 |
PDBsum entry 4b9b
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The structure of the omega aminotransferase from pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Beta-alanine-pyruvate transaminase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: aminotransferase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Organism_taxid: 287. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 511693.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.64Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.177
|
R-free:
|
0.219
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Sayer,M.N.Isupov,A.Westlake,J.A.Littlechild
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Sayer
et al.
(2013).
Structural studies of Pseudomonas and Chromobacterium ω-aminotransferases provide insights into their differing substrate specificity.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
69,
564-576.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
03-Sep-12
|
Release date:
|
27-Mar-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9I700
(BAUA_PSEAE) -
Beta-alanine--pyruvate aminotransferase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
448 a.a.
436 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.18
- beta-alanine--pyruvate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-oxopropanoate + L-alanine = beta-alanine + pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-oxopropanoate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
+
|
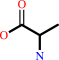 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
=
|
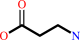 beta-alanine
beta-alanine
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
69:564-576
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural studies of Pseudomonas and Chromobacterium ω-aminotransferases provide insights into their differing substrate specificity.
|
|
C.Sayer,
M.N.Isupov,
A.Westlake,
J.A.Littlechild.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

