(S)-hydroxynitrile lyase
Hydroxynitrile lyases (HNLs) are important members of the alpha/beta-hydrolase superfamily, and they catalyze the cleavage of cyanohydrins into aldehyde (or ketone) and hydrocyanic acid (HCN). The release of HCN not only protects plant systems from herbivores and microbial attack, but also provides a nitrogen source for the biosynthesis of asparagine.
The enzyme from Hevea brasiliensis tolerates aliphatic (including alpha,beta-unsaturated), aromatic and heterocyclic aldehydes, whereas the enzyme from Manihot esculenta catalyses the addition of hydrogen cyanide to aliphatic, aromatic, heteroaromatic aldehydes and methyl ketones. Both are specific to the S enantiomer. The overall reaction catalysed is very reversible and of importance to synthetic organic chemists.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P52704
 (4.1.2.47)
(4.1.2.47)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Hevea brasiliensis (Para rubber tree)

- PDB
-
1sc9
- Hydroxynitrile Lyase from Hevea brasiliensis in complex with the natural substrate acetone cyanohydrin
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1sc9)
(see all for 1sc9)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.2.47)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Although this mechanism utilises the traditional Ser-His-Asp triad of the alpha/beta-hydrolase superfamily, it proceeds via general acid/base catalysis, rather than nucleophilic attack of the serine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1sc9) | ||
| His235 | His235A | Part of the Ser-His-Asp triad. Acts as a general acid/base, first to deprotonate Ser80, then to donate a proton to the cyanate ion product. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys236 | Lys236A | This residue is instrumental for catalysis in several ways by: correctly positioning the substrate, stabilising the negatively charged reaction product CN(-), and modulating the basicity of the catalytic base. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Asp207 | Asp207A | Part of the Ser-His-Asp triad, activates the histidine to act as a general acid/base. | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Ser80 | Ser80A | Part of the Ser-His-Asp triad. Acts as a general acid/base, first donating its proton to His235, and then abstracting a proton from the substrate. | proton relay, proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Thr11, Cys81 | Thr11A, Cys81A | Form part of the oxyanion hole. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, proton relay, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Zhao Y et al. (2014), Phys Chem Chem Phys, 16, 26864-26875. A full picture of enzymatic catalysis by hydroxynitrile lyases from Hevea brasiliensis: protonation dependent reaction steps and residue-gated movement of the substrate and the product. DOI:10.1039/c4cp04032e. PMID:25375265.
- Gartler G et al. (2007), J Biotechnol, 129, 87-97. Structural determinants of the enantioselectivity of the hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis. DOI:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.12.009. PMID:17250917.
- Gruber K et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 20501-20510. Reaction Mechanism of Hydroxynitrile Lyases of the α/β-Hydrolase Superfamily. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m401575200. PMID:14998991.
- Lauble H et al. (2001), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 57, 194-200. Structure of hydroxynitrile lyase fromManihot esculentain complex with substrates acetone and chloroacetone: implications for the mechanism of cyanogenesis. DOI:10.1107/s0907444900015766. PMID:11173464.
- Lauble H et al. (2001), Protein Sci, 10, 1015-1022. Mechanistic aspects of cyanogenesis from active-site mutant Ser80Ala of hydroxynitrile lyase from Manihot esculenta in complex with acetone cyanohydrin. DOI:10.1110/ps.01301. PMID:11316882.
- Hasslacher M et al. (1996), J Biol Chem, 271, 5884-5891. Molecular cloning of the full-length cDNA of (S)-hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis. Functional expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and identification of an active site residue. PMID:8621461.
- Wagner UG et al. (1996), Structure, 4, 811-822. Mechanism of cyanogenesis: the crystal structure of hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis. PMID:8805565.
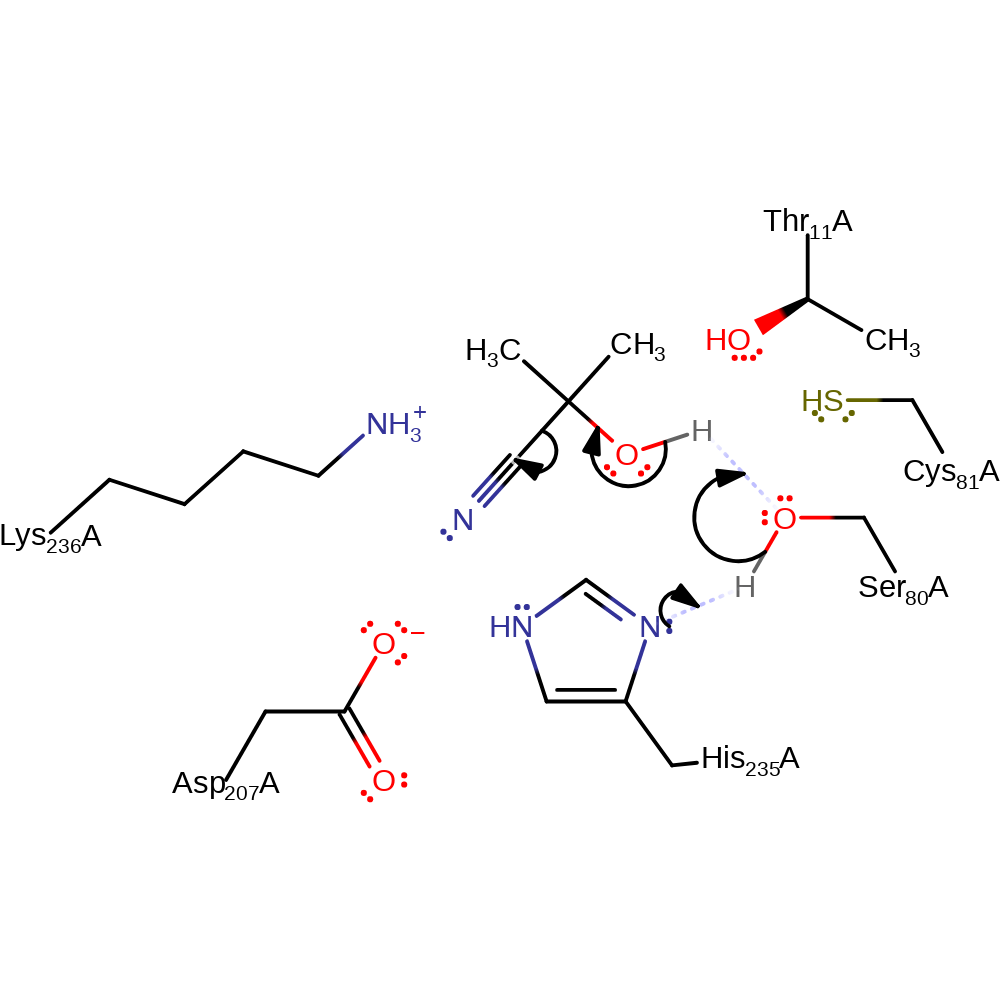
Step 1. His235 (which is present as part of a Ser-His-Asp triad) deprotonates Ser80, deprotonates the hydroxide of the nitrile, initiating an elimination of the cyanate ion.
Binding of the cyanohydrin causes a change in conformation of the Ser80, bringing it into hydrogen bonding distance of the His235. Cleavage of the C-C bond is facilitated by the stabilisation of the evolving negative charge by the positive charge of Lys236, which also shifts the pKa of His235 from 2.5 to 10 [PMID:14998991].
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp207A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His235A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr11A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys236A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator, steric role |
| Ser80A | proton relay |
| Cys81A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp207A | increase basicity |
| Ser80A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His235A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, proton relay
Step 2. The cyanate ion deprotonates His235. Upon protonation of the cyanide ion by His235, the hydrogen cyanide is displaced by water. The HCN leaves the active site first, followed by the aldehyde product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp207A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His235A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr11A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys236A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Thr11A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser80A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys81A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp207A | increase acidity |
| His235A | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: