Catechol oxidase
Catechol oxidase is a type 3 copper protein that exclusively catalyses the oxidation of catechols (e.g. o-diphenols) to the corresponding o-quinones. The enzyme can also act on a variety of substituted catechols. Although a member of the same superfamily as tyrosinase, it is a different enzyme.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9ZP19
 (1.10.3.1)
(1.10.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Ipomoea batatas (Sweet potato)

- PDB
-
1bt3
- CATECHOL OXIDASE FROM IPOMOEA BATATAS (SWEET POTATOES) IN THE NATIVE CU(II)-CU(II) STATE
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.1280.10
 (see all for 1bt3)
(see all for 1bt3)
- Cofactors
- Cu-o-cu linkage (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.10.3.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
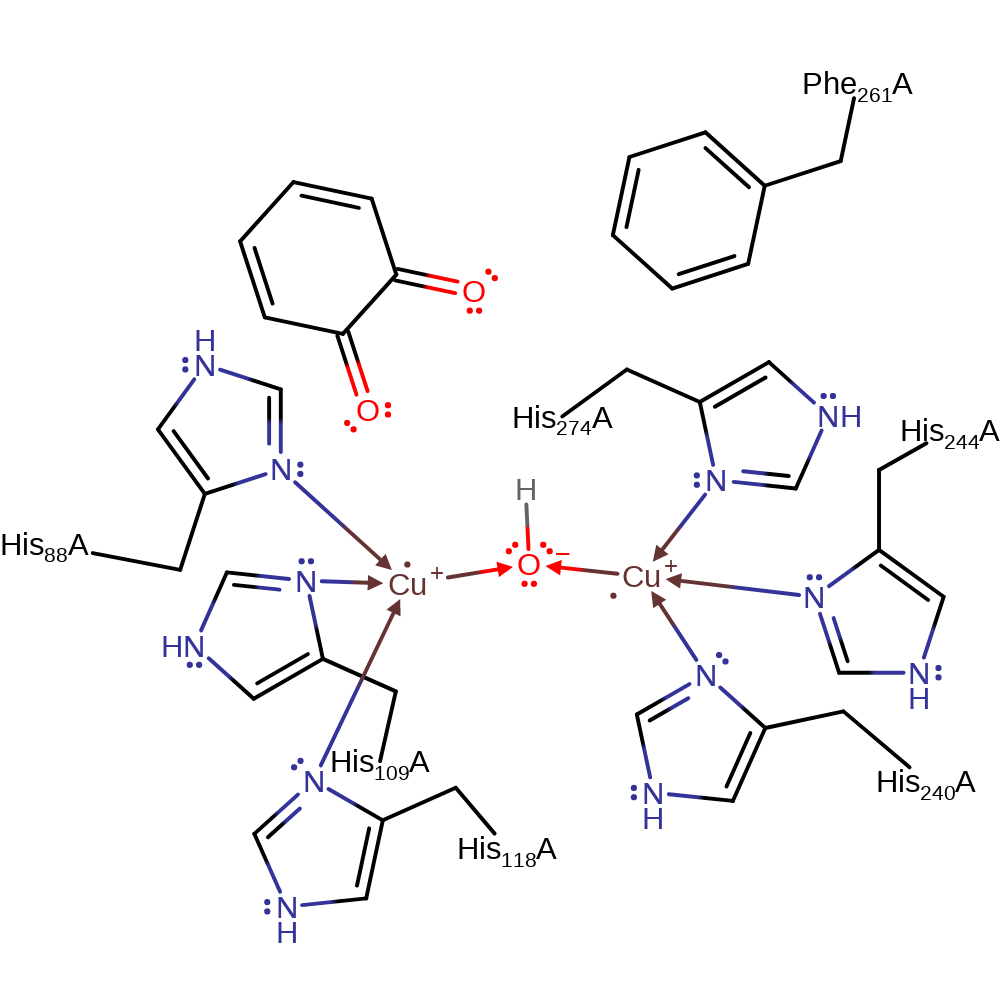
There is little or no direct involvement of amino acid residues in the proposed mechanism. A hydroxide ion (activated water) bridges the two copper centres. This activates the diphenol, resulting in an electron transfer from one of the copper centres to the dioxygen molecule. The dioxygen radical abstracts a hydrogen from the other hydroxyl group on the Cu-bound intermediate. The phenolic racidal then donates a second electron to the copper centre. The anionic oxygen of the peroxide group deprotonates the second molecule of benzene-1,2-diol, which causes a hydride to be eliminated from the second phenol group, and cleaved of the peroxo bond. The second Cu(I) centre donates a single electron to the second phenol group. The anionic oxygen of the peroxide group deprotonates the second molecule of benzene-1,2-diol, which causes a hydride to be eliminated from the second phenol group, and cleaved of the peroxo bond. The second Cu(I) centre donates a single electron to the second phenol group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bt3) | ||
| His274, His244, His240 | His274A, His244A, His240A | Forms the Copper B binding site. | metal ligand |
| Phe261 | Phe261A | Phe261 blocks access of the ortho protons of the phenolic ring thus limiting the enzyme to oxygenase activity and not hydroxylase activity. | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| His118, His88, His109 | His118A, His88A, His109A | Forms the Copper A binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, redox reaction, bimolecular homolytic addition, radical formation, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, cofactor used, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall product formed, hydrogen transfer, radical propagation, electron transfer, radical termination, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, hydride transfer, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Siegbahn PE (2004), J Biol Inorg Chem, 9, 577-590. The catalytic cycle of catechol oxidase. DOI:10.1007/s00775-004-0551-2. PMID:15185133.
- Güell M et al. (2007), J Biol Inorg Chem, 12, 1251-1264. Theoretical study of the catalytic mechanism of catechol oxidase. DOI:10.1007/s00775-007-0293-z. PMID:17891425.
- Tepper AW et al. (2005), J Am Chem Soc, 127, 567-575. Interaction between the Type-3 Copper Protein Tyrosinase and the Substrate Analoguep-Nitrophenol Studied by NMR. DOI:10.1021/ja0454687. PMID:15643881.
- Olivares C et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 679-686. Identification of Active Site Residues Involved in Metal Cofactor Binding and Stereospecific Substrate Recognition in Mammalian Tyrosinase. Implications to the Catalytic Cycle†. DOI:10.1021/bi011535n.
- Klabunde T et al. (1998), Nat Struct Biol, 5, 1084-1090. Crystal structure of a plant catechol oxidase containing a dicopper center. DOI:10.1038/4193. PMID:9846879.
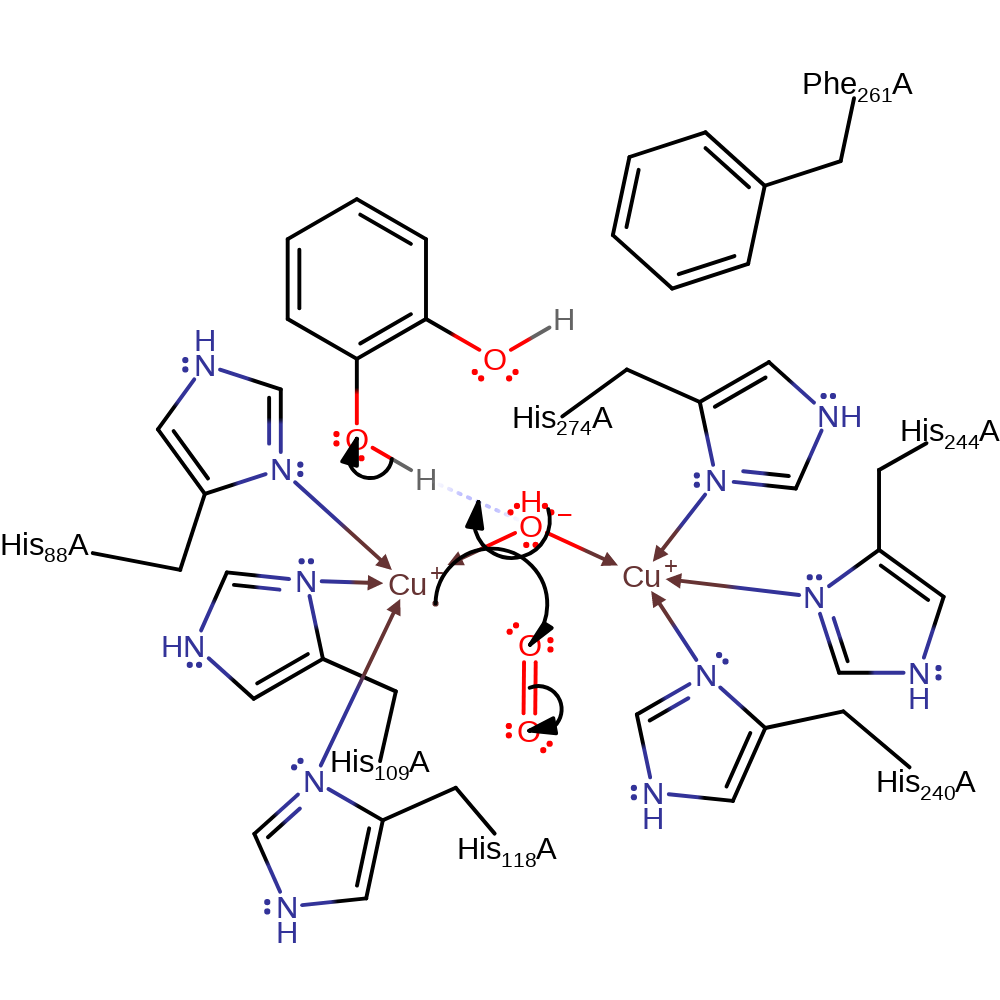
Step 1. The bridging hydroxide deprotonates the benzene-1,2-diol, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the Cu(I) centre, initiating a single electron transfer to dioxygen. The dioxygen radical then replaces the water as the bridging ligand between the two copper centres.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His109A | metal ligand |
| His118A | metal ligand |
| His240A | metal ligand |
| His244A | metal ligand |
| His274A | metal ligand |
| Phe261A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, redox reaction, ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, radical formation, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, cofactor used, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall product formed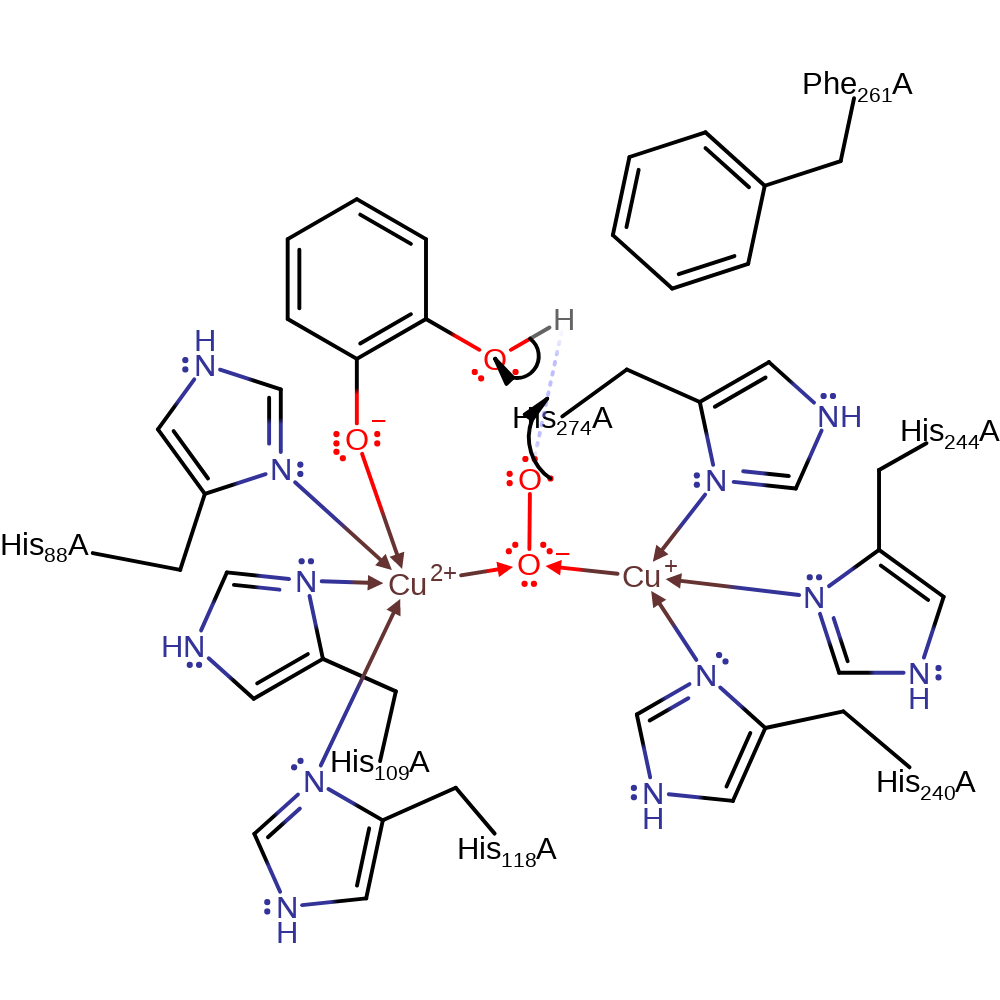
Step 2. The dioxygen radical abstracts a hydrogen from the other hydroxyl group on the Cu-bound intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His109A | metal ligand |
| His118A | metal ligand |
| His240A | metal ligand |
| His244A | metal ligand |
| His274A | metal ligand |
| Phe261A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, radical propagation, intermediate formation
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, initiating double bond rearrangement that forms 1,2-benzoquinone and causes a single electron to be transferred to the Cu(II) centre.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His109A | metal ligand |
| His118A | metal ligand |
| His240A | metal ligand |
| His244A | metal ligand |
| His274A | metal ligand |
| Phe261A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical termination, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed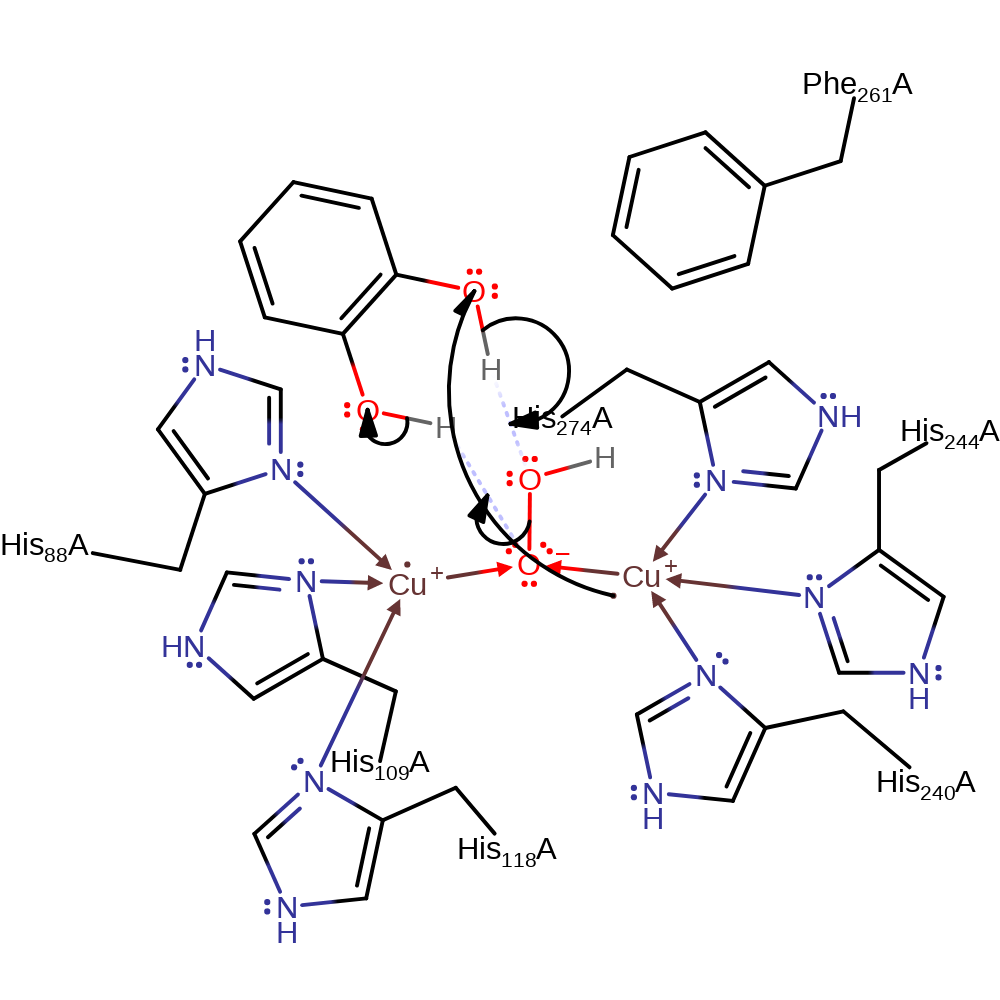
Step 4. The anionic oxygen of the peroxide group deprotonates the second molecule of benzene-1,2-diol, which causes a hydride to be eliminated from the second phenol group, and cleaved of the peroxo bond. The second Cu(I) centre donates a single electron to the second phenol group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His109A | metal ligand |
| His118A | metal ligand |
| His240A | metal ligand |
| His244A | metal ligand |
| His274A | metal ligand |
| Phe261A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, redox reaction, hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, radical formation, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate collapse, overall product formed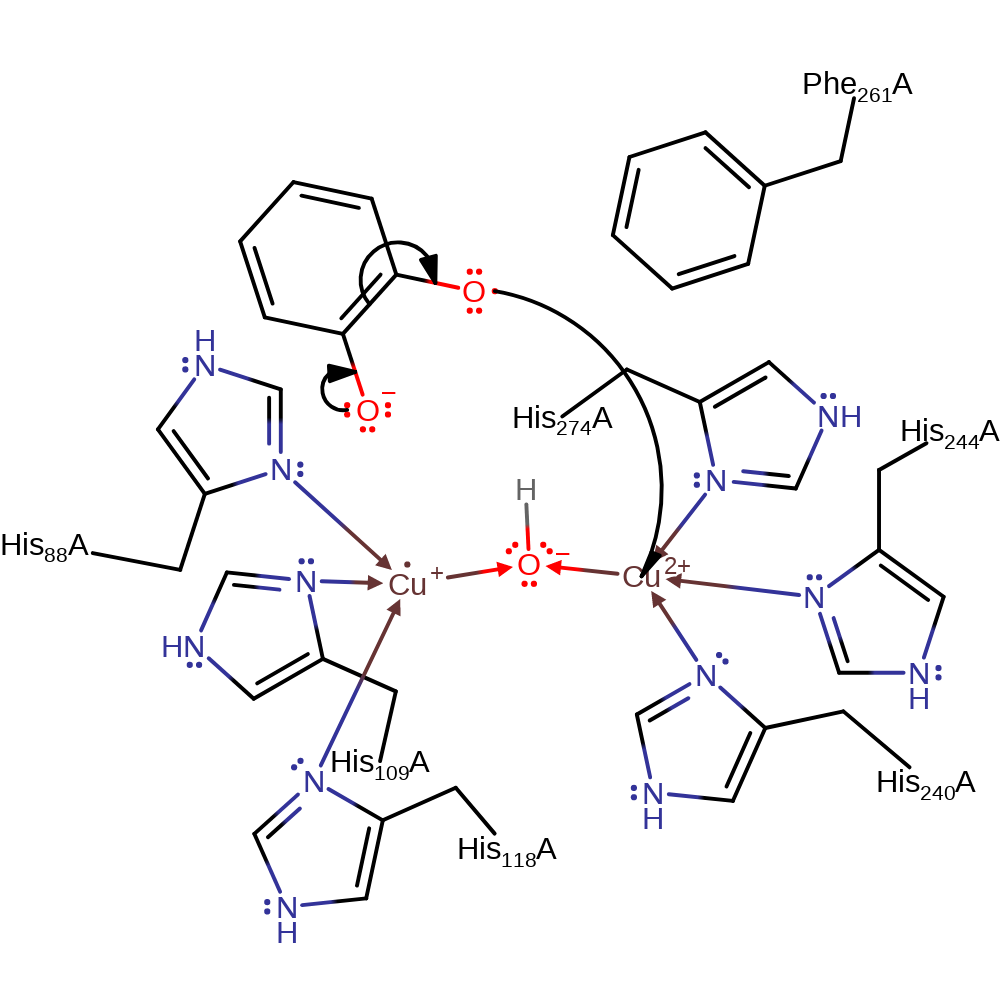
Step 5. The phenolate undergoes double bond rearrangement that causes a single electron to be donated back to the Cu(II) centre, and formation of 1,2-benzoquinone.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His88A | metal ligand |
| His109A | metal ligand |
| His118A | metal ligand |
| His240A | metal ligand |
| His244A | metal ligand |
| His274A | metal ligand |
| Phe261A | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role |




 Download:
Download: