Prostaglandin-E synthase
Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase Type 2 (mPGES-2), sourced from Macaca fascicularis catalyses the isomerization reaction of PGH2 (Prostaglandin H2) to PGE2 (Prostaglandin E2). PGH2 is formed from arachidonic acid. It is an unstable intermediate and so is converted into PGE2. PGE2 exerts control over various biological activities such as relaxation/ contraction of smooth muscle, excretion of Na+, body temperature and the physiological sleep/ wake cycle.
The enzyme is active in the absence of an R-SH reagent, but the catalytic activity is increased by the presence of an R-SH reagent, suggesting that a water molecule and the SH group of an R-SH bind the same site and participate in the same catalytic role. An R-SH or water molecule bound between O-eta of Tyr107 and C9 of PGH2 is polarised by forming a H-bond with Tyr107, and consequently, the SH group of R-SH or water is deprotonated at neutral pH.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9N0A4
 (5.3.99.3)
(5.3.99.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Macaca fascicularis (crab-eating macaque)

- PDB
-
1z9h
- Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase type-2
(2.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.30.10
 (see all for 1z9h)
(see all for 1z9h)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.99.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The pKa of Cys 110 is lowered by hydrogen bonds from Phe 112 and Cys 113. Cys 110 protonates O11 of PGH2, causing O11 to become positively charged. The deprotonated Cys 110 residue then nucleophilically attacks the O9 of PGH2. This results in formation of a covalent O9-gamma S bond between PGH2 and Cys 110 and breaking of the O9-O11 bond. Water is polarised through hydrogen bonding to Tyr 107. The water molecule then acts as a base to abstract the hydrogen atom attached to C9. This causes elimination of Cys 110. The C9=O9 carbonyl group forms and the O9-gamma S bond is broken. No evidence supports either mechanism strongly.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1z9h) | ||
| Tyr107 | Tyr107(20)A | Tyr 107 polarises a water molecule through hydrogen bonding, causing it to become basic. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110 | Cys110(23)A | Cys 110 protonates O11 of PGH2, causing O11 to become positive. The deprotonated Cys 110 residue then nucleophilically attacks the O9 of PGH2. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge |
| Phe112 (main-N), Cys113 | Phe112(25)A (main-N), Cys113(26)A | Lowers pKa of Cys 110, allowing it to act as a proton donor and then a nucleophile. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, acidic bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, decyclisation, bimolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Yamada T et al. (2005), J Mol Biol, 348, 1163-1176. Crystal Structure and Possible Catalytic Mechanism of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase Type 2 (mPGES-2). DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.035. PMID:15854652.

Step 1. The peroxide bond in prostaglandin H2 deprotonates the thiol group of Cys110. The SG of Cys110 is surrounded by two positive character protons, and thus, its pKa is decreased to about 7.0 [PMID:15854652].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr107(20)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys113(26)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Cys110(23)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe112(25)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys110(23)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The thiolate of Cys110 attacks the non-protonated oxygen of the peroxide bond in a nucleophilic substitution which results in the cleavage of the peroxide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr107(20)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys113(26)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe112(25)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: acidic bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, decyclisation
Step 3. An R-SH (or a water) bound between OH of Tyr107 and C9 of PGH2 is polarised by forming a H-bond with Tyr107, and consequently, the thiol group of R-SH (or water) is deprotonated at neutral pH. The resulting thiolic anion (or hydroxyl anion) removes the hydrogen atom attached to C9 [PMID:15854652] of the covalently bound intermediate initiating an elimination reaction that releases the thiolate form of Cys110 and the prostaglandin E2 product
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr107(20)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys113(26)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe112(25)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, intermediate formation, overall product formed
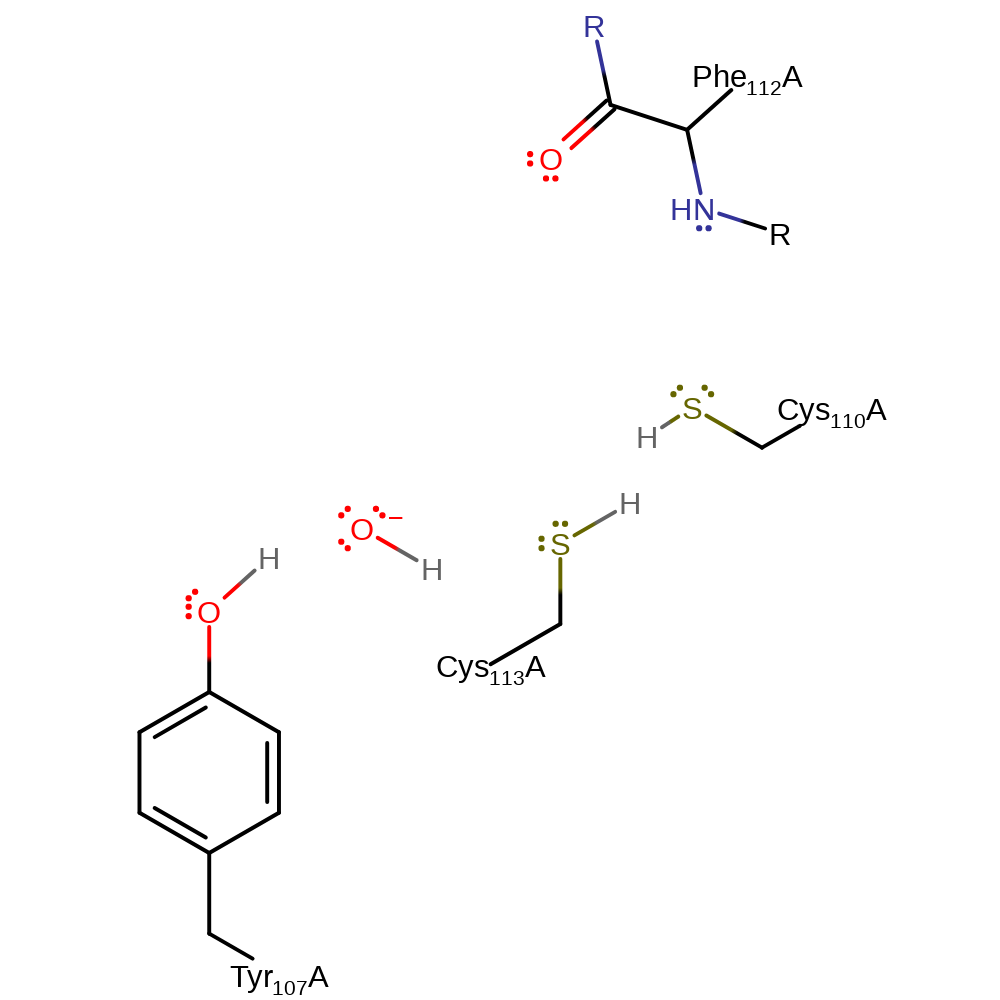
Step 4. The thiolate of Cys110 deprotonates water in an inferred return step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr107(20)A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Cys113(26)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe112(25)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
In this mechanism Cys110 abstracts the hydrogen atom attached to C9 of the substrate and the O9-O11 bond is cleaved by acid catalysis with a water or R-SH molecule. No evidence supports either mechanism strongly.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1z9h) | ||
| Tyr107 | Tyr107(20)A | Tyr 107 polarises a water molecule through hydrogen bonding, causing it to become basic. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110 | Cys110(23)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Phe112 (main-N), Cys113 | Phe112(25)A (main-N), Cys113(26)A | Lowers pKa of Cys 110, allowing it to act as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
decyclisation, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Yamada T et al. (2005), J Mol Biol, 348, 1163-1176. Crystal Structure and Possible Catalytic Mechanism of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase Type 2 (mPGES-2). DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.035. PMID:15854652.

Step 1. The thiolate of Cys110 abstracts the proton from the substrate, cleaving the peroxo bond with concomitant deprotonation of a water (or thiol).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr107(20)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys113(26)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe112(25)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
decyclisation, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used
Step 2. A water (or thiol) abstracts a proton from Cys110 in an inferred return step to regenerate the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr107(20)A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Cys113(26)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe112(25)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(23)A | proton donor |


 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: