Beta-lactamase (Class B1)
Beta-lactamase is a key enzyme in antibiotic resistance, catalysing the cleavage of the essential beta-lactam ring structure in penicillin and cephalosporinase type antibiotics. Substrate specificity varies considerably within the beta-lactamases, with some enzymes preferring penicillins and some cephalosporins.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P04190
 (3.5.2.6)
(3.5.2.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus cereus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1bc2
- ZN-DEPENDENT METALLO-BETA-LACTAMASE FROM BACILLUS CEREUS
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.15.10
 (see all for 1bc2)
(see all for 1bc2)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.2.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This entry describes the monometallic mechanism where the zinc ion is bound in the His3 site. Here the zinc activated water initiates the reaction, Asp90 deprotonates the OH of the tetrahedral intermediate and finally, the intermediate collapses, with the nitrogen group re-protonating from Asp90. The active site starting state is regenerated from bulk solvent, the zinc activates the water to re-form the initiating hydroxide ion (not shown).
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bc2) | ||
| Asp120 | Asp90A | Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting a proton from the added water molecule. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn210 | Asn180A | Helps stabilise the negatively charged intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His116, His179, His118 | His86A, His149A, His88A | Binds the Zn(II) ion. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseReferences
- Garau G et al. (2005), J Mol Biol, 345, 785-795. A Metallo-β-lactamase Enzyme in Action: Crystal Structures of the Monozinc Carbapenemase CphA and its Complex with Biapenem. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.070. PMID:15588826.
- Page MI et al. (2008), Bioinorg Chem Appl, 2008, 1-14. The Mechanisms of Catalysis by Metallo -Lactamases. DOI:10.1155/2008/576297. PMID:18551183.
- Wang Z et al. (1999), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 3, 614-622. Metallo-β-lactamase: structure and mechanism. DOI:10.1016/s1367-5931(99)00017-4. PMID:10508665.
- Carfi A et al. (1998), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 54, 313-323. 1.85 Å Resolution Structure of the ZincII β-Lactamase from Bacillus cereus . DOI:10.1107/s0907444997010627.
- BOUNAGA S et al. (1998), Biochem J, 331, 703-711. The mechanism of catalysis and the inhibition of the Bacillus cereus zinc-dependent β-lactamase. DOI:10.1042/bj3310703.

Step 1. The Zinc-activated water initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the beta-lactam ring in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp90A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn180A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His149A | metal ligand |
| His86A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp90A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn180A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His149A | metal ligand |
| His86A | metal ligand |
| Asp90A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation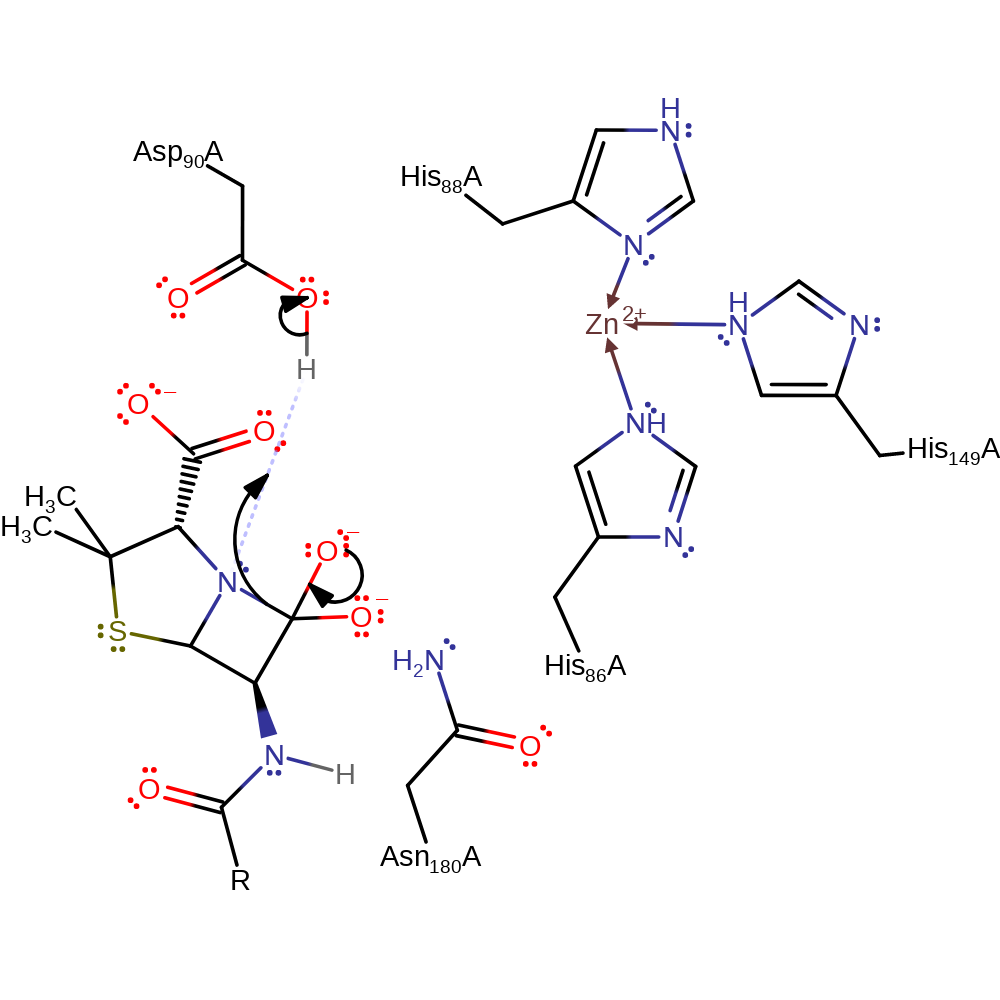
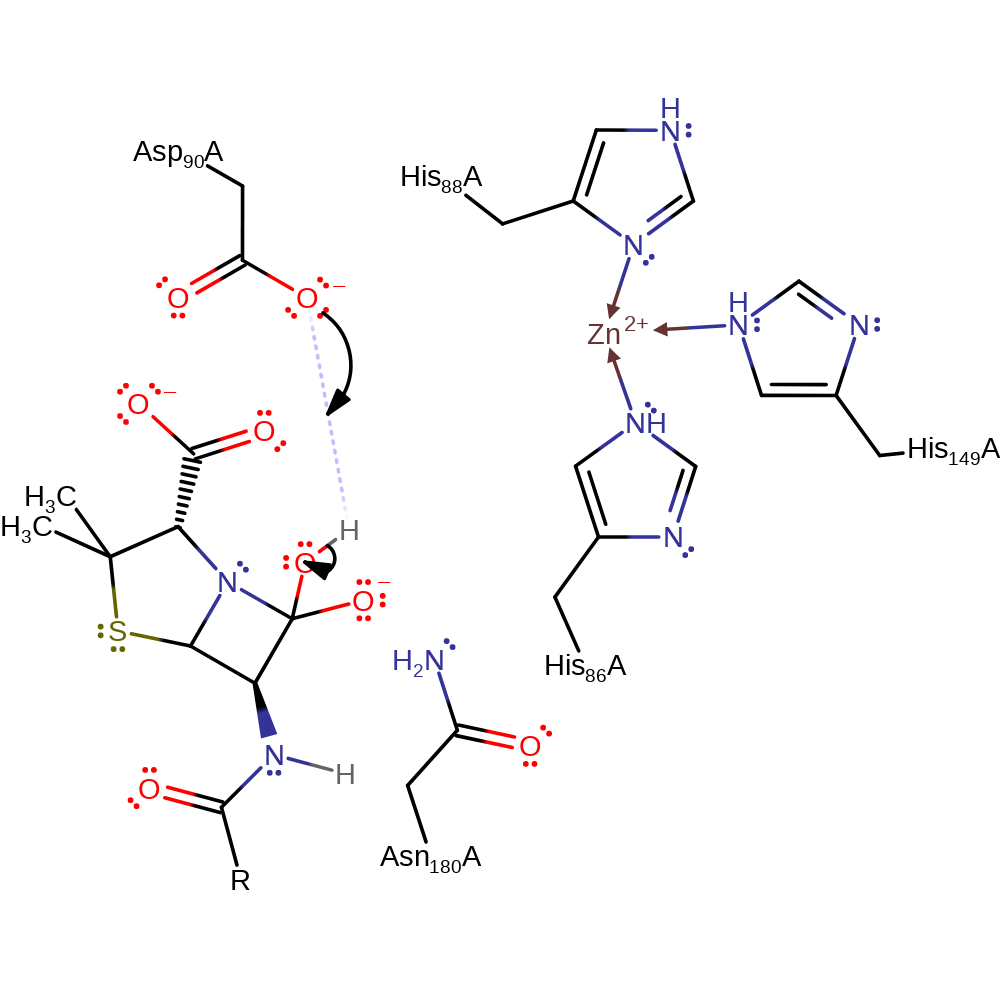
Step 3. The oxyanion formed from the initial attack performs an elimination reaction, breaking the C-N bond, the nitrogen of which deprotonates the Asp90.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp90A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn180A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His149A | metal ligand |
| His86A | metal ligand |
| Asp90A | proton donor |



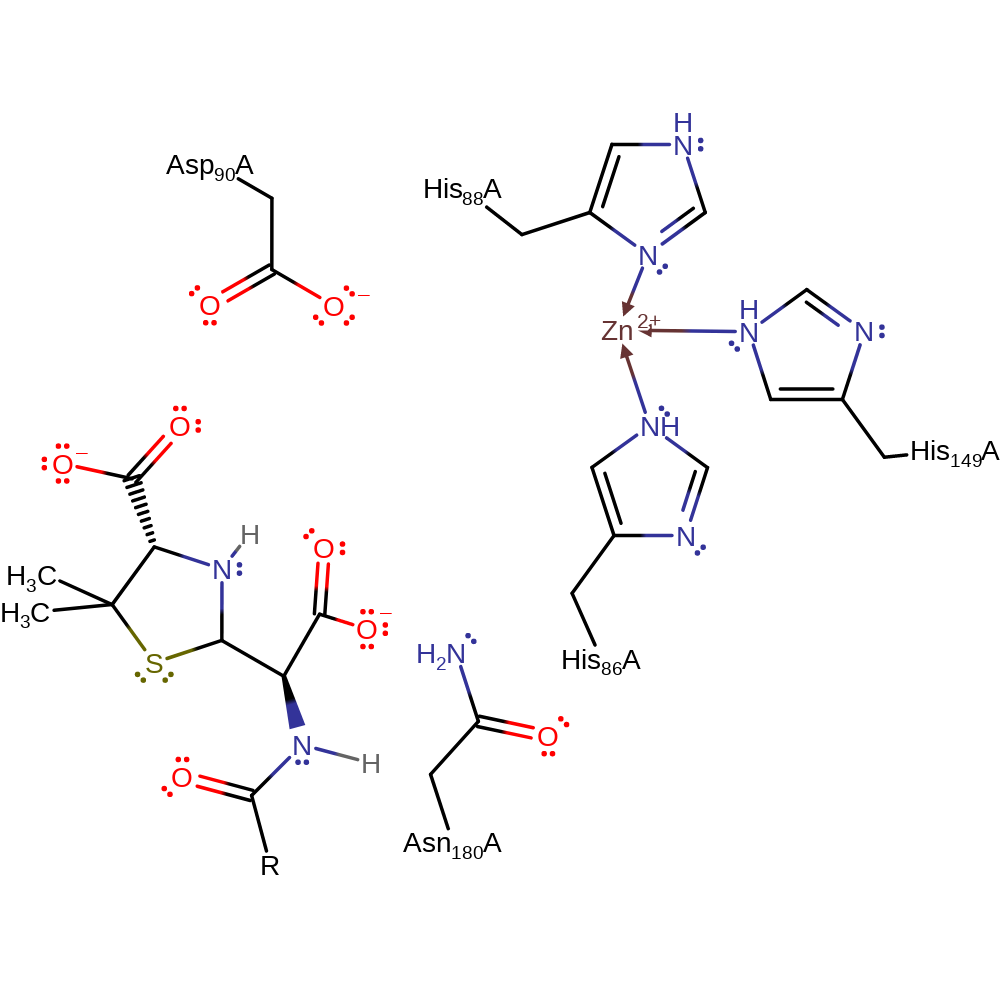 Download:
Download: