Protein disulfide-isomerase (eukaryotic)
Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) from humans is a 57 kDa protein present in the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotes. It is involved in disulfide bond formation, breakage, and rearrangement during the folding of proteins translocated into the endoplasmic reticulum. PDI contains two active sites with the amino acid sequence -Cys-Gly-His-Cys-, each of which is cycled between the dithiol and the disulfide forms as in the related redox protein thioredoxin. In addition, PDI is the beta subunit of prolyl-4-hydroxylase, which has an alpha2beta2 quaternary structure, and it is one subunit of the heterodimeric triglyceride transfer protein complex.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P07237
 (5.3.4.1)
(5.3.4.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1mek
- HUMAN PROTEIN DISULFIDE ISOMERASE, NMR, 40 STRUCTURES
(solution nmr
Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.30.10
 (see all for 1mek)
(see all for 1mek)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Cys36 is activated by His38 and Gly37 and then attacks the first of the disulfide bonds in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that results in an enzyme bound intermediate with a new thiolate. The newly formed thiolate attacks the second of the disulfide bonds in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that results in a new disulfide bond and second thiolate. The second newly formed thiolate attacks the disulfide bond between the intermediate and the Cys36 in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that results in the final new disulfide bond and free Cys36, with enzyme restored to its native state. With complex substrates (i.e. those with more than 2 disulfide bonds) this enzyme uses both catalytic cysteines (Cys36 and Cys39). With simple substrates (i.e. those with only 2 disulfide bonds) this enzyme uses only Cys36. The reaction is shown only for the simple case.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mek) | ||
| Gly54, His55 | Gly37A, His38A | Acts to modulate pKa of neighbouring cysteine. | activator, modifies pKa |
| Cys53, Cys56 | Cys36A, Cys39A | In the deprotonated form acts as a nucleophile to a pre-existing disulphide bond. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, decyclisation, proton transfer, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, enzyme-substrate complex cleavageReferences
- Kersteen EA et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 12168-12178. Catalysis of Protein Disulfide Bond Isomerization in a Homogeneous Substrate†. DOI:10.1021/bi0507985. PMID:16142915.
- Neves RPP et al. (2017), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 114, E4724-E4733. Mechanistic insights on the reduction of glutathione disulfide by protein disulfide isomerase. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1618985114. PMID:28559343.
- Kemmink J et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 7684-7691. Structure Determination of the N-Terminal Thioredoxin-like Domain of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Using Multidimensional Heteronuclear13C/15N NMR Spectroscopy†. DOI:10.1021/bi960335m. PMID:8672469.
- Darby NJ et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 16770-16780. Characterization of the active site cysteine residues of the thioredoxin-like domains of protein disulfide isomerase. DOI:10.1021/bi00051a027. PMID:8527452.
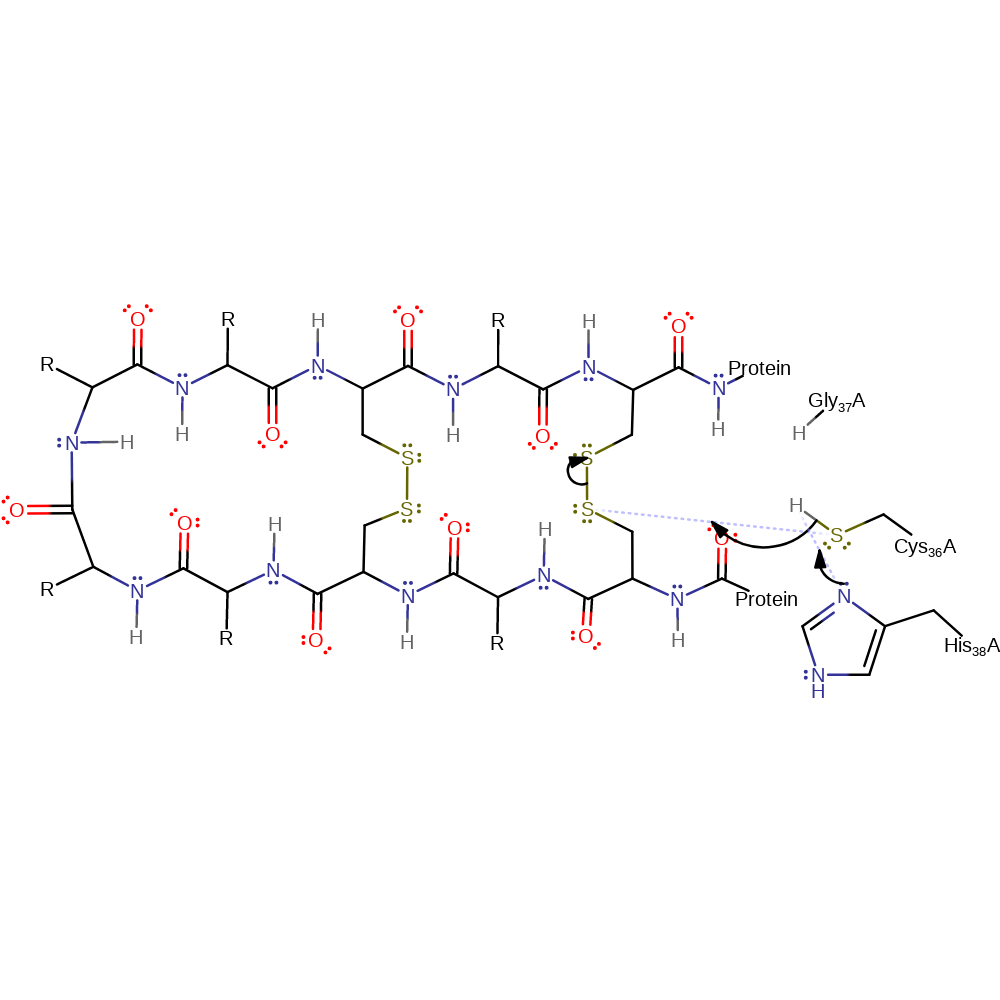
Step 1. The thiol of Cys36 attacks the first of the disulfide bonds in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that results in an enzyme bound intermediate with a new thiolate. Cys36 is activated by deprotonation from His38. If a second set of S-S bonds are present, Cys39 also acts as a catalytic nuclephile (not shown for simplicity).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly37A | modifies pKa |
| His38A | modifies pKa |
| Cys36A | proton donor |
| His38A | proton acceptor |
| Cys36A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, decyclisation, proton transfer
Step 2. The newly formed thiolate attacks attacks the adjacent disulphide bond in a second nucleophilic substitution reaction, leading to a new disulphide bond and thiolate being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, decyclisation
Step 3. The second newly formed thiolate attacks the disulfide bond between the intermediate and the Cys36 in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that results in the final new disulfide bond and free Cys36 and deprotonated His 38.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly37A | activator |
| Cys36A | proton acceptor |
| His38A | proton donor |
| Cys36A | nucleofuge |


 Download:
Download: