L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)
The flavo-cytochrome enzyme is a lactate dehydrogenase that catalyses the transfer of a hydride equivalent from its hydroxy acid substrate to the enzyme bound flavin, and thence to proteins of the mitochondrial electron transport chain via a bound cytochrome. The enzyme contains two domains, the flavin domain, capable of converting lactate to pyruvate by itself, and the heme domain which contains the prosthetic group involved in electron transfer from the reduced flavin to an acceptor cytochrome.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00175
 (1.1.2.3)
(1.1.2.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
1fcb
- MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF FLAVOCYTOCHROME B2 AT 2.4 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 1fcb)
(see all for 1fcb)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (1), Fmnh2(2-) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.2.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
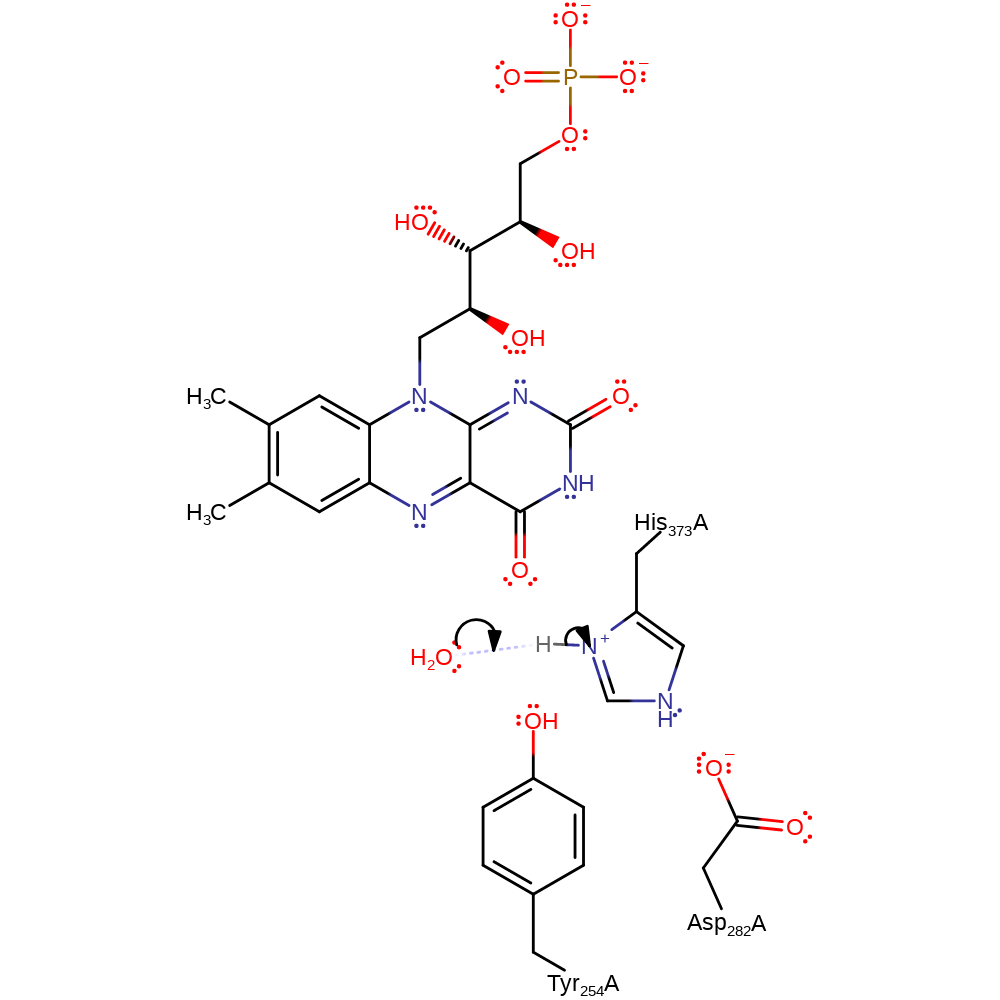
The enzyme catalyses the oxidation of lactate to pyruvate. In the wild type enzyme the OH and CH bond cleavages in lactate are highly asynchronous. The lactate hydroxyl proton is abstracted by His 373 to form the alkoxide either early in the reaction or in a pre-equilibrium. The developing charge on the oxygen is stabilised by Tyr254. The hydride is then transferred to the flavin, forming pyruvate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fcb) | ||
| Tyr334 | Tyr254A | The residue's phenolic hydroxy group hydrogen bonds to the substrate alkoxide anion, lowering the intermediate's energy, and so facilitating its formation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp362 | Asp282A | Electrostatic interactions between Asp282 and the general base His373 orientates the residue towards the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His453 | His373A | The residue acts as a base towards the lactate hydroxyl, forming an alkoxide which then drives the transfer of the alpha hydrogen to the flavin cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, radical formation, electron transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated, proton transfer, radical termination, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Tsai CL et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 7844-7851. Mechanistic and Structural Studies of H373Q Flavocytochromeb2: Effects of Mutating the Active Site Base†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi7005543. PMID:17563122.
- Dellero Y et al. (2015), J Biol Chem, 290, 1689-1698. Experimental Evidence for a Hydride Transfer Mechanism in Plant Glycolate Oxidase Catalysis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m114.618629. PMID:25416784.
- Mowat CG et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 9519-9526. Altered Substrate Specificity in Flavocytochromeb2: Structural Insights into the Mechanism ofl-Lactate Dehydrogenation†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi049263m. PMID:15260495.
- Gondry M et al. (2001), Eur J Biochem, 268, 4918-4927. The catalytic role of tyrosine 254 in flavocytochrome b2 (L-lactate dehydrogenase from baker's yeast). Comparison between the Y254F and Y254L mutant proteins. PMID:11559361.
- Sobrado P et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 994-1001. Probing the Relative Timing of Hydrogen Abstraction Steps in the Flavocytochromeb2Reaction with Primary and Solvent Deuterium Isotope Effects and Mutant Enzymes†. DOI:10.1021/bi002283d. PMID:11170421.
- Brown BD et al. (1990), Genes Dev, 4, 1925-1935. Endonucleolytic cleavage of a maternal homeo box mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. DOI:10.1101/gad.4.11.1925. PMID:1980477.
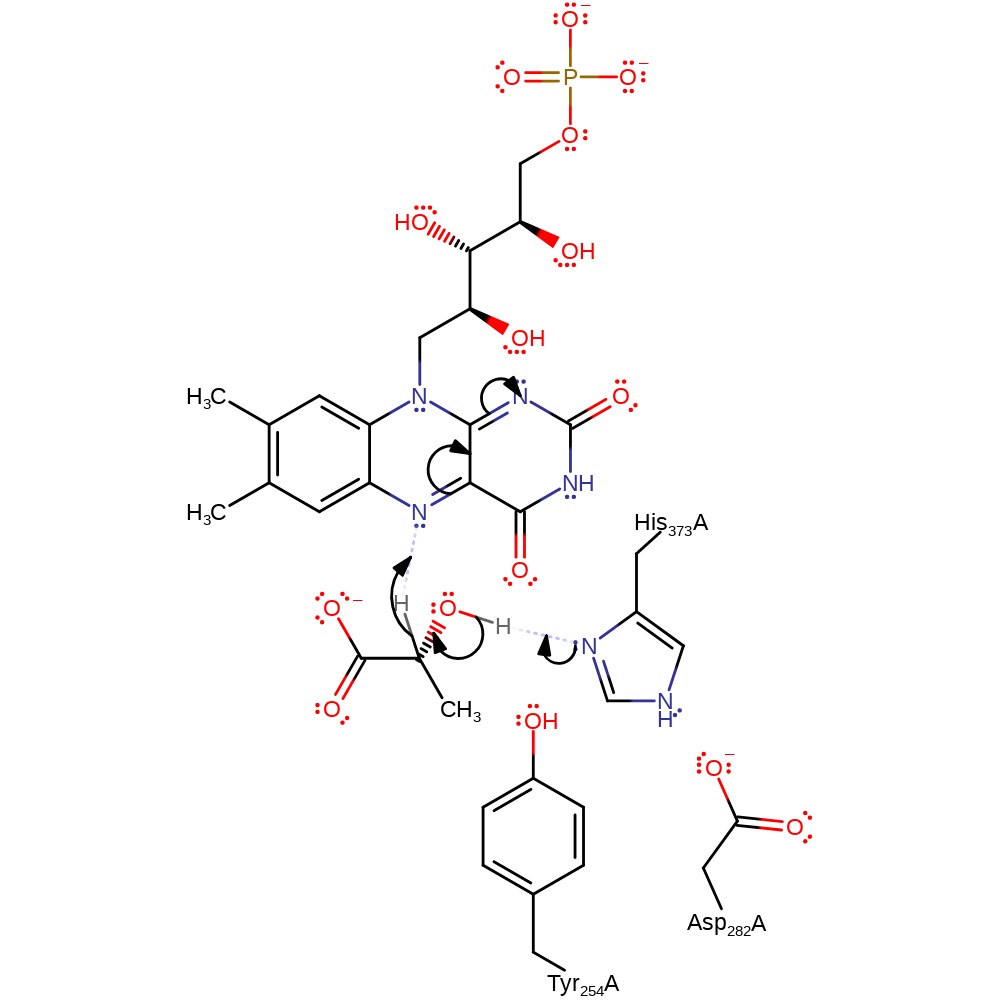
Step 1. His373 deprotonates the alcohol of the lactate which eliminates a hydride ion that is added to FAD.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His373A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His373A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 2. A single electron is transferred from the FAD to the haem cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formation, electron transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated
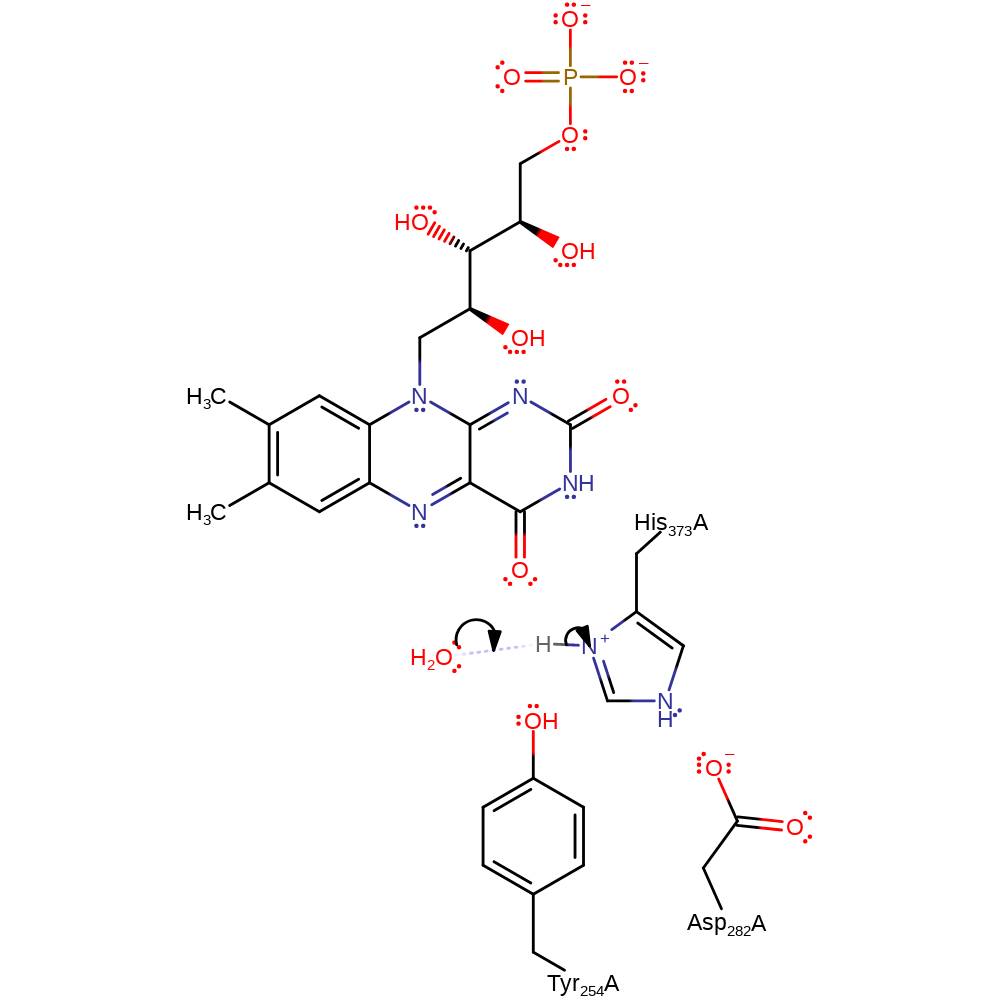
Step 4. Water deprotonates the FAD, initiating the second single electron transfer from FAD to the haem cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical termination, native state of cofactor regenerated, cofactor usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, native state of cofactor regeneratedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
In this proposal, the His373 abstracts the alpha carbon's proton, forming a negatively charged intermediate, which then eliminates the hydride.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fcb) | ||
| Tyr334 | Tyr254A | The residue's phenolic hydroxy group hydrogen bonds to the substrate, lowering the intermediate's energy, and so facilitating its formation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp362 | Asp282A | Electrostatic interactions between Asp282 and the general base His373 orientates the residue towards the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His453 | His373A | The residue acts as a base towards the lactate alpha carbon. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, electron transfer, radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formation, native state of cofactor regenerated, radical termination, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Mowat CG et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 9519-9526. Altered Substrate Specificity in Flavocytochromeb2: Structural Insights into the Mechanism ofl-Lactate Dehydrogenation†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi049263m. PMID:15260495.
- Dewanti AR et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 1883-1890. Esters of Mandelic Acid as Substrates for (S)-Mandelate Dehydrogenase fromPseudomonas putida: Implications for the Reaction Mechanism†. DOI:10.1021/bi036021y. PMID:14967029.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp282A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. The enolate undergoes rearrangment to eliminate a hydride from the hydroxyl group of the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp282A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base
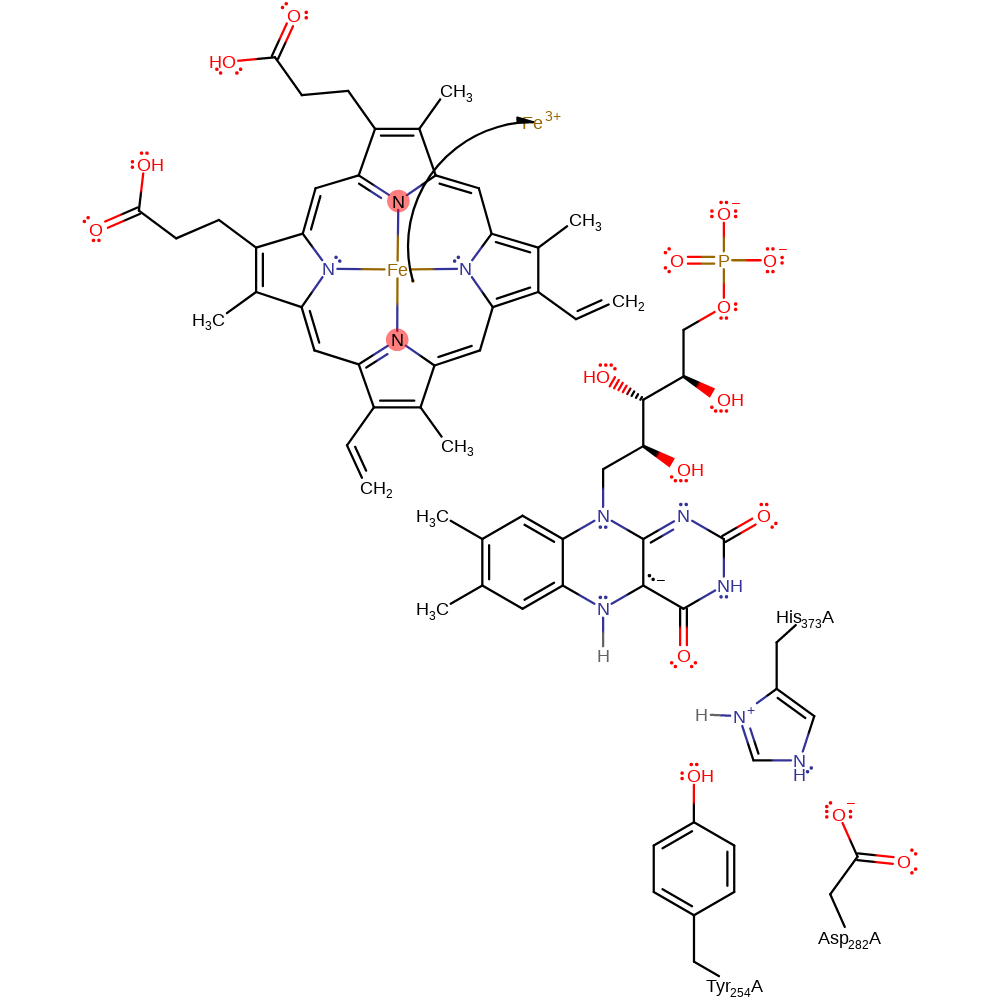
Step 3. A single electron is transferred from the FAD to the haem cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated
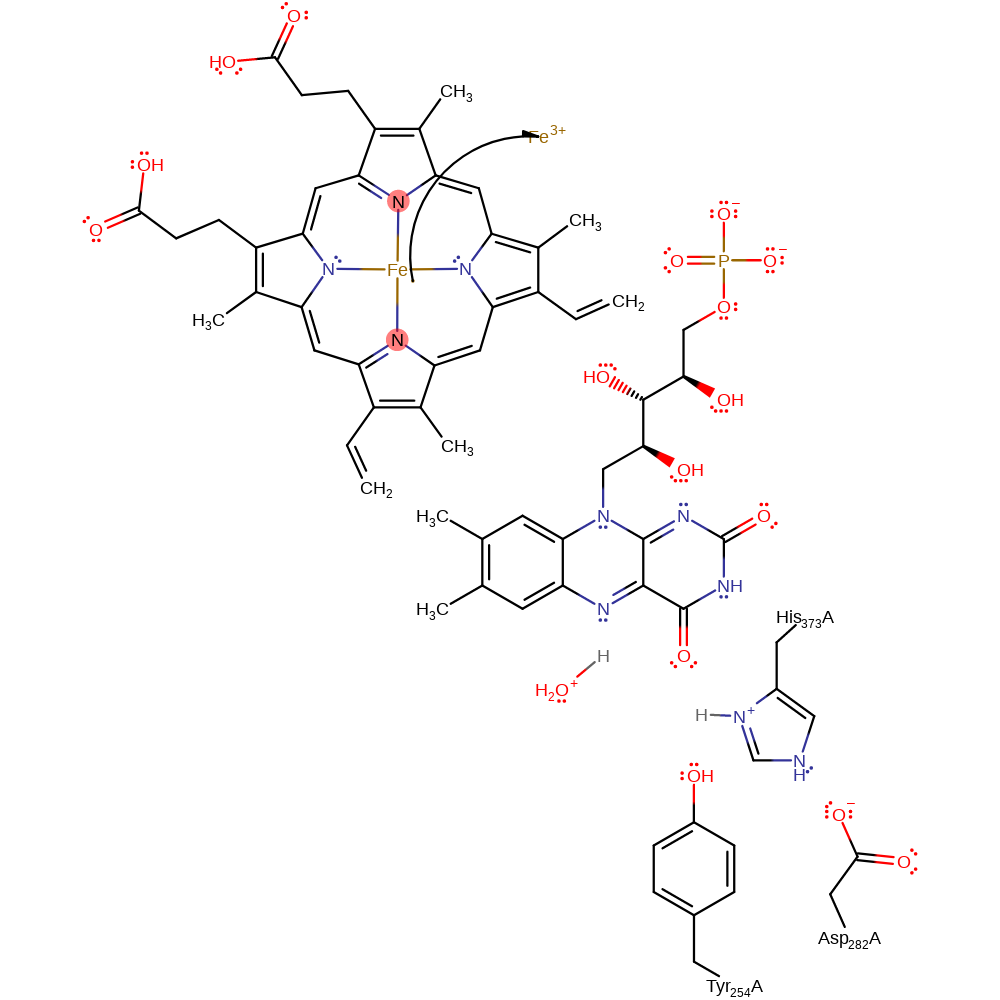
Step 5. Water deprotonates the FAD, initiating the second single electron transfer from FAD to the haem cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical termination, native state of cofactor regenerated, cofactor usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, native state of cofactor regeneratedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr254A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp282A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His373A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |







 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: