8-oxoguanine DNA-glycosylase (type-1 OGG1 family)
N-glycosylase/DNA lyase; Belongs to the type-1 OGG1 family. This is a DNA repair enzyme that incises DNA at 8-oxoG residues to excise 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine and 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-N-methylformamidopyrimidine (FAPY) from damaged DNA. Has a beta-lyase activity that nicks DNA 3' to the lesion.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O15527
 (3.2.2.-, 4.2.99.18)
(3.2.2.-, 4.2.99.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1lwy
- hOgg1 Borohydride-Trapped Intermediate without 8-oxoguanine
(2.01 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.1670.10
 1.10.340.30
1.10.340.30  (see all for 1lwy)
(see all for 1lwy)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.99.18)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Lys249 attacks the DNA 8-oxoguanine substrate in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that yields enzyme bound DNA and the conjugate base of 8-oxoguanine. Lys249 initiates an intramolecular elimination, cleaving the C-O bond in the DNA ribose ring and resulting in the deprotonation of 8-oxoguanine. The conjugate base of 8-oxoguanine deprotonates the C2 of the open-form ribose. Lys249 initiates an elimination resulting in the loss of the 3' phosphate-end of the DNA from the ribose ring. Water attacks the ribose at the carbon where Lys249 is bound in a nucleophilic addition reaction. The released phosphate deprotonates the hydroxyl group, initiating an elimination of the covalently bound Lys249. Cyclisation of the final DNA with 3-terminal trans-a,b-unsaturated sugar product occurs outside the enzyme active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1lwy) | ||
| Lys249 | Lys249(246)A(C) | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleophile, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Asp268 | Asp268(265)A(C) | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, intramolecular elimination, decyclisation, schiff base formed, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, bimolecular electrophilic addition, bimolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regenerated, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, cyclisationReferences
- Chung SJ et al. (2004), Chem Biol, 11, 1643-1649. Structures of End Products Resulting from Lesion Processing by a DNA Glycosylase/Lyase. DOI:10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.09.014. PMID:15610848.
- Sowlati-Hashjin S et al. (2015), Phys Chem Chem Phys, 17, 24696-24706. Quantum mechanical study of the β- and δ-lyase reactions during the base excision repair process: application to FPG. DOI:10.1039/c5cp04250j. PMID:26352486.
- Kellie JL et al. (2012), J Phys Chem B, 116, 10786-10797. Mechanistic and conformational flexibility of the covalent linkage formed during β-lyase activity on an AP-site: application to hOgg1. DOI:10.1021/jp306344g. PMID:22877319.
- Norman DP et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 1564-1572. Structural and Biochemical Exploration of a Critical Amino Acid in Human 8-Oxoguanine Glycosylase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi026823d. PMID:12578369.
- Fromme JC et al. (2003), Nat Struct Biol, 10, 204-211. Product-assisted catalysis in base-excision DNA repair. DOI:10.1038/nsb902. PMID:12592398.
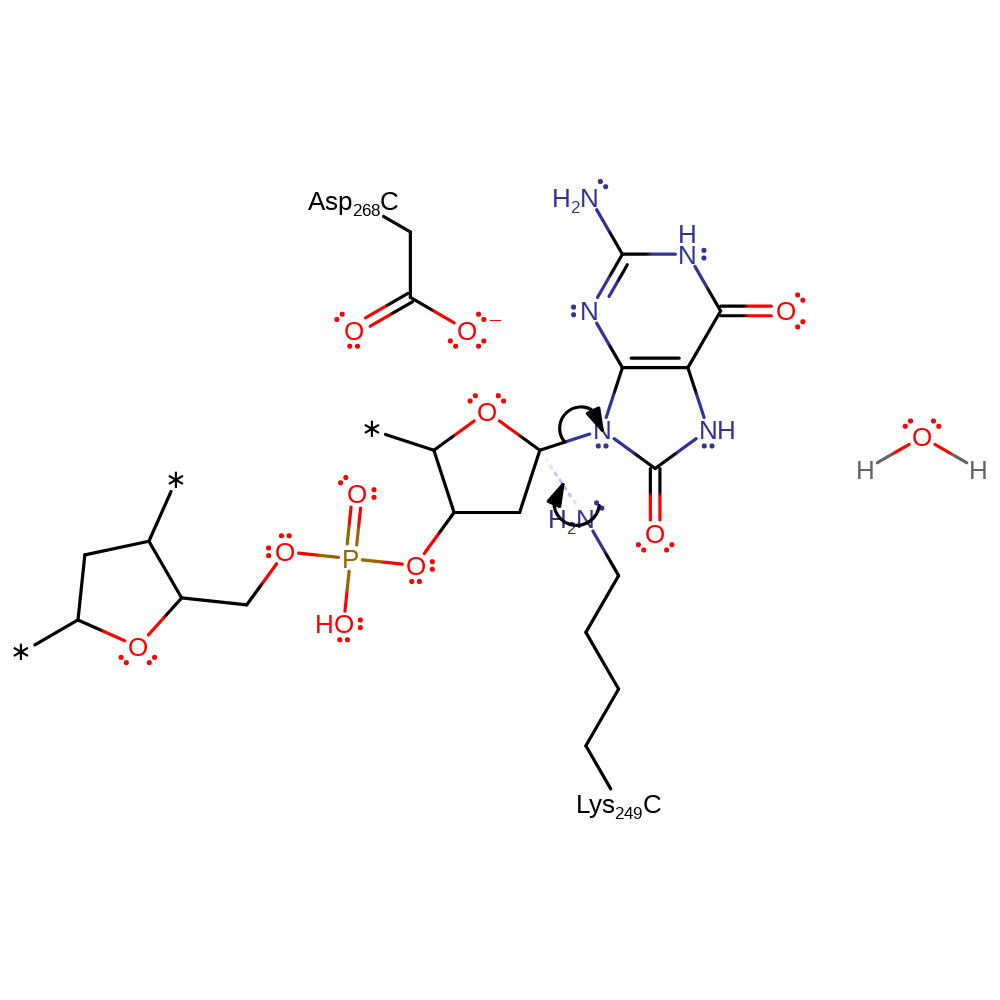
Step 1. Lys249 attacks the DNA 8-oxoguanine substrate in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that yields enzyme bound DNA and the conjugate base of 8-oxoguanine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp268(265)A(C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys249(246)A(C) | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation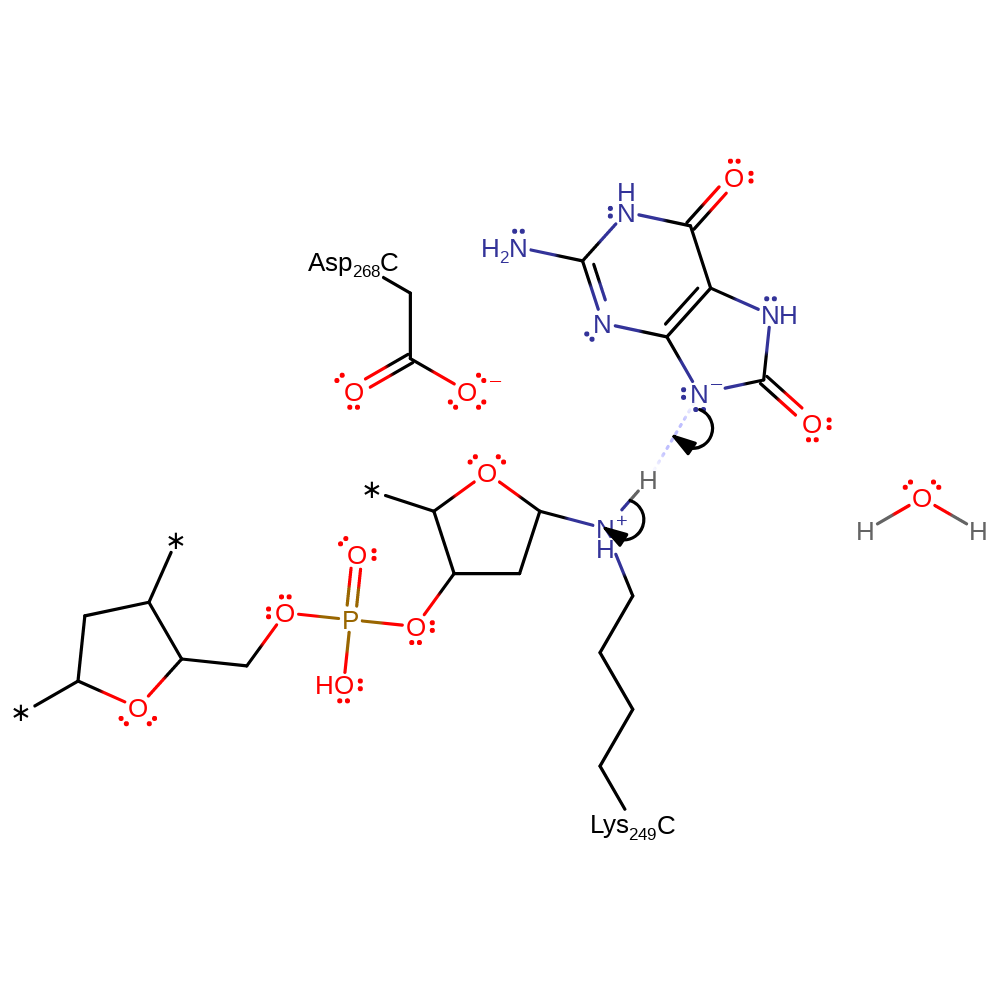
Step 2. The conjugate base of 8-oxoguanine deprotonates the covalently bound Lys249.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys249(246)A(C) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 3. Lys249 initiates an intramolecular elimination, cleaving the C-O bond in the DNA ribose ring and resulting in the deprotonation of 8-oxoguanine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys249(246)A(C) | covalently attached, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, proton transfer, intermediate formation, decyclisation, schiff base formed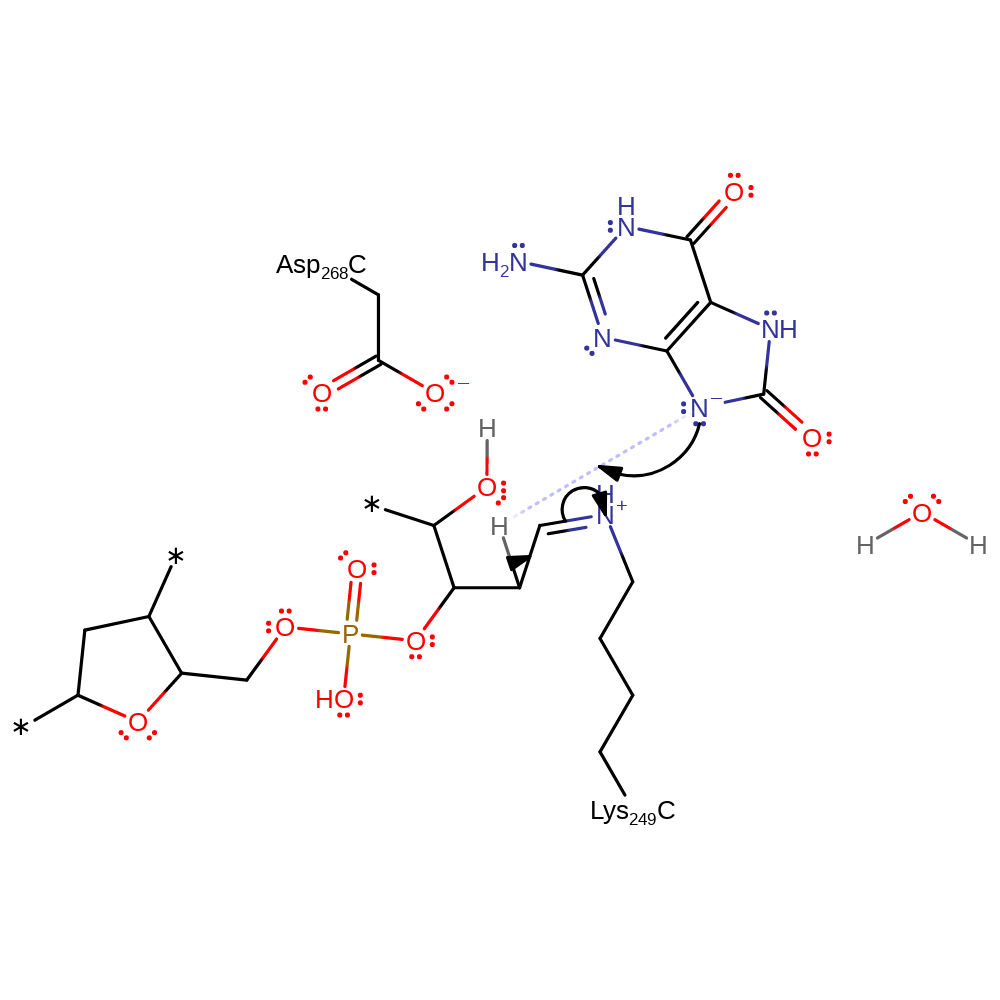
Step 4. The conjugate base of 8-oxoguanine deprotonates the C2 of the open-form ribose. Evidence suggests both proR and proS deprotonation are possible however proS is thought to be more likely.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys249(246)A(C) | covalently attached |
| Asp268(265)A(C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys249(246)A(C) | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall product formed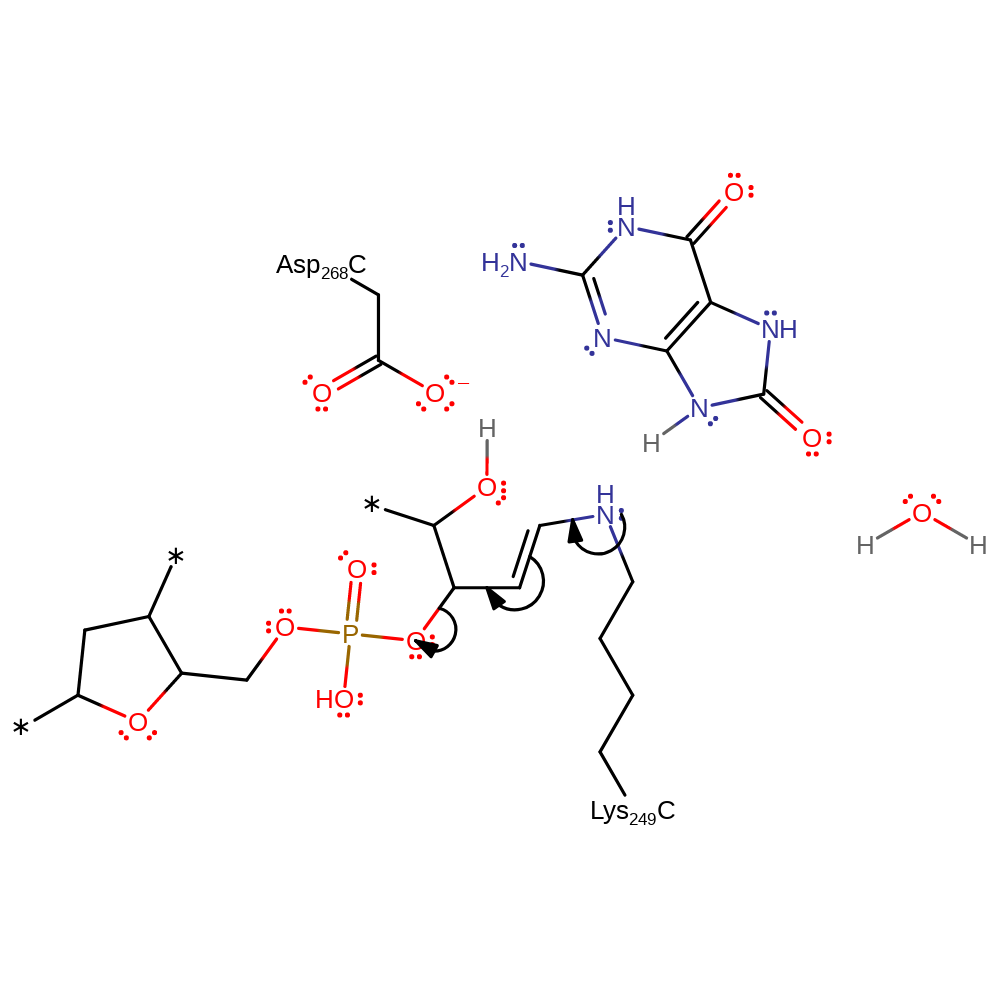
Step 5. Lys249 initiates an elimination resulting in the loss of the 3' phosphate-end of the DNA from the ribose ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys249(246)A(C) | covalently attached |
| Asp268(265)A(C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys249(246)A(C) | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation
Step 6. Water attacks the ribose at the carbon where Lys249 is bound in a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys249(246)A(C) | covalently attached |
| Asp268(265)A(C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys249(246)A(C) | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular electrophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation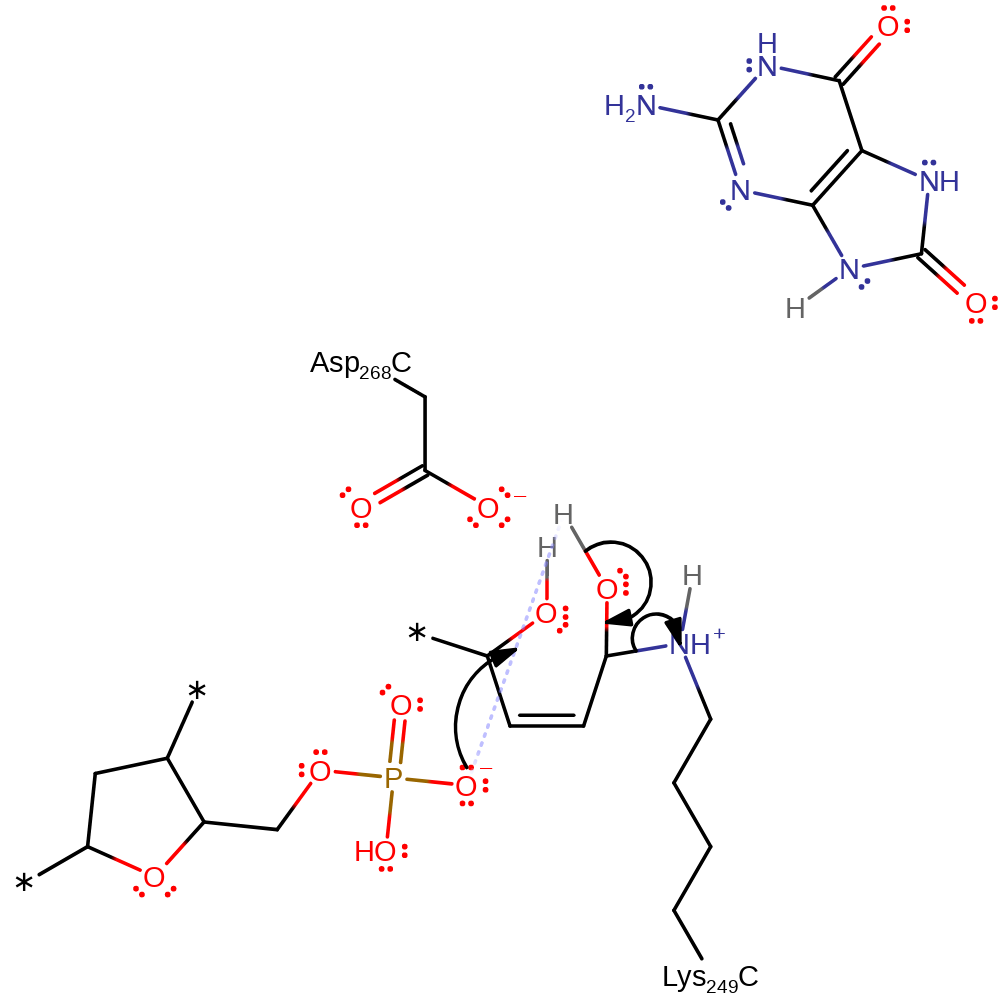
Step 7. The released phosphate deprotonates the hydroxyl group, initiating an elimination of the covalently bound Lys249.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp268(265)A(C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys249(246)A(C) | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated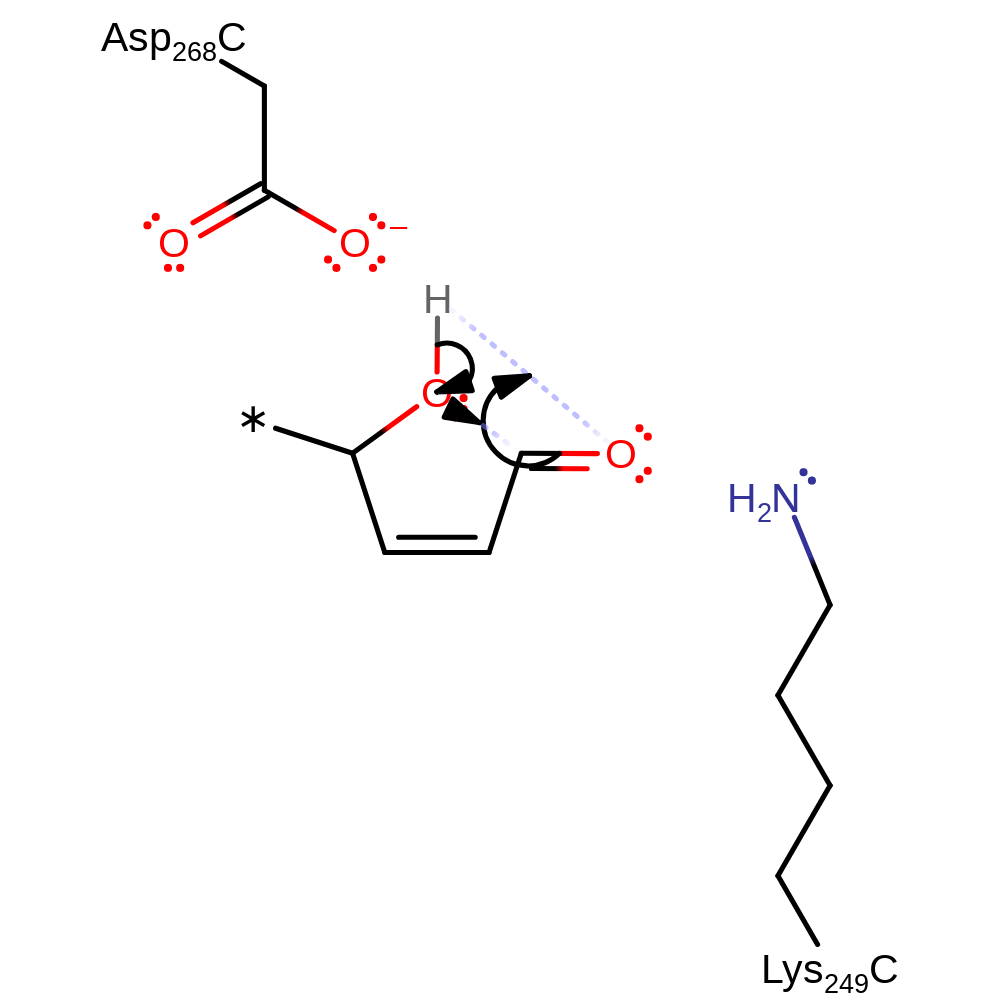
Step 8. The a,b-unsaturated aldehyde then undergoes spontaneous ring closure to furnish the DDR end product. The double bond geometry of the Schiff base is not known; if the double bond is configured trans, it would have to isomerise prior to ring closure, because a trans double bond cannot exist in a 5-membered ring, owing to ring strain. Such an isomerisation could foreseeably take place at the stage of either the Schiff base or the a,b-unsaturated aldehyde due to relatively acidic C2' hydrogens in these species.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|






 Download:
Download: