Fumarylacetoacetase
Fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) catalyses hydrolytic cleavage of a carbon-carbon bond in fumarylacetoacetate to give fumarate and acetoacetate - this step occurs as the final step in Phe and Tyr degradation. FAH functions as a metalloenzyme.
Herditary tyrosinemia type I is a fatal disease caused by loss of FAH activity. This enzyme also catalyses reactions required by soil bacteria to degrade aromatic hydrocarbons, and so understanding of this enzyme may have possible applications in bioengineering efforts to bioremediate toxic hydrocarbon wastes.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P35505
 (3.7.1.2)
(3.7.1.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mus musculus (house mouse)

- PDB
-
1hyo
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF FUMARYLACETOACETATE HYDROLASE COMPLEXED WITH 4-(HYDROXYMETHYLPHOSPHINOYL)-3-OXO-BUTANOIC ACID
(1.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.850.10
 (see all for 1hyo)
(see all for 1hyo)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Calcium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.7.1.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic mechanism of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase begins with binding of the fumarylacetoacetate substrate, which is activated by the Ca ion. A nucleophilic water molecule is activated by the His 133 and Glu 199, which is itself primed by the calcium ion, and it attacks the substrate facilitated by proton abstraction by His 133, which is being activated in turn by Glu 364. The formation of a tetrahedral alkoxide transition state is stabilised by the oxyanion hole formed by Gln 240, Lys 253 and Arg 237 as well as the Ca ion. Collapse of the transition state occurs with proton donation by Lys 253, with formation of the acetoacetate leaving group stabilised by the Ca ion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hyo) | ||
| Lys253 (main-C), Thr257 | Lys253(255)A (main-C), Thr257(259)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu364 | Glu364(366)A | Activates His 133 as part of the His-Glu dyad. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu199 | Glu199(201)A | Activates water for nucleophilic attack. Also forms part of the calcium binding site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, steric role |
| Asp233 | Asp233(235)A | Acts as a bridging ligand between the two metal ions. | metal ligand |
| Arg237, Gln240 | Arg237(239)A, Gln240(242)A | Forms part of the oxyanion hole. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys253 | Lys253(255)A | Forms part of the oxyanion hole, and donates a proton as a general acid catalyst in the collapse of the tetrahedral transition state. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His133 | His133(135)A | Activates water by proton abstraction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp126, Glu201 | Asp126(128)A, Glu201(203)A | Forms part of the calcium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Bateman RL et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 15284-15291. Mechanistic Inferences from the Crystal Structure of Fumarylacetoacetate Hydrolase with a Bound Phosphorus-based Inhibitor. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m007621200. PMID:11154690.
- Ran T et al. (2013), Biochem J, 449, 51-60. Crystal structures of Cg1458 reveal a catalytic lid domain and a common catalytic mechanism for the FAH family. DOI:10.1042/BJ20120913. PMID:23046410.
- Timm DE et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 1023-1033. Crystal structure and mechanism of a carbon–carbon bond hydrolase. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80170-1. PMID:10508789.
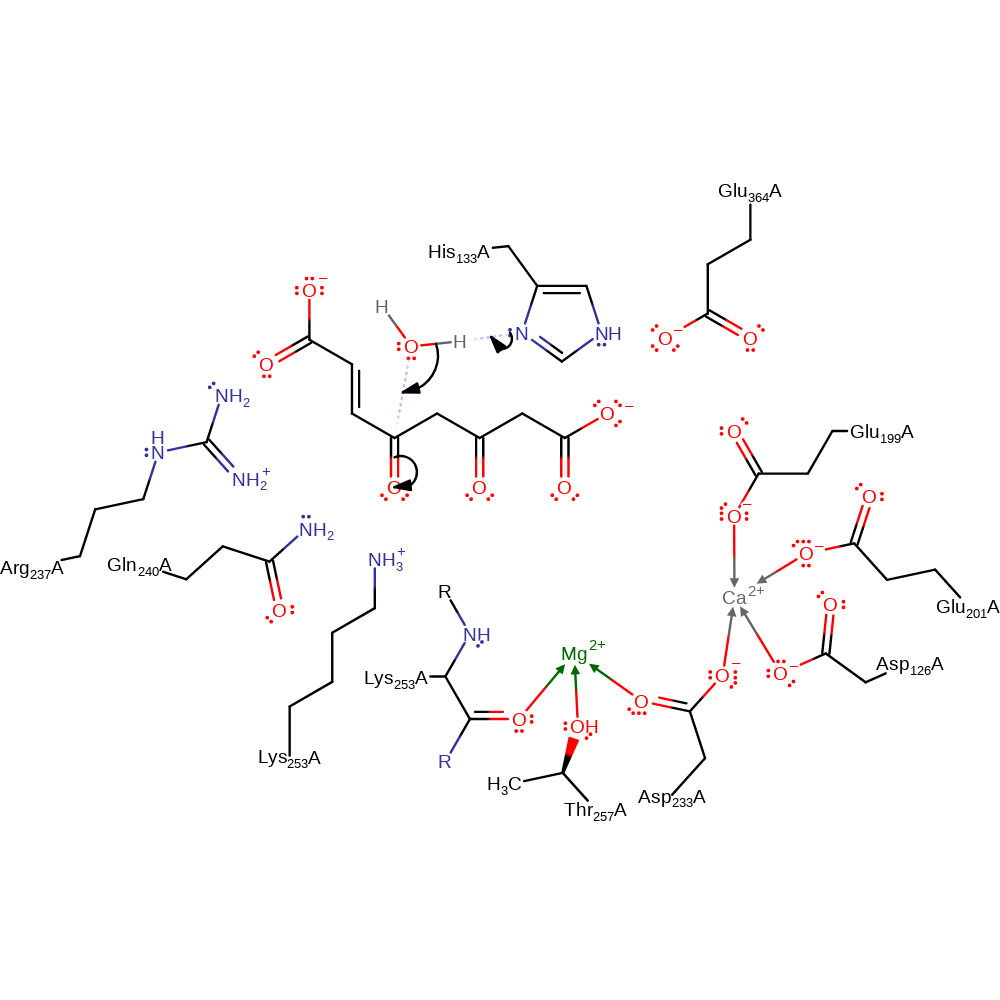
Step 1. His133 deprotonates water, which attacks the carbonyl carbon in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg237(239)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln240(242)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys253(255)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu199(201)A | metal ligand, steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His133(135)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu364(366)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp233(235)A | metal ligand |
| Thr257(259)A | metal ligand |
| Asp126(128)A | metal ligand |
| Glu201(203)A | metal ligand |
| Lys253(255)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| His133(135)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation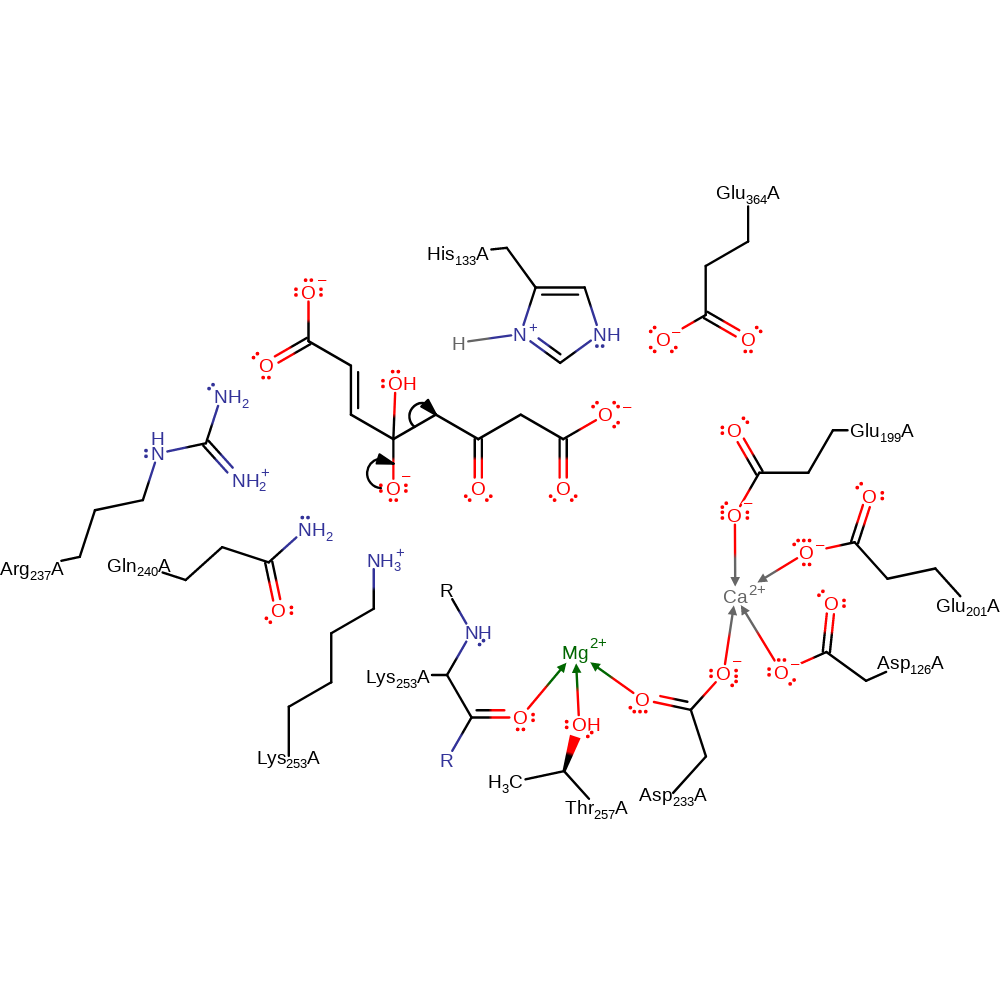
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the C-C bond, resulting in a carbanion and the fumarate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg237(239)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln240(242)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys253(255)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu199(201)A | metal ligand |
| His133(135)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu364(366)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp233(235)A | metal ligand |
| Thr257(259)A | metal ligand |
| Asp126(128)A | metal ligand |
| Glu201(203)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 3. The carbanion deprotonates Lys253, forming the acetoacetate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg237(239)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln240(242)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys253(255)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu199(201)A | metal ligand |
| His133(135)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu364(366)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp233(235)A | metal ligand |
| Thr257(259)A | metal ligand |
| Asp126(128)A | metal ligand |
| Glu201(203)A | metal ligand |
| Lys253(255)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
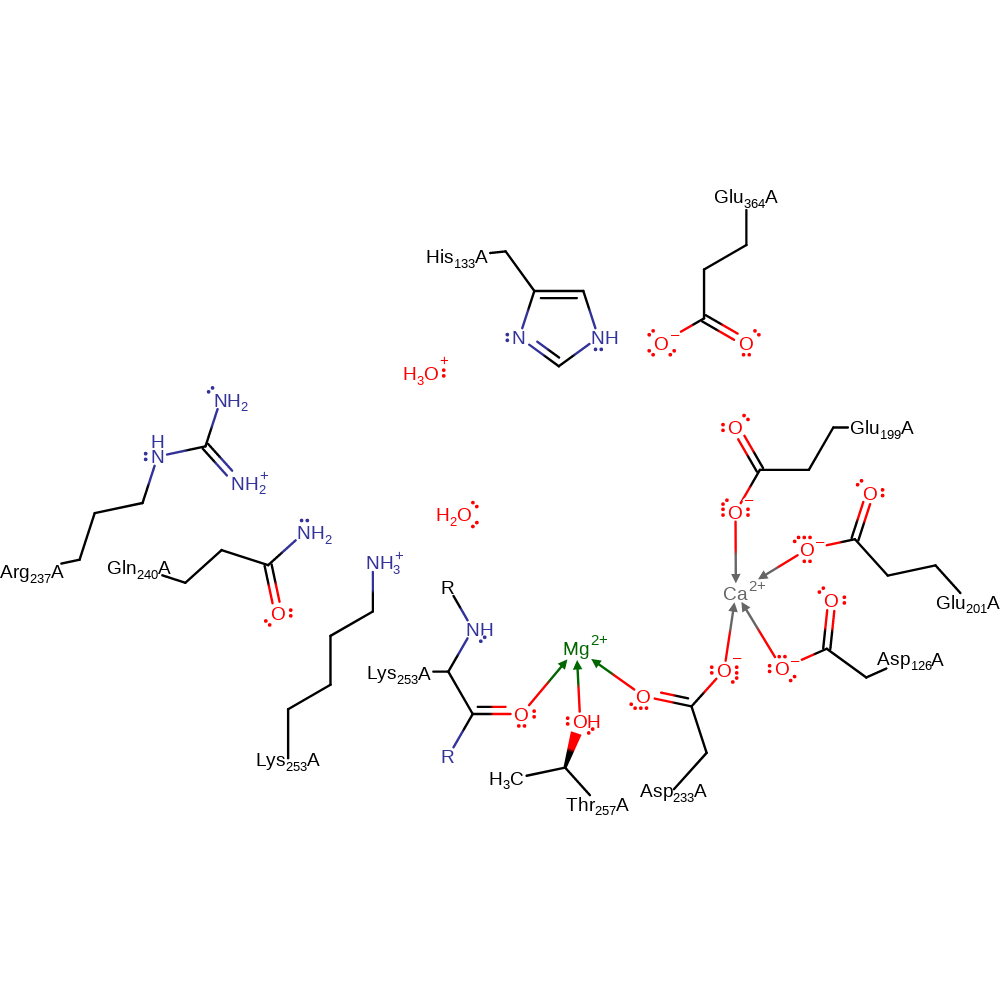
proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed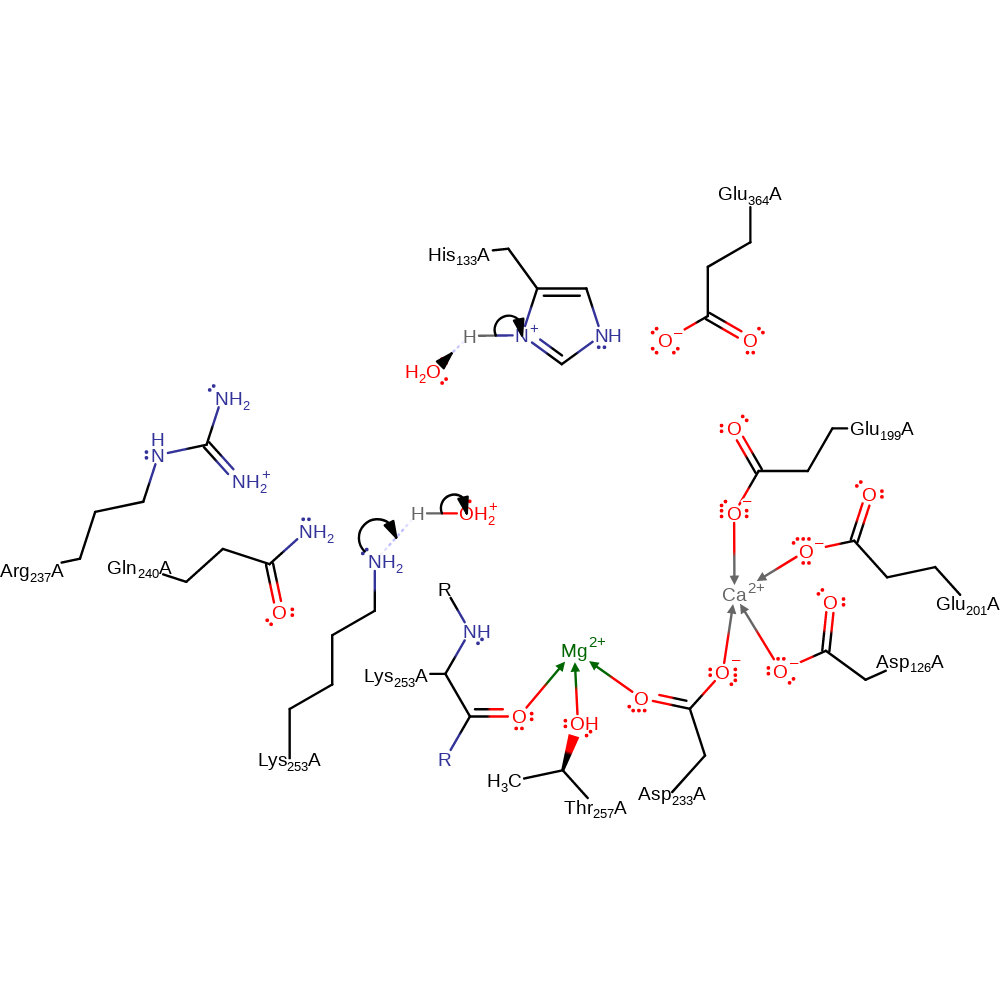
Step 4. Water deprotonates His133 and Lys253 deprotonates water to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys253(255)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu199(201)A | metal ligand |
| His133(135)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu364(366)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp233(235)A | metal ligand |
| Thr257(259)A | metal ligand |
| Asp126(128)A | metal ligand |
| Glu201(203)A | metal ligand |
| His133(135)A | proton donor |
| Lys253(255)A | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: