3-hydroxydecanoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase
In Escherichia coli, the enzyme beta-hydroxydecanoyl thiol ester dehydrase is responsible for the key step, where an unsaturated intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway of saturated fatty acids is intercepted and shunted into the pathway leading to unsaturated products. Dehydrase catalyses two reactions on fatty acid thiol esters of acyl carrier protein (ACP): the dehydration of (R)-3-hydroxydecanoyl-ACP to (E)-2-decenoyl-ACP, a reaction that also occurs in the elongation of saturated fatty acids; and the isomerization of (E)-2-decenoyl-ACP to (Z)-3-decenoyl-ACP. (E)-2-decenoyl-ACP can be reduced to decanoyl-ACP, which is elongated to the usual saturated fatty acids; in contrast, the cis (Z) double bond of (Z)-3-decenoyl-ACP is retained through the further cycles of fatty-acid elongation. The isomerisation catalysed by dehydrase is an allylic rearrangement, which is a relatively simple, single-substrate reaction. Both the dehydration and isomerization reactions seem to occur in the same active site.
3-hydroxydecanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] dehydratase (dehydrase) is required for the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, by shunting a 10-carbon intermediate from the saturated fatty acid pathway into the unsaturated fatty acid pathway.
Dehydratase catalyses dehydration and isomerisation reactions by a mechanism that does not involve metals or other cofactors, unlike the majority of the enzymes that catalyse similar reactions. The catalytic site is isolated from solution and is predominantly hydrophobic apart from histidine (A HIS 70) and aspartic acid (B ASP 84), which together are proposed to catalyse the reactions. The reactions take place in a bifunctional active site.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A6Q3
 (4.2.1.59, 5.3.3.14)
(4.2.1.59, 5.3.3.14)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1mkb
- ESCHERICHIA COLI BETA-HYDROXYDECANOYL THIOL ESTER DEHYDRASE AT PH 5 AND 21 DEGREES C
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.10.129.10
 (see all for 1mkb)
(see all for 1mkb)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.1.59)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The two base hypothesis for the dehydration reaction proceeds as follows: His70 deprotonates the substrate, initiating double bond rearrangement and the formation of an oxyanion. The oxyanion collapses, initiating double bond rearrangement and the elimination of water with concomitant deprotonation of Asp84B.
Peptide dipoles from Gly79 and Cys80 at the N terminus of the central alpha helix (alpha 3) may provide stabilisation to the presumed enol/enolate intermediate and to the leaving hydroxyl group.
His70 in the free enzyme donates a proton in a hydrogen bond, to the backbone carbonyl of Val76. This is consistent with the catalytic role for histidine, because this results in a basic lone pair of electrons. The hydrogen bond also positions the imidazole ring rather precisely. Thus we infer that His70 is in the correct tautomeric state and optimal orientation for catalysis in the free enzyme.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mkb) | ||
| Asp85 | Asp84B | Acts as a general acid to protonate the leaving hydroxyl group to form water. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His71 | His70A | Acts as a a base to deprotonate the fatty acid to initiate double bond rearrangement. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Val77 (main-C) | Val76A (main-C) | Forms a hydrogen bond to His70 to ensure correct tautomeric state and orientation. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly80 (main-N), Cys81 (main-N) | Gly79A (main-N), Cys80A (main-N) | Stabilises negative charge build up, by hydrogen bonding to form an oxyanion hole. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, dehydration, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Leesong M et al. (1996), Structure, 4, 253-264. Structure of a dehydratase–isomerase from the bacterial pathway for biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids: two catalytic activities in one active site. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00030-5. PMID:8805534.
- Moynié L et al. (2013), J Mol Biol, 425, 365-377. Structural Insights into the Mechanism and Inhibition of the β-Hydroxydecanoyl-Acyl Carrier Protein Dehydratase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.017. PMID:23174186.
- Heath RJ et al. (1996), J Biol Chem, 271, 27795-27801. Roles of the FabA and FabZ -Hydroxyacyl-Acyl Carrier Protein Dehydratases in Escherichia coli Fatty Acid Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.271.44.27795.
- Schwab JM et al. (1986), J Am Chem Soc, 108, 5304-5308. A thorough study of the stereochemical consequences of the hydration/dehydration reaction catalyzed by .beta.-hydroxydecanoyl thioester dehydrase. DOI:10.1021/ja00277a040.

Step 1. His70 deprotonates the substrate, initiating double bond rearrangement and the formation of an oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp84B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val76A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His70A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly79A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys80A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, initiating double bond rearrangement and the elimination of water with concomitant deprotonation of Asp84B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp84B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val76A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly79A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys80A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, dehydration, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated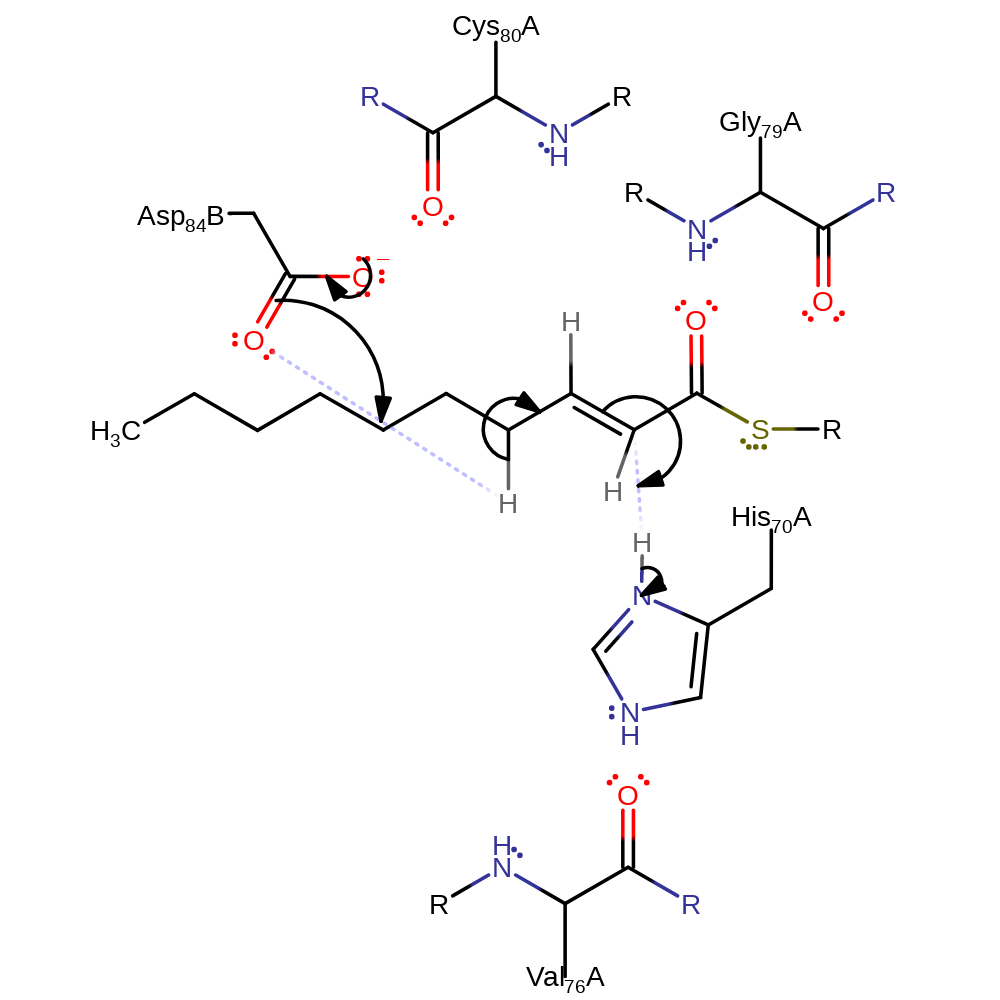
Step 3. The enzyme is able to catalyse the isomerisation of the trans double bond, shown here, to the cis geometric isomer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Val76A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly79A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys80A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84B | proton acceptor |
| His70A | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: