Peptidylprolyl isomerase (cyclophilin-type)
The cyclophilin family of enzymes catalyses the cis-trans isomerisation of peptide bonds preceding proline residues. This activity accelerates protein folding in vitro and may underlie some of the many roles of cyclophilins, which include signalling, mitochondrial function, chaperone activity, RNA splicing, stress response, gene expression and regulation of kinase activity. The biological activities of cyclophilin A (CypA) in humans include binding the HIV-1 CA protein in the virions and facilitating viral replication; the basis for this is unclear and isomerase activity is not required for HIV-1 infectivity.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P62937
 (5.2.1.8)
(5.2.1.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1m9c
- X-ray crystal structure of Cyclophilin A/HIV-1 CA N-terminal domain (1-146) M-type Complex.
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.100.10
 (see all for 1m9c)
(see all for 1m9c)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.2.1.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The 'reaction' is only a rotation of a peptide bond preceding the substrate proline. The proline itself remains more or less stationary, with the N-terminal residues rotating anticlockwise 180 degrees. The catalysis is mainly through stabilisation of the transition state. There is also a steric clash between the side chain of the residue preceding the substrate Pro and Arg 55 in the trans conformation. (HIV-1 CA protein has a Gly residue in this position so binding of the trans conformation is more favourable compared to other substrates.)
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1m9c) | ||
| Arg55 | Arg55A | The guanidinium group of this residue hydrogen bonds to and stabilises the sp3 hybridisation of the substrate Pro nitrogen in the transition state, stabilising the sp3 geometry and lowering the energy barrier to peptide bond rotation. This residue also sterically clashes with the side chain of the substrate residue preceding Pro when in the trans conformation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Gln63 | Gln63A | Preferentially H-bonds to the substrate peptide bond on the N-terminal side of the residue preceding the proline in the (product) trans-conformation. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn102 (main-C) | Asn102A (main-C) | Forms a hydrogen bond, between its side chain nitrogen and the substrate main chain oxygen preceding Pro, during the trans to cis peptide bond rotation. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe60, Phe113, Leu122 | Phe60A, Phe113A, Leu122A | Forms part of the hydrophobic pocket that holds substrate Pro in place while the N-terminal residues change conformation. There is an increase in van der Waals interaction strength between several conserved, hydrophobic residues (Phe 60, Phe 113, Leu 122) and the substrate Pro during the cis to trans reaction pathway. | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| His126 | His126A | Forms part of the hydrophobic pocket that mediates the rotation reaction. | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
isomerisation reaction (not covered by named reactions), overall reactant used, overall product formedReferences
- Howard BR et al. (2003), Nat Struct Biol, 10, 475-481. Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of cyclophilin A. DOI:10.1038/nsb927. PMID:12730686.
- Ladani ST et al. (2015), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1850, 1994-2004. Computational perspective and evaluation of plausible catalytic mechanisms of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases. DOI:10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.12.023. PMID:25585011.
- Tork Ladani S et al. (2014), Mol Simul, 40, 765-776. Intricacies of interactions, dynamics and solvent effects in enzyme catalysis: a computational perspective on cyclophilin A. DOI:10.1080/08927022.2014.919498.
- Agarwal PK (2004), Proteins, 56, 449-463. Cis/trans isomerization in HIV-1 capsid protein catalyzed by cyclophilin A: Insights from computational and theoretical studies. DOI:10.1002/prot.20135. PMID:15229879.
- Li G et al. (2003), J Am Chem Soc, 125, 15028-15038. What Is So Special about Arg 55 in the Catalysis of Cyclophilin A? Insights from Hybrid QM/MM Simulations. DOI:10.1021/ja0367851. PMID:14653737.
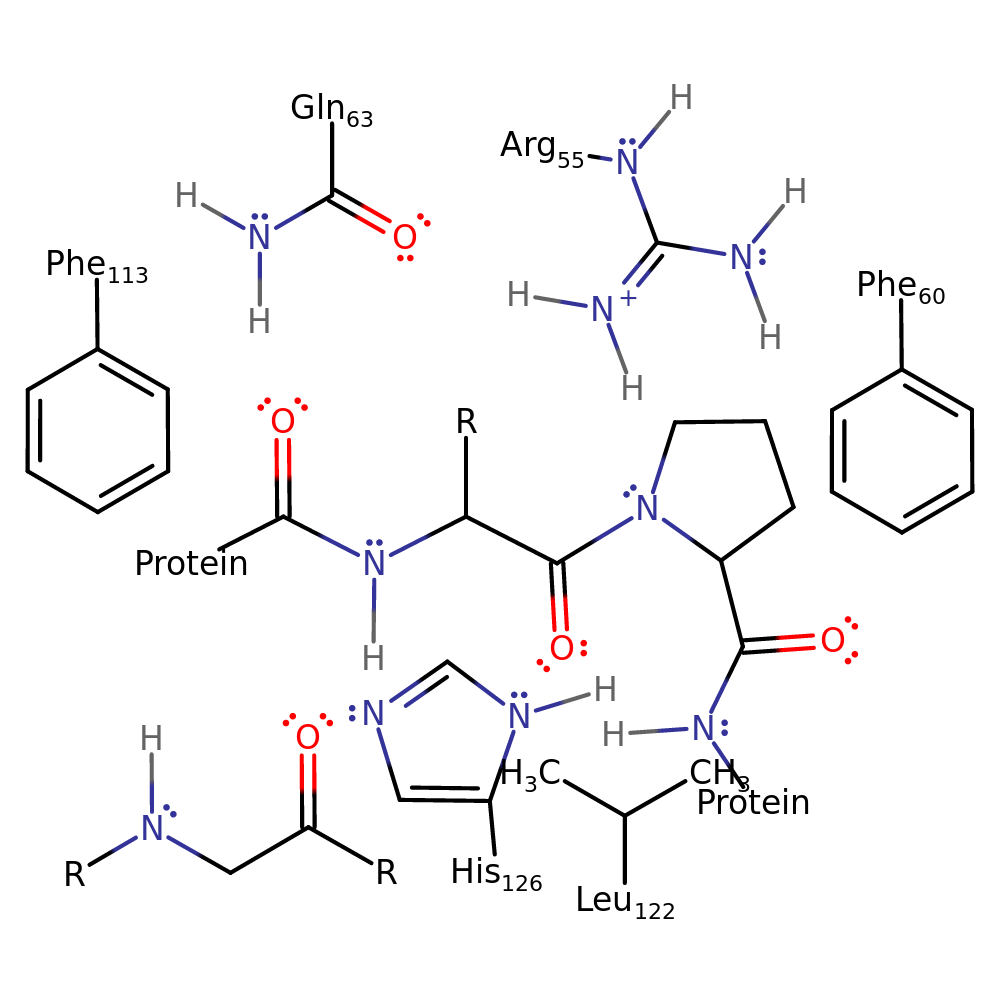
Step 1. The enzyme stabilises the transition state of the isomerisation of peptidylproline omega=180 to peptidylproline omega=0.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg55A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Phe60A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |
| Gln63A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn102A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe113A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |
| Leu122A | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| His126A | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |

