the nucleotide precursor xanthosine 5'-monophosphate to form GMP in the de novo purine biosynthesis pathway. The amidotransferase domain is found in related enzymes of the purine, pyrimidine, tryptophan, arginine, histidine and folic acid pathways. This domain includes a conserved Cys-His-Glu triad, responsible for the abstraction of the amide nitrogen from glutamine.
Despite the apparent catalytic readiness of the GMP synthetase active site, the Class I aminotransferase domain is actually a very poor glutaminase in the absence of the substrates XMP and ATP, which is consistent with the biological role of this enzyme, in which the hydrolysis of glutamine is tightly couple with the formation of GMP. The synthetase domain catalyses the addition of ammonia to an acceptor substrate. They are designed to work in concert to ensure efficient coupling of catalytic functions, it is suggested that a flexible hinge exists to bring the two sites together for concerted ammonia transfer.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
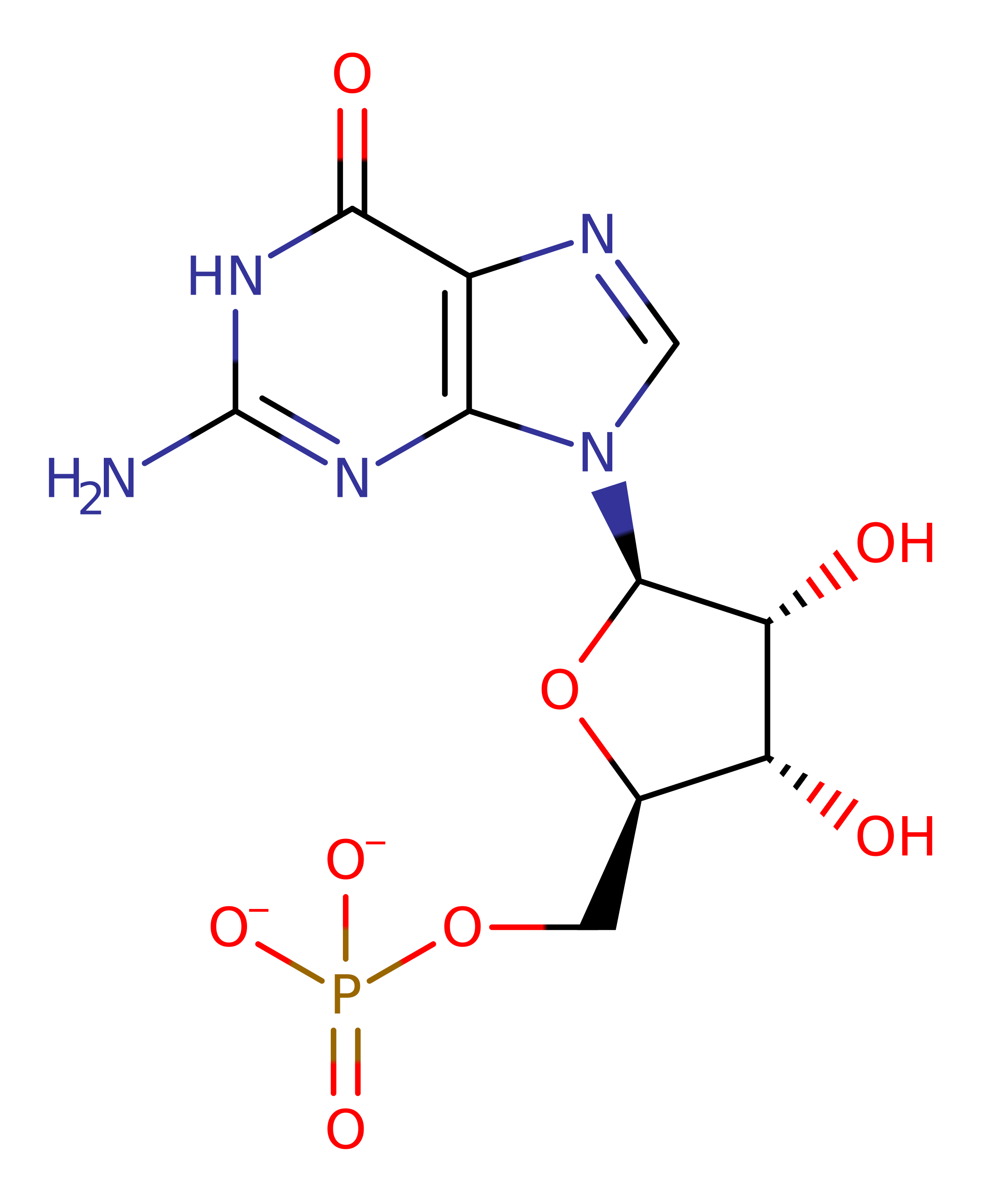
P04079
 (6.3.5.2)
(6.3.5.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1gpm
- ESCHERICHIA COLI GMP SYNTHETASE COMPLEXED WITH AMP AND PYROPHOSPHATE
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.620
 3.40.50.880
3.40.50.880  (see all for 1gpm)
(see all for 1gpm)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.3.5.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The beta-phosphate deprotonates the XMP substrate, which then initiates a nucleophilic attack on the alpha-phosphate of ATP, eliminating pyrophosphate aided by Asp239 and Lys381. His181 deprotonates Cys86, activating it for a nucleophilic attack upon L-glutamine, forming an enzyme-substrate covalent bond. The negative charge is stabilised, by an oxyanion hole involving Tyr87 and Gly59. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, liberating ammonia, which deprotonates His181 and then passes to the other catalytic domain. Ammonia is deprotonated by the phosphate of the intermediate, activating it for a nucleophilic attack on the intermediate, which liberates AMP and the GMP product. In the glutamine site His181 deprotonates a water molecule, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the Cys-bound intermediate. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, liberating Cys86, which deprotonates His181, and the glutamate product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1gpm) | ||
| His181 | His181A | Part of the catalytic Glu-His-Cys triad. Acts as a general acid/base, activates the cysteine of the triad. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys381 | Lys381A | Helps to stabilise the build up of negative charge in the ATP-pyrophosphatase domain. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys86 | Cys86A | Part of the catalytic Glu-His-Cys triad. Acts as a general acid/base and as the catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Glu183 | Glu183A | Part of the catalytic Glu-His-Cys triad. Responsible for stabilising and activating the His of the triad. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Asp239, Asp239 | Asp239A, Asp239A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. Also acts to stabilise and hold the reactants in the correct orientation for the reaction to occur. | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr87 (main-N), Gly59 (main-N) | Tyr87A (main-N), Gly59A (main-N) | Form the oxyanion hole that stabilises the negatively charged intermediates and transition states in the glutaminase domain. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, deamination, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Tesmer JJ et al. (1996), Nat Struct Biol, 3, 74-86. The crystal structure of GMP synthetase reveals a novel catalytic triad and is a structural paradigm for two enzyme families. DOI:10.1038/nsb0196-74. PMID:8548458.
- Ballut L et al. (2015), Nat Commun, 6, 8930-. Active site coupling in Plasmodium falciparum GMP synthetase is triggered by domain rotation. DOI:10.1038/ncomms9930. PMID:26592566.
- Massière F et al. (1998), Cell Mol Life Sci, 54, 205-222. The mechanism of glutamine-dependent amidotransferases. DOI:10.1007/s000180050145. PMID:9575335.

Step 1. The beta-phosphate deprotonates the XMP substrate, which then initiates a nucleophilic attack on the alpha-phosphate of ATP, eliminating pyrophosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys381A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp239A | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, overall reactant used
Step 2. His181 deprotonates Cys86, activating it for a nucleophilic attack upon L-glutamine, forming an enzyme-substrate covalent bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly59A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys86A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His181A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu183A | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr87A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His181A | proton acceptor |
| Cys86A | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 3. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, liberating ammonia, which deprotonates His181 and then passes to the other catalytic domain. The ammonia produced is transferred from the glutaminase domain to the ATP pyrophosphatase domain. However, the glutaminase and ATP pyrophosphatase domain are approximately 30 Angstroms apart, and it is not yet entirely clear how the liberated ammonia is transported from the glutaminase to the ATP pyrophosphatase domain. It has been suggested that the most likely route is by channelling through the protein in a manner analogous to the classical channelling of common metabolites between sequential enzyme pairs [PMID:9575335]. However, a hinging movement between the two domains has also been suggested [PMID:8548458].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly59A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys86A | covalently attached |
| His181A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu183A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Tyr87A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His181A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, deamination, intermediate formation
Step 4. Ammonia is deprotonated by the phosphate of the intermediate, activating it for a nucleophilic attack on the intermediate, which liberates AMP and the GMP product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys381A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp239A | metal ligand, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 5. His181 deprotonates a water molecule, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the Cys-bound intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly59A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys86A | covalently attached |
| His181A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu183A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| Tyr87A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His181A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 6. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, liberating Cys86, which deprotonates His181, and the glutamate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly59A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys86A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His181A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu183A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Tyr87A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His181A | proton donor |
| Cys86A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |








 Download:
Download: