Carboxypeptidase A
A zinc dependent carboxypeptidase that catalyses the release of a C-terminal amino acid, but little or no action with -Asp, -Glu, -Arg, -Lys or -Pro.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00730
 (3.4.17.1)
(3.4.17.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1m4l
- STRUCTURE OF NATIVE CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A AT 1.25 RESOLUTION
(1.25 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.630.10
 (see all for 1m4l)
(see all for 1m4l)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.17.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This mechanism proposal involves the general acid/general base mechanism in which the water that attacks the peptide carbonyl is initially activated by the Zn/Glu270 system or by the C terminal carboxylic group of the substrate. We show the general acid/general base mechanism in which the water is activated by Zn/Glu270.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1m4l) | ||
| Arg237 | Arg127A | Stabilises the oxyanion hole that is formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His179, Glu182, His306 | His69A, Glu72A, His196A | Forms part of the zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu380 | Glu270A | Acts as a general acid/base to deprotonate the zinc activated water molecule. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, rate-determining step, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Kilshtain-Vardi A et al. (2002), Int J Quantum Chem, 88, 87-98. Mechanism of action of zinc proteinases: A MNDO/d/H study of alternative general-acid general-base catalytic pathways for carboxypeptidase-A. DOI:10.1002/qua.10094.
- Wu S et al. (2011), J Phys Chem B, 115, 10360-10367. pH-Dependent reactivity for glycyl-L-tyrosine in carboxypeptidase-A-catalyzed hydrolysis. DOI:10.1021/jp2046504. PMID:21732684.
- Wu S et al. (2010), J Phys Chem B, 114, 9259-9267. Catalysis of carboxypeptidase A: promoted-water versus nucleophilic pathways. DOI:10.1021/jp101448j. PMID:20583802.
- Kilshtain AV et al. (2009), Proteins, 77, 536-550. On the origin of the catalytic power of carboxypeptidase A and other metalloenzymes. DOI:10.1002/prot.22466. PMID:19480013.
- Xu D et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 9780-9788. Quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical and density functional theory studies of a prototypical zinc peptidase (carboxypeptidase A) suggest a general acid-general base mechanism. DOI:10.1021/ja9027988. PMID:19552427.
- Kilshtain-Vardi A et al. (2003), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 59, 323-333. Refined structure of bovine carboxypeptidase A at 1.25 Å resolution. DOI:10.1107/s0907444902015706. PMID:12554943.
- Jensen F et al. (2002), J Biol Inorg Chem, 7, 490-499. Three high-resolution crystal structures of cadmium-substituted carboxypeptidase A provide insight into the enzymatic function. DOI:10.1007/s00775-001-0324-0. PMID:11941507.
- Greenblatt HM et al. (1998), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 54, 289-305. Carboxypeptidase A: Native, Zinc-Removed and Mercury-Replaced Forms. DOI:10.1107/s0907444997010445. PMID:9867434.
- Rawlings ND et al. (1995), Methods Enzymol, 248, 183-228. [13] Evolutionary families of metallopeptidases. DOI:10.1016/0076-6879(95)48015-3. PMID:7674922.
- Kim H et al. (1990), Biochemistry, 29, 5546-5555. Crystal structure of the complex of carboxypeptidase A with a strongly bound phosphonate in a new crystalline form: comparison with structures of other complexes. DOI:10.2210/pdb6cpa/pdb. PMID:2386784.
- Christianson DW et al. (1986), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 83, 7568-7572. X-ray crystallographic investigation of substrate binding to carboxypeptidase A at subzero temperature. DOI:10.1073/pnas.83.20.7568. PMID:3463986.
- D. W. Christianson SpringerReference, 62-69. Carboxypeptidase N. DOI:10.1007/springerreference_37827.

Step 1. Glu270 deprotonates the zinc activated water molecule. This activated hydroxide then attacks the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
| Glu270A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg127A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu270A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation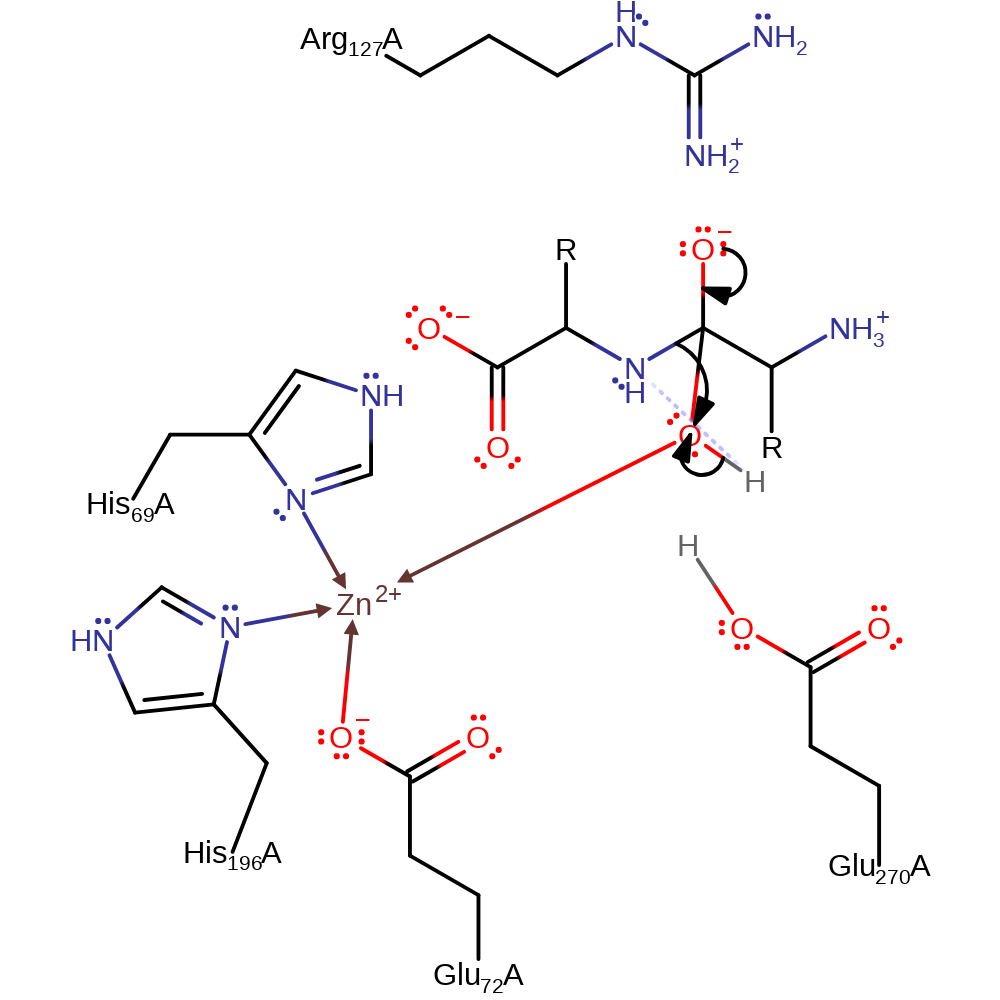
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the peptide bond. The amine side of the bond then deprotonates the carboxylic side.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu270A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg127A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, rate-determining stepCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu270A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
| Glu270A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
This represents the nucleophilic mechanism in which Glu270 becomes covalently attached to the substrate and elimination of the amine portion of the substrate results in an anhydride intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1m4l) | ||
| Arg237 | Arg127A | Stabilises the oxyanion hole that is formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His179, Glu182, His306 | His69A, Glu72A, His196A | Forms part of the zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu380 | Glu270A | Acts as a nucleophile, forming an enzyme-substrate complex during the course of the reaction. During the final hydrolysis, the water substrate becomes incorporated into the glutamate. | covalently attached, electrofuge, electrophile, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Kilshtain AV et al. (2009), Proteins, 77, 536-550. On the origin of the catalytic power of carboxypeptidase A and other metalloenzymes. DOI:10.1002/prot.22466. PMID:19480013.
- Wu S et al. (2011), J Phys Chem B, 115, 10360-10367. pH-Dependent reactivity for glycyl-L-tyrosine in carboxypeptidase-A-catalyzed hydrolysis. DOI:10.1021/jp2046504. PMID:21732684.
- Wu S et al. (2010), J Phys Chem B, 114, 9259-9267. Catalysis of carboxypeptidase A: promoted-water versus nucleophilic pathways. DOI:10.1021/jp101448j. PMID:20583802.
- Xu D et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 9780-9788. Quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical and density functional theory studies of a prototypical zinc peptidase (carboxypeptidase A) suggest a general acid-general base mechanism. DOI:10.1021/ja9027988. PMID:19552427.

Step 1. Glu270 attacks the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg127A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
| Glu270A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation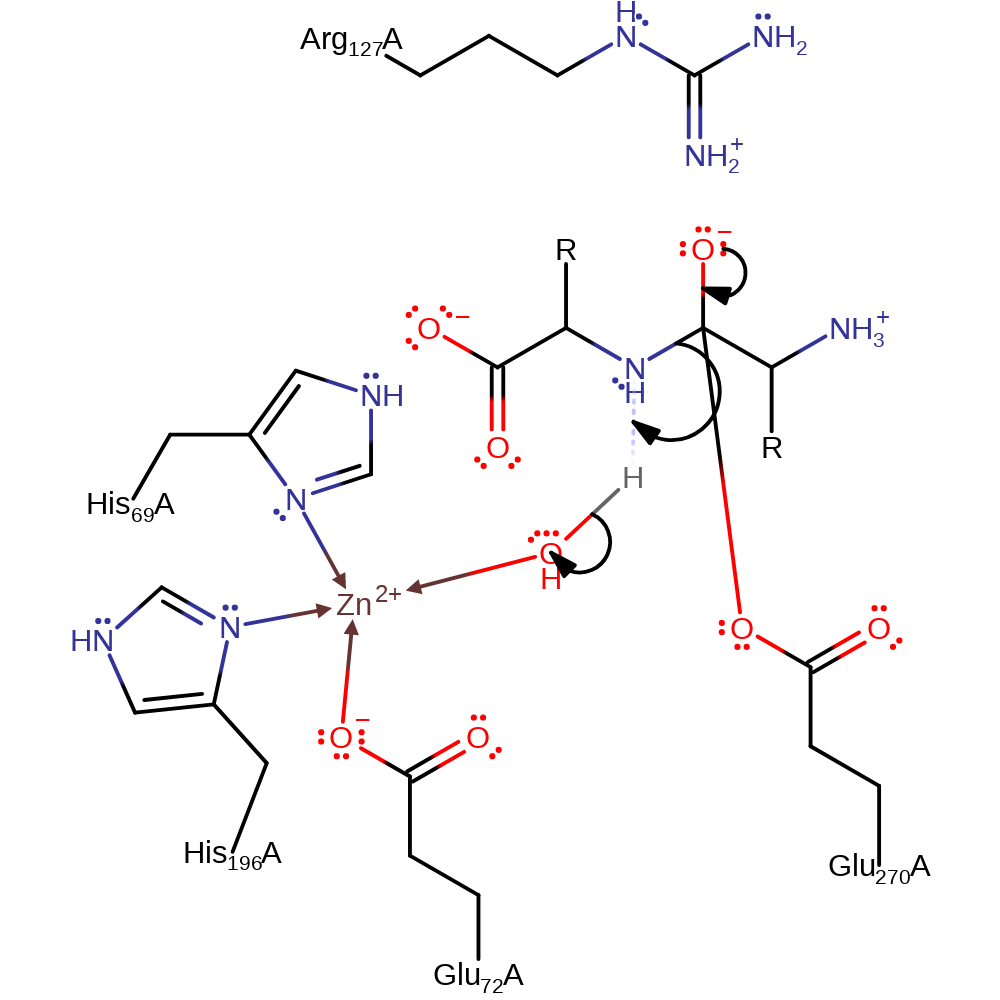
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses to eliminate the amine product with concomitant deprotonation of the zinc activated water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu270A | covalently attached |
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
| Arg127A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed
Step 3. The activated water attacks the carbonyl group of the bound glutamate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg127A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu270A | covalently attached |
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
| Glu270A | electrophile |
Chemical Components
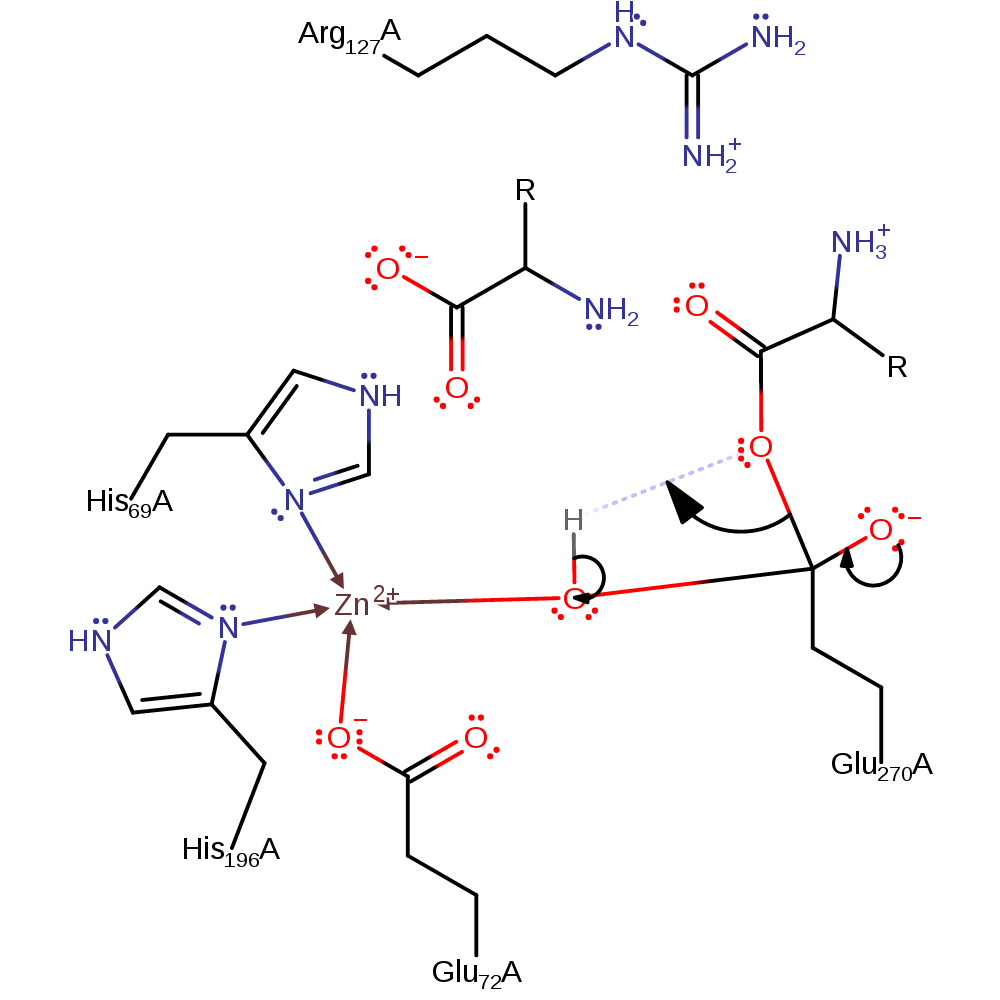
Step 4. The oxyanion collapses to form the final product and regenerate the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg127A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His69A | metal ligand |
| His196A | metal ligand |
| Glu72A | metal ligand |
| Glu270A | electrofuge |




 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: