Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (adrenodoxin-type)
Bovine adrenodoxin (Adx) is a ferredoxin involved in the electron transfer from the flavoenzyme NADPH-adrenodoxin-reductase (AdR) to two P450 cytochromes; this process occurs in the production of steroid hormones.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P08165
 (1.18.1.6)
(1.18.1.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1e6e
- ADRENODOXIN REDUCTASE/ADRENODOXIN COMPLEX OF MITOCHONDRIAL P450 SYSTEMS
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.50.50.60
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1e6e)
(see all for 1e6e)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.18.1.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
AdR has a bound FAD cofactor. NADPH docks and transfers its hydride to FAD. An electron from FADH- is transferred, via the main chain atoms of Ile 376 and then Thr 377, to the bound half of an Adx dimer (to its Cys 52, then to the [2Fe-2S] centre). The electron is then transferred to the non-AdR-bound Adx molecule which dissociates. The second electron from FADH. is transferred the remaining Adx by the same route; this is concomitant with proton transfer from FADH. to a water molecule bound, and made more basic, by Asp 159 and His 55.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1e6e) | ||
| His87 | His55A | His 55 binds water and makes it more basic. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp191 | Asp159A | Asp 159 binds water and makes it more basic. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile408 (main-N) | Ile376A (main-N) | The main chain of Ile 276 is part of an electron transfer chain from FADH- and FADH. to adrenodoxin. | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor, polar interaction |
| Thr409 (main-C) | Thr377A (main-C) | The main chain of Thr 377 is part of an electron transfer chain from FADH- and FADH. to adrenodoxin. | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor, polar interaction |
Chemical Components
aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, redox reaction, radical formation, electron relay, proton transfer, electron transfer, radical termination, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Ziegler GA et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 10986-10995. Crystal Structures of Adrenodoxin Reductase in Complex with NADP+and NADPH Suggesting a Mechanism for the Electron Transfer of an Enzyme Family†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi000079k. PMID:10998235.
- Beilke D et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 7969-7978. A New Electron Transport Mechanism in Mitochondrial Steroid Hydroxylase Systems Based on Structural Changes upon the Reduction of Adrenodoxin†. DOI:10.1021/bi0160361. PMID:12069587.
- Müller JJ et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 2786-2789. Adrenodoxin Reductase-Adrenodoxin Complex Structure Suggests Electron Transfer Path in Steroid Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m008501200. PMID:11053423.
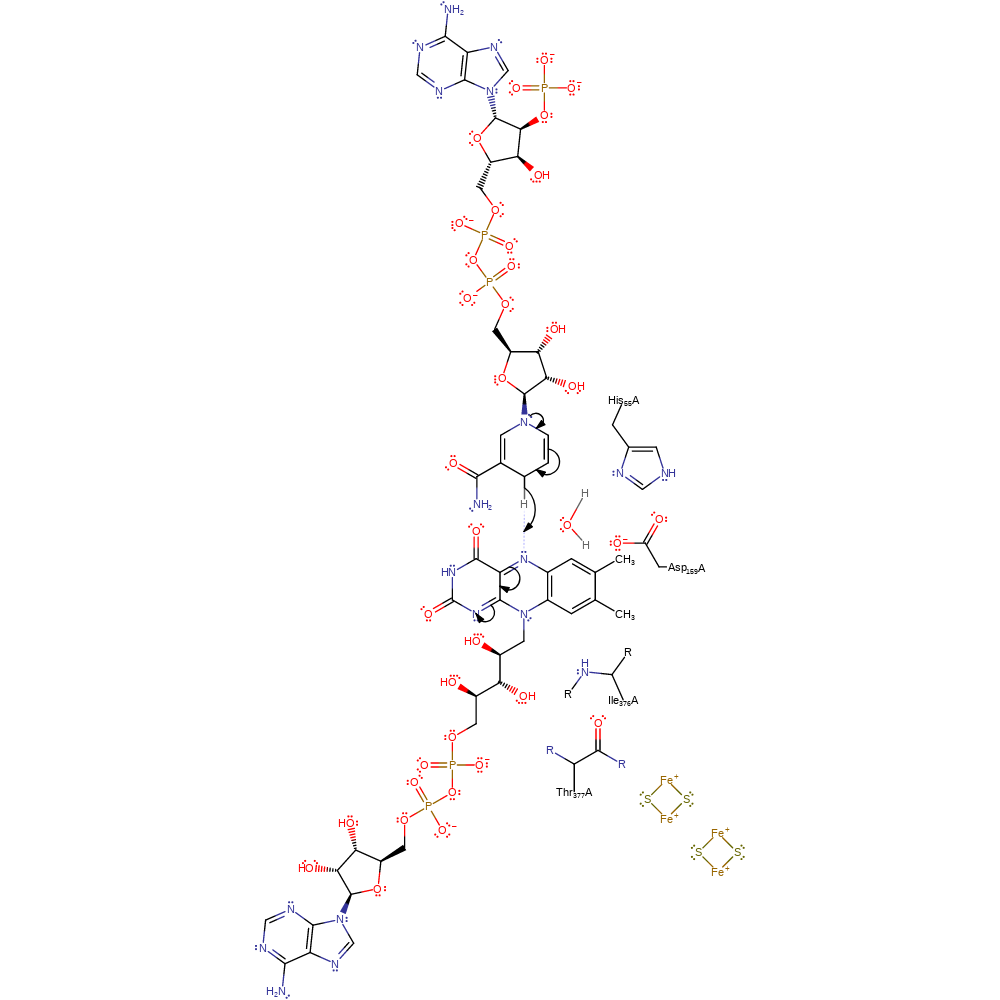
Step 1. A hydride ion is transferred from the substrate NADP to the cofactor, FAD461.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His55A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp159A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ile376A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Thr377A (main-C) | polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall product formed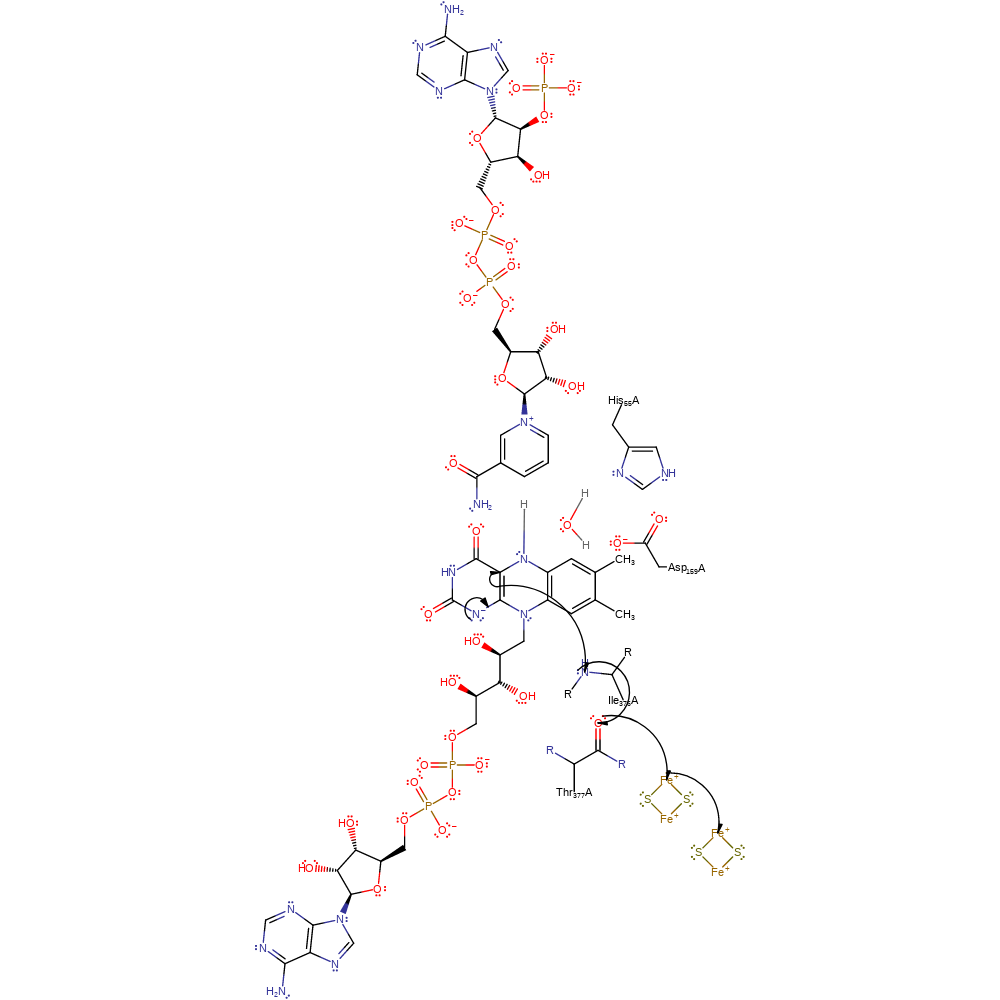
Step 2. A single electron is transferred from the FAD461 to one of the substrate adrenodoxin dmers via the main chains of Ile376 and Thr377 and a second adrenodoxin dimer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His55A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp159A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ile376A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Thr377A (main-C) | polar interaction |
| Ile376A (main-N) | single electron relay |
| Thr377A (main-C) | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Ile376A (main-N) | single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, radical formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, electron relay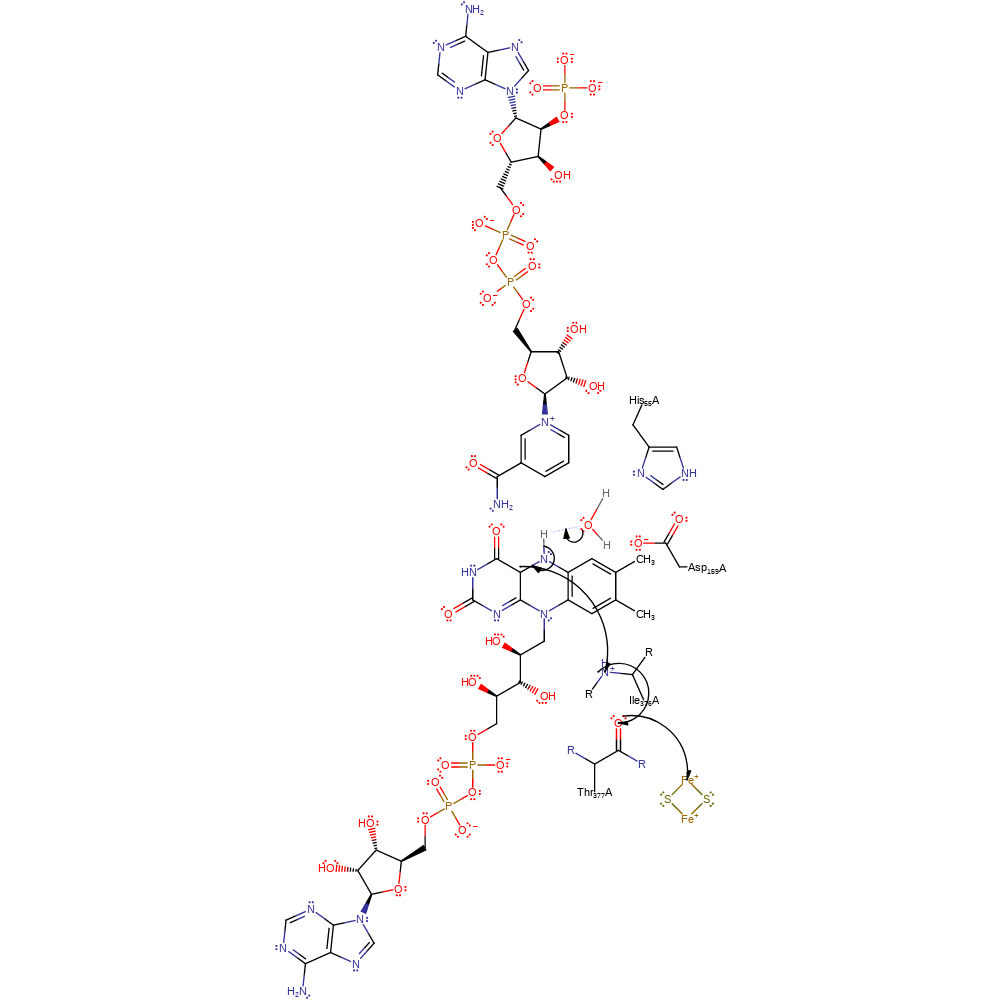
Step 3. FAD461 is deprotonated by a water molecule activated by Asp159. This results in the second electron transfer from FAD461 to the second adrenodoxin dimer via the main chains of Ile376 and Thr377.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His55A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp159A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile376A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Thr377A (main-C) | polar interaction |
| Ile376A (main-N) | single electron donor |
| Thr377A (main-C) | single electron acceptor |
| Ile376A (main-N) | single electron relay |
| Thr377A (main-C) | single electron relay |
| Ile376A (main-N) | single electron acceptor |
| Thr377A (main-C) | single electron donor |





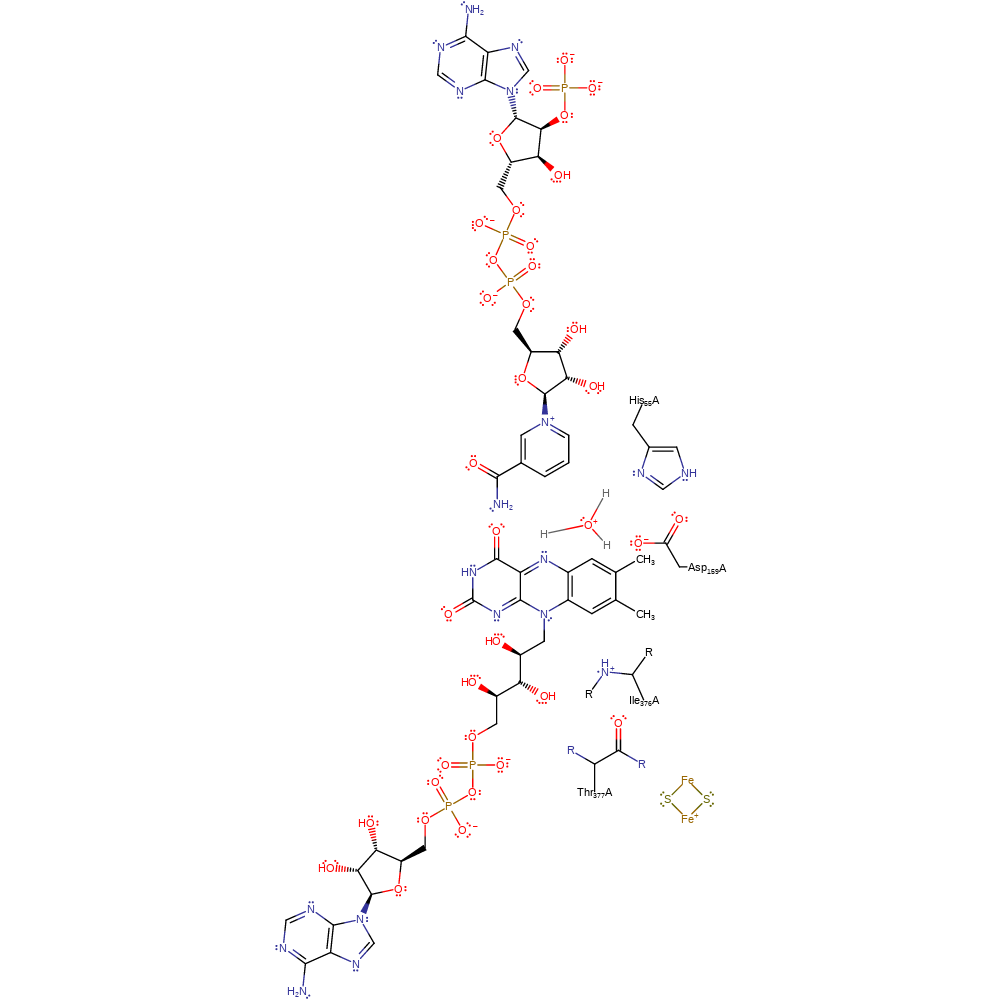 Download:
Download: