Ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase (class II)
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of the four standard ribonucleotides, 5V -di(or tri)-phospho -adenosine, -cytidine, -guanosine, and -uridine, to their 2V -deoxyribonucleotide counterparts and thereby provides the precursors needed for both synthesis and repair of DNA. Class II enzymes are found in bacteria that can live under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, and also in some of their phages. The prototype from this class is the monomeric enzyme from Lactobacillus leichmannii , but as more and more members of this class have been found that are predominately homodimers, the Lactobacillus enzyme seems to be rather an extreme of the class. They all, however, utilize a cobaltous cofactor, adenosylcobalamin, a vitamin B12 derivative, that interacts directly with an active site cysteine to form the reactive cysteine radical needed for ribonucleotide reduction.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q59490
 (1.17.4.2)
(1.17.4.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Lactobacillus leichmannii (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1l1l
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF B-12 DEPENDENT (CLASS II) RIBONUCLEOTIDE REDUCTASE
(1.75 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.70.20
 (see all for 1l1l)
(see all for 1l1l)
- Cofactors
- Cob(iii)alamin (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.17.4.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
The cofactor adenosylcobalamin generates a 5-deoxyadenosyl radical by homolytic cleavage of its carbon-cobalt bond generate a protein thiyl radical on the side chain of Cys408 via a hydrogen transfer reaction. The radical on the sulfur of Cys408 is transferred to the ribonucleoside triphosphate substrate via a hydrogen transfer reaction. Glu410 deprotonates the ribonucleoside radical, reducing the secondary alcohol group to a ketone group and transfers the radical to the next carbon along, resulting in the elimination of water and concomitant deprotonation of Cys119. The deoxyibonucleoside intermediate acquires a hydrogen from Cys419, transferring the radical to this residue. Cys419 then undergoes attack from Cys119, forming a disulfide bond. The radical on the Cys419-Cys119 species is transferred through a chain of hydrogen bonded active site residues, Asn406 and Glu410, to the substrate 2'-position. The ketone group is then re-oxidised to a secondary alcohol with concomitant deprotonation of Glu410. The 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate product is formed by hydrogen transfer from Cys408, generating a thiyl radical. The thiyl radical of Cys408 is transferred back to the deoxyadenosine via a hydrogen transfer. The cofactor is regenerated via a colligation reaction between the cobalamine portion and the deoxyadenosyl portion. The disulfide bond between Cys119 and Cys419 is transferred to Cys419 and Cys731 with concomitant proton transfer to Cys119. The disulfide bond between Cys419 and Cys731 is transferred to Cys731 and Cys736 with concomitant proton transfer to Cys419. The disulfide bond between Cys731 and Cys736 is transferred to Cys736 and the thioredoxin acceptor with concomitant proton transfer to Cys731. The disulfide bond between Cys736 and thioredoxin is transferred to the second free thiol of thioredoxin with concomitant proton transfer to Cys736, regenerating the enzyme and producing the fully oxidised thioredoxin.The exact order of events is unclear in the latter stages.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l1l) | ||
| Cys119 | Cys119A | Acts as a general acid to eliminate water from the riboside radical. Then nucleophilically attacks Cys419 to form a disulphide bridge. Later bridge is transferred to Cys419 and Cys731 with concomitant proton transfer to Cys119. Also the radical on Cys419 is transferred to the riboside via a redox chain, from Cys119 to Asn406. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge |
| Cys408 | Cys408A | Forms thiyl radical via hydrogen exchange with 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical, which exchanges a hydrogen to form a radical at the ribonucleoside triphosphate substrate. Later on return step occurs to regenerate original resting state. | hydrogen radical acceptor, hydrogen radical donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys736, Cys731 | Cys736A, Cys731A | Cys731 and Cys736 are involved in recycling the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, nucleofuge, proton donor |
| Glu410 | Glu410A | Deprotonates riboside radical hydroxyl group to form a ketone and transfer radical to next carbon atom, with concomitant deprotonation of Cys119 and elimination of water. Later acts as a general acid to oxidise ketone to secondary alcohol. Forms part of redox chain with Asn406 to form radical on riboside again. | single electron relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Cys419 | Cys419A | Acts as an electrophile to form disulphide bridge with Cys119, in concert with forming a radical via hydrogen exchange with the riboside radical. Later forms disulphide bridge with Cys731, then abstracts proton from Cys736 to return to original resting state. | hydrogen radical donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, single electron donor, electrofuge, electrophile |
| Asn406 | Asn406A | Helps stabilise the radical formed on the sugar ring during the course of the reaction. It is also involved in the single electron relay step. | single electron relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, single electron acceptor, single electron donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
homolysis, radical formation, cofactor used, decoordination from a metal ion, hydrogen transfer, radical propagation, proton transfer, electron transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), dehydration, coordination, electron relay, colligation, radical termination, coordination to a metal ion, native state of cofactor regenerated, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, decyclisation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Kolberg M et al. (2004), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1699, 1-34. Structure, function, and mechanism of ribonucleotide reductases. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.02.007. PMID:15158709.
- Nordlund P et al. (2006), Annu Rev Biochem, 75, 681-706. Ribonucleotide Reductases. DOI:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142443. PMID:16756507.
- Stubbe J et al. (1998), Chem Rev, 98, 705-762. Protein Radicals in Enzyme Catalysis. DOI:10.1021/cr9400875. PMID:11848913.

Step 1. The cofactor (a deoxy derivative of vitamin B12) decomposes via a homolysis reaction to produce B12 (the cobalamine, cobalt containing, portion) and deoxyadenosyl portion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
homolysis, radical formation, cofactor used, decoordination from a metal ion
Step 2. The deoxyadenosyl radical is transferred to Cys408 via a hydrogen transfer reaction
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys408A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys408A | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, radical propagation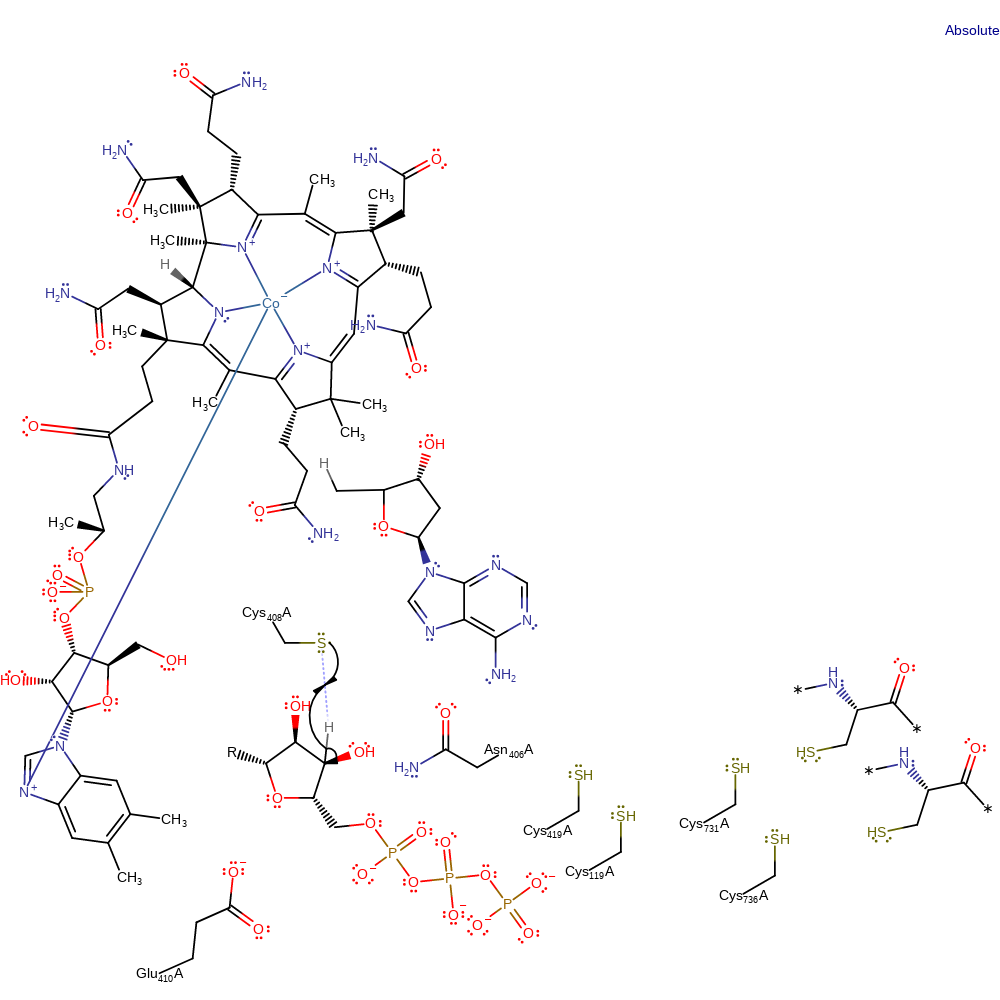
Step 3. The radical on the sulfur of Cys408 is transferred to the ribonucleoside triphosphate substrate via a hydrogen transfer reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys408A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys408A | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, radical propagation
Step 4. Glu410 deprotonates the ribonucleoside radical, reducing the secondary alcohol group to a ketone group and transfers the radical to the next carbon along, resulting in the elimination of water and concomitant deprotonation of Cys119.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys119A | proton donor |
| Glu410A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), radical propagation, dehydration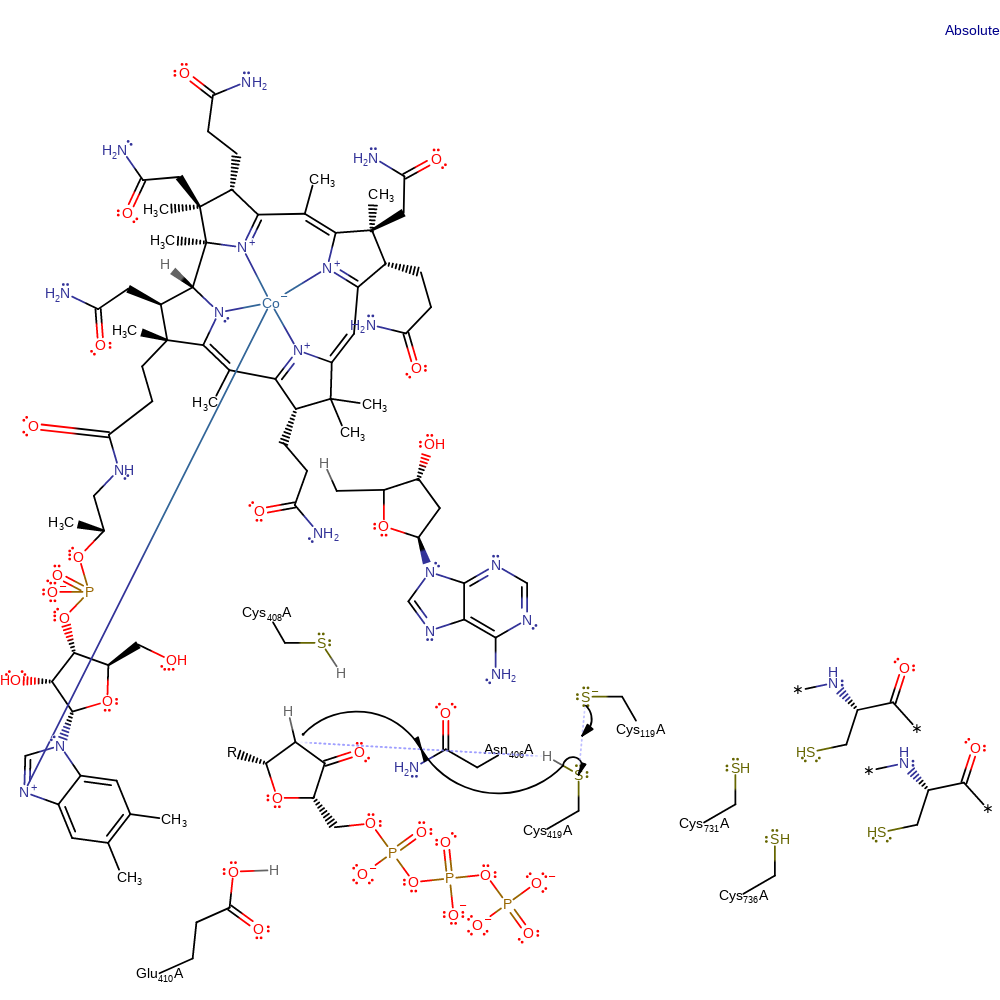
Step 5. The deoxyibonucleoside intermediate acquires a hydrogen from Cys419, transferring the radical to this residue. Cys419 then undergoes attack from Cys119, forming a disulfide bond
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys419A | electrophile |
| Cys119A | nucleophile |
| Cys419A | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, coordination, radical propagation
Step 6. The radical on the Cys419-Cys119 species is transferred through a chain of hydrogen bonded active site residues, Asn406 and Glu410, to the substrate 2'-position. The ketone group is then re-oxidised to a secondary alcohol with concomitant deprotonation of Glu410
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | single electron donor |
| Glu410A | proton donor |
| Asn406A | single electron relay |
| Glu410A | single electron relay |
| Asn406A | single electron acceptor |
| Cys419A | single electron donor |
| Glu410A | single electron donor, single electron acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, radical propagation, electron relay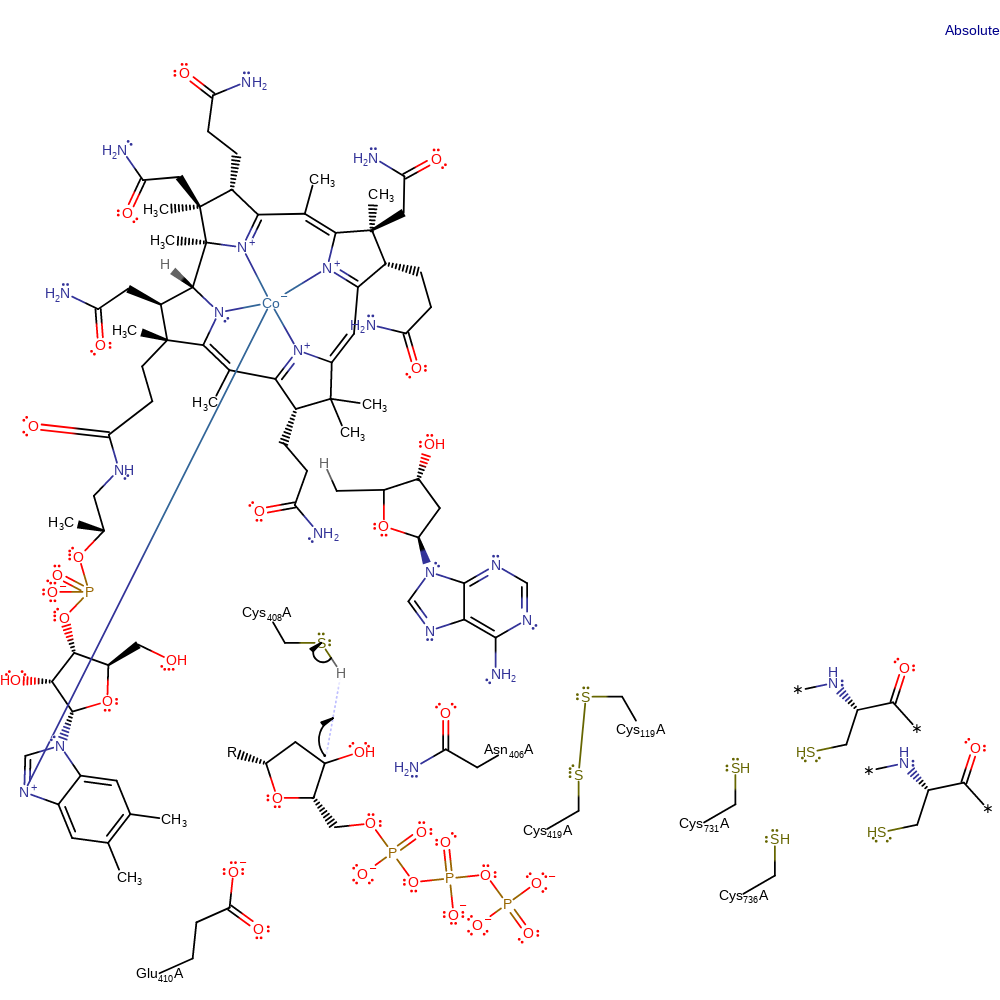
Step 7. The 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate product is formed by hydrogen transfer from Cys408, generating a thiyl radical
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys408A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys408A | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, radical propagation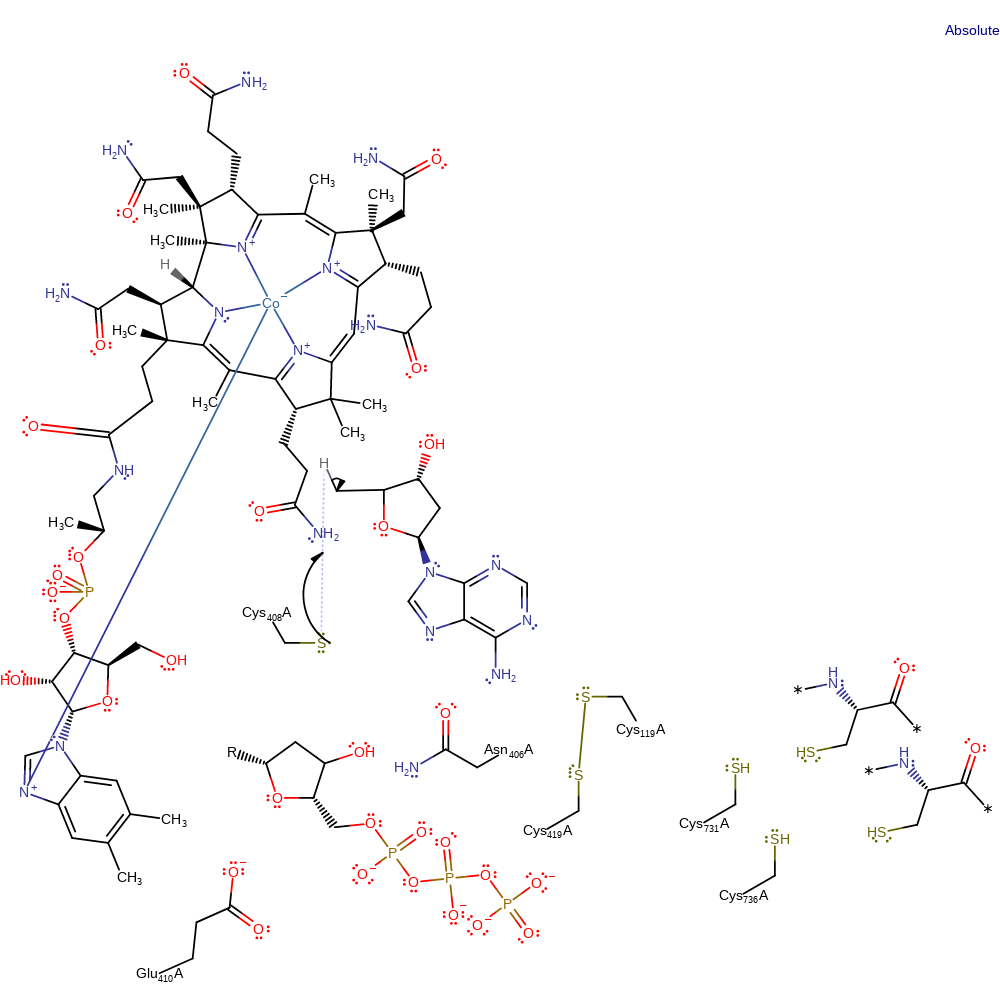
Step 8. The thiyl radical of Cys408 is transferred back to the deoxyadenosine via a hydrogen transfer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys408A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys408A | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, radical propagation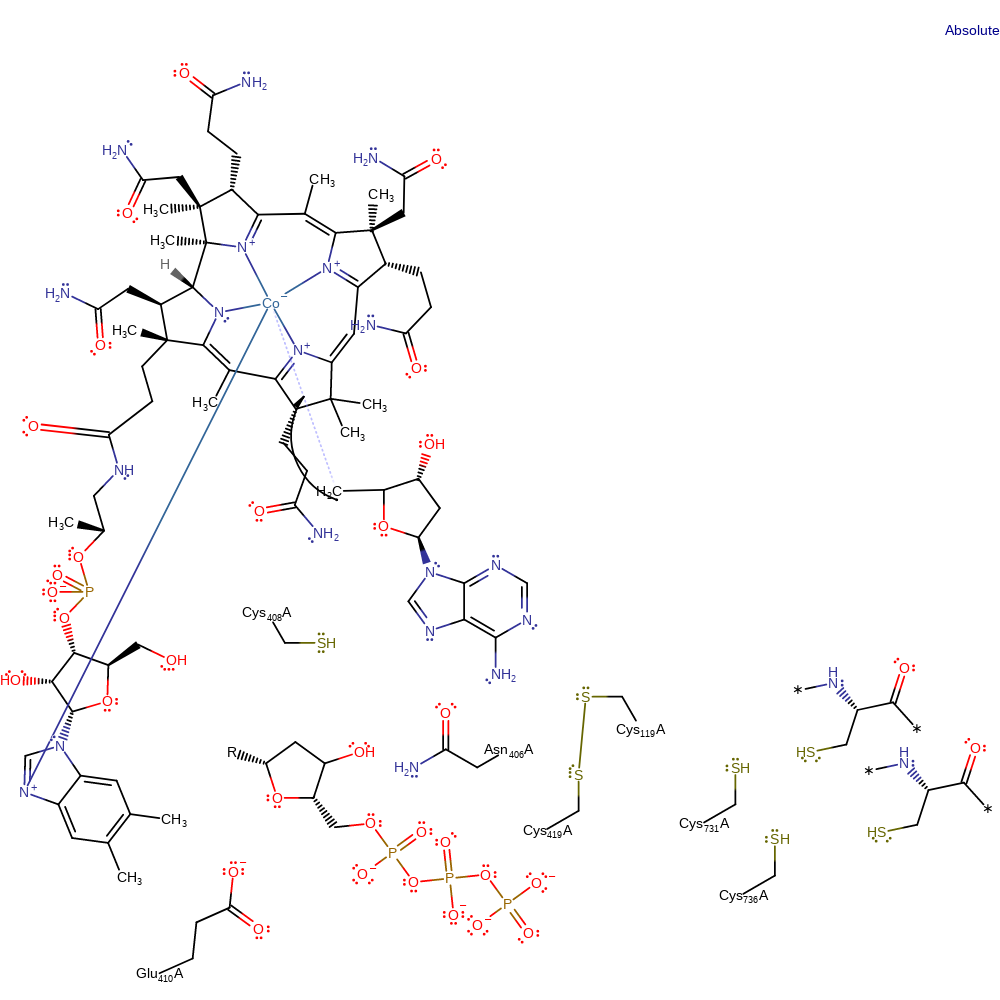
Step 9. The cofactor is regenerated via a colligation reaction between the cobalamine portion and the deoxyadenosyl portion
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
colligation, radical termination, coordination to a metal ion, native state of cofactor regenerated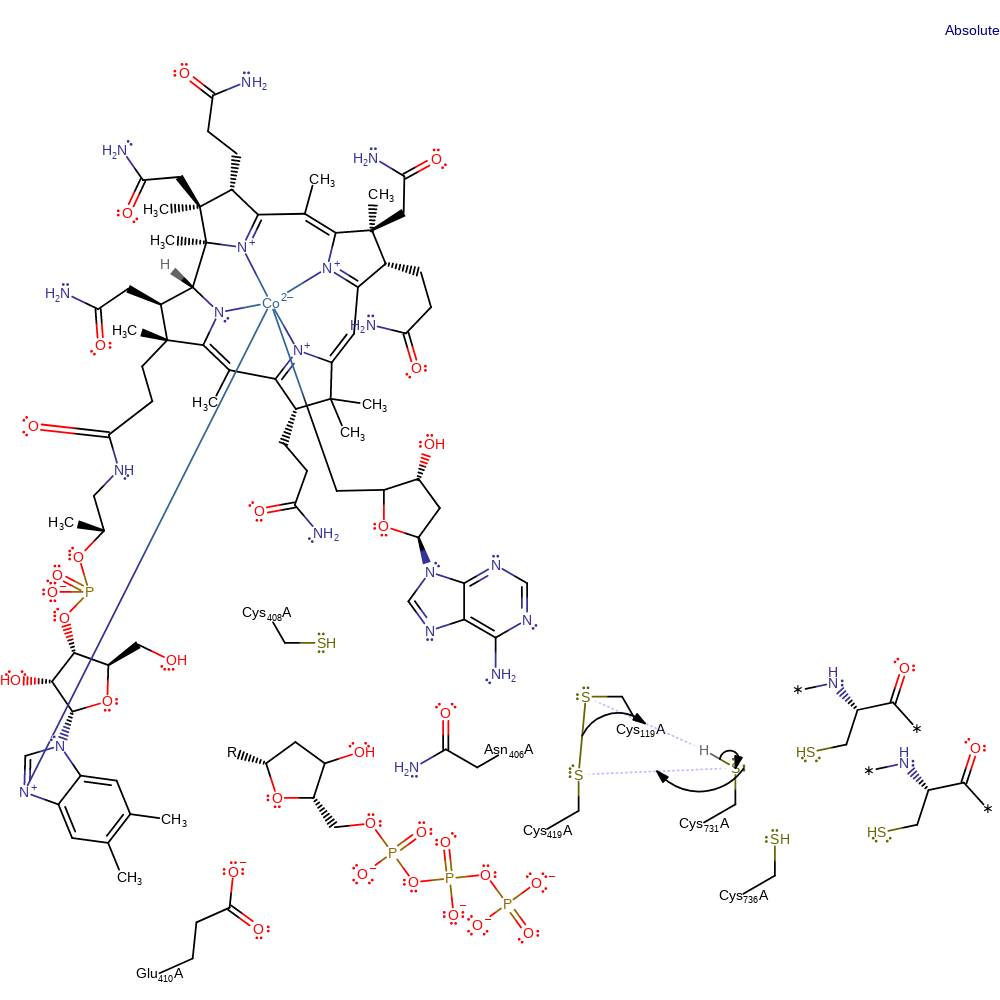
Step 10. The disulfide bond between Cys119 and Cys419 is transferred to Cys419 and Cys731 with concomitant proton transfer to Cys119. The exact order of events is unclear
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys736A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys731A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys119A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |
| Cys419A | electrophile |
| Cys731A | nucleophile |
| Cys419A | electrofuge |
| Cys731A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, decyclisation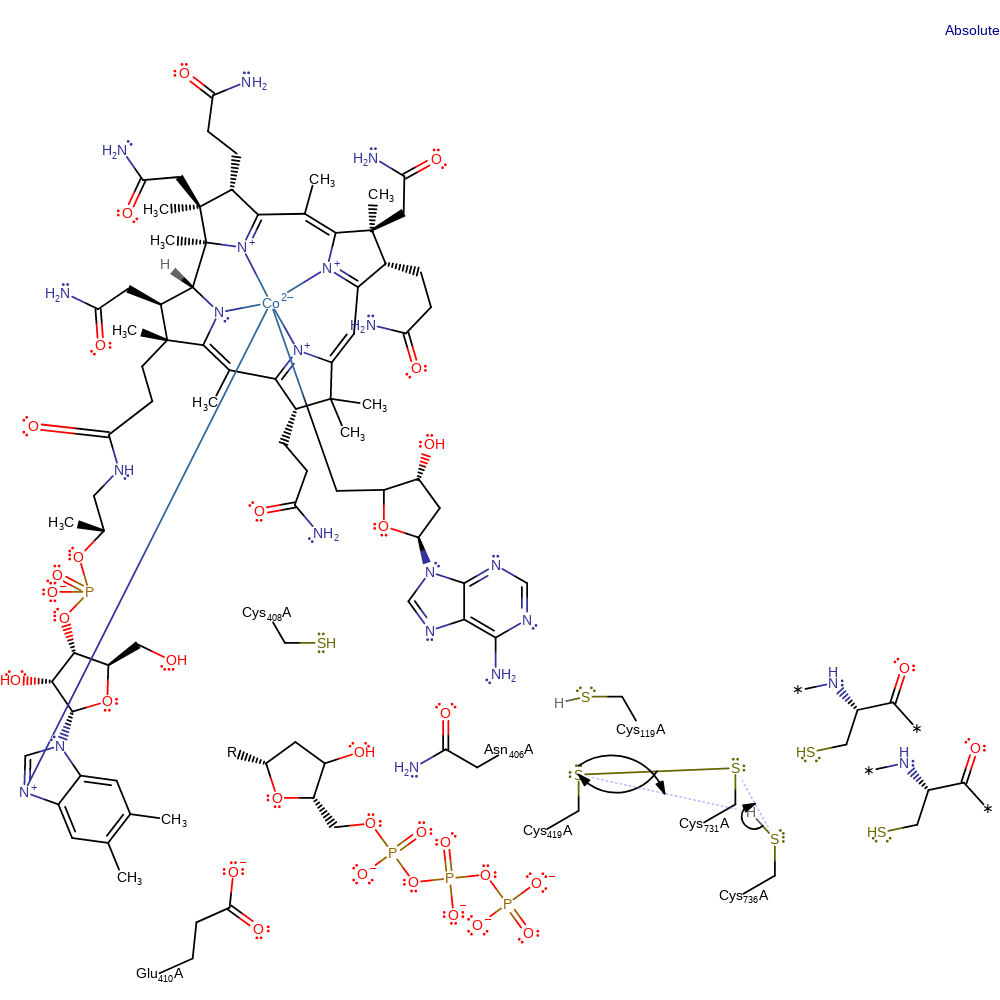
Step 11. The disulfide bond between Cys419 and Cys731 is transferred to Cys731 and Cys736 with concomitant proton transfer to Cys419. The exact order of events is unclear
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys736A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys731A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrofuge, electrophile |
| Cys419A | nucleofuge |
| Cys736A | nucleophile, proton donor |
| Cys419A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, decyclisation, cyclisation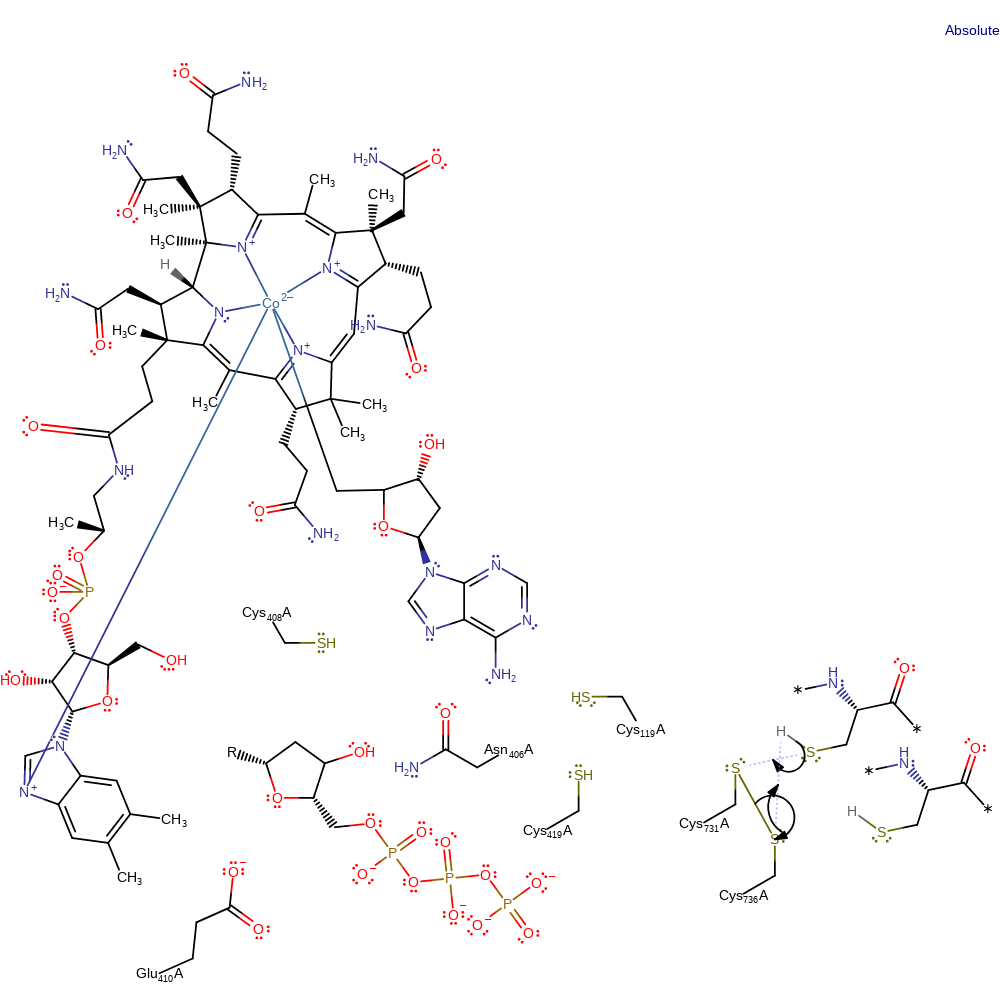
Step 12. The disulfide bond between Cys731 and Cys736 is transferred to Cys736 and the thioredoxin acceptor with concomitant proton transfer to Cys731. The exact order of events is unclear
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys736A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys731A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys736A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| Cys731A | electrophile, electrofuge |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, decyclisation, intermediate formation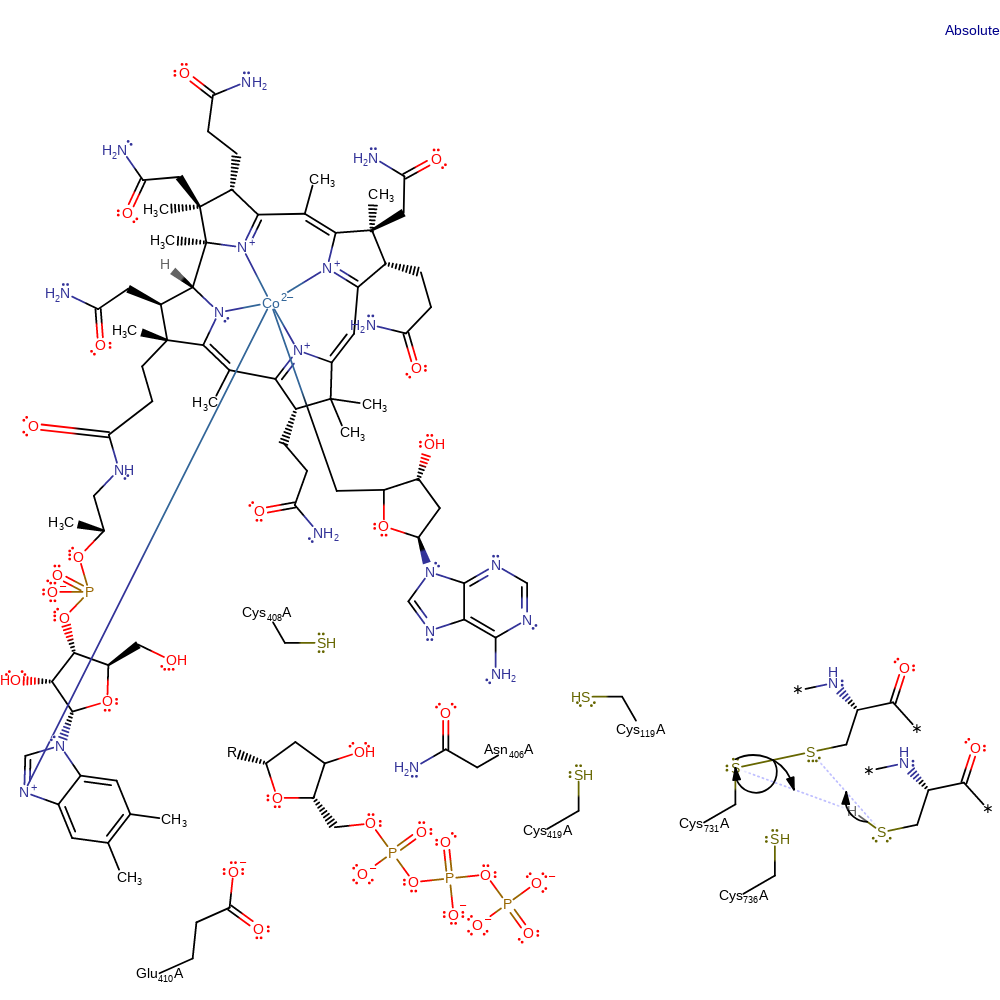
Step 13. The disulfide bond between Cys736 and thioredoxin is transferred to the second free thiol of thioredoxin with concomitant proton transfer to Cys736, regenerating the enzyme and producing the fully oxidised thioredoxin. The exact order of events is unclear
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys119A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn406A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu410A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys736A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys731A | hydrogen bond acceptor, nucleofuge, proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: